长余辉海藻酸钠纤维的制备及其性能







摘 要:为了制备出具有长余辉功能的海藻酸钠纤维,拓宽海藻酸钠纤维和长余辉发光材料的应用领域,文章首先以硝酸锶、二氧化硅、氧化镁、氧化硼、氧化铕和氧化镝为原料,通过高温固相法制备了长余辉发光材料,再采用共混方式结合海藻酸钠制备出纺丝液,最后通过湿法纺丝制备了不同浓度的长余辉海藻酸钠纤维。利用扫描电子显微镜、红外光谱仪、荧光光谱仪、荧光余辉亮度测试仪和多功能力学测试仪对长余辉海藻酸钠纤维的微观形貌、化学结构、余辉性能及力学性能进行分析。结果表明:随着加入的长余辉发光材料质量增加,长余辉海藻酸钠纤维的余辉性能在不断提高,但纤维的强力呈下降趋势;当加入的长余辉发光材料质量分数为2.0%时,所制备的长余辉海藻酸钠纤维的综合性能达到最优。所制备的长余辉海藻酸钠纤维在夜行服和防伪标志等方面具有良好的应用前景。
关键词:海藻酸钠纤维;长余辉发光材料;长余辉海藻酸钠纤维;余辉性能;力学性能
中图分类号:TS15
文献标志码:A
文章编号:1009-265X(2024)10-0078-07
长余辉发光材料,又叫蓄光材料,是一种在受到外界光源激发的时候能够将光能储存于材料之中并在黑暗条件下发光的材料[1-3]。其主要发光体系有3种,分别为硫化物体系、铝酸盐体系和硅酸盐体系[4-6]。由于硫化物体系长余辉发光材料具有放射性,现已逐渐被硅酸盐体系和铝酸盐体系的长余辉发光材料所替代。与铝酸盐体系长余辉发光材料相比,硅酸盐体系长余辉发光材料不仅具有化学稳定性好、成本低的特点,同时还具有优异的耐水性[7-8]。此外,在制备长余辉发光纤维之前,硅酸盐体系长余辉发光材料
无需用硅烷偶联剂进行预处理[9-11],减少了发光纤维的制备工序。因此,硅酸盐体系长余辉发光材料是制备长余辉发光纤维的首选。
长余辉发光纤维是通过特定的纺丝方法,将长余辉发光材料封闭于纤维中而获得具有长余辉性能的纤维[12-13]。例如:He等[14]使用静电纺丝的方法制备了直径为200 nm的Sr2MgSi2O7:Eu2+,Dy3+/PVA纳米纤维,经过后续的煅烧工序(还原
氛围)后得到在471 nm 处有蓝色发射峰的发光纤维;Ye 等[15]以聚乳酸为纤维基质,以溶胶-凝胶法结合静电纺丝制备了具有良好的蓝色长余辉性能的Sr2MgSi2O7:Eu2+,Dy3+/PLA复合纤维,该复合纤维不仅具有良好的余辉性能,同时具有自降解特性。
海藻酸钠纤维是一种由海藻中提取的海藻酸钠经特种工艺所制备成的纤维。其制备原料来源广泛,同时还具有良好的自降解能力,是一种绿色环保材料。将长余辉发光材料应用于海藻酸钠纤维中,不仅可以制作效果奇特的舞台服饰,同时也可以制作具有防伪功能的标志[9]。本文将不同质量分数的硅酸镁锶长余辉发光材料(Sr2MgSi2O7:Eu2+,Dy3+)掺入到海藻酸钠纺丝液中,制备出不同质量分数的长余辉海藻酸钠纤维,并对其基本性能和余辉性能进行研究,为硅酸镁锶长余辉发光材料在纺织领域的应用提供理论参考。
1 实验
1.1 实验材料
硝酸锶,上海化工试剂一厂;二氧化硅、氧化镁、氧化硼、氧化铕、氧化镝、海藻酸钠、无水氯化钙、去离子水和无水乙醇,上海麦克林生化试剂公司;氮气和氢气,杭州今工特种气体有限公司。
1.2 实验设备
管式炉(OTF-1200X,合肥科晶材料技术有限公司),注射泵(TYD01-01-CEhPTJLMVv5tchqlUf3gYq+w==,保定雷弗流体科技有限公司),电子天平(BSA124S,赛多利斯科学仪器有限公司),集热式恒温加热磁力搅拌器(DF-101S,邦西仪器科技有限公司),电热恒温干燥箱(202-00AB,天津市通利信达仪器厂),场发射扫描电镜(FE-SEM-S4800,日本日立),傅里叶红外光谱仪(Nicolet-5700,美国热电公司),荧光光谱仪(F-4600 日本日立),荧光余辉亮度测试仪(PR-305,杭州浙大三色仪器公司),拉伸仪(KES-G 日本Kato-Tech公司)。
1.3 实验方法
按照一定的摩尔比将硝酸锶、二氧化硅、氧化镁、氧化硼、氧化铕和氧化镝粉末倒入研钵中研磨。粉末混合均匀后,倒入方舟并将其放入管式炉中进行热处理。反应条件为:升温速率5 ℃/min,保温温度1100 ℃保温时间3 h,降温速率3 ℃/min,气氛为还原氛围(氮气与氢气的物质的量百分比为9∶1)。反应完成后,得到长余辉发光材料Sr2MgSi2O7:Eu2+,Dy3+。
用电子天平和称量纸称取所需质量的长余辉发光材料,加入100 mL去离子水中,配制成一系列质量分数为1.5%、2.0%、2.5%的发光液,并放在磁力搅拌器上搅拌。称取4 g海藻酸钠粉末,缓慢加入盛有发光液的烧杯中,同时不断搅拌,直至海藻酸钠完全溶解,形成均匀稳定的长余辉海藻酸钠纺丝液。
将配制好的长余辉海藻酸钠纺丝液加入到微量注射器中,在0.9 mL/min的挤出速度,以质量分数为4%无水氯化钙溶液为凝固浴的条件下进行纺丝。最终得到的掺杂不同质量分数长余辉发光材料的海藻酸钠纤维按照上述顺序被标记为:1.5% 长余辉海藻酸钠纤维、2.0% 长余辉海藻酸钠纤维和2.5% 长余辉海藻酸钠纤维。
1.4 测试与表征
对样品喷金处理后,使用场发射扫描电镜观察纯海藻酸钠纤维和长余辉海藻酸钠纤维的纵向形貌和截面形貌;使用Nicolet-5700傅里叶红外光谱仪(FTIR)对纯海藻酸钠纤维和长余辉海藻酸钠纤维在400~4000 cm-1波数内的结构进行表征,得到透过率随波数变化的FTIR光谱图;使用F-46001荧光光谱仪测试分析长余辉海藻酸钠纤维和硅酸镁锶长余辉发光材料的激发谱和发射谱,使用荧光余辉亮度测试仪测试和分析长余辉海藻酸钠纤维和硅酸镁锶长余辉发光材料的余辉性能;使用拉伸仪对海藻酸钠纤维和长余辉海藻酸钠纤维的断裂强力进行测试,拉伸速度为0.02 cm/s。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 表面形貌分析
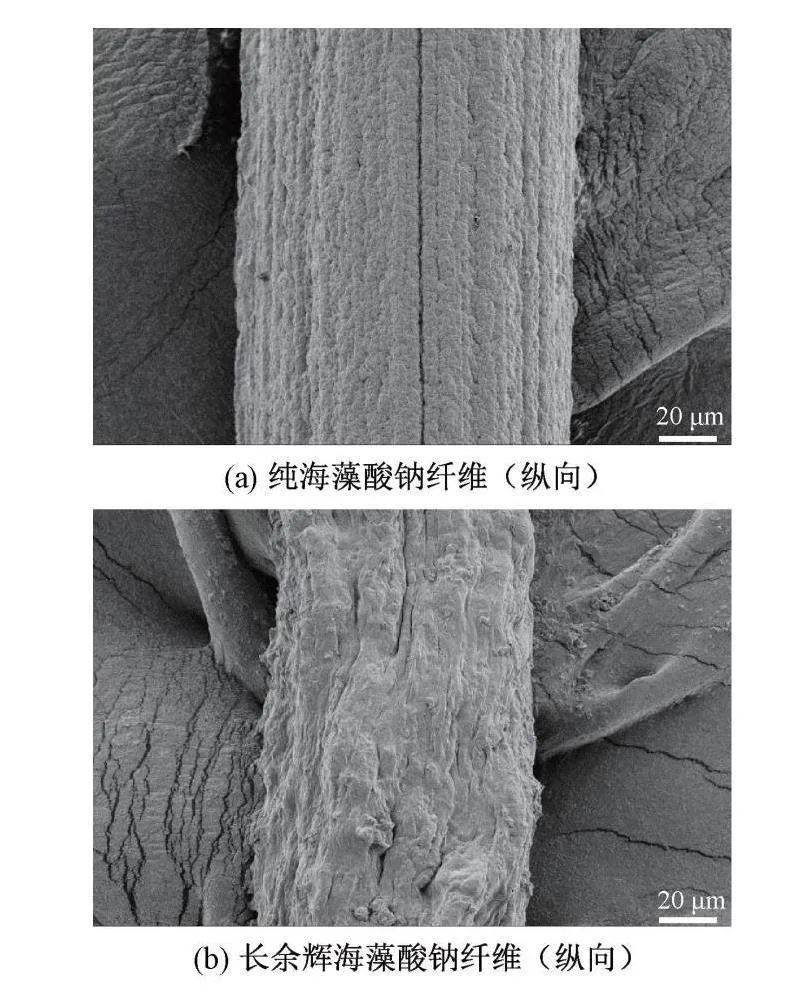
海藻酸钠纤维和长余辉海藻酸钠纤维的横向表面和纵向截面的扫描电镜照片如图1所示。从图1(a)中可以看出:纯海藻酸钠纤维表面非常光滑,没有附着颗粒和凸起,但表面有沟槽,其原因是形成的纤维与凝固浴之间存在双重扩散。由图1(b)可知:长余辉海藻酸钠纤维表面经长余辉发光材料的掺入后变得粗糙,说明长余辉发光材料已成功掺入到海藻酸钠纤维当中。图1(c)显示了纯海藻酸钠纤维横向截面形状均匀,接近为圆形。而从图1(d)中可以看出:长余辉海藻酸钠纤维的横向截面形状为锯齿状,这是由于长余辉发光材料与海藻酸钠相互挤压所造成的。
从EDS谱图(见图2)可知:长余辉海藻酸钠纤维截面中含有Sr,Si,Mg和O元素,说明长余辉发光材料被包覆在海藻酸钠纤维中。
2.2 红外光谱分析
海藻酸钠纤维和长余辉海藻酸钠纤维的红外光谱图如图3所示。由海藻酸钠纤维的红外光谱可知:3335 cm-1处又宽又强的吸收峰为氢键缔合状态下—OH的伸缩振动峰,这与海藻酸钠纤维表面自由水有关。1598 cm-1与1428 cm-1的两个强峰分别表示COO-反对称伸缩振动与对称伸缩振动,1012 cm-1处为C—O—C的吸收振动峰,上述所提及的吸收峰都为海藻酸钠的特征吸收峰[16]。此外,从图3中可以看出,长余辉海藻酸钠纤维的红外光谱基本与海藻酸钠纤维的一致,推测长余辉发光材料与海藻酸钠的结合方式为物理结合[17]。同时,在1646、1502 cm-1和671 cm-1 处存在吸收峰,分别对应硅酸镁锶长余辉发光材料中Mg—O键的伸缩振动峰、Sr—O键的伸缩振动峰和Si—O键的弯曲振动峰[18]。综上所述,长余辉发光材料已成功掺入海藻酸钠纤维中。
2.3 荧光光谱分析
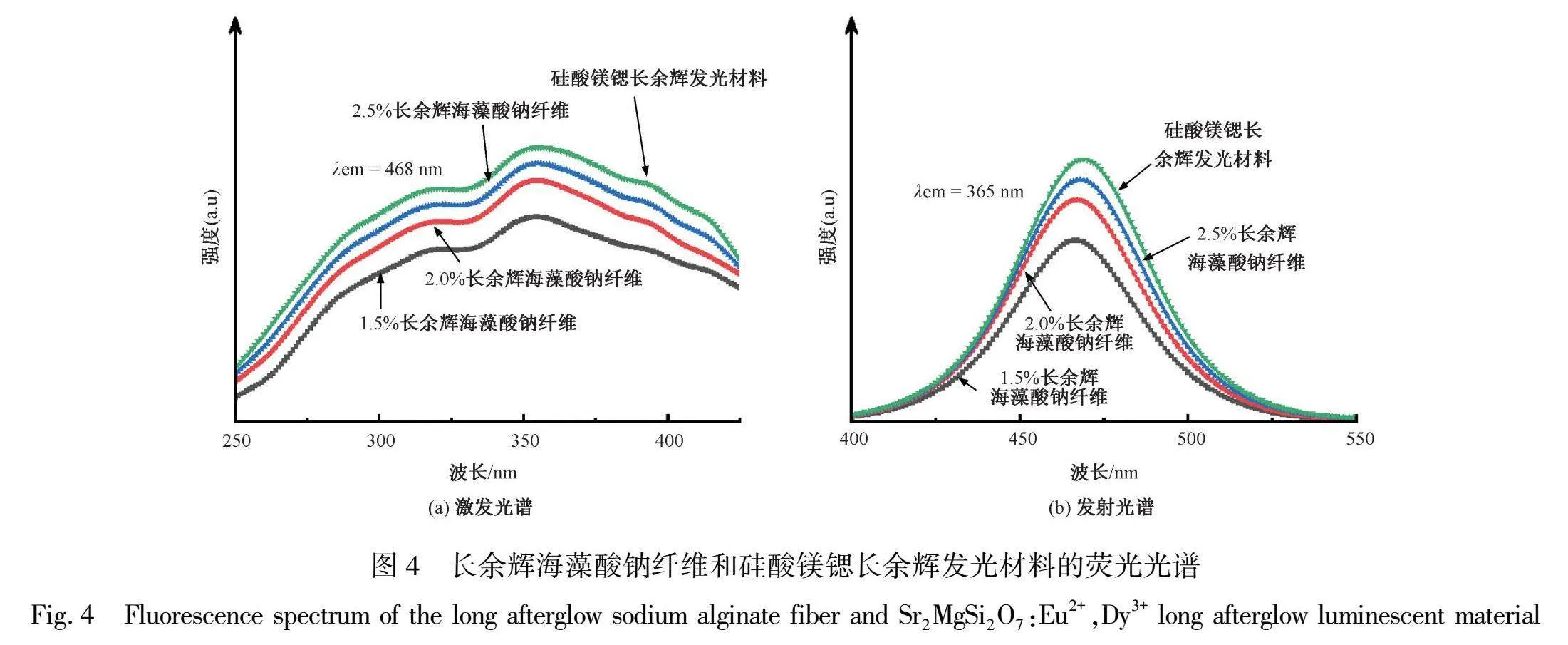
长余辉海藻酸钠纤维和硅酸镁锶长余辉发光材料的激发光谱如图4(a)所示,由图可知:长余辉海藻酸钠纤维和硅酸镁锶长余辉发光材料的激发光谱均由连续波长组成的宽带谱构成,在330 nm和365 nm处分别有一个激发峰,其中365 nm处的激发峰较高。同时,随着掺杂在海藻酸钠纤维中的长余辉发光材料质量的增加,纤维所对应的发光强度也在增加。长余
辉海藻酸钠纤维和硅酸镁锶长余辉发光材料的发射光谱如图4(b)所示。由图可知:长余辉海藻酸钠纤维和硅酸镁锶长余辉发光材料的发射光谱由一个连续分布在400~550 nm范围内的宽发射带组成,并且在468 nm处有一个发射峰。该发射峰对应于掺杂在海藻酸钠纤维中的长余辉发光材料中Eu2+离子的4f65d1→4f7跃迁[13]。同时,长余辉海藻酸钠纤维的发光强度也随着掺杂在纤维中的长余辉发光材料质量的增加而增大。
综上所述,长余辉海藻酸钠纤维的激发谱和发射谱均与硅酸镁锶长余辉发光材料的激发谱和发射谱基本一致,说明长余辉发光材料已成功掺入到海藻酸钠纤维中,并且所制备的长余辉海藻酸钠纤维具有较好的PL性能。
2.4 余辉性能分析
长余辉海藻酸钠纤维和硅酸镁锶长余辉发光材料的余辉衰减曲线如图5所示,用Origin软件对曲线进行了指数拟合,拟合公式为:
I=I0+A1*exp-tτ1+A2*exp(-tτ2)(1)
式中:I代表发光强度,I0为初始发光强度,A1和A2是常数,t为时间,τ1和τ2表示余辉寿命。
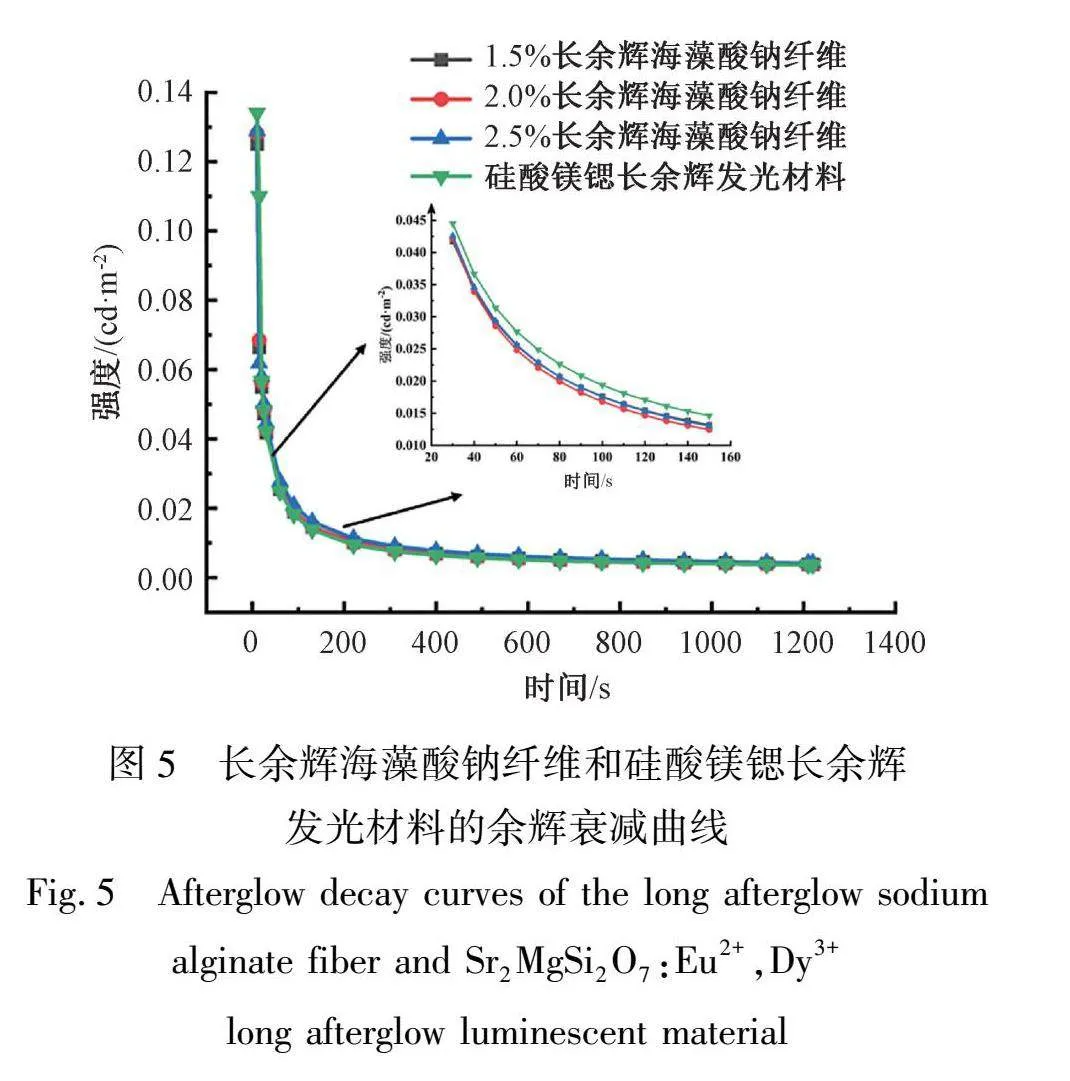
衰减过程分为2个阶段:快衰减和慢衰减阶段。由图5可知:随着掺杂在海藻酸钠纤维中的长余辉发光材料质量的增加,长余辉海藻酸钠纤维的初始亮度也在增大。同时,硅酸镁锶长余辉发光材料的初始亮度大于掺入的长余辉发光材料质量分数为2.5% 的长余辉海藻酸钠纤维的初始亮度,原因可能为海藻酸钠包覆了长余辉发光材料,导致长余辉发光材料所能够吸收的光能减少。表1为长余辉海藻酸钠纤维和硅酸镁锶长余辉发光材料各阶段的初始亮度和余辉寿命数据表,由表可知:随着掺杂在海藻酸钠纤维中的长余辉发光材料质量的增加,长余辉海藻酸钠纤维的初始发光亮度和余辉寿命时间也在增大。除此之外,长余辉海藻酸钠纤维的初始发光亮度和余辉寿命小于硅酸镁锶长余辉发光材料的初始发光亮度和余辉寿命。
2.5 力学性能分析
纯海藻酸钠纤维与长余辉海藻酸钠纤维的应力应变曲线如图6所示。从图6中可知:纯海藻酸钠纤维的拉伸应变为36%左右,断裂强力为20.5 MPa。随着掺杂在海藻酸钠纤维中的长余辉发光材料质量的增加,长余辉海藻酸钠纤维的拉伸应变和断裂强力在减小,说明长余辉发光材料的掺入使得海藻酸钠纤维的力学性能降低,这是因为长余辉发光材料的掺入降低了海藻酸钠聚合物在纤维中的取向度和海藻酸钠大分子间的结合力[19]。
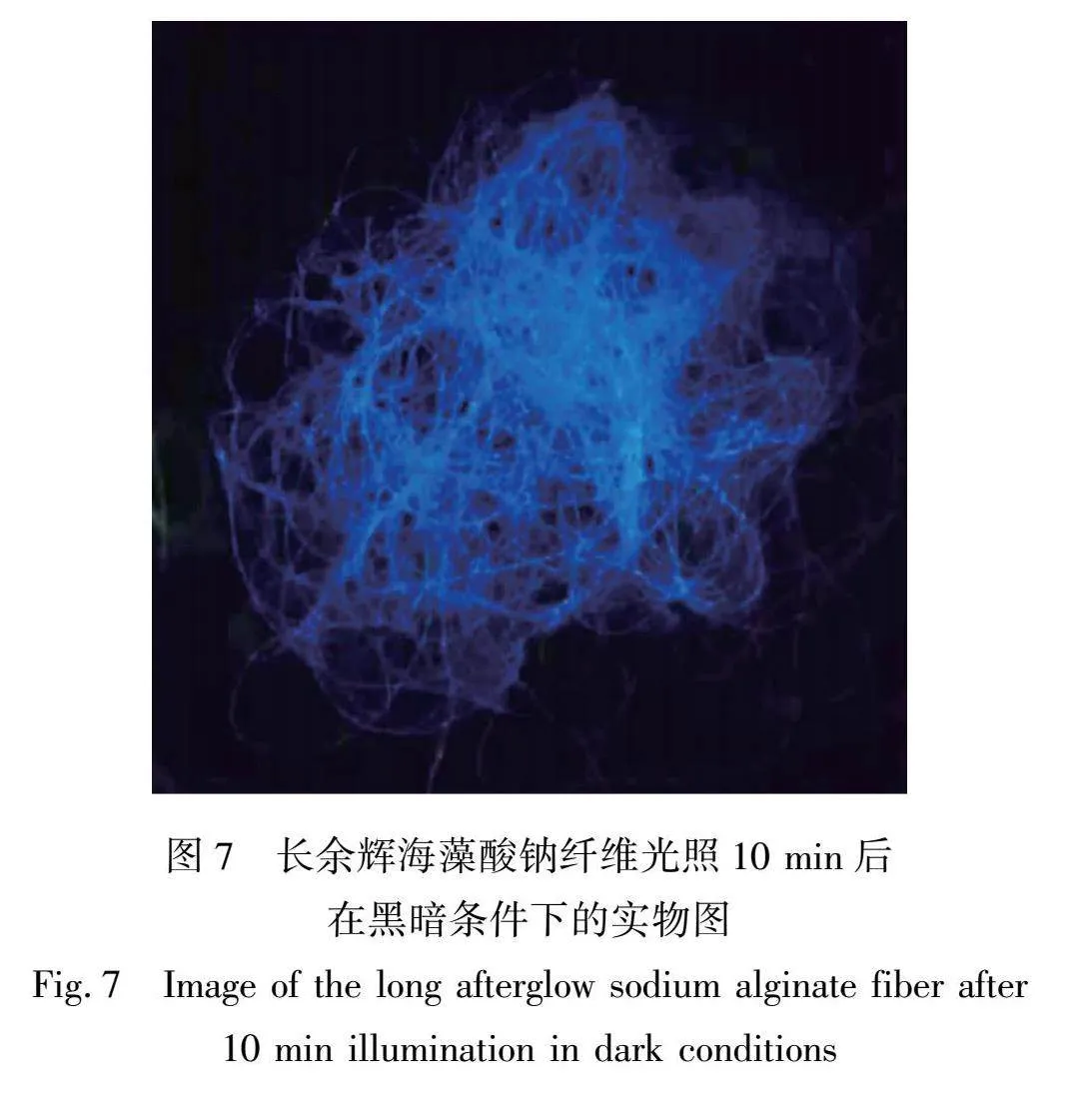
长余辉海藻酸钠纤维光照10 min后在黑暗条件下的实物图如图7所示。从图8中可以看出:长余辉海藻酸钠纤维在光照之后能够在黑暗的条件下发出蓝色的光,说明制备的长余辉海藻酸钠纤维具有良好的余辉性能,可以用于防伪标志和舞台装饰等应用领域。
3 结论
本文采用湿法纺丝工艺成功制备出了外观形貌较好的硅酸镁锶长余辉海藻酸钠纤维,并探究了不同质量分数的长余辉发光材料对长余辉海藻酸钠纤维的性能影响,得出以下结论:
a)当海藻酸钠的质量分数为4%,掺入的长余辉发光材料的质量分数为2.0%时,得到的长余辉海藻酸钠纤维不仅具有良好的余辉性能(0.129 cd/m2),同时具有较好的力学性能(19.6 MPa, 16.5%)。
b)随着掺入长余辉发光材料质量的增加,长余辉海藻酸钠纤维的余辉性能也在增强,但因其打破了海藻酸钠纤维内部固有的有序排列,纤维的机械强力有所下降。
c)长余辉发光材料的掺入让海藻酸钠纤维的形貌发生了改变,纵向表面由光滑变得粗糙,横截面形状由圆形变成了锯齿形。
本文所制备长余辉纤维可用于舞台装饰、夜行服和防伪标志等应用领域,具有良好的应用前景。
参考文献:
[1]高晗, 迟祥, 宋晓雪, 等. 发光纤维的研究进展[J]. 功能材料, 202 52(2): 2085-2097.
GAO Han, CHI Xiang, SONG Xiaoxue, et al. Research progress of luminescent fiber[J]. Journal of Function Materials, 202 52(2): 85-97.
[2]LIU Y L, KUANG J Y, LEI B F, et al. Color-control of long-lasting phosphorescence (LLP) through rare earth ion-doped cadmium metasilicate phosphors[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2005, 15(37): 4025-4031.
[3]ABDUKAYUM A, CHEN J T, ZHAO Q, et al. Functional near infrared-emitting Cr3+/Pr3+ co-doped zinc galloger-manate persistent luminescent nanoparticles with superlong afterglow for in vivo targeted bioimaging[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(38): 14125-14133.
[4]TERRASCHKE H, WICKLEDER C. UV, blue, green, yellow, red, and small: Newest developments on Eu2+-doped nanophosphors[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2015, 115(20): 11352-11378.
[5]LI Y, GECEVICIUS M, QIU J R. Long persistent phosphors: From fundamentals to applications[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2016, 45(8): 2090-2136.
[6]ARRAS J, BRAESE S. The world needs new colors: Cutting edge mobility focusing on long persistent luminesc-ence materials[J]. Chemphotochem, 2018, 2(2): 55-66.
[7]HAI O, ZHANG Z H, REN Q, et al. The preparation and functional studies of the porous long afterglow luminescent materials[J]. Dyes and Pigments, 2018, 156: 160-166.
[8]HAI O, REN Q, WU X L, et al. Insights into the element gradient in the grain and luminescence mechanism of the long afterglow material Sr2MgSi2O7:Eu2+,Dy3+[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019,779: 892-899.
[9]卞雪艳, 朱平, 王怀芳, 等. 长余辉发光海藻纤维的制备及性能研究[J]. 合成纤维, 2017, 46(12): 11-14.
BIAN Xueyan, ZHU Ping, WANG Huaifang, et al. Preparation and properties of long afterglow luminescent alginate fiber[J]. Synthetic Fiber in China, 2017, 46(12): 11-14.
[10]史晨, 侯雪斌, 晋阳, 等. 长余辉发光再生纤维素纤维的制备[J]. 纺织学报, 2016, 37(12): 1-5.
SHI Chen, HOU Xuebin, JIN Yang, et al. Preparation of long-afterglow luminescent regenerated cellulose fiber[J]. Journal of Textile Research, 2016, 37(12): 1-5.
[11]郭雪峰. 发光纤维用纳米铝酸盐发光材料的研究进展[J]. 现代纺织技术, 2020, 28(1): 21-26.
GUO Xuefeng. Research progress of nanoscale aluminate luminescent materials for luminous fiber[J]. Advanced Textile Technology, 2020, 28(1): 21-26.
[12]芦博慧, 魏新, 朱亚楠, 等. 稀土夜光纤维光色的研究与进展[J]. 化工新型材料, 202 49(12): 210-214.
LU Bohui, WEI Xin, ZHU Yanan, et al. Research and development on light color property of rare earth luminous fiber[J]. New Chemical Materials, 202 49(12): 210-214.
[13]梁小平, 刘凯, 王欢, 等. 纳米SrAl2O4: Eu2+, Dy3+长余辉发光材料的制备与表征[J]. 天津工业大学学报, 2014, 33(6): 25-29.
LIANG Xiaoping, LIU Kai, WANG Huan, et al. Synthesis and characterization of nanosized SrAl2O4: Eu2+, Dy3+ long afterglow luminescent material[J]. Journal of Tianjin Polytechnic University, 2014, 33(6): 25-29.
[14]HE L, JIA B L, CHE L Y, et al. Preparation and optical properties of afterglow Sr2MgSi2O7:Eu2+,Dy3+ electrospun nanofibers[J]. Journal of Luminescence, 2016, 172(2): 317-322.
[15]YE F, DONG S J, TIAN Z, et al. Fabrication of the PLA/Sr2MgSi2O7:Eu2+,Dy3+ long-persistent luminescence composite fibers by electrospinning[J]. Optical Materials, 2013, 36(2): 463-466.
[16]狄纯秋, 郭静, 管福成, 等. 双金属离子交联海藻酸盐复合相变纤维的制备与性能[J]. 纺织学报, 2023, 44(5): 54-62.
DI Chunqiu, GUO Jing, GUAN Fucheng, et al. Preparation and characterization of phase change fibers of bimetal ion crosslinked alginate composites[J]. Journal of Textile Research, 2023, 44(5): 54-62.
[17]卞雪艳, 朱平, 楚旭东, 等. 光致变色海藻纤维的制备及性能研究[J]. 合成纤维, 2018, 47(8): 1-5.
BIAN Xueyan, ZHU Ping, CHU Xudong, et al. Preparation and performance of photochromic alginate fiber[J]. Synthetic Fiber in China, 2018, 47(8): 1-5.
[18]XIONG M, XI X, GONG H, et al. Effects of SiO2 coating on luminescence property and thermostability of Sr2MgSi2O7:Eu2+,Dy3+ phosphors[J]. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 2017, 81(2): 894-902.
[19]ZHANG Y S, YIN H B, WANG A L, et al. Deposition and characterization of binary Al2O3/SiO2 coating layers on the surfaces of rutile TiO2 and the pigmentary properties[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2010, 257(4): 1351-1360.
Preparation of long afterglow sodium alginate fibers and their properties
WANG Yong, DU Pingfan
(College of Textile Science and Engineering (International Institute of Silk),
Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, Hangzhou 310018, China)
Abstract:
As the concept of green environmental protection continues to be deeply rooted in people's minds, long afterglow luminescent materials, as a kind of green energy-saving environmental protection materials, have gradually attracted widespread attention from researchers. At the same time, most of the studies on the application of long afterglow luminescent materials in the textile field are aluminate long afterglow luminescent materials, and there is relatively little research on the application of silicate long afterglow luminescent materials. In addition, silicate long afterglow luminescent materials have excellent water resistance compared with aluminate materials, so there is no need for coupling modification before incorporating them into the spinning solution, which can reduce the process of preparing long afterglow fibers with afterglow properties.
To prepare sodium alginate fibers with afterglow properties, a series of sodium alginate spinning solutions with mass gradients (1.5%, 2.0% and 2.5%) doped with Sr2MgSi2O7:Eu2+,Dy3+ long afterglow luminescent materials were set up, and a series of long afterglow sodium alginate fibers with different mass fractions of long afterglow luminescent materials were prepared by wet spinning. The surface microstructure, chemical structure, afterglow properties and mechanical properties of sodium alginate fibers and sodium alginate fibers were tested and analyzed by field emission scanning electron microscope, Fourier infrared instrument, fluorescence spectrometer, fluorescence brightness tester and tension meter, and the best doping quality of Sr2MgSi2O7:Eu2+,Dy3+ long afterglow luminescent material was explored. It provides a theoretical basis for determining the doping quality of Sr2MgSi2O7:Eu2+,Dy3+ long afterglow luminescent materials in other kinds of fiber spinning solution. The results show that the surface of sodium alginate fiber changes from being smooth to being rough and its cross section shape changes from being round to being sawtooth after the addition of Sr2MgSi2O7:Eu2+,Dy3+ long afterglow luminescent material. At the same time, as the Sr2MgSi2O7:Eu2+,Dy3+ long afterglow luminescent material is successfully incorporated into the sodium alginate fiber, the sodium alginate fiber has the afterglow performance, and has a wide and strong emission peak in its emission spectrum, which is attributed to the characteristic emission peak of Sr2MgSi2O7:Eu2+,Dy3+ long afterglow sodium alginate. In addition, the mechanical properties of sodium alginate fiber decrease due to the addition of Sr2MgSi2O7:Eu2+,Dy3+ long afterglow luminescent materials. All the experimental results show that when the mass fraction of sodium alginate is 4% and the mass fraction of Sr2MgSi2O7:Eu2+,Dy3+ is 2%, the prepared sodium alginate fiber not only has good surface morphology and mechanical properties, but also has good afterglow properties.
In this paper, a series of long afterglow sodium alginate fibers with different mass fractions were prepared by wet spinning and their properties were characterized. The influence of doping different mass fractions of Sr2MgSi2O7:Eu2+,Dy3+ afterglow luminescent materials on the properties of sodium alginate fibers was studied. The optimal doping concentration of Sr2MgSi2O7:Eu2+,Dy3+ long afterglow luminescent material was determined, providing a theoretical basis for the incorporation of other kinds of spinning fluids into the material. At the same time, the prepared long afterglow sodium alginate fiber has good afterglow performance and excellent mechanical properties, and can be used in night clothing, stage decoration and anti-counterfeiting signs and other applications.
Keywords:
sodium alginate fiber; long afterglow luminescent materials; long afterglow sodium alginate fiber; afterglow property; mechanical property

