重型乙型脑炎患者肾上腺皮质激素的作用
林建英
【摘要】 目的 探讨地塞米松对乙型脑炎患儿的病情、预后及脑脊液α-肿瘤坏死因子(TNF-α)与干扰素(IFN)的影响。方法 把33例重型极期乙脑患儿随机分为两组,地塞米松组18例给予静脉地塞米松针4~5 d; 对照组15例则不用地塞米松。观察比较两组的临床过程和脑脊液TNF-α与IFN的变化。结果 入院时两组的主要临床特点和脑脊液TNF-α与IFN的水平相似, 4~5 d后地塞米松组的临床症状改善情况优于对照组,但两组的脑脊液TNF-α与IFN的水平却无明显改变,并经过1个月的观察地塞米松组的恢复期症状发生率也低于对照组。结论 对重型极期乙脑患儿给予静脉地塞米松可以改善病情,减轻症状,减少恢复期症状的发生。
【关键词】乙脑; 地塞米松; 病情; 预后; TNF-α; IFN
Effect of adrenal cortical hormone on the severe type of patients with epidemic encephalitis B
LIN Jian-ying.
The First Affiliated Hospital of Henan Medical University,xinxiang, 453100,China
【Abstract】 Objective To investigate the influence of adrenal cortical hormone on the patients condition, prognosis and the levels of TNF-α and TNF-γ in cerebrospinal fluid in children with epidemic encephalitis B.Methods 33 cases of severe type of patients with epidemic encephalitis B were divided into two groups randomly, i e dexamethasone-treated group (18) and the control group(15) . In the treated group, patients were treated with intravenous injection of dexamethasone at a dosage of 8 mg/(kgday) for 0.4~0.8 or 5 days; while in the control, no dexammethasone was given. The clinical courses and the changes on levels of TNF-α and IFN-γ in cerebrospinal fluid were compared between these two groups of patients.Results It was demonstrated that the clinical courses and the levels of cytokines in cerebrospinal fluid at time of admission appeared to be similar, however, the improvement of clinical course in the-treated group was better than those of the control group. As to the levels of cytokines in cerebrospinal fluid, there were no significant difference between these two groups. In addition, after one month observation, the rate of symptom development in the convalescence of the treated group was lower than that of the control group.Conclusion From the above observations, it is evident that treatment with intravenous injection of dexamethasone in severe cases with epidemic encephalitis B can improve the clinical course, lessen the clinical symptoms and reduce the rate of development of symptoms in convalescence.
【Key words】 Epidemic encephalris B; Dexamethasone; Patients condition; Prognosis; Tumor
necrosis factor-α; Interferon
流行性乙型脑炎(epidemic encephalitis B,简称乙脑)由乙型脑炎病毒引起的以脑实质炎性反应为主要病变的人兽共患的急性传染病;重型患儿病死率仍在10%左右,并且多数发生在极期。由于乙脑没有特效的治疗方法,主要是积极对症治疗和护理。目前激素在乙脑中的作用仍有不同看法,Hoke等[1]报道使用大剂量激素没有满意疗效;而何时军等[2]报道大剂量激素能抑制颅内炎症反应水平,阻止病情恶化。因此激素的应用及其作用机制有待进一步探讨。
1 材料与方法
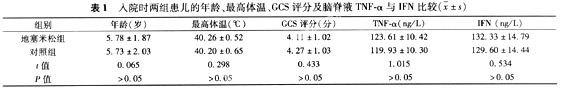
1.1 一般资料 33例重型乙脑患儿均来自2007年11~12月新乡医学院第一附属医院感染科住院病例。患儿血清乙脑特异性IgM抗体均阳性,符合乙脑诊断及分型标准[3]。将33例随机分为地塞米松组18例,男10例,女8例;对照组15例,男9例,女6例;年龄2~11岁。
1.2 方法 两组年龄、最高体温、GCS评分及脑脊液TNF-α与IFN水平均具可比性,见表1。地塞米松组给予静脉地塞米松针0.4~0.8 mg/(kgd),2次/d,4~5 d;对照组则不用地塞米松;其余治疗相同。停用地塞米松后比较两组最高体温、GCS评分及脑脊液TNF-α与IFN水平;极期后经过1个月观察比较恢复期症状的发生率。TNF-α与IFN检测采用ELISA法,试剂盒购自深圳晶美生物工程有限公司,按说明书操作。
1.3 统计学方法 采用SPSS 14.0软件包进行统计学分析,计量资料用t检验,计数资料用χ2检验。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
经治后,地塞米松组的最高体温明显低于对照组,GCS评分则明显高于对照组,差异均有统计学意义,地塞米松组恢复期症状发生率要低于对照组,但差异无统计学意义,两组的脑脊液TNF-α与IFN的水平却无明显改变,差异无统计学意义,见表2、3。

