Synthesis and Application of Solid-phase Reagents with Formzane Groups in Environmental Analysis
PERVOVA I G, SKORYKH T V, MASLAKOVA T I, MEL’NIK T A,LIPUNOVA G N, LIPUNOV I N, WANG Li, CHEN Chen
(1.Urals State Forest Engineering University,Ekaterinburg 620100,Russia; 2.Institute of Organic Synthesis Ural Division of RAS,Ekaterinburg 620990,Russia; 3.Shenyang University of Chemical Technology,Shenyang 110142,China)
Modern analysis of aqueous medium was paid special attention to synthesis optical sensor elements on the base of immobilized organic reagents,and develops solid-phase spectroscopy techniques for determining elements and visual testing.Determining optimal combination of an organic element,matrix and interaction with an analyte is the major problem when constructing analyte detection systems.
Hetarylformazanes are of interest as surface modifiers of inorganic and organic matrixes.Due to the presence definite functional groups which are responsible for interaction between an organic reagent and analyte,formazanes are general chromophoric polydentate complex-forming reagents.The introduction of substituents(chemical-analytical groups)into the formazane molecule allows to manage chemical-analytical characteristics of the reagents enhancing selectivity,contrast,velocity and stability of analytical effect when complexing with metal ions.
Several approaches have been developed for synthesis of solid-phased reagents with formazane groups.The results of their properties studies are generalized.Special emphasis is focused on analytical and practical applications of solid-phased rea-gents with formazane groups.
1 Solid-phase Reagents Synthesized by Surface Assembling with Polymer Intermediate
The technique allows to change chemical composition of a polymer without any significant changing its nature by chemical interactions between reactive functional groups incorporated in polymersupportand monomerorganiccompounds.Using aldehyde-containing polystyreneco-divinyl benzene[1]as an intermediate has allowed to synthesized polymerformazanes(Ⅰ) according to the scheme:
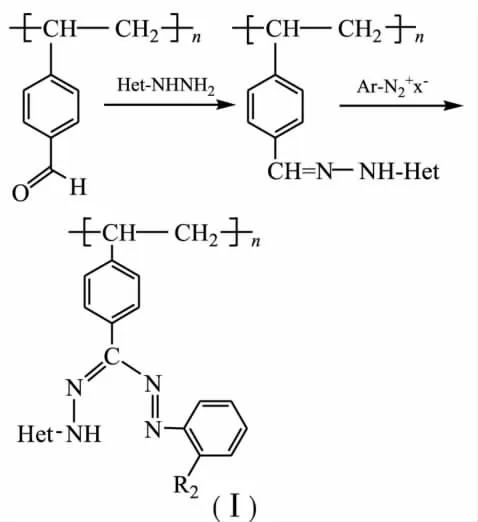
Synthesized by this technique,new sorbents with hetarylformazane groups have been used for selective extraction of copper ions from aqueous solutions containing ions Ni(Ⅱ),Zn(Ⅱ)and Cd(Ⅱ)as well as group extraction and concentration Cu(Ⅱ),Ni(Ⅱ),Zn(Ⅱ)and Cd(Ⅱ)[1].
Absorbing cellulose paper has been used as a matrix for immobilization reagents;the matrix has been used for synthesis the group of analytic ready to use chromogen reagents.The interaction between aldehydecellulose and hetarylhydrazones with the subsequent linking with diazo compounds[2],was used to afford numerous cellulose analogues(Ⅱ)of hetarylformazanes with the shared formula:

2,6-and 4,6-disubstituted pyrimidines,thiazole,pyrazole,benzazoles etc.were used as a heterocycle.It has been shown that cellulose residue influences on formazanes colourity in the same way like alkyl substituent at the position 3 of the formazane chain does. Reactions between formazane-6-cellulose and a number of heavy,precious and rare-earth metals leading to bathochromic shift have been studied.Reagent indicator papers were synthesised on the base of polydentate irregular 1-aryl-5-(benzazolyl-2)formazane-6-αcelluloses.It has been shown that formazane grafted onto cellulose through covalent bonds are more selective and stable in comparison with formazane sorbed in other ways.The higher stability might be connected with their higher structural rigidity.Cellulose benzoxazolyl-formazanesare perspective analytical reagents for test methods for the determination of metals.
Modified benzothiazolyl-,benzoxazolyl-and 4,6-dimethylpyrimidinyl formazanes of cellulose are studied in detail in papers[3-6].The compounds are characterized with diffuse reflectance spectra.Complex-forming with ions of copper,nickel,cadmium,zinc,lead,silver,mercury has been studied.Modified α-selluloses demonstrate different sorptive capacities for the metals ions:the quantities of metal ions complexed varied from 0.04~0.23 mg/g.Influence of the structure of the sorbed formazane group and conditions for complex-forming on the efficiency of the metal ions extraction has been observed.Reagents for concentration of certain metal ions from the mixture:Cu(Ⅱ),Ni(Ⅱ),Pd(Ⅱ),Hg(Ⅱ)have been identified.New reagent indicator papers for drinking water assay are proposed.
Produced by modification of cellulose sheets,membranes are shaped as painted paper disks with diameters 24,38 and 41 mm and the specifical gravity 80~200 g/m2.Heavy metals sorption by membranes is accompanied by changing colour.Membranes were used for removing traces of heavy metals with iron from sodium rhenate,dimethylformamide as well as distillate and running water.Removed traces of heavy metals with iron were determined in membranes using visual and X-ray fluorescence methods.Synthesized membranes have sorption and chromogens'ability to form complexes of palladium,silver and a number of rare-earth metals.The technique of determining palladium(Ⅱ)ions in solutions using 1-phenyl-5-(4,6-diphenylpyrimidin-2-yl)formazane-6-α-cellulose.Hetarylformazanyl-6-celluloses are perspective,high performance chromogenic and ion-exchange polymeric reagents which exercise both colour complex-forming and redox reactions,are able to regenerate and present novel indicators.
2 Solid-phase Reagents Synthesized by Covalent Immobilization of Formazanes onto Solid Support
Formazanes can be covalently bound onto cellulose,amino-and chloromethylated polystyrene matrix,silica gel.Condensation of 3-chloro (bromo)methyl hetarylformazanes on amine-containing anion exchange resin was used to afford sorbents(Ⅲ)with the following structure[7-8]:
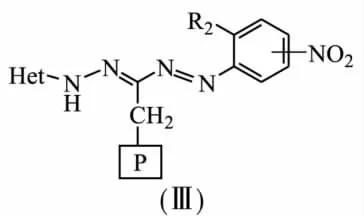
Crosslinked amine-containing anion exchange resins AN-20,AN-22,AN-18,AN-31 with different basicities were used as polymer support.Fragments of benzothiazole,benzoxazole,benzimidazole,4,6-disubstituted pyrimidine were used as heterocycles in formazane groups.Sorption properties of the modified anion exchange resins(Ⅲ)towards a wide range of metals were investigated.It was shown synthesized sorbents can be used for determination of micro elements in environmental and waste waters.Possibility of selective extraction of copper and lead ions from solutions containing accompanying elements-Ni(Ⅱ),Zn(Ⅱ),Cd(Ⅱ)is revealed.
Analytical reagents in test systems can be used in two kinds:immobilized onto solid matrix and as weighted and packed powder divided into doses;so sorbents(Ⅲ)on the base of anion exchange resins AN-20,AN-22 were synthesized in powdered form.While investigating sorption properties of powdered anion exchange resins modified by 3-(bromomethyl)benzothiazolylformazanes,increasing recovery of ions Cu(Ⅱ)and reducing sorption of ions Pb(Ⅱ)has been noticed.
Method of covalent immobilisation was applied for binding formazane groups on fibre materials filled with anion exchange resins AN-31 which have more advanced sorption and kinetic properties in comparison with ones of granular and porous materials[9].Due to strong covalent binding,synthesized fiber sorbents of type(Ⅲ)are characterized by stability in range pH 2~9.Immobilization of benzothiazolyl-and pyrimidinylformazanes onto fibre has resulted in advancing sorption ability of sorbents in comparison with initial fiber filled with AN-31.While sorption of ions Cu(Ⅱ),Ni(Ⅱ),Zn(Ⅱ),Cd(Ⅱ),Pb(Ⅱ),colour of fibres modified with formazanes has been changing as the result of complex-forming reaction.This phenomenon affords to use the diffuse reflectance method for qualitative and quantitative assaying metal ions.
3 Solid-phase Reagents Synthesized by Noncovalent Immobilization of Formazanes onto Solid Support
Immobilisation of formazanes onto a solid support can be realized if there are some ionizable groups in a reagent molecular and support.In this case immobilisation is established by a chemical bond of the ionic type.
Immobilisation of sulfo-containing benzothiazolyl formazanes onto anion exchange resins has been realized[10-14].Crosslinked amine-containing anion exchange resins AN-18,AN-20,AV-17 were used as polymer supports.Treatment of amine-containing support with weak acid aqueousethanol solution of formazane afforded to synthesis a number of modified anion exchange resins(Ⅳ) with the following structure:
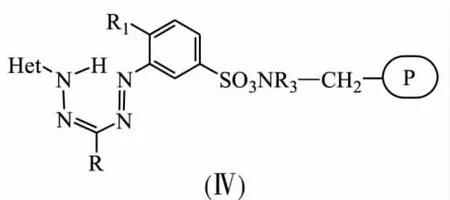
Influence of anion exchange resins basicity on stability of synthesized solid-phase reagents (Ⅳ)in different medium has been studied.Sorption properties of modified anion exchange resins for different metal ions were investigated.It is shown they can be used as selective sorbents as well as ligands for synthesis of polymer metal complexes. For example, polybenzoxazolylformazanes on the base of anion exchange resins AN-20 sorb in selective way ions Sc(Ⅲ)from solutions containing ions Ti(Ⅳ),Zr(Ⅲ)while benzothiazolylformazanes reveal definite selectivity for ions Cu(Ⅱ)and hardly sorb ions Ni(Ⅱ).Solid-phase reagents immobilized onto anion exchange resins AN-18 in depending on added heterocycling fragments are used for selective extraction by sorption of ions Zn(Ⅱ)and Cd(Ⅱ)when both of them are presented at the same time,ions Cu(Ⅱ),Co(Ⅱ),Pb(Ⅱ)in presence of Zn(Ⅱ) and Co(Ⅱ),Pb(Ⅱ)in presence of Cd(Ⅱ).
In case of using fibres filled with anion exchange resins AV-17,AN-31 as a support,immobilisation benzozolylsulfo-containing formazanes is also established due to a chemical bond of the ionic type with synthesis of sorbents(Ⅳ)[9,15].The synthesized solid-phase reagents can be used for visual and spectrochemical(the diffuse reflectance method)determining metal ions due to their metallochromic properties.The most contrast changing colour occurs in case of fibres filled with anion exchange resins AN-31 and modified by pyrimidyneformazanes[9].Synthesized on the base of fibres AV-17,sorbents containing benzothiazolylformazanes can be used for concentration ions Zn(Ⅱ)and Cd(Ⅱ)from dilute solutions then separation them from ions Cu(Ⅱ)and Ni(Ⅱ).Modified by benzylbenzimidazolylformazanes,fibres filled with anion exchange resins AV-17 facilitate concentration of ions Cu(Ⅱ)from dilute solutions and separation them from ions Ni(Ⅱ)and Cd (Ⅱ)when both of them are in presence[15].
Chemical-analytical characteristics of sulphocontaining 3-methyl-5-hetaryl formazanes(Ⅴ) immobilized onto silica gel DIASORB-100-TA with 3-methyl ammonic groups in according to ionic mechanism owing to the electrostatic force have been investigated[16-17].Quantity offormazane groups immobilized onto a mineral solid support depends on basicity of the heterocyclic fragment of formazane molecular.The quantity increase with sorbents modified by benzylbenzymidazolyl-<benzoxazolyl-<benzothiazolyl formazanes.
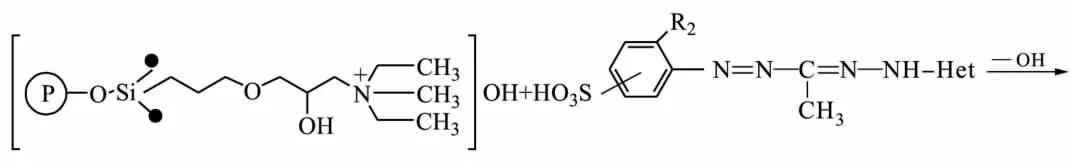
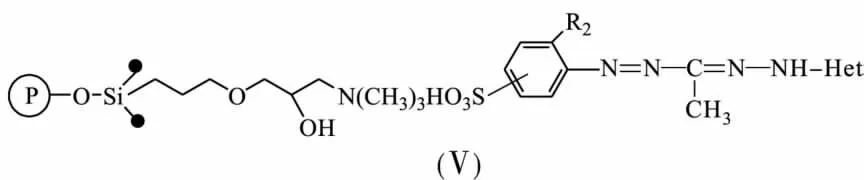
The structure of a heterocyclic fragment defines a form of the formazane molecular synthesising during immobilization:benzothiazolyl-and benzylbenzymidizolylformazanes immobilize as non-ionic,in contrast to benzoxazolylformazanes immobilizing as ionic bond.It happens due to the polarising effect of silica gel surface on NH-and OH-groups of ligand molecular.
As a result of the experiments it was established that during immobilization of benzazolyl formazanes onto silica gel DIASORB-100-ТA increasing selectivity and sensibility of the complexforming reaction occurs in comparison with a solution.Thisafforded to develop techniquesof sorptive extraction,solid-spectroscopy and test-determining toxic metal ions.
Extraction of metal ions from solutions during complex-forming with formazane groups immobilized onto a solid support is almost always being accompanied by chromogenic reaction when the concentration of metal reaches 30 mg/L and more,that facilitate significantly monitoring sorption process.It was established influence basicity of the heterocyclic fragment in the formazane molecular on analytical properties of solid-phase reagents (Ⅴ)revealing increasing significantly the rate of the chromogenic reaction of benzoxazolyl-,benzothiazolyl-containing sorbents in comparison with their benzylbenzimidazolyl-containing analogues.For instance,the chromogenic reaction on the surface of sorbentsⅤmodified by benzylbenzimidazolylformazanes begins to develop in 5 min after interaction with metal ions(ρM≥30 mg/L) while in case with benzoxazolyl-,benzothiazolylcontaining sorbents changing colour appears immediately.
Techniques of solid-spectroscopic and test-determining ions Ni(Ⅱ)and Cd(Ⅱ)by 1-(4-sulfophenyl)-3-methyl-5-(benzoxazol-2-yl)-and 1-(2-hydroxy-5-sulfophenyl)-3-methyl-5-(benzothiazol-2-yl)formazanes immobilized onto silica gel are developed respectively.To determine ions Ni(Ⅱ) indicator powder is added into a sample,mixed for 3 min and determined concentration by means of either solid-spectroscopic technique in according to prepared before calibration curve or using visual colour scale matching depending on sorbent colour strength.Presence of ions Со(Ⅱ),Pb(Ⅱ),ions of alkali and alki-earth in the ratio 1∶5 don’t interfere in determining ions Ni(Ⅱ).In the case of determining Cd(Ⅱ)the indicator tube was used; it enhanced sensibility of analytical effect[18].Metal concentration is determined in according to colour strength of the reaction site of an indicator sorbent after flowing analyzed solution through it.Durability of the analyze is not longer than 15 min.Presence of ions Co(Ⅱ),Ni(Ⅱ),Sc(Ⅲ),Yb(Ⅲ)in the ratio 1∶10 don’t interfere in determining ions Cd(Ⅱ).One of advantages of the developed solid-phase reagents is the fact that light and oxygen in the air don’t effect on the reagents stability.Modified sorbents has not been changing their colour for 3 years;it makes them as readyto-use analytical forms.
Physical adsorption of organic reagents onto a solid support is characterized relatively weak fixation adsorptively immobilized groups what results in partly washing them off by a solution.This is the main disadvantage of such method of immobilization[19].It was proposed to make preliminary concentration of metal ions on a solid support then to treat with pyrimidylformazanes solution to enhance sensibility and selectivity ofsuch sorbents[20].Exercising reaction of complex forming of 1-(2-carboxyphenyl)-3-phenyl-5-(4,6-diphenylpyrimidin-2-yl)formazane on the solid state of fibers filled with cation exchange resin КU-2 allowed to develop the technique of visual detection and spectral determination of ions Ag(I)and Cu(Ⅱ) in aqueoussolutionscontaining ions Ni(Ⅱ),Zn(Ⅱ),Co(Ⅱ).
Approach ofpreliminary concentration of ions on nonfunctionalized silica gel then treatment by formazane solution is considered[21].It is recommended to use 1-(2-carboxyphenyl)-3-furfurane-5-(4,6-diphenylpyrimidinyl)formazane for visual and spectrometric detection of ions Cu(Ⅱ),Ag(I),Co(Ⅱ),as well as 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-isopropyl-5-(2-benzoxazolyl)formazane for express determination of ions Cu(Ⅱ)with concentration less than 5 mg/L.
1-(4-Methylphenyl)-3-furfurane-5-(1-benzylbenzimidazol-2-yl)formazane has great promise for quantitative test-determination of ions Co(Ⅱ)[22].This compound forms painted complex compound with cobalt in terms of 620 nm on the solid state polyacrylnitryl fibre filled with anion exchange resin AN-20.A test spot was produced by impregnation of material with solution of chromogenic reagent and following depositing drops of analyzed solution onto wet modified support.Determination limit of ions Co(Ⅱ)is 10 mg/L.
To avoid chemical influence from a matrix on spectral properties of being immobilized formazane groups,chemical-analytical characteristics of a wide range of benzazolylformazanes(Ⅵ)on solid state fiber POLIORGS-34n and natural flax matrix were investigated.
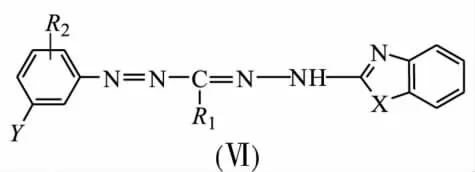
X=O,S,NCH2C6H5;R1=CH3,C2H5,CH(CH3)2;R2= H,2-OH,4-SO3H,4-CH3,4-NO2;Y=H,5-SO3H,5-NO2
Method of comparison of maximum absorbance spectra of organic reagents in solution and on solid state was used to established that immobilization of formazane groups(Ⅵ) occurs in nonionized form both on synthetic and natural supports in contrast to silica gel.
Using the method with preliminary sorption of an analyzed metal ion(ρm<1 mg/L)on the matrix with the following treatment with a reagent solution allowed to establish the fact that complex forming reaction are higher selective on the fibre POLIORGS-34n,howeverusingflaxenhances sensibility and analytical effect rate due to hydrophilic nature and finer structure of the material for instance,interaction between 1-(4-sulfophenyl)-3-methyl-5-(benzylbenzimidazol-2-yl) formazane and ions Cu(Ⅱ)occurring on a fabric support is characterized by higher contrast analytical effect (Δλ=170 nm)when concentration of metal ions≥0.03 mg/L and colour has been changing for 3~5 min.In the case of using fibre POLIORGS-34n chromogenic effect can be observed when concentration of metal ions≥0.1~3 mg/L,durability of analytical reaction is two times as large.High contrast of the reaction of complex forming 1-(4-sulfophenyl)-3-methyl-5-(benzylbenzimidazol-2-yl)formazane resulted in considering it as the most promise as an analytical reagent for determination of ions Cu(Ⅱ)[23].Moreover,presence of sulfo-group in the structure of a reagent molecular determines good solubility of formazane in ethanol solution what facilitates investigation.
Active influence of an additional hydroxy group in benzoxazolylformazanes on selectivity of complex forming and contrast of an analytical reaction is established.For instance,presence of OH-group in 1-(2-hydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-3-isopropyl-5-(benzoxazol-2-yl)formazane enhanses analyticalparameterswhile interaction with ions Cd(Ⅱ),pay attention visual effect can be observed when ρm≥0.1 mg/L due to forming metalcomplex composition CdL[24]. Chromogenic reactions occur only due to complex forming with benzazolylformazane because it was established there is no influence of interaction between ions Cd(Ⅱ)and amidoxime groups of the fibre POLIORGS-34n in the experimentofmodeling process of complex forming in aqueous system“ethylenamin-dimethylglyoxime”.
The technique of semiquantative express-determination of ions Sc(Ⅲ)using 1-(2-hydroxy-5-sulphophenyl)-3-methyl-5-(benzothiazol-2-yl) formazanes on solid state matrix of the fibre POLIORGS-34n is developed[25].The reaction of complex forming on surface of saturated with metal ions(ρm=0.1 mg/L)fibre with a solution of an analytical reagent added in drops results in forming a complex compound colouring in lilac when λmax=580 nm.Increasing concentration of metal ions makes changing fibre colour proportionately to concentration of Sc(Ⅲ)within range 0.1~1 mg/L.Conditions for exercising the testreaction was optimized:matching optimal pH for aqueous solution of Sc(Ⅲ)providing the most visual contrast while changing colour of an indicator fibre;quantity of formazane added on the matrix;time for achieving sorption equilibrium state for system“sorbent-metal solution”as well as fibre mass.Detection limit for metal under the visual technique is 0.05 mg/L,ρ(Sr)<0.3 mg/L.Durability of the analysis is not longer than 10 min.
Proposed analytical systems are characterized with satisfied correctness,ecological safety,simplicity of carrying out experiments.The methods are featured with the same range of concentrations like other methods for determining metal ions however in some cases they are more advanced in sensibility of an analytical reaction in comparison with other methods.
4 Conclusions
Considered approaches to synthesis of solidphase formazane-containing reagents show their great potential in developing techniques for express determining toxic metal ions in environmental samples.The ability of the formazane group to form metal complexes which is kept after binding on a support is responsible for high selectivity,sensibility and contrast of an analytical reaction.Wide range of synthetic possibilities for synthesis of formazanes and for their immobilisation onto a polymeric support determine sorption properties and analytical characteristics of solid-phase reagents which allow to determine trace toxic elements in environmental samples and processing medium.
[1] Pervova I G,Yushkova O G,Lipunova G N,et al.Synthesis and Properties of the Sorbents with Covalently Immobilized Hetarylformazanes[J].Sorption and Chromatographic Processes,2002,2(5/6):616-620.
[2] Ostrovskaya V M,Zaporozhetz O A,Budnikov G K,et al.Water Indicator Systems[M].Murmansk: EKONIKS,2002:265.
[3] Lipunov I N,Yushkova O G,Ostrovskaya V M,et al.Sorption PropertiesofPolydentate Irregular Hetarylformazane-α-celluloses[J].Sorption and Chromatographic Processes,2001,1(2):288-289.
[4] Ostrovskaya V M,Lyamina O P,Kupreyanova T A,et al.Membranes Based on Polydentate Cellulose with Hetarylformazane Groups for the Isolation of Heavy Metals[J].Series Critical Technologies Membrane,2001,11:32-35.
[5] Ostrovskaya V M,Lyamina O P,Yushkova O G,et al.Membranes Based on Polydentate Cellulose with Hetarylformazane Groups for the Isolation of Palladium,Silver,and Some Rare Earth Metals[J].Series Critical Technologies Membrane,2001,12:14-17.
[6] Ostrovskaya V M,Lyamina O P,Kupreyanova T A,et al.Synthesis and Properties of Polydentate Polymeric 1(5)-hetarylformazanyl-substituted Reagents[C].Ekaterinburg:GOSNEE MO RF,2002:243-245.
[7] Pervova I G,Lipunov I N,Yushkova O G,et al.Synthesis,Properties and Application of a Anion Exchangers,Modified by Hetarylformazanes[J].Sorp-tion and Chromatographic Processes,2001,1(5): 870.
[8] Lipunov I N,Mel'nik T A,Pervova I G,et al.Synthesis and Properties of Complexforming Ion Exchangers[J].Sorption and Chromatographic Processes,2003,3(6):680-687.
[9] Lipunov I N,Mel'nik T A,Pervova I G,et al.Synthesis and Properties of New Complexforming Fibrous Ion Exchangers[J].Sorption and Chromatographic Processes,2003,3(3):292-298.
[10]Lipunova G N,Pervova I G,Lipunov I N.Synthesis and Complex-forming Properties of Polymeric Formazans[J].Macromolecular Compounds.Series A,1997,39(9):1523-1526.
[11]Lipunova G N,Pervova I G,Lipuynov I N.Synthesis and Complex-forming Properties of Polymeric Formazans[J].Polymer Science.Series A,1997,39 (9/10):325-328.
[12]Lipunov I N,Pervova I G,Lipunova G N.Synthesis and Properties of Ion Exchangers Containing Formazan Grouping[M].Voronezh:Theory and Practice of Sorption Processes,1997:108-116.
[13]Lipunov I N,Pervova I G,Lipunova G N.Synthesis and Properties of Polymer with Hetarylformazan Groups[R].Marseille:Trans-Mediteranean Colloquium on Heterocyclic Chemistry,2000:112.
[14]Pervova I G,Lipunov I N,Yushkova O G,et al.Sorption Properties of Anion Exchanger AN-18-10p,Modified by Hetarylformazanes[J].Sorption and Chromatographic Processes,2001,1(1):6-11.
[15]Pervova I G,Lipunova G N,Melnik T A,et al.Synthesis and Sorption Properties of the"Filled"Fibrous Sorbents with Immobilized Hetarylformazane Groups[J].Russian Journal of Applied Chemistry,2003,76(7):1088-1091.
[16]Maslakova T I,Pervova I G,Skorych T V,et al.New Sorbents with Immobilized Hetarylformazane Groups[J].Sorption and Chromatographic Processes,2009,9(3):354-363.
[17]Pervova I G,Maslakova T I,Skorych T V,et al.Sorption-analytic PropertiesofMineralSorbents with Immobilized Hetarylformazane Groups[J].Sorption and Chromatographic Processes,2009,9 (3):383-390.
[18]Skorych T V,Pervova I G,Maslakova T I,et al.Adsorption-photometric and Test-determination of Cadmium(Ⅱ)with Hetarylformazanes[J].Russian Journal of Analytical Chemistry,2009,64(6):592-597.
[19]Amelin V G.Chemical Test Methods for Determining of Components in Liquid Media[J].Russian Journal of Analytical Chemistry,2000,55(9):902-932.
[20]Mel'nik T A,Pervova I G,Maslakova T I,et al.Color Reactions of Pyrimidinylformazanes with Metal I-ons in Solution and on a Solid Support[J].Russian Journal of Inorganic Chemistry,2006,51(6):986-991.
[21]Mel'nik T A,Skorych T V,Pervova I G,et al.The Study of Adsorption-analytic and Metallochromic Properties of Immobilized Hetarylformazanes[R].Moscow:IX Scientific School-Conference on Organic Chemistry,2006:327.
[22]Lipunov I N,Maslakova T I,Mel'nik T A,et al.Sorbents for Chromatographic Separation and Sorption Concentration of Toxic Metals from Dilute Solutions[J].Sorption and ChromatographicProcesses,2007,7(6):975-980.
[23]Skorych T V,Pervova I G,Maslakova T I,et al.The Determination of Copper(Ⅱ)Ions on Natural Matrix Using Benzylbenzimidazolylformazane[J].Laboratory Diagnostics of Materials,2009,75(9):12-15.
[24]Skorych T V,Mel'nik T A,Pervova I G,et al.Solidphase Test-determination of Cd(Ⅱ)by Reaction with Benzoxazolylformazane[R].Voronezh:Ⅱ International Symposium of Analysis and analysts,2008:148.
[25]Skorych T V,Pervova I G.Semi-quantitative Solidphase Rapid Determination of Scandium(Ⅲ)Ions[R].Ekaterinburg:In Proceedings of the All-Russian Scientific Conference of Creativity of Young Scientists for the Russian Forest Industry,2008:388-389.

