集中式MIMO组网雷达系统波形设计
摘 要:波形设计是集中式MIMO组网雷达信号处理的关键技术之一。为了提高该系统在杂波或干扰下的目标探测能力,同时兼顾硬件兼容性以及所设计波形良好的模糊函数和脉冲压缩特性,本文考虑在恒模约束和波形相似性度量下构建关于雷达输出信杂噪比(SCNR)的优化模型;通过对原非凸问题的等价转换,提出了一种基于连续凸近似的多项式时间迭代算法,并分析了其收敛性;为了进一步降低计算复杂度,提出了一种基于梯度投影(GP)的算法。最后,对所提方法进行了仿真验证,结果表明,该方法能够为组网雷达系统下各发射站点的波形设计提供一种新的可行方法。
关键词:组网雷达系统; 波形相似性; 可行点追踪-连续凸近似; 梯度投影
中图分类号:TN958 文献标识码:A DOI:10.19452/j.issn1007-5453.2024.08.010
基金项目: 航空科学基金 (20182098002)
与发射特定波形的相控阵雷达相比,多输入多输出(MIMO)雷达可经其不同的天线发射不同的波形(波形分集)。这种波形分集也是其在目标探测、估计和跟踪方面优于传统雷达的关键因素[1-2]。根据不同的天线间隔,MIMO雷达可以分为分布式MIMO雷达和集中式MIMO雷达两类[3-5]。前者天线间隔较大,使得各个天线阵元从不同的视角观测目标,因此能够充分利用空间分集增益;后者天线间隔较小,各个天线阵元对目标的观测角近似相同,能够获得波形分集增益。
近年来,波形设计作为雷达领域中的一个重要问题已经引起了研究人员的广泛关注。一般来说,与集中式MIMO雷达波形设计相关的工作主要集中在以下4个方面:(1)设计具有良好自相关/互相关特性的波形,这意味着发射波形与其自身或者其他发射波形在任意时延处互不相关[6-8];(2)通过最大化雷达回波信号与目标冲激响应之间的互信息来设计波形[9-11];(3)设计期望的MIMO雷达发射波束方向图,使得发射功率在期望的角度下达到最大,同时抑制杂波等干扰所在角度的发射功率[12-14];(4)着眼于收发处理,通过最大化信干噪比来完成对发射波形的设计或发射波形和接收滤波器的联合设计[15-21]。
为了使接收机区分来自不同发射机的回波,分布式MIMO雷达的大部分波形设计标准旨在获得彼此正交的发射波形[26-35]。Stoica等[27]提出了三种新的计算效率高的用于MIMO雷达恒模波形设计的循环算法。Chen Yifan等[28]基于认知雷达开发了一个自适应分布式MIMO雷达框架,并在该框架下设计了一种新的两阶段波形优化算法。Xu Leilei等[30]考虑了多普勒灵敏度对恒模分布式MIMO发射波形自相关和互相关旁瓣的影响。随后又提出了一种正交相位编码信号和失配滤波器组的设计方法[30-31]。Dontamsetti等[32]提出了一种发射和接收信号联合优化的分布式MIMO雷达方案,基于信道矩阵的估计情况来最大限度地提高输出信噪比。Luo Xi等[33]利用遗传算法设计了步进频分线性调频和步进频分脉冲编码调制两种正交波形。
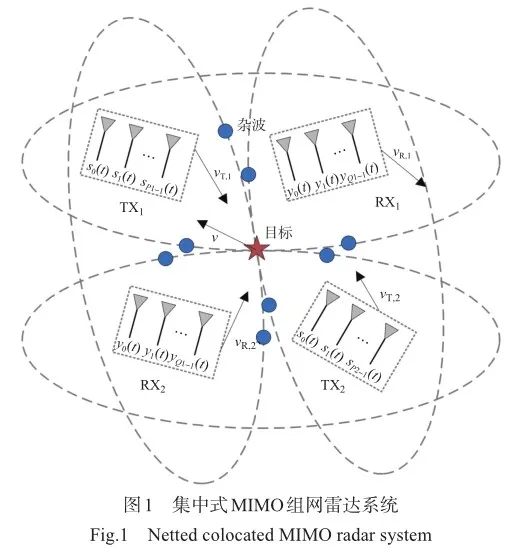
值得注意的是,之前大部分学者对分布式MIMO雷达波形设计问题的研究都是基于每个波形站点是相控阵的情况下进行的。而本文中所提到的集中式MIMO组网雷达系统对分布式和集中式MIMO雷达的优点进行了融合,在这种情况下不仅能够利用分布式MIMO雷达的空间分集增益,同时也能够充分利用集中式MIMO雷达波形分集的优势来对每一个站点的波形进行重新设计。目前,在这种组网雷达系统下的波形设计研究相对较少,主要的研究工作集中在总功率约束下对发射波形进行设计[36],但没有考虑实际的系统实现问题。事实上,雷达放大器往往工作在饱和条件,若没有恒模约束,则不能有效利用非线性功率放大器。此外,现有设计没有考虑到目标方向上波形的模糊特性和脉冲压缩特性,本文拟对发射波形施加相似性约束,以保证所设计波形在目标方向上获得优良的模糊特性[15, 37-39]。
本文讨论的是一种集中式MIMO组网雷达系统,该系统的各节点由集中式MIMO雷达构成,因而同时具备了分布式和集中式MIMO雷达的优点。目前,针对这种组网雷达系统的研究大多集中在资源管理方面[40-44],但波形设计也对提升该系统目标探测性能具有重要意义。
具体来说,本文的主要贡献如下:(1)研究了在恒模约束下的集中式MIMO组网雷达系统各发射站点的波形设计问题。为了使设计的波形具有优良的模糊特性,本文将波形相似性度量作为惩罚项引入优化问题和信杂噪比(SCNR)一起构成新的优化目标。为了解决这个NP-Hard问题,本文提出了基于可行点追踪-连续凸近似(FPPSCA)和梯度投影(GP)算法框架下的两种解决方案,然后对两种算法的收敛性和复杂性进行了分析。(2)与以往相似性约束中参考波形的选取有所不同。在之前的工作中往往选取线性调频信号来使设计波形拥有好的模糊函数和脉冲压缩特性,但在实际应用中仅仅需要使目标方向上的波形拥有好的波形特性。因此,本文设计了一种新的角度依赖的参考波形以及相应的波形相似性度量。(3)仿真结果验证了所提解决方案在不同的模拟场景中的性能。对基于FPP-SCA和GP框架下所设计的波形进行了对比,试验结果表明FPP-SCA算法的性能优于GP算法,但GP算法的计算复杂度低于FPP-SCA算法。
1 集中式MIMO组网雷达信号模型











 rdAT8L4Rn7lA9UrkmajDmlw/jCCUtlkysYoqHFJUaXY=
rdAT8L4Rn7lA9UrkmajDmlw/jCCUtlkysYoqHFJUaXY=

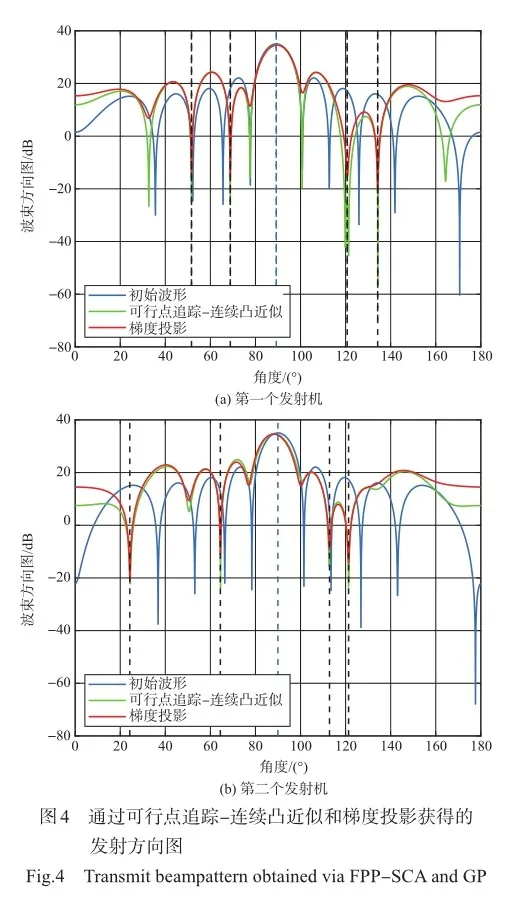
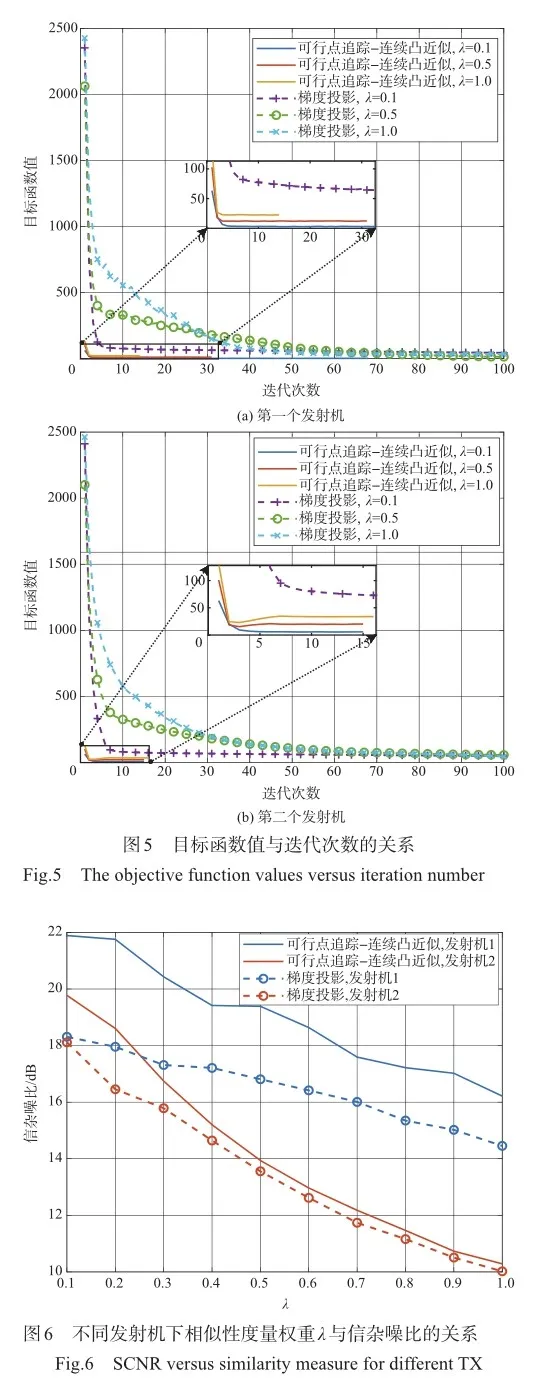
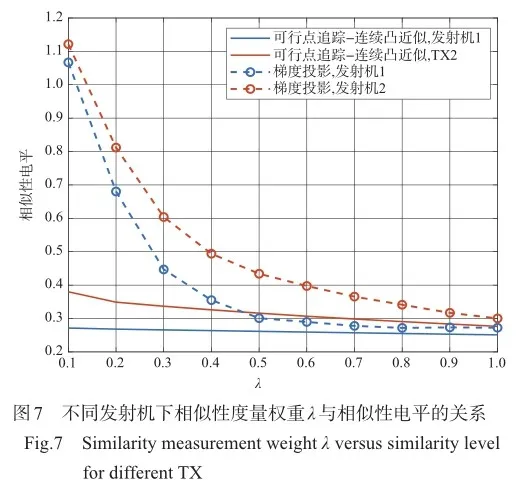
同时,本文考虑了设计波形在目标方向上的模糊特性。从图7中两种算法下不同的相似性水平曲线,不难推测出在FPP-SCA算法下设计波形在目标方向上的模糊特性基本不会随着相似性度量权重λ的变化而变化,而在GP算法下设计波形在目标方向上的模糊特性会随着相似性度量权重λ的增大越来越好。这也在图10中得以验证,可以看到在λ=0.1时FPP-SCA算法下的设计波形和参考波形在目标方向的模糊特性已基本相同,而GP算法下设计波形在目标方向的模糊特性在λ=0.5时才能达到同样的效果。
5.2 天线数目的影响
最后,考虑天线数目对设计波形的影响,本文分别设置了Pm=Qn?{810}m=12;n=12,每次试验中只考虑天线数目单个变量的影响。从图11中可以清楚地看到,不论是哪一个TX,设置的天线数目越多,所得到的SCNR越高。这是因为随着天线数目的增多,波形优化的自由度和杂波抑制能力也随之增加,能够获得更好的性能。
6 结束语

本文讨论了在集中式MIMO平台组网雷达系统下发射波形的设计问题,以提高该系统在杂波干扰下的探测能力。在各节点波形设计中,考虑到如何保持波形恒模特性以及波形模糊特性,以便于实际系统应用。本文把波形设计问题表述为一个非凸的优化问题,并引入了多项式复杂度的FPPSCA算法或GP算法求解发射波形。此外,本文设计了一种新的角度依赖的参考波形。仿真结果表明,通过所提算法设计的波形在目标方向上确实拥有好的模糊特性和脉冲压缩特性。未来潜在方向为涉及多目标情况的研究,以及在非均匀杂波干扰情况下的自适应波形设计。

参考文献
[1]曹兰英,董晔,郭维娜. 机载火控雷达发展趋势探究[J].航空科学技术,2021,32(6): 1-8. Cao Lanying, Dong Ye, Guo Weina. Development trend analysis of airborne fire-control radars[J]. Aeronautical Science& Technology, 2021,32(6): 1-8.(in Chinese)
[2]宋婷,贺丰收,程宇峰. 深度学习技术在雷达目标检测中的研究进展[J].航空科学技术,2020,31(10): 12-20. Song Ting, He Fengshou, Cheng Yufeng. Research progress of deep learning technology in radar target detection[J]. Aeronautical Science & Technology, 2020, 31(10): 12-20. (in Chinese)
[3]Li Jian, Stoica P. MIMO radar signal processing[M]. U. S.: Wiley-IEEE Press, 2009.
[4]Haimovich A M, Blum R S, Cimini L J. MIMO radar with widely separated antennas[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Maga‐zine, 2008, 25(1): 116-129.
[5]Li Jian, Stoica P. MIMO radar with colocated antennas[J].IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2007, 24(5): 106-114.
[6]Song Junxiao, Babu P P. Palomar D. Sequence set design with good correlation properties via majorization-minimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(11): 2866-2879.
[7]Li Yongzhe, Vorobyov S A. Fast algorithms for designing unimodular waveform(s) with good correlation properties[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(5): 1197-1212.
[8]Alaee-Kerahroodi M, Modarres-Hashemi M, Naghsh M M. Designing sets of binary sequences for MIMO radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(13): 3347-3360.
[9]Yang Yang, Blum R S. MIMO radar waveform design based on mutual information and minimum mean-square error estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2007, 43(1): 330-343.
[10]Leshem A, Naparstek O, Nehorai A. Information theoretic adaptive radar waveform design for multiple extended targets[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2007, 1(1): 42-55.
[11]Chen Yifan, Nijsure Y, Yuen C, et al. Adaptive distributed mi‐mo radar waveform optimization based on mutual information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2013, 49(2): 1374-1385.
[12]Cheng Ziyang, He Zishu, Zhang Shengmiao, et al. Constant modulus waveform design for mimo radar transmit beampattern[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(18): 4912-4923.
[13]Cheng Ziyang, Han Chunlin, Liao Bin, et al. Communicationaware waveform design for mimo radar with good transmit beampattern[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(21): 5549-5562.
[14]Yu Xianxiang, Qiu Hui, Yang Jing, et al. Multispectrally constrained mimo radar beampattern design via sequential convex approximation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(4): 2935-2949.
[15]Cui Guolong, Li Hongbin, Rangaswamy M. MIMO radar waveform design with constant modulus and similarity constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(2): 343-353.
[16]Cui Guolong, Yu Xianxiang, Carotenuto V, et al. Space-time transmit code and receive filter design for colocated MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(5): 1116-1129.
[17]Cheng Ziyang, He Zishu, Fang Min, et al. Spectrally compati‐ble waveform design for mimo radar transmit beampattern with par and similarity constraints[C]. 2018 IEEE International Con‐ference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2018: 3286-3290.
[18]Cheng Ziyang, Liao Bin, He Zishu, et al. Spectrally compatible waveform design for mimo radar in the presence of multiple targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(13): 3543-3555.
[19]Yu Xianxiang, Alhujaili K, Cui Guolong, et al. MIMO radar waveform design in the presence of multiple targets and practi‐cal constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 1974-1989.
[20]Liu Rang, Li Ming, Liu Qian, et al. Joint waveform and filter designs for STAP-SLP-based MIMO-DFRC systems[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2022, 40(6): 1918-1931.
[21]Tsinos C G, Arora A, Chatzinotas S, et al. Joint transmit waveform and receive filter design for dual-function radarcommunication systems[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2021, 15(6): 1378-1392.
[22]Wen Cai, Peng Jinye, Zhou Yan, et al. Enhanced ThreeDimensional joint domain localized STAP for airborne FDAMIMO radar under dense false-target jamming scenario[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(10): 4154-4166.
[23]Wen Cai, Huang Yan, Peng Jinye, et al. Slow-time FDAMIMO technique with application to STAP radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(1): 74-95.
[24]Wen Cai, Huang Yan, Davidson T. Efficient transceiver design for MIMO dual-function radar-communication systems [J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2023, 71: 1786-1801.
[25]Wen Cai, Huang Yan, Zheng Le, et al. Transmit waveform design for dual-function radar-communication systems via hybrid linear-nonlinear precoding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2023, 71: 2130-2145.
[26]Qu Junliang, Jia Xu, Peng Yingning, et al. Optimal waveform design for MIMO radar detection with clutter and noise[C]. IEEE CIE International Conference on Radar, 2011: 559-563.
[27]He Hao, Stoica P, Li Jian. Designing Unimodular sequence sets with good correlations:including an application to MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(11): 4391-4405.
[28]Chen Yifan, Nijsure Y, Yuen C, et al. Adaptive distributed MIMO radar waveform optimization based on mutual information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2013, 49(2): 1374-1385.
[29]Zhou Shenghua, Liu Hongwei, Zang Huikai. Doppler sensitivity of MIMO radar waveforms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2016, 52(5): 2091-2110.
[30]Xu Leilei, Liu Hongwei, Li Qiang, et al. Distributed MIMO ra‐dar orthogonal waveforms and mismatched filters design with expanded mainlobe[C]. 2016 CIE International Conference on Radar (RADAR), 2016.
[31]徐磊磊,周生华,刘宏伟,等. 一种分布式MIMO雷达正交波形和失配滤波器组联合设计方法[J]. 电子与信息学报,2018,40(6): 1476-1483. Xu Leilei, Zhou Shenghua, Liu Hongwei, et al. Joint design of distributed Mimo radar orthogonal waveforms and mismatched filter bank[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2018, 40(6): 1476-1483. (in Chinese)
[32]Dontamsetti S G, Kumar R V. A Distributed MIMO radar with joint optimal transmit and receive signal combining[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(1): 623-635.
[33]Luo Xi, Guo Lixin, Song Dawei, et al. The research of orthogonal waveform design for ambiguity feature based on distributed MIMO radar[C]. 2021 6th International Conference on Communication, Image and Signal Processing (CCISP), 2021: 425-429.
[34]Tang Bo, Zhang Ning, Zhang Shuo, et al. MMSE-based waveform design for the distributed MIMO radar in spectrally crowded environments[J]. The Journal of Engineering, 2019, 20: 6603-6607.
[35]Shi Chengguang, Wang Fei, Sellathurai M, et al. Low probability of intercept‐based distributed MIMO radar waveform design against barrage jamming in signal‐dependent clutter and coloured noise[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2019, 13(4): 415-423.
[36]Chen Peng, Zheng Le, Wang Xiaodong, et al. Moving target detection using colocated MIMO radar on multiple distributed moving platforms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(17): 4670-4683.
[37]Wu Linlong, Babu P, Palomar D P. Transmit waveform/receive filter design for MIMO radar with multiple waveform constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(6): 526-1540.
[38]Maio A D, Nicola S D, Huang Yongwei, et al. Design of phase codes for radar performance optimization with a similarity constraint[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(2): 610-621.
[39]Yu Xianxiang, Cui Guolong, Kong Lingjiang, et al. Con‐ strained waveform design for colocated MIMO radar with un‐certain steering matrices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2019, 55(1): 356-370.
[40]Yan Junkun, Liu Hongwei, Pu Wenqiang, et al. Joint beam selection and power allocation for multiple target tracking in netted colocated MIMO radar system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(24): 6417-6427.
[41]Yi Wei, Yuan Ye, Hoseinnezhad R, et al. Resource scheduling for distributed multi-target tracking in netted colocated MIMO radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 1602-1617.
[42]Sun Hao, Li Ming, Zuo Lei, et al. Optimal beampattern design for resource-aware multitarget tracking in netted colocated MIMO radar systems[C]. 2021 International Conference on Control, Automation and Information Sciences (ICCAIS), 2021: 199-204.
[43]Su Yang, Cheng Ting, He Zishu, et al. Joint waveform control and resource optimization for maneuvering targets tracking in netted colocated MIMO radar systems[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2022, 16(3): 3960-3971.
[44]Zhang Haowei, Liu Wejian, Xie Junwei, et al. Joint Subarray selection and power allocation for cognitive target tracking in large-scale MIMO radar networks[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2020, 14(2): 2569-2580.
[45]Mehanna O, Huang Kejun, Gopalakrishnan B, et al. Feasible point pursuit and successive approximation of non-convex QC‐QPs[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2015, 22(7): 804-808.
[46]Lieven V, Stephen B. Convex optimization[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2004.
[47]Lobo M S, Vandenberghe L, Boyd S, et al. Applications of second-order cone programming[J]. Linear Algebra and Its Applications, 1998, 284(1-3): 193-228.
[48]Bertsekas D P. Nonlinear Programming[M]. Athena: Athena Scientific Press, 1999.
Waveform Design for Netted Colocated-MIMO Radar System
Zhang Xiang, Wen Cai, Xu Jinjin, Meng Yinuo Northwestern University, Xi’an 710127, China
Abstract: Waveform design is one of the key technologies in radar signal processing for the netted collocated Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) radar system. To improve the target detection capability of the system under clutter interference while taking into account hardware compatibility, good ambiguity and pulse compression properties of the designed waveform, the paper considers constructing a model for the radar output Signal to Clutter and Noise Ratio(SCNR) under constant modulus constraints and waveform similarity metrics; then by equivalent transformation of the original non-convex problem, a polynomial-time iterative algorithm based on successive convex approximation is proposed and analyzed for convergence. To further reduce the computational complexity, the paper also proposes an algorithm based on Gradient Projection (GP). Finally, the proposed method is simulated and verified, and the results show that the method can provide a new feasible method for the waveform design of each transmitting site under the netted radar system.
Key Words: netted radar system; waveform similarity; feasible point pursuit-successive convex approximation; gradient projection

