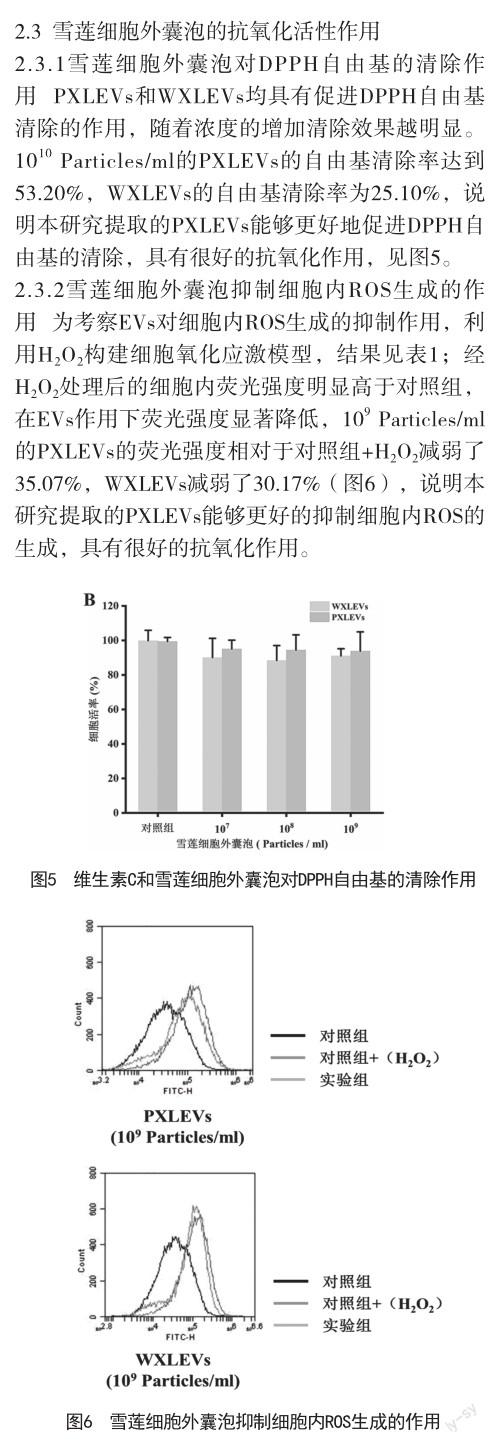
不同种类雪莲愈伤组织细胞外囊泡的抗氧化和美白活性比较
王夜宇 张振兴 张旭辉 高琦
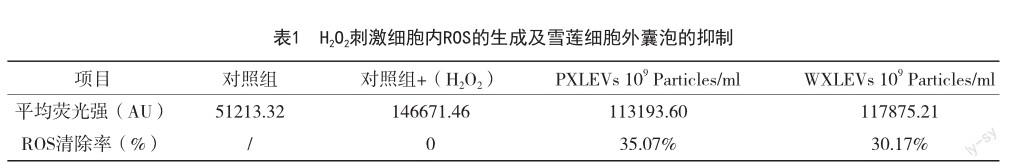
[摘 要]目的 探究天山雪莲紫色愈伤组织细胞外囊泡(PXLEVs)和天山雪莲白色愈伤组织细胞外囊泡(WXLEVs)的分离方法及抗氧化和美白活性差异。方法 采用切向流过滤和柱层析相结合的方法从愈伤组织培养上清液中分离纯化PXLEVs和WXLEVs,透射电子显微镜(TEM)和纳米颗粒跟踪分析(NTA)表征其形貌、粒径和浓度,通过体外DPPH自由基清除实验和细胞内ROS抑制实验研究其抗氧化功效,通过酪氨酸酶活性及细胞黑色素生成抑制实验研究其美白功效。结果 PXLEVs和WXLEVs均呈茶托状结构,PXLEVs的粒径为(152.10±61.30)nm,WXLEVs的粒径为(180.20±76.40)nm;PXLEVs的体外DPPH自由基清除率、细胞内ROS清除率均高于WXLEVs;PXLEVs的酪氨酸酶活性和细胞黑色素含量均低于WXLEVs。结论 与WXLEVs相比PXLEVs具有更好的抗氧化和美白活性,为细胞培养物的选择和天然活性护肤原料的开发提供了理论依据。
[关键词] 雪莲;细胞外囊泡;切向流;柱层析
[中图分类号] Q945 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1004-4949(2024)01-0041-06
Comparison of Antioxidant and Whitening Activities of Extracellular Vesicles from Different Kinds of Snow Lotus Callus Culture Supernatant
WANG Ye-yu, ZHANG Zhen-xing, ZHANG Xu-hui, GAO Qi
(Beijing Youngen Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing 100000, China)
[Abstract]Objective To explore the separation methods of extracellular vesicles from purple callus of snow lotus (PXLEVs) and extracellular vesicles from white callus of snow lotus (WXLEVs) and the differences in antioxidant and whitening activities. Methods PXLEVs and WXLEVs were isolated and purified from callus culture supernatant by tangential flow filtration and column chromatography. The morphology, particle size and concentration were characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA). In vitro DPPH free radical scavenging experiment and intracellular ROS inhibition experiment were used to study its antioxidant effect. Tyrosinase activity and cell melanin generation inhibition experiments were used to study its whitening effect. Results Both PXLEVs and WXLEVs showed a saucer-like structure. The particle size of PXLEVs was (152.10±61.30) nm, and the particle size of WXLEVs was (180.20±76.40) nm. The DPPH free radical scavenging rate and intracellular ROS scavenging rate of PXLEVs were higher than those of WXLEVs. The tyrosinase activity and cell melanin content of PXLEVs were lower than those of WXLEVs. Conclusion Compared with WXLEVs, PXLEVs have better antioxidant and whitening activities, which provides a theoretical basis for the selection of cell culture and the development of natural active skin care materials.
[Key words] Snow lotus; Extracellular vesicles; Tangential flow filtration; Column chromatography
天山雪蓮是我国高山地区常用的一类名贵药用植物,具有很好的抗氧化、抗炎镇痛、活血化瘀和抗衰老等作用[1-3],已被列为我国国家二级保护野生植物[4]。通过植物细胞培养技术获取含有大量生物活性物质的天山雪莲细胞可以有效解决野生雪莲资源问题[5,6]。近年来研究发现[7],植物细胞能够分泌一种细胞外囊泡(EVs),直径30~500 nm,其内选择性包裹脂质、蛋白质、核酸和其他小分子成分[8],具有明确的减轻组织损伤程度、促进损伤组织形态学及功能学修复的作用[9,10]。现有的植物细胞外囊泡提取技术存在很多弊端,不仅需要耗费大量的愈伤组织或,还需要将植株绞碎,对滤渣进行充分的过滤,操作繁琐费时[11-13]。采用磷酸盐缓冲液在长时间的提取过程中也会因渗透压差异导致EVs结构破裂失去功效[7]。本研究采用一种切向流过滤和柱层析相结合的方法从天山雪莲愈伤组织培养上清液中分离出了天山雪莲紫色愈伤组织细胞外囊泡(PXLEVs)和天山雪莲白色愈伤组织细胞外囊泡(WXLEVs),并对其抗氧化和美白活性进行了研究比较,现报道如下。
1.1 试验材料 人类永生化表皮细胞(HaCaT)和小鼠黑色素瘤细胞(B16)购自ATCC细胞库;RPMI-1640培养基,青链霉素混合液和10%胎牛血清(FBS)购自北京中生奥邦生物科技有限公司;达尔伯克氏改良伊格尔培养基(Dulbecco ’ s Modified Eagle ’ s Medium,DMEM)购自美国Gibco公司;总酮定量检测试剂盒、总酚定量检测试剂盒、CCK8试剂、DPPH试剂、酪氨酸酶活性检测试剂盒均购自北京索莱宝科技有限公司;BCA蛋白定量试剂盒和总活性氧簇(ROS)检测试剂盒购自赛默飞世尔科技公司。
1.2 方法
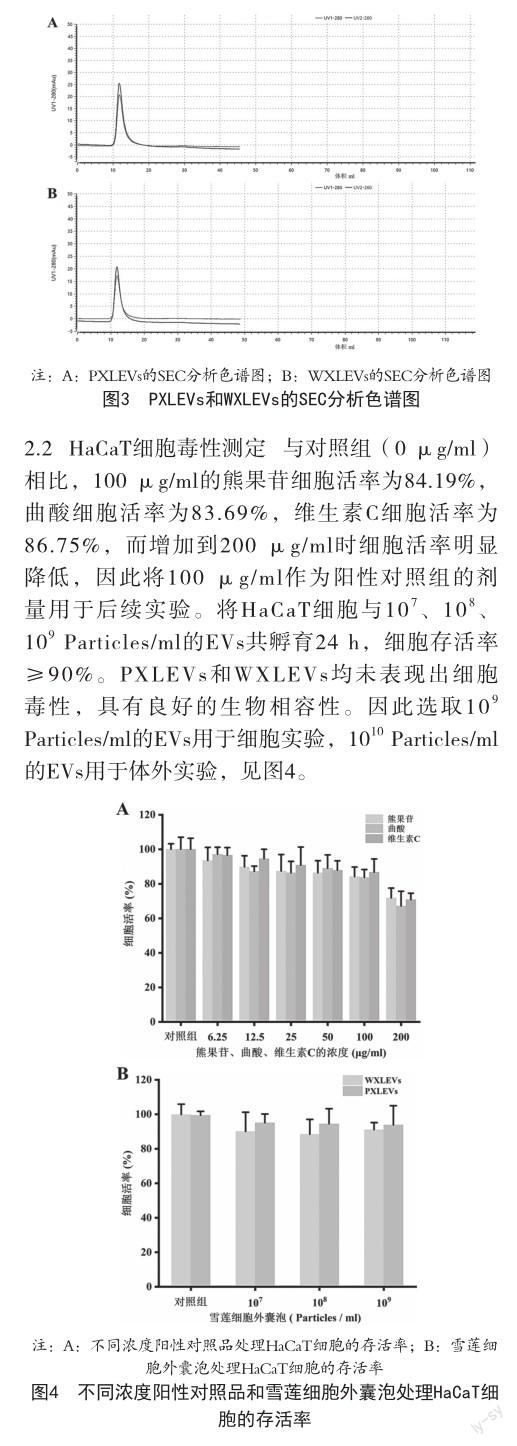
1.2.1雪莲细胞外囊泡的分离及鉴定 采用切向流过滤和柱层析相结合的方法分离纯化PXLEVs和WXLEVs。收集2 L天山雪莲愈伤组织的培养液进行梯度离心,4 ℃下300 g/min离心10 min收集上清液;然后将上清液于4 ℃下2000 g/min离心20 min,再次收集上清液;再将上清液4℃下10 000 g/min离心30 min,用0.45 μm的滤膜过滤最后的上清液并收集滤液。使用截流分子量为500 kD的中空纤维将滤液浓缩到50 ml,用500 ml的PBS进行换液,得到溶剂为PBS的浓缩液50 ml;最后将得到的浓缩液通过SEC纯化柱纯化得到天山雪莲愈伤组织细胞外囊泡,-80 ℃冻存备用。利用透射电子显微镜FEI Tecnai F20观察EVs的形态;采用粒径分析仪Particle Metrix PMX-120检测EVs的粒径和浓度信息;使用SEC色谱柱验证所提 EVs的分散性和均一性。采用BCA蛋白定量试剂盒测定了所提EVs的蛋白含量。采用总酮定量检测试剂盒和总酚定量检测试剂盒检测所提EVs的总酮和总酚含量。





植物细胞外囊泡参与植物免疫系统调节、植物防御反应、植物-微生物共生,并通过穿梭 RNA、蛋白质和生物活性化合物来介导细胞间通讯和跨界通讯[14,15],在抗炎、抗肿瘤、哺乳动物微生物群调节和药物输送方面具有巨大的治疗潜力[10]。研究发现[16],植物细胞外囊泡具有促进皮肤再生的功效,故其在化妆品领域的应用研究逐渐增多[17]。来自马尾藻和羊栖菜的EVs已被证明可下调人黑色素瘤细胞系(MNT-1)中黑素生成相关蛋白TYR、TYRP-1和MITF[18]。另一项研究表明[19],松柏叶和茎中提取的EVs通过降低黑色素水平在小鼠黑色素瘤细胞系(B16BL6)中发挥美白作用。最近的一项研究发现[20],从芦荟果皮中分离出细胞外囊泡(A-EVs)可通过激活抗氧化防御机制,促进伤口愈合,使得皮肤再生。可见,植物细胞外囊泡具有适合化妆品应用的细胞相容性、抗氧化、美白和促进愈合的特性,但天山雪莲细胞外囊泡的提取及其护肤功效的研究并没有相关报道。


综上所述,本项研究使用切向流过滤和柱层析相结合的方法从天山雪莲愈伤组织培养上清液中分离EVs,为植物细胞外囊泡的提取提供了新思路。对提取的PXLEVs和WXLEVs的抗氧化和美白活性进行了研究比较,发现PXLEVs能够更好的促进DPPH自由基的清除,抑制ROS的产生,同时对酪氨酸酶活性及细胞黑色素生成有具有更为明显的抑制作用,展示出了良好的抗氧化和美白效果。本研究为细胞定向培养和天然活性化妆品原料的开发提供了理论依据,但关于其作用机制的研究还不够详细全面,后续会进一步探究PXLEVs更具体清晰的抗氧化和美白机制。
[1]Gong G,Huang J,Yang Y,et al.Saussureae Involucratae Herba (Snow Lotus):Review of Chemical Compositions and Pharmacological Properties[J].Frontiers in Pharmacology,2020,10:1549.
[2]Chik W-I,Zhu L,Fan L-L,et al.Saussurea involucrata:A review of the botany,phytochemistry and ethnopharmacology of a rare traditional herbal medicine[J].Journal of Ethnopharmacol ogy,2015,172:44-60.
[3]Zhang Q,He L,Jiang Q,et al.Systems Pharmacology-Based Dissection of Anti-Cancer Mechanism of Traditional Chinese Herb Saussurea involucrata[J].Frontiers in Pharmacology,2021,12:678203.
[4]Guo B,Gao M,Liu CZ.In vitro propagation of an endangered medicinal plant Saussurea involucrate Kar.et Kir[J].Plant Cell Reports,2007,26(3):261-265.
[5]Zhang H,Li X,Meng X,et al.Comparison of Differences in Chemical Composition and Related Antioxidant Activity of Snow Lotus from Different Origins[J].Chem Biodivers,2023, 20(1):e202200885.
[6]Qiu J,Xue X,Chen F,et al.Quality evaluation of snow lotus(Saussurea):quantitative chemical analysis and antioxidant activity assessment[J].Plant Cell Reports,2010,29(12):1325-1337.
[7]Wang Y,Wang J,Ma J,et al.Focusing on Future Applications and Current Challenges of Plant Derived Extracellular Vesicles[J].Pharmaceuticals,2022,15(6):708.
[8]Rome S.Biological properties of plant-derived extracellular vesicles[J].Food & Function,2019,10(2):529-538.
[9]Kim J,Li S,Zhang S,et al.Plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles and their therapeutic activities[J].Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences,2022,17(1):53-69.
[10]Urzi O,Raimondo S,Alessandro R.Extracellular Vesicles from Plants:Current Knowledge and Open Questions[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2021,22(10):5366.
[11]Cho E-G,Choi S-Y,Kim H,et al.Panax ginseng-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Facilitate Anti-Senescence Effects in Human Skin Cells:An Eco-Friendly and Sustainable Way to Use Ginseng Substances[J].Cells,2021,10(3):486.
[12]Deng Z,Rong Y,Teng Y,et al.Broccoli-Derived Nanoparticle Inhibits Mouse Colitis by Activating Dendritic Cell AMPActivated Protein Kinase[J].Mol Ther,2017,25(7):1641-1654.
[13]Mu J,Zhuang X,Wang Q,et al.Interspecies communication between plant and mouse gut host cells through edible plant derived exosome-like nanoparticles[J].Molecular Nutrition & Food Research,2014,58(7):1561-1573.
[14]Kedare SB,Singh RP.Genesis and development of DPPH method of antioxidant assay[J].J Food Sci Technol,2011,48(4):412-422.
[15]Hoshino A,Kim HS,Bojmar L,et al.Extracellular Vesicle and Particle Biomarkers Define Multiple Human Cancers[J]. Cell,2020,182(4):1044-1061.
[16]Li Y,Xiao Q,Tang J,et al.Extracellular Vesicles:Emerging Therapeutics in Cutaneous Lesions[J].Int J Nanomedicine,2021,16:6183-6202.
[17]Kim MK,Choi YC,Cho SH,et al.The Antioxidant Effect of Small Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Aloe vera Peels for Wound Healing[J].Tissue Eng Regen Med,2021,18(4):561-571.
[18]Jang B,Chung H,Jung H,et al.Extracellular Vesicles from Korean Codium fragile and Sargassum fusiforme Negatively Regulate Melanin Synthesis[J].Mol Cells,2021,44(10):736-745.
[19]Lee R,Ko HJ,Kim K,et al.Anti-melanogenic effects of extracellular vesicles derived from plant leaves and stems in mouse melanoma cells and human healthy skin[J].J Extracell Vesicles,2020,9(1):1703480.
[20]Quispe C,Villalobos M,Borquez J,et al.Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Aloe vera from the Pica Oasis(Tarapaca,Chile) by UHPLC-Q/Orbitrap/MS/MS[J].Journal of Chemistry,2018,2018:6123850.
[21]Li HB,Wong CC,Cheng KW,et al,Antioxidant properties in vitro and total phenolic contents in methanol extracts from medicinal plants[J].Lwt-Food Science and Technology,2008,41(3):385-390.
收稿日期:2023-11-6 編辑:刘雯

