无卤阻燃含磷环氧树脂的研究进展
叶龙健,钱立军*,佟芍朋,许国志
(1.北京工商大学材料科学与工程系,北京100048;2.北京理工大学材料科学与工程学院,北京100081)
0 前言
阻燃环氧树脂除了拥有高效的阻燃性外,还具有优异的黏结性、绝缘性、热稳定性、耐化学品性、低收缩性,因而被广泛应用于表层涂料、胶黏剂、粉末涂料、层压板成型、复合材料以及半导体密封材料和电绝缘材料等领域[1-6]。目前对环氧树脂的阻燃改性主要以引入卤系元素为主[7-9],如溴化环氧树脂[10-12]。但是,有卤环氧树脂燃烧会产生大量酸性气体和浓烟,在环境中降解容易产生可持续污染物[13-14]。因此对于阻燃环氧树脂的研究和应用方向已转向环境友好的无卤阻燃环氧树脂,特别是含磷阻燃环氧树脂。与有卤阻燃环氧树脂相比,具有同样优异的热稳定性和阻燃性能的含磷环氧树脂,在燃烧和降解过程中烟气释放量小,其降解产物环境友好[15-19]。
含磷环氧树脂具有优异的阻燃性能,这主要是由于在燃烧过程中,磷在凝聚相发挥催化成炭的作用使材料表面形成炭保护层;而在气相中磷化合物产生PO·,以此来淬灭 H·和 HO·等自由基,使燃烧的连锁反应中断[20-23]。而且磷与固化剂中氮或树脂中的硅等元素具有协同作用,可以通过复合使用进一步提高环氧树脂的阻燃性能。显然,含磷阻燃环氧树脂以其优异的阻燃性能以及降解产物环境友好,而成为无卤阻燃环氧树脂中最重要的研究方向[24]。
目前研究的含磷环氧树脂主要包括DOPO型环氧树脂、磷酸酯型环氧树脂、磷腈型环氧树脂、磷/硅复合环氧树脂和环氧树脂的含磷固化剂等类型。
1 DOPO环氧树脂体系
1.1 DOPO环氧树脂
DOPO结构中含有 P—H键,可与萘醌、苯醌、衣康酸、马来酸、环氧乙烷和甲醛等反生成具有新功能的衍生物,这些衍生物进一步与环氧树脂反应可以获得DOPO含磷环氧树脂。
人们首先研究了DOPO与萘醌或苯醌反应合成DOPO-NQ和DOPO-BQ与双酚A二缩水甘油醚(DGEBA)反应获得的含磷环氧树脂[27-29],如图1所示。含磷环氧树脂与4,4′-二氨基二苯砜(DDS)、PN线形酚醛树脂、二异氰酸酯固化体系具有较高的玻璃化转变温度(Tg>160℃),且固化后两种含磷环氧树脂的磷质量分数>2.1%时,UL 94测试达到了V-0级,700℃时的残炭量20%左右,点燃时间大大减少,燃烧过程中低烟、无滴落。研究还发现,在热分解的初始阶段,随着磷含量的增加体系稳定性会稍有下降,这主要是由于键比C—C键稳定性弱造成的。另外,含磷环氧树脂的残炭量均比普通环氧树脂高,含磷体系在降解初始阶段发挥催化作用,并形成富含磷的残炭隔绝层以防止可燃性气体转移至材料表面[30,31-33]。

图1 DOPO与萘醌或苯醌反应产物及其含磷环氧树脂的结构Fig.1 The structures of DOPO-NQ,DOPO-BQ and their phosphorus-containing epoxy resins
C S Wang等[34]用DOPO分别与马来酸(MA)和衣康酸(ITA)反应合成DOPO-MA及DOPO-ITA(图2),然后进一步与DGEBA进行反应,可以得到DOPOMA/DGEBA和DOPO-ITA/DGEBA含磷环氧半固化物,再用DDS固化。结果表明,引入柔性脂肪羧酸链段的两种含磷环氧树脂Tg>150℃,比DOPO-NQ、DOPO-BQ有所下降,但阻燃性能仍然优异,在磷质量分数为1.7%时,UL94测试达到V-0级。

图2 DOPO与马来酸、衣康酸反应产物的结构Fig.2 The structures of DOPO-MA and DOPO-ITA
1.2 DOPO基固化剂
通常情况下获得DOPO阻燃环氧树脂的方法有3种:第一,合成含DOPO的环氧化合物,然后再用不同的固化剂固化;第二,通过反应型的DOPO衍生物与环氧树脂反应将DOPO基团引入;第三,通过对普通环氧树脂使用DOPO改性固化剂获得含DOPO的环氧树脂。因此,将DOPO引入环氧树脂的固化剂也是制备含磷环氧树脂的重要途径。
C S Wang等[35]通过DOPO与甲醛反应,再分别与酚醛树脂和三聚氰胺、苯酚反应制备了两种酚醛环氧固化剂DOPO-FP和DOPO-FMP,如图3所示。研究表明,这两种固化剂固化的树脂在700℃时,残炭量>30%。DOPO-FP固化的树脂在磷质量分数为1.45%时达到 UL 94 V-0级,DOPO-FMP固化的树脂达到UL94 V-0级的磷和氮质量分数分别为0.81%和2.36%。

图3 含DOPO酚醛环氧固化剂的结构Fig.3 The structures of the phenolic epoxy curing agents containing DOPO
Y L Liu等[36]通过DOPO和4-羟基苯甲醛反应制得新型的含磷酚醛树脂固化剂DOPO-PN,如图4所示。由该固化剂固化的酚醛环氧树脂的Tg高达160℃,在300℃以下无热分解。在磷质量分数为2%时,UL 94测试达到V-0级。
此外,Wu等[37-39]还研究了将阻燃固化剂DOPOSN用于固化含硅环氧树脂,如图4所示。结果表明,由此固化的含硅环氧树脂(P/Si=4.71/2.22)初始热分解温度为 319℃,在700℃时残炭量可以达到40.4%,极限氧指数达到29.5%,热稳定性阻燃性能良好。

图4 DOPO-PN与DOPO-SN固化剂的结构Fig.4 The structures of the curing agents DOPO-PN and DOPO-SN
1.3 添加型DOPO改性聚合物
相对于小分子阻燃剂,添加型DOPO改性聚合物阻燃剂与环氧树脂的相容性好,加工和使用过程中不迁移,热性能和力学性能良好,阻燃效率高。这是将DOPO引入环氧树脂的又一个途径。
Y Z Wang等[40]合成了1种添加型聚合物阻燃剂DOPO-PO,如图5所示。因为其主链和侧基上均有含磷阻燃基团,磷质量分数高达13.8%,而且结构中富含芳香结构,材料中酸源、炭源丰富。将其应用于环氧体系中磷质量分数只为0.70%时,即达到UL 94 V-0级,阻燃效率非常高。与其他小分子添加型阻燃剂会明显降低体系的力学性能不同,添加该阻燃剂对体系的拉伸强度、弹性模量等几乎没有影响。
Altstädt等[41]制备1种新型的含磷改性聚砜DOPO-PUS,如图5所示。并研究了其对DDS/DGEBA环氧体系阻燃性能的影响。研究表明,添加质量分数为5%DOPO-PUS的环氧树脂体系的极限氧指数为27.4%,与纯树脂相比,提高了6.6%。当DOPO-PUS的质量分数提高至20%,残炭量提高至41%,热释放速率峰值降至472 kW/m2,表明该添加型含磷改性聚砜对环氧树脂的阻燃性有明显提高。
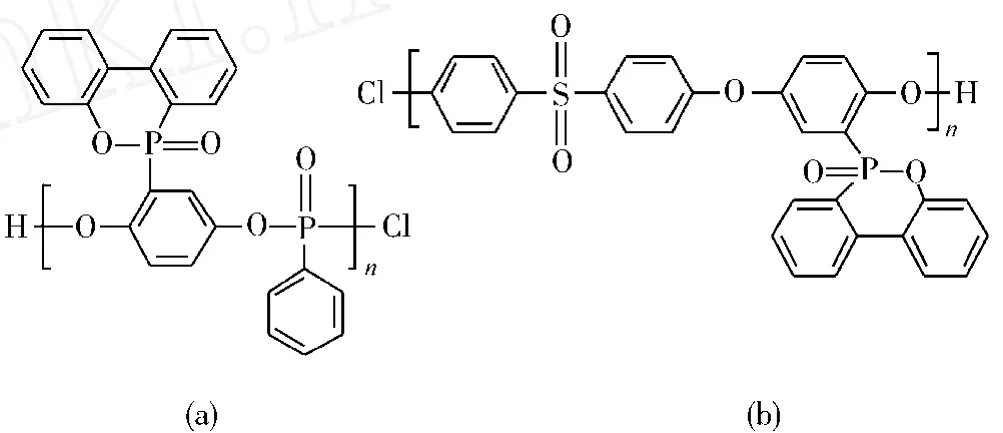
图5 DOPO-PO与DOPO-PUS改性聚合物的结构Fig.5 The structures of the modified polymers DOPO-PO and DOPO-PUS
2 磷酸酯环氧树脂体系
磷酸酯类环氧树脂是有机磷系无卤阻燃环氧树脂的重要系列,主链上连接有含磷酸酯类的环氧化合物与纯树脂相比表现出优异的阻燃性能。
2.1 磷酸酯环氧化合物
W F Shi等[42]合成了环氧端超支化聚磷酸酯(E-HBPP),用于DGEBA/间苯二胺(m-PDA)体系的阻燃研究。结果表明,E-HBPP作为酸源,m-PDA作为发泡剂,高温下 E-HBPP降解形成聚磷酸,与DGEBA的羟基反应生成酯基,该酯基很容易脱水并促进树脂交联生成膨胀性焦炭层。
Thompson等[43]制备了不同的主链上键接含磷环氧化合物,如图6所示。结果表明,环氧树脂的磷质量分数达到1.5%,在800℃时的残炭量大于37%。研究发现,磷键接的每个单元的质量均提高,而热分解温度和活化能降低,综合表现出磷的优异的催化成炭作用。薛敬和等[44]对二缩水甘油基苯基磷酸/DDS体系的研究表明,在燃烧过程中,含磷环氧树脂降解形成磷-氧自由基,然后与酯基反应生成聚磷酸酯,进一步降解后形成聚炭。因此,含磷组分对于树脂在降解过程中聚集成炭和减少可燃性气体具有重要作用。
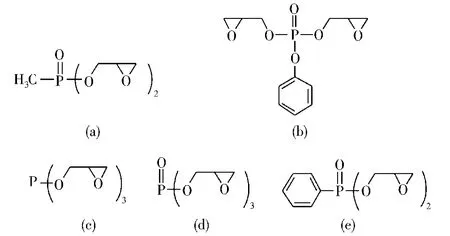
图6 不同磷酸酯环氧化合物的结构Fig.6 The structures of the phosphate epoxy compounds
2.2 环状磷酸酯环氧树脂
多羟基化合物在阻燃体系中通常作为炭源使用,通过多羟基化合物与三氯氧磷反应可以获得环状结构磷酸酯环氧树脂。这类环氧树脂在燃烧时本身会形成一层焦炭保护膜,抑制进一步燃烧。且环状分子中P、O、C 3种元素组成了稳定的杂环结构,兼具气液两相阻燃作用,热稳定性好,比脂肪类磷酸酯拥有更优良的阻燃效率[45]。
Y Z Wang等[46]合成了具有环状结构的反应型含磷单体,与DGEBA反应获得了含磷环氧树脂,如图7所示。低相对分子质量聚酰胺(LWPA)与环氧树脂混合时,磷质量分数达到2.5%,UL 94测试为V-0级,极限氧指数为30.2%。研究发现,含磷环氧树脂与LWPA体系生成的焦炭为致密多孔型,阻碍了燃烧过程中的热释放,提高了树脂的阻燃性能[47,48]。

图7 环状磷酸酯环氧树脂的结构Fig.7 The structure of the cyclic phosphate epoxy resin
X Li等[49]在环氧树脂中引进双环笼状磷酸酯(PEPA)(图 8)。研究表明,PEPA质量分数为19.2%,在600℃时的残炭量为12%,极限氧指数为36%,UL 94测试V-0级。研究还发现,这种笼状结构对于生成膨胀性残炭,发挥着至关重要的作用。

图8 双环笼状磷酸酯(PEPA)的结构Fig.8 The structure of the caged bicyclic phosphate
2.3 磷酸酯固化剂
C S Wang等[50]制备了含磷反应型固化剂二(3-羟基苯基)苯氧基膦酸酯(BHPP)(图9)。研究表明,由BHPP固化环氧树脂的磷质量分数达到1.5%时,UL 94测试达到 V-0级,极限氧指数为31%,在700℃时残炭量为32%,而达到相同阻燃级别的含溴环氧树脂的残炭量为24%。这是由于含磷基团在380℃左右首先分解,然后生成富含磷的残留物延缓了树脂进一步的降解,并导致高残炭量。

图9 BHPP的结构Fig.9 The structure of BHPP
3 其他含磷固化剂体系
通过含磷固化剂与环氧树脂反应是制备含磷环氧树脂的一个重要途径,而且已有的研究表明,通过该途径制备的含磷环氧树脂具有同样优异的阻燃性能。以下介绍的是除DOPO型和磷酸酯型以外的环氧树脂的含磷固化剂体系。
Galià等[51]将二 -(间 -氨基苯基)-甲基氧化膦苯并噁嗪(Bz-BAMPO)与双酚A缩水甘油醚共聚获得一种热固性酚醛环氧树脂[52],如图10所示。研究表明,含磷质量分数为2%的热固性树脂的极限氧指数为34.9%。这是由于燃烧过程中含磷基团催化生成了炭绝缘保护层,其能抑制可燃性气体转移至材料表面,增加了材料高温热稳定性并提高了阻燃性。
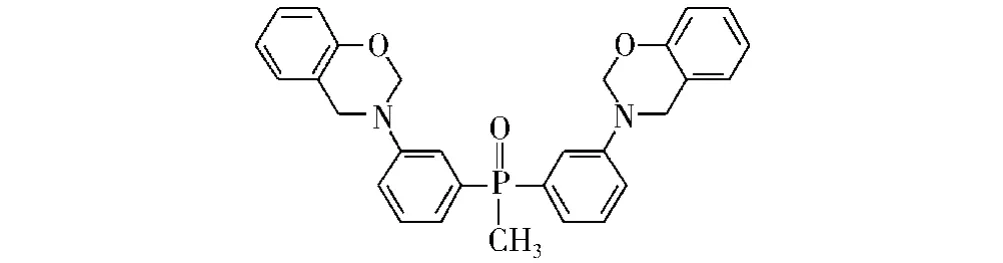
图10 Bz-BAMPO的结构Fig.10 The structure of the Bz-BAMPO
Varma等[53]研究了含磷固化剂对DGEBA环氧树脂的热性能的影响,如图11所示。在800℃时树脂的残炭量分别为34.8%、38.5%、39.3%,并且随着磷含量的增加成线性递增,残炭量越高也表明该树脂具有更好的阻燃性。Levchik等[54]将二 -(间 -氨基苯)甲基氧化膦(DNMP)固化DGEBA环氧树脂,如图12所示。研究发现,在600℃的残炭量从12%提高至30%,阻燃机理可能是由于延缓了环氧树脂的断裂链的挥发。
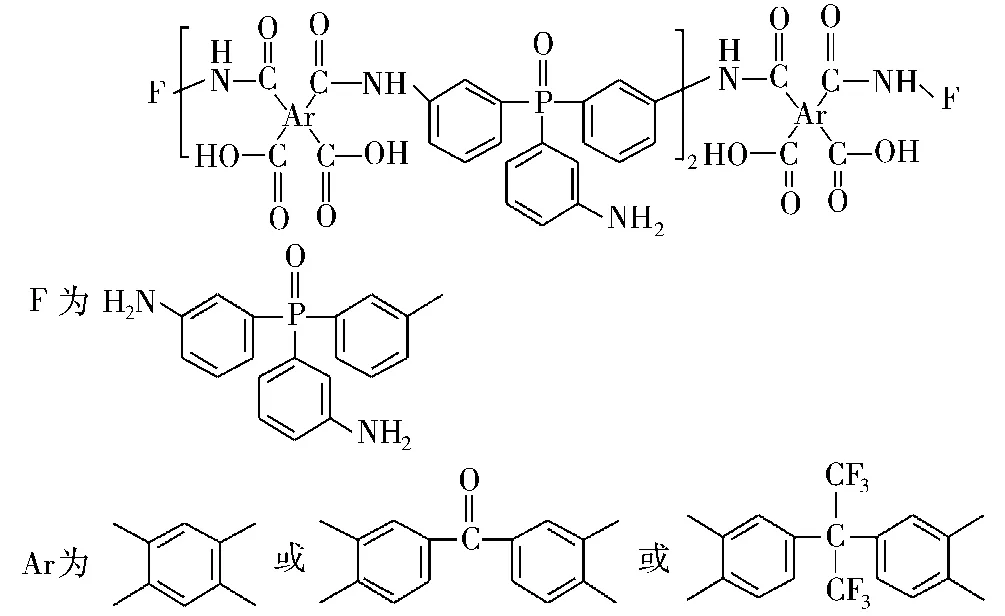
图11 含磷固化剂的结构Fig.11 The structures of the phosphorus-containing curing agents
Wu等[37-39]研究了阻燃固化剂二 -(间 -氨基苯)苯基氧化膦(DNBP)对含硅环氧树脂阻燃性的影响,如图12所示。结果表明,DNBP固化的含硅环氧树脂(P/Si为1.33/5.20)在800 ℃时,残炭量为28.6%,极限氧指数值为49%,这是由于磷/硅复合作用形成耐高温残炭的结果。

图12 固化剂DNMP和DNBP的结构Fig.12 The structures of the curing agents DNMP and DNBP
4 磷腈环氧树脂体系
磷腈化合物磷氮骨架结构具有较高的热稳定性、优异的磷氮协效阻燃作用。将该结构引入环氧树脂体系中环氧树脂也能够获得优异的阻燃性能。
X D Wang等[55]制备出了磷腈环氧树脂 PN-EP,如图13所示。其由线形酚醛树脂固化的含磷环氧树脂具有比纯树脂高的Tg(144.6℃)和初始分解温度(378.6℃,3%),在600℃时该树脂的残炭量高达56.2%。如此高的残炭量可能是由于环三磷腈部分降解产生的磷酸和偏磷酸在固相表面促进成炭的缘故。该树脂的(P/N为2.18/0.98)极限氧指数为33.8%,UL 94测试达到V-0级。其阻燃性能优异除去其促进成炭的原因外,其环三磷腈部分产生PO·,能淬灭 H·和OH·自由基终止燃烧反应[56],也是重要原因之一。
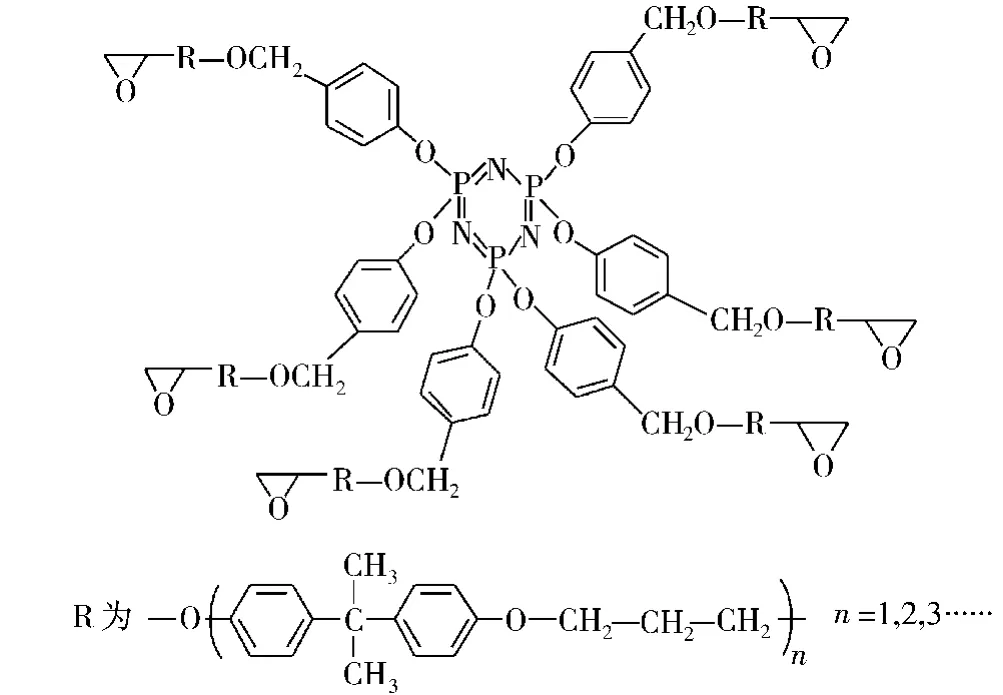
图13 磷腈基环氧树脂(PN-EP)的结构Fig.13 The structures of the phosphazene-based epoxy resin
5 磷硅复合环氧树脂
磷-硅体系在燃烧过程中,硅的存在使富含磷的残炭的热稳定性有所提高[57,58],这是由于稳定的硅迁移至聚合物表面形成保护层抑制了焦炭在高温下的进一步降解,但是硅本身对促进成炭没有明显作用[59-64]。总而言之,磷 -硅的协同阻燃作用要视不同的体系而论[65-66]。
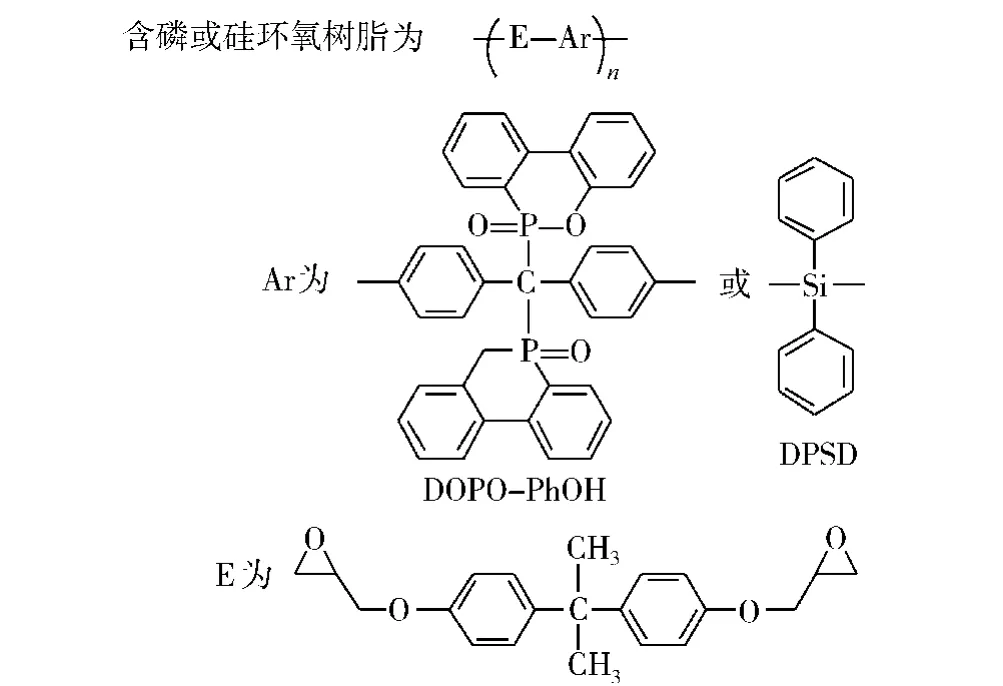
图14 磷 -硅环氧树脂的结构Fig.14 The structure of the phosphorus-silicon epoxy resin
Wu等[37-39]研究了DOPO-PhOH与二苯基二羟基硅烷(DPSD)双酚A型环氧树脂的热稳定性和阻燃性,如图14所示。结果表明,P/Si为3.21/0.73的磷 -硅环氧树脂的阻燃效果最好。初始分解温度为365℃,在700℃时残炭量为25.2%。这是由于含磷基团在相对较低的温度分解形成耐热炭层,而硅由于其低表面能和高抗氧化性在高温下迁移至材料表面形成保护层,进一步增强了材料的耐热性。Y L Liu等[65]还研究了DGEBA、亚磷酸二乙酯及不同含量的硅添加剂固化后得到的磷-硅复合环氧树脂。其中添加质量分数为10%的四乙氧基硅烷的磷 -硅环氧树脂的残炭量在850℃时为45.3%,而未添加的含磷的环氧树脂的残炭量为24.1%。研究表明,四乙氧基硅烷能很好地从材料中迁移至表面,形成保护层,从而使材料获得了更高的残炭量。用这种方法获得的环氧-硅杂原子体系证实了磷和硅的阻燃性具有协同作用。
而 Galià等[66]研究的一类 P/Si复合环氧树脂有很好的阻燃效果,却未发现磷硅协效作用,该体系为(2,5-二羟基苯)二苯膦分别与二缩水甘油基氧甲基苯基硅烷和1,4-二(缩水甘油基氧基二甲基硅烷)-苯环氧单体反应获得的磷-硅复合环氧树脂。
6 结语
含磷阻燃环氧树脂作为高效、低毒、低烟的环境友好型材料,具有广阔的发展前景。目前的研究虽然取得较大进展,但由于含磷环氧树脂或含磷改性单体的合成难度普遍较高,导致其实际应用成本高、价格高,这个因素限制了含磷环氧树脂大规模的使用,因此有必要通过研究新型含磷阻燃环氧树脂的体系或探讨不同组分与磷组分的协同作用来进一步提高含磷环氧树脂的阻燃效率并降低应用成本。所以在今后的研究中需要重点研究优化现有含磷环氧树脂的制备工艺、研制复合型环氧树脂以及新型的含磷固化剂等。
[1] Wang C S,Liao Z K.Synthesis of High Purity O-cresol Formaldehyde Novolac Epoxy[J]. Polymer Bulletin,1991,25(5):559-565.
[2] LudaMP,Balabanovich A I,Zanetti M,et al.The rmal Decomposition of Fire Retardant Brominated Epoxy Resins Cured with Different Nitrogen Containing Hardeners[J].Polymer Degradation and Stability,2007,92(6):1088-1100.
[3] Leu T S,Ho T H,Sun Y M,et al.The rmal Degradation Kinetics and Flame Retardancy of Phosphorus-containing Dicyclopentadiene Epoxy Resins[J].Polymer Degradation and Stability,2006,91(10):2347-2356.
[4] Walters R N,Lyon R E.Fire-resistant Cyanate Esterepoxy Blends[J].Fire Materials,2003,27(4):183-194.
[5] Wang C S,Berman J R,Walker L L,et al.Meta-bromobiphenol Eepoxy Resins:Applications in Electronic Packaging and Printed Circuit Board[J].Journal of Applied Polymer Science,1991,43(7):1315-1321.
[6] Bernhard S,Ulrike B,Aliaksandr,et al.Influence of the Oxidation State of Phosphorus on The Decomposition and Fire Behaviour of Flame-retarded Epoxy Resin Composites[J].Polymer,2006,47(26):8495-8508.
[7] Shau MD,Wang T S.Syntheses,Structure,Reactivity,and The rmal Properties of NewCyclic Phosphine Oxide Epoxy Resins Cured by Diamines[J].Journal of Polymer Science,Part A:Polymer Chemistry,1996,34(3):387-396.
[8] Wichmann H,Dettmer F T,Bahadir M.The rmal Formation of PBDD/F from Tetrabromobisphenol A—A Comparison of Polymer linked TBBP A with Its Additive Incorporation in The rmoplastics[J].Chemosphere,2002,47(4):349-355.
[9] Fang Z P,Ma H Y,Tong L F.Preferential Melt Intercalation of Clay in ABS/Brominated Epoxy Resin-antimony Oxide(BER-AO)Nanocomposites and Its Synergistic Effect on The rmal Degradation and Combustion Behavior[J].Polymer Degradation and Stability,2006,91(9):1972-1979.
[10] Balabanovich A I,Hornung A,Merz D,et al.The Effect of a Curing Agent on the The rmal Degradation of Fire Retardant Brominated Epoxy Resins[J].Polymer Degradation and Stability,2004,85(1):713-723.
[11] Levchik S,Piotrowski A,Weil E,et al.NewDevelopments in Flame Retardancy of Epoxy Resins[J].Polymer Degradation and Stability,2005,88(1):57-62.
[12] Barontini F,Cozzani V,Marsanich K,et al.An Experimental Investigation of Tetrabromobisphenol a Decomposition Pathways[J].Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis,2004,72(1):41-53.
[13] Tange L,Drohmann D.Environmental Issues Related to End- of-life Options ofPlastics Containing Brominated Flame Retardants[J].Fire Materials,2004,28(5):403-410.
[14] Hakk H,Letcher R J.Metabolismin The Toxicokinetics and Fate of Brominated Flame Retardants—A Review[J].Environment International,2003,29(6):801-828.
[15] Liu Y L,Li S H,Lee H C,et al.Selective Reactivity of Aromatic Amines Toward 5-maleimidoisophthalic Acid for Preparation of Polyamides Bearing N-phenylmaleimide Moieties[J].Reactive and Functional Polymers,2006,66(9):924-930.
[16] Martin C,Hunt B J,Ebdon JR,et al.Synthesis,Crosslinking and Flame Retardance of Polymers of Boroncontaining Difunctional Styrenic Monomers[J].Reactive and Functional Polymers,2006,66(10):1047-1054.
[17] Wang C S,Lee MC.Synthesis and Properties of Epoxy Resins Containing 2-(6-ox-ido-6H-dibenz(c,e)(1,2)oxaphosphorin-6-yl)-1,4-benzenediol(II)[J].Polymer,2000,41(10):3631-3638.
[18] L u S Y,Hamerton I.Reacent Developments in the Chemistry ofHalogen-free Flame RetardantPolymers[J].Polymer Degradation and Stability,2002,27(8):1661-1712.
[19] Leu T S,Wang C S.Synergistic Effect of a Phosphorusnitrogen Flame Retardant on Engineering Plastics[J].Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2004,92(1):410-417.
[20] Levchik S V,Camino G,Luda MP,et al.Epoxy Resins Cured with Aminophenylmethylphosphine Oxide 1:Combustion Performance[J].Polymers for Advanced Technologies,1996,7(11):823-830.
[21] Kampke T K,Lenoir D,Kettrup A,et al.Isolation,Characterization,and Toxicological Aspects of Volatile Organophosphorus Compounds from the Combustion of Flame-retardedEpoxy Resins withPhosphonate Substructures[J].Chemistry—A European Journal,1998,4(8):1581-1586.
[22] Hörold S.Phosphorus Flame Retardants in The rmoset Resins[J].Polymer Degradation and Stability,1999,64(3):427-431.
[23] Kuo P L,Chang J M,Wang T L.Flame-retarding Materials I.Syntheses and Flame-retarding Property of Alkylphosphate-type Polyols and Corresponding Polyurethanes[J].Journal of Applied Polymer Science,1998,69(8):1635-1643.
[24] Mauerer O.NewReactive,Halogen-free Flame Retardant Systemfor Epoxy Resins[J].Polymer Degradation and Stability,2005,88(1):70-73.
[25] Wang C S,Lin C H.Synthesis and Properties of Phosphorus Containing Advanced Epoxy Resins[J].Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2000,75(3):429-436.
[26] Wang C S,Shieh J Y.Synthesis and Flame Retardancy of Phosphorus Containing Polycarbonate[J].Journal of Polymer Research,1999,6(3):149-154.
[27] Hwang H J,Ho T H,Chung MC,et al.The rmal and PhysicalProperties ofFlame-retardantEpoxy Resins Containing 2-(6-oxido-6H-dibenz(c,e)(1,2)oxaphosphorin-6-yl)-1,4-naphthalenediol and Cured with Dicyanate ester[J].Polymer Degradation and Stability,2008,93(12):2077-2083.
[28] Wang C S,Lin C H.Novel Phosphorus-containing Epoxy Resins Part I.Synthesis and Properties[J].Polymer,2001,42(5):1869-1878.
[29] Hwang H J,Ho T H,Shieh J Y,et al.The rmal,Physical and Flame-retardant Properties of Phosphorus-containing Epoxy Cured with Cyanate Ester[J].Reactive and Functional Polymers,2009,69(3):176-182.
[30] Wang C S,Shieh J Y.Synthesis and Properties of Epoxy Resins Containing 2-(6-oxido-6H-dibenz(c,e)(1,2)oxaphosphorin-6-yl)-1,4-benzenediol[J].Polymer,1998,39(23):5819-5826.
[31] Hsiue G H,Liu Y L,ChiuY S,et al.Synthesis and Flame-retardant Properties of Phosphorus-containing Polymers Based on Poly(4-hydroxystyrene)[J].Journal of Applied Polymer Science,1998,59(10):1619-1625.
[32] Wang C S,Shieh JY.Phosphorus-containing Epoxy Resin for an Electronic Application[J].Journal of Applied Polymer Science,1999,73(3):353-361.
[33] Wang C S,Shieh J Y.Synthesis and Properties of Novel Phosphorus-containing Hardener for Epoxy Resins[J].Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2000,78(9):1636-1644.
[34] Wang C S,Lin C H,Wu C Y.Synthesis and Properties of Phosphorus-containing Advanced Epoxy Resins II[J].Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2000,78(1):228-235.
[35] Wang C S,Shieh J Y.Synthesis of Novel Flame Retardant Epoxy Hardeners and Properties of Cured Products[J].Polymer,2001,42(18):7617-7625.
[36] Liu Y L.Flame-retartantEpoxy Resins from Novel Phosphorus-containing Novolac[J].Polymer,2001,42(8):3445-3454.
[37] Ying L L,Chuan S W,Yie C C,et al.The rmal Stability of Epoxy Resins Containing Flame Retardant Components:An Evaluation with The rmogravimetric Analysis[J].Polymer Degradation and Stability,2002,78(1):41-48.
[38] Wu C S,Liu Y L,Chiu Y S.Epoxy Resins Possessing Flame RetardantElements from Silicon Incorporated Epoxy Compounds Cured with Phosphorus or Nitrogen Containing Curing Agents[J].Polymer,2002,43(15):4277-4284.
[39] Liu YL.Epoxy Resins from Novel Monomers with a Bis-(9,10-dihydro-9-oxa-10-oxide-10-phosphaphenanthrene-10-yl)Substituent[J].Journal of Polymer Science,Part A:Polymer Chemistry,2002,40(3):359-368.
[40] Wang Y Z,Yang B,Chang Y L,et al.A Novel Phosphorus-containing Polymer as Highly Effective Flame Retardants[J].Macromolecular Materials and Engineering,2004,289(8):703-707.
[41] Altstädt V,Perez R M,Sandler J K W,et al.Novel Phosphorus-modified Polysulfone as a Combined Flame Retardant and Toughness Modifier for Epoxy Resins[J].Polymer,2007,48(3):778-790.
[42] Shi W F,Wang H L,Wang Q F,et al.Synthesis and The rmal Degradation Behaviors of Hyperbranched Polyphosphate[J].Polymer Degradation and Stability,2007,92(10):1788-1794.
[43] Hergenrother P M,Thompson C M,Connell J W,et al.Flame Retardant Aircraft Epoxy Resins Containing Phosphorus[J].Polymer,2005,46(14):5012-5024.
[44] Hsiue G H,Liu Y L,Lan C W,et al.Phosphorus-containing Epoxy for Flame Retardance:IV.Kinetics and Mechanism of The rmal Degradation[J].Polymer Degradation and Stability,1997,56(3):291-299.
[45] Gaёlle F,Serge B,Sophie D.Neutralized Flame Retardant Phosphorus Agent:Facile Synthesis,Reaction to Fire in PP and Synergy with Zinc Borate[J].Polymer Degradation and Stability,2008,93(1):68-76.
[46] Wang Y Z,Gao L P,Wang D Y,et al.A Flame-retardant Epoxy Resin Based on a Reactive Phosphorus-containing Monomer of DODPP and Its The rmal and Flameretardant Properties[J].Polymer Degradation and Stability,2008,93(7):1308-1315.
[47] Lin C H.Synthesis of Novel Phosphorus-containing Cyanate Esters and The ir Curing Reaction with Epoxy Resin[J].Polymer,2004,45(23):7911-7926.
[48] Chen Y W,Lee H F,Yuan C Y.A Flame-retardant Phosphate and Cyclotriphosphazene-containing Epoxy Resin:Synthesis and Properties[J].Journal of Polymer Science,Part A:Polymer Chemistry,2000,38(6):972-981.
[49] Li X,Ou Y X,Shi Y S.Combustion Behavior and The rmal Degradation Properties of Epoxy Resins with a Curing Agent Containing a Caged Bicyclic Phosphate[J].Polymer Degradation and Stability,2002,77(3):383-390.
[50] Wang C S,Shieh J Y.Synthesis and Properties of Epoxy Resins Containing Bis(3-hydroxyphenyl)Phenyl Phosphate[J].Chemistry—A European Journal,2000,36(3):443-452.
[51] Gali M,Ronda J C,Spont N M,et al.Studies on The rmal and Flame Retardant Behaviour of Mixtures of Bis-(m-aminophenyl)methylphosphine Oxide Based Benzoxazine and Glycidylether or Benzoxazine of Bisphenol A[J].Polymer Degradation and Stability,2008,93(12):2158-2165.
[52] Ghosh N N,Kiskan B,Yagci Y.Polybenzoxazines-newHigh Performance The rmosetting Resins:Synthesis and Properties[J].Progress in Polymer Science,2007,32(11):1344-1391.
[53] Varma I K,Jain P,Choudhary V.Effect of Structure on The rmal Behaviour of Epoxy Resins[J].Chemistry—A European Journal,2003,39(1):181-187.
[54] Levchik S V,Camino G,Luda MP,et al.Epoxy Resins Cured with Aminophenylmethylphosphine Oxide II.Mechanism of The rmal Decomposition[J].Polymer Degradation and Stability,1998,60(1):169-183.
[55] Wang X D,Liu R.Synthesis,Characterization,The rmal Properties and Flame Retardancy of a Novel Nonflammable Phosphazene-based Epoxy Resin[J].Polymer Degradation and Stability,2009,94(4):617-624.
[56] Zhang T,Cai Q,Wu D Z,et al.Phosphazene Cyclomatrix Network Polymers:Some Aspects of The Synthesis,Characterization,and Flame-retardantMechanisms of Polymer[J].Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2005,95(4):880-889.
[57] Hsiue G H,Liu YL,Liao H H.Flame-retardant Epoxy Resins:An Approach from Organic-inorganicHybrid Nanocomposites[J].Journal of Polymer Science,Part A:Polymer Chemistry,2001,39(7):986-996.
[58] Liu Y L,Wu C S,Chiu Y S,et al.Preparation,The rmal Properties,and Flame Retardance ofEpoxy-silica Hybrid Resins[J].Journal of Polymer Science,Part A:Polymer Chemistry,2003,41(15):2354-2367.
[59] Chiang C L,Chang R C.Synthesis,Characterization and Properties of Novel Self-extinguishing Organic-inorganic Nanocomposites Containing Nitrogen,Silicon and Phosphorus via Sol-gel Method[J].Composites Science and Technology,2008,68(14):2849-2857.
[60] Kannan P,Kishore K.Novel Flame Retardant Polyphosphor-amide Esters[J].Polymer,1992,33(2):418-422.
[61] Banks M,Ebdon J R,Johnson M.Influence of Covalently Bound Phosphorus-containing Groups on the Flammability of Poly(vinyl alcohol),Poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol)and Low-density Polyethylene[J].Polymer,1993,34(21):4547-4556.
[62] Spontón M,Ronda J C,GaliàM,et al.Flame Retardant Epoxy Resins Based on Diglycidyl Ether of(2,5-dihydroxy-phenyl)Diphenyl Phosphine Oxide[J].Journal of Polymer Science,Part A:Polymer Chemistry,2007,45(11):2142-2151.
[63] Mercado L A,Reina J A,GaliàM.Flame Retardant Epoxy Resins Based on Diglycidyloxymethyl Phenylsilane[J].Journal of Polymer Science,Part A:Polymer Chemistry,2006,44(19):5580-5587.
[64] Hsiue G H,Liu Y L,Tsiao J.Phosphorus Containing Epoxy Resins for Flame Retardancy V:Synergistic Effect of Phosphorus Silicon on Flame Retardancy[J].Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2000,78(1):1-7.
[65] Liu Y L,Chou C I.The Effect of Silicon Sources on the Mechanism of Phosphoruse Silicon Synergism of Flame Retardation of Epoxy Resins[J].Polymer Degradation and Stability,2005,90(3):515-522.
[66] GaliàM,Mercado L A,Spontón M,et al.Preparation,The rmal Properties and Flame Retardancy of Phosphorus-and Silicon-containing Epoxy Resins[J].Polymer Degradation and Stability,2008,93(11):2025-2031.

