补体C1q/肿瘤坏死因子相关蛋白家族在动脉粥样硬化中的作用
通信作者:尹虹,E-mail:1986ly0583@hust.edu.cn
【摘要】补体C1q/肿瘤坏死因子相关蛋白(CTRP)是高度保守的脂联素旁系同源物,具有与脂联素相似的结构及功能。动脉粥样硬化是冠心病的主要病理表现,CTRP家族在动脉粥样硬化、缺血性心肌病、高血压等心血管疾病中作用广泛。大量的研究数据表明补体CTRP家族中,CTRP1、CTRP5促进动脉粥样硬化的发展,CTRP3、CTRP6、CTRP9、CTRP12、CTRP13、CTRP15可抑制动脉粥样硬化的进程。现综述CTRP在动脉粥样硬化中作用的最新进展。
【关键词】C1q/肿瘤坏死因子相关蛋白;冠心病;动脉粥样硬化
【DOI】10.16806/j.cnki.issn.1004-3934.2024.06.017
Role of the Complement C1q/Tumour Necrosis Factor-Related Protein Family in Atherosclerosis
GUI Lin1,DONG Rui2,WU Xuelian1,WANG Qianyan1,HE Yan1,YIN Hong1
(1.Cardiovascular Center,Liyuan Hospital,Tongji Medical College,Huazhong University of Science and Technology,Wuhan 430077,Hubei,China;2.Department of Respiratory Medicine,Liyuan Hospital,Tongji Medical College,Huazhong University of Science and Technology,Wuhan 430077,Hubei,China)
【Abstract】Complement C1q/tumor necrosis factor-related protein(CTRP) is a highly conserved lipocalin paralog with similar structure and function as lipocalin.Atherosclerosis is the main pathological manifestation of coronary heart disease.CTRP family plays wide-ranging roles in cardiovascular diseases,such as atherosclerosis,ischemic cardiomyopathy,and hypertension.Numerous studies have shown that among the complement CTRP family,CTRP1 and CTRP5 promote the development of atherosclerosis,and CTRP3,CTRP6,CTRP9,CTRP12,CTRP13,and CTRP15 inhibit atherosclerotic progression.This article reviews recent advances on the role in atherosclerosis.
【Keywords】C1q/tumor necrosis factor-related protein;Coronary heart disease;Atherosclerosis
心脏病(尤其是冠心病)和脑卒中全球导致死亡的两个主要原因。冠状动脉疾病(coronary artery disease,CAD)是心血管疾病中最常见的疾病,其潜在的病理改变是动脉粥样硬化(atherosclerosis,AS)[1]。
补体C1q/肿瘤坏死因子相关蛋白(C1q/tumor necrosis factor-related protein,CTRP)是脂联素的同源蛋白,CTRP家族(除CTRP4外)的结构共享四个不同的结构域:N端信号肽,短可变区,具有不同长度Gly-X-Y重复序列的胶原结构域,以及与补体成分C1q相似的结构区域[2]。CTRP家族蛋白在糖脂代谢、炎症等方面有一定作用,深入了解CTRP在冠状动脉粥样硬化过程中的作用机制,可为CAD的治疗提供新思路。现综述CTRP蛋白家族在AS中作用的最新进展。
1" CTRP家族及AS
1.1" AS
AS是一种进行性的病理变化,自19世纪50年代Rudolf Virchow的观察以来,人们已经充分认识到AS不仅是动脉壁内脂质积累的结果,而且是一种涉及多种炎症介质和免疫细胞的慢性炎症性疾病[3]。AS主要影响大动脉和中动脉[4]。在主要危险因素的影响下,受损的内皮细胞允许低密度脂蛋白胆固醇进入内膜,并在内膜被修饰成氧化型低密度脂蛋白(oxidized low-density lipoprotein,oxLDL),oxLDL激活内皮细胞中趋化因子和黏附因子的表达,募集循环单核细胞,这些单核细胞在富含生长因子和促炎细胞因子的局部微环境中分化为巨噬细胞。通过巨噬细胞表面的清道夫受体,巨噬细胞迅速识别并吞噬oxLDL,转化为泡沫细胞,形成最早的AS病变[5]。血管平滑肌细胞(vascular smooth muscle cell,VSMC)的异常增殖和迁移是AS发生的重要病理基础[6],加载胆固醇后VSMC向巨噬细胞样细胞的转化是AS发病机制之一。随着疾病的发展,泡沫细胞的积累、局部坏死和纤维帽的形成导致稳定或不稳定斑块的发展。在AS晚期,由于血流动力学改变、应激和炎症反应,斑块不稳定最终导致斑块破裂、出血和血栓形成。血管炎症不仅促进脂质代谢失调,而且有助于粥样斑块破裂和急性冠脉综合征(acute coronary syndrome,ACS)的发生。
1.2" CTRP的结构及作用
1.2.1" CTRP1
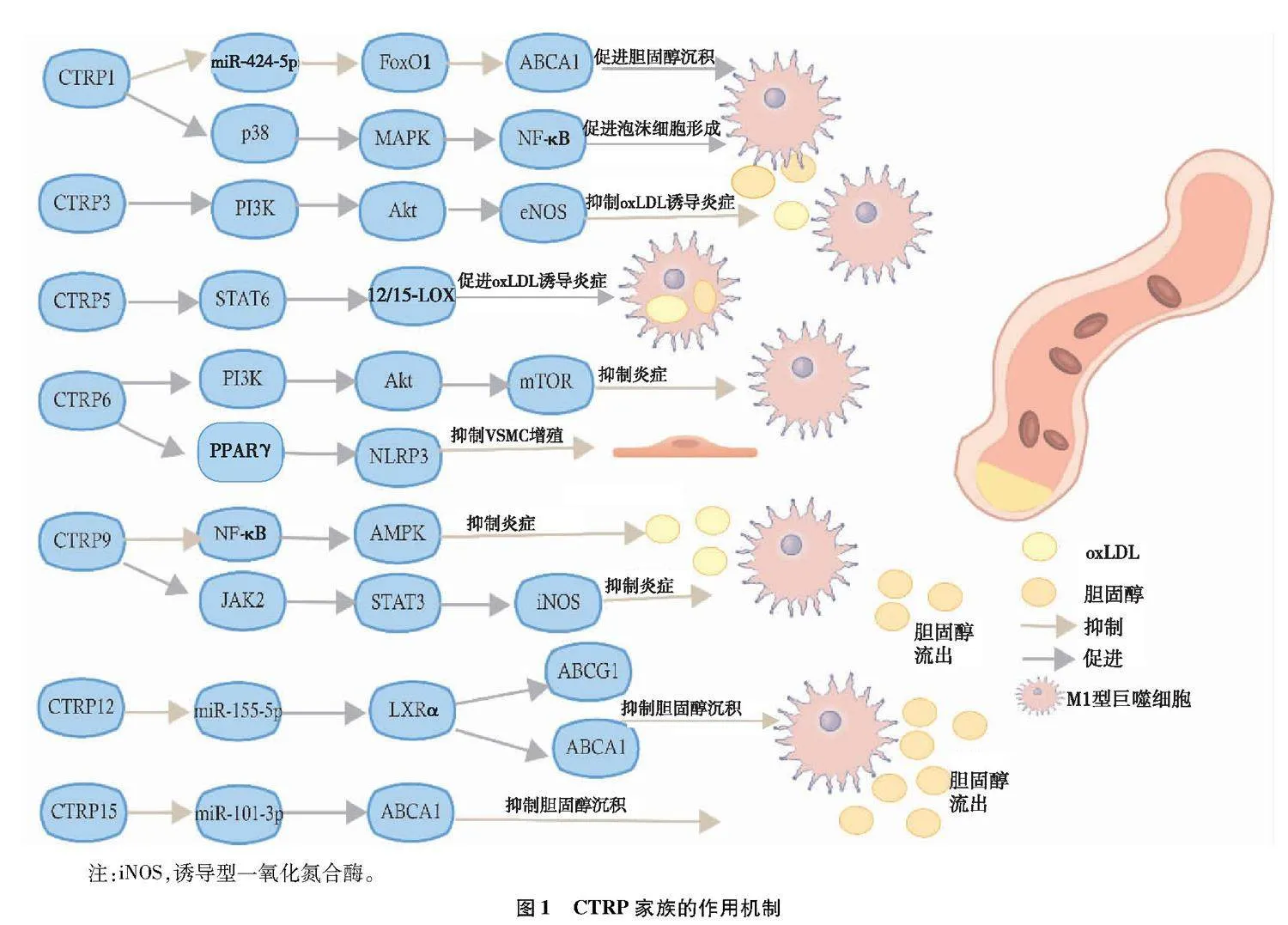
人的CTRP1蛋白是由281个氨基酸组成的蛋白质。在脉管系统中,CTRP1主要表达于VSMC,其次是血管内皮细胞[7]。在血流紊乱的条件下,CTRP1破坏血管内皮屏障功能,增加斑块破裂的风险。CTRP1通过降低miR-424-5p的表达,介导AS中的巨噬细胞miR-424-5p/FoxO1/ABCA1轴,抑制
ATP结合盒转运体A1(ATP-binding cassette transporter A1,ABCA1)的表达[8],干扰胆固醇流出细胞,从而导致脂质积累和加速斑块形成。在CAD中,CTRP1可通过p38-MAPK/NF-κB通路增加黏附分子和趋化因子的表达,促进了AS斑块中巨噬细胞和巨噬细胞来源的泡沫细胞的形成,从而发挥了促炎、促AS的作用[9]。
1.2.2" CTRP3
CTRP3是包含246个氨基酸序列的蛋白,CTRP3主要在软骨中表达,在小鼠和人的脂肪组织以及单核细胞和骨肉瘤细胞中均有发现[10]。CTRP3通过抑制脂多糖与Toll样受体4的结合和减少单核细胞中肿瘤坏死因子-α和白细胞介素-6的分泌[11],表现出强大的抗炎特性。CTRP3可以刺激内皮细胞的增殖和迁移,调节炎症反应。CTRP3通过促进PI3K/Akt/eNOS通路抑制oxLDL诱导的内皮炎症来延缓AS进展[12]。CTRP3主要通过抗炎作用来延缓AS的进程。
1.2.3" CTRP4
CTRP4是一种脂肪细胞因子,有两个球状C1q结构域[13],在炎症和代谢的负向调节中具有重要功能,主要在脑组织、脂肪组织和骨髓干细胞中表达,并且还作为血液中的循环蛋白被发现[14]。CTRP4有效减轻高血糖诱导的内质网应激,CTRP4诱导磷酸化AMP活化蛋白激酶(AMP-activated protein kinase,AMPK)表达上调和自噬[15]。CTRP4主要通过NF-κB通路介导细胞因子调节巨噬细胞向M1型极化,从而发挥其抗炎作用[16]。
1.2.4" CTRP5
CTRP5在许多组织中都有表达,特别是在基质血管细胞部分。CTRP5诱导AMPK的磷酸化,从而刺激细胞对葡萄糖摄取和脂肪酸氧化[17]。CTRP5通过STAT6信号通路上调12/15-LOX的表达促进低密度脂蛋白氧化及进入内皮细胞。gCTRP5通过促进氧化应激诱导和Nox-1介导的线粒体细胞死亡途径促进血管内皮细胞凋亡[18]。
1.2.5" CTRP6
CTRP6的表达在人类AS组织和血小板衍生生长因子-BB刺激的人主动脉平滑肌细胞中显著下调。CTRP6过表达有效地阻止了人主动脉平滑肌细胞中PI3K/Akt/mTOR对血小板衍生生长因子-BB的反应[19]。已有研究[20]证明,
过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ(peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ,PPARγ)激动剂——罗格列酮可降低肥胖小鼠的CTRP6转录水平。CTRP6可以改善PPARγ激活并减轻血管紧张素Ⅱ诱导的高血压和自发性高血压大鼠的血管内皮功能障碍[19]。CTRP6可通过PPARγ/NLRP3抑制同型半胱氨酸诱导的VSMC增殖、迁移和去分化[21]。
1.2.6" CTRP9
CTRP9与脂联素的氨基酸同源性最高,是由脂肪组织分泌的糖蛋白[22]。首先,CTRP9可以消除巨噬细胞中oxLDL的刺激[23]。CTRP9通过激活JAK2/STAT3信号通路以时间和剂量依赖性方式诱导诱导型一氧化氮合酶表达增加[24]。其次,CTRP9促进oxLDL诱导的人类单核细胞系人单核细胞白血病细胞在巨噬细胞中的胆固醇流出,表明CTRP9通过促进胆固醇流出减少泡沫细胞的形成来防止AS[25]。最后,CTRP9的过表达抑制了人主动脉血管内皮细胞中活性氧的产生并增强了线粒体的生物合成[26]。用肿瘤坏死因子-α预处理人主动脉血管内皮细胞以诱导炎症,然后用CTRP9处理显著阻止NF-κB的激活,随后增加AMPK的磷酸化以减少血管内皮细胞中的炎症细胞因子[27],表明CTRP9激活AMPK或抑制NF-κB信号通路是减少AS斑块形成所必需的。在巨噬细胞和VSMC共培养系统中,CTRP9促进巨噬细胞向M1表型的转化,并下调由JNK信号通路激活诱导的VSMC凋亡和增殖[28]。
1.2.7" CTRP12
CTRP12已被证明可以减少肥胖小鼠脂肪组织中促炎细胞因子的表达和巨噬细胞的积累[29]。Wang等[30]的研究发现,CTRP12的过表达显著减少了细胞内脂滴并降低了巨噬细胞中的胆固醇和甘油三酯含量。CTRP12降低miR-155-5p水平,然后增加肝X受体α(liver X receptor α,LXRα)表达,从而促进ABCA1和ATP结合盒转运体G1(ATP-binding cassette transporter G1,ABCG1)依赖性胆固醇流出并减轻炎症反应[30]。体内实验表明,过表达CTRP12的载脂蛋白E(apolipoprotein E,ApoE)-/-小鼠的主动脉斑块负荷明显低于ApoE-/-同窝小鼠。CTRP12的过表达导致循环高密度脂蛋白胆固醇水平增加,同时斑块内的脂质沉积减少[30]。
1.2.8" CTRP13
CTRP13在进化上高度保守,在人和小鼠之间只有一个氨基酸变化。CTRP13主要由人类的脂肪组织表达,可增加胰岛素介导的葡萄糖摄取,减少糖异生[31]。越来越多的研究表明,人类白细胞分化抗原36可能通过调节巨噬细胞骨架而促进AS,CTRP13通过自噬溶酶体降解人类白细胞分化抗原36抑制AS。CTRP13通过减少对修饰脂蛋白的摄取而抑制巨噬细胞泡沫细胞的形成。CTRP13可以减轻斑块形成、巨噬细胞浸润和激活,进而限制AS的发展[31]。
1.2.9" CTRP14
研究表明,CTRP14的过表达会升高血浆高密度脂蛋白胆固醇,但它与ApoE-/-小鼠中存在的主动脉粥样硬化无关,而这又反过来表明高密度脂蛋白胆固醇水平的增加并没有改善CTRP14诱导的AS斑块的形成。总之,CTRP14的过表达与ApoE-/-小鼠的主动脉粥样硬化无关。CTRP14蛋白在脑外和脂肪细胞(如主动脉脂肪细胞)中的功能特性对炎症、脂质代谢、巨噬细胞胆固醇代谢或与AS相关的分子通路没有影响[32]。
1.2.10" CTRP15
CTRP15是一种新发现的脂肪因子[33]。Tan等[34]的实验表明,CTRP15与T-钙黏蛋白结合并下调miR-101-3p水平,导致ABCA1表达增加从而促进胆固醇的流出,减少泡沫细胞形成。故CTRP15可防止ApoE-/-小鼠发生AS。CTRP家族中各蛋白在AS中的作用如图1所示。
2" CTRP家族在临床中的研究
与对照组和非AS样本相比,严重CAD患者血清、冠状动脉内膜切除术样本、AS斑块和外周血单核细胞中的CTRP1水平显著升高[35]。在临床研究中,CAD患者血清CTRP1水平显著升高,且随着CAD的严重程度而升高。急性心肌梗死组CTRP1水平明显高于稳定型心绞痛组、不稳定型心绞痛组和非CAD组。CTRP1在单支病变和三支病变之间也存在显著差异。多元logistic回归分析[36]显示,CTRP1是心肌梗死发生的独立危险因素。CTRP1可能作为CAD患病率和进展的指标。
在临床研究[37]中发现,患有ACS和稳定型心绞痛的患者通常表现出低CTRP3水平。与对照组相比,ACS或稳定型心绞痛患者的CTRP3浓度显著降低(P均<0.001)[38]。
Dai等[39]的一项横断面研究表明,与ACS患者相比,非ACS患者的CTRP4较低。Gao等[40]的一项横断面研究表明,血清CTRP4浓度与CAD的发生及严重程度呈正相关。
Liu等[18]的研究表明,与非AS相比,CAD患者以及人类冠状动脉内膜切除术标本中的CTRP5蛋白水平显著升高。该研究发现了血清CTRP5水平显著升高,与CAD患者AS的范围和严重程度呈正相关,并且CTRP5与支架内再狭窄有关。
临床研究[41]表明,降低CTRP9水平和升高同型半胱氨酸水平是冠心病患者薄帽纤维AS的独立危险因素。
在一项260人参与的病例对照研究[42]中发现,CAD患者与对照组相比血清中CTRP15明显升高,并且三支病变的CTRP15高于两支病变和一支病变,CTRP15的升高程度与CAD的严重程度相关。
综上所述,CTRP1、CTRP4、CTRP5、CTRP15等在CAD患者中呈明显升高并与CAD的严重程度有关,具有统计学意义,而CTRP3、CTRP9、CTRP13水平与CAD呈负相关,具有保护作用。CTRP6和CTRP12在CAD中的影响还需要进一步进行研究。
3" 结论
从脂质代谢的途径来说,CTRP1通过抑制ABCA1的表达来阻止胆固醇的流出,而CTRP12、CTRP15可以通过增加ABCA1的表达增加胆固醇的流出来减缓脂质斑块的形成从而延缓AS的发生。
从炎症的角度来说,CTRP1通过促进NF-κB的表达,增加炎症因子促进AS的产生,CTRP3通过内皮型一氧化氮合酶,CTRP9通过诱导型一氧化氮合酶和阻止NF-κB的激活的途径阻止AS的发生。血液循环中的CTRP5通过促进氧化应激诱导产生炎症,CTRP6则通过抑制平滑肌的增殖来减缓AS的发展。
在现有的临床研究来看,CTRP1、CTRP4、CTRP5、CTRP15可能作为CAD患病率和进展的指标。而CTRP3、CTRP9、CTRP13可以作为未来生物制剂的补充来减缓AS的进展。需进行更深入的临床研究后才能了解CTRP家族具体作用机制以及其在临床治疗中的潜在应用价值。
综上所述,CTRP家族在AS过程中是双刃剑的作用,如CTRP1、CTRP5能促进AS的发生,而CTRP3、CTRP6、CTRP9、CTRP12、CTRP13、CTRP15能够抑制AS的发生。需要指出的是,尽管CTRP家族与AS存在相关性,但仍需要更多的研究来全面了解其具体作用机制以及在临床治疗中的潜在应用价值。
CTRP家族中各蛋白的作用通路及特征靶点尚未完全明确,但CTRP家族与ABCA1蛋白和MAPK及氧化应激相关蛋白的作用被部分证实,还需要进一步明确其作用机制和受体。CAD是发病率最高的心血管疾病,而AS与炎症、糖脂代谢及内皮损伤有关,对CTRP家族中各蛋白的作用机制的研究将为未来冠状动脉粥样硬化性疾病提供更精准的治疗及预测方法。CTRP3、CTRP6、CTRP9、CTRP12、CTRP13、CTRP15给药可能是预防不良心血管事件的潜在疗法。
参考文献
[1]Libby P.The changing landscape of atherosclerosis[J].Nature,2021,592(7855):524-533.
[2]Schanbacher C,Hermanns HM,Lorenz K,et al.Complement 1q/tumor necrosis factor-related proteins(CTRPs):structure,receptors and signaling[J].Biomedicines,2023,11(2):559.
[3]Moriya J.Critical roles of inflammation in atherosclerosis[J].J Cardiol,2019,73(1-2):22-27.
[4]Jinnouchi H,Guo L,Sakamoto A,et al.Diversity of macrophage phenotypes and responses in atherosclerosis[J].Cell Mol Life Sci,2020,77(10):1919-1932.
[5]Blagov AV,Markin AM,Bogatyreva AI,et al.The role of macrophages in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis[J].Cells,2023,12(4):522.
[6]Durham AL,Speer MY,Scatena M,et al.Role of smooth muscle cells in vascular calcification:implications in atherosclerosis and arterial stiffness[J].Cardiovasc Res,2018,114(4):590-600.
[7]Wang Y,Li H,Yu XH,et al.CTRP1:a novel player in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases[J].Cytokine,2023,164:156162.
[8]Zhang ZZ,Chen JJ,Deng WY,et al.CTRP1 decreases ABCA1 expression and promotes lipid accumulation through the miR-424-5p/FoxO1 pathway in THP-1 macrophage-derived foam cells[J].Cell Biol Int,2021,45(11):2226-2237.
[9]Si YQ,Fan WJ,Sun LX.A review of the relationship between CTRP family and coronary artery disease[J].Curr Atheroscler Rep,2020,22(6):22.
[10]Hofmann C,Chen N,Obermeier F,et al.C1q/TNF-related protein-3(CTRP-3) is secreted by visceral adipose tissue and exerts antiinflammatory and antifibrotic effects in primary human colonic fibroblasts[J].Inflamm Bowel Dis,2011,17(12):2462-2471.
[11]Guo SR,Mao XH,Liu J.Multi-faceted roles of C1q/TNF-related proteins family in atherosclerosis[J].Front Immunol,2023,14:11.
[12]Chen L,Qin LJ,Liu X,et al.CTRP3 alleviates ox-LDL-induced inflammatory response and endothelial dysfunction in mouse aortic endothelial cells by activating the PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway[J].Inflammation,2019,42(4):1350-1359.
[13]Mei J,Gui JF.Bioinformatic identification of genes encoding C1q-domain-containing proteins in zebrafish[J].J Genet Genomics,2008,35(1):17-24.
[14]Wang L.CTRP4:a new member of the adipocytokine family[J].Cell Mol Immunol,2017,14(10):868-870.
[15]Cho WJ,Oh H,Choi SW,et al.CTRP4 attenuates apoptosis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers in podocytes through an AMPK/autophagy-dependent pathway[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2023,682:104-110.
[16]Cao LL,Tan WF,Chen W,et al.CTRP4 acts as an anti-inflammatory factor in macrophages and protects against endotoxic shock[J].Eur J Immunol,2021,51(2):380-392.
[17]Li C,Chen JW,Liu ZH,et al.CTRP5 promotes transcytosis and oxidative modification of low-density lipoprotein and the development of atherosclerosis[J].Atherosclerosis,2018,278:197-209.
[18]Liu J,Meng ZJ,Gan L,et al.C1q/TNF-related protein 5 contributes to diabetic vascular endothelium dysfunction through promoting Nox-1 signaling[J].Redox Biol,2020,34:101476.
[19]Chi LY,Hu XJ,Zhang WT,et al.Adipokine CTRP6 improves PPARγ activation to alleviate angiotensin Ⅱ-induced hypertension and vascular endothelial dysfunction in spontaneously hypertensive rats[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2017,482(4):727-734.
[20]Dong XZ,Hu HJ,Fang ZD,et al.CTRP6 inhibits PDGF-BB-induced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration[J].Biomed Pharmacother,2018,103:844-850.
[21]Liu JL,Yan XN,Wang ZL,et al.Adipocyte factor CTRP6 inhibits homocysteine-induced proliferation,migration,and dedifferentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells through PPARγ/NLRP3[J].Biochem Cell Biol,2021,99(5):596-605.
[22]Zeng M,Wei X,He YL,et al.Ubiquitin-specific protease 11-mediated CD36 deubiquitination acts on C1q/TNF-related protein 9 against atherosclerosis[J].ESC Heart Fail,2023,10(4):2499-2509.
[23]Zhang H,Gong XY,Ni SM,et al.C1q/TNF-related protein-9 attenuates atherosclerosis through AMPK-NLRP3 inflammasome singling pathway[J].Int Immunopharmacol,2019,77:105934.
[24]Chen JY,Lei SY,Li TT,et al.CTRP9 induces iNOS expression through JAK2/STAT3 pathway in Raw 264.7 and peritoneal macrophages[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2020,523(1):98-104.
[25]Zhang L,Liu Q,Zhang H,et al.C1q/TNF-related protein 9 inhibits THP-1 macrophage foam cell formation by enhancing autophagy[J].J Cardiovasc Pharmacol,2018,72(4):167-175.
[26]Scheja L,Heeren J.The endocrine function of adipose tissues in health and cardiometabolic disease[J].Nat Rev Endocrinol,2019,15(9):507-524.
[27]Guan H,Wang YL,Li XY,et al.C1q/tumor necrosis factor-related protein 9:basics and therapeutic potentials[J].Front Physiol,2022,13:816218.
[28]Chen JY,Song CX,Lei SY,et al.CTRP9 induces macrophages polarization into M1 phenotype through activating JNK pathway and enhances VSMCs apoptosis in macrophages and VSMCs co-culture system[J].Exp Cell Res,2020,395(1):112194.
[29]Tan SY,Lei X,Little HC,et al.CTRP12 ablation differentially affects energy expenditure,body weight,and insulin sensitivity in male and female mice[J].Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab,2020,319(1):E146-E162.
[30]Wang G,Chen JJ,Deng WY,et al.CTRP12 ameliorates atherosclerosis by promoting cholesterol efflux and inhibiting inflammatory response via the miR-155-5p/LXRα pathway[J].Cell Death Dis,2021,12(3):254.
[31]Wang C,Xu WJ,Liang ML,et al.CTRP13 inhibits atherosclerosis via autophagy-lysosome-dependent degradation of CD36[J].FASEB J,2019,33(2):2290-2300.
[32]Guan H,Shi T,Liu MM,et al.C1QL1/CTRP14 is largely dispensable for atherosclerosis formation in apolipoprotein-E-deficient mice[J].J Cardiovasc Dev Dis,2022,9(10):341.
[33]Seldin MM,Peterson JM,Byerly MS,et al.Myonectin(CTRP15),a novel myokine that links skeletal muscle to systemic lipid homeostasis[J].J Biol Chem,2012,287(15):11968-11980.
[34]Tan WH,Peng ZL,You T,et al.CTRP15 promotes macrophage cholesterol efflux and attenuates atherosclerosis by increasing the expression of ABCA1[J].J Physiol Biochem,2022,78(3):653-666.
[35]Lu L,Zhang RY,Wang XQ,et al.C1q/TNF-related protein-1:an adipokine marking and promoting atherosclerosis[J].Eur Heart J,2016,37(22):1762-1771.
[36]Shen LH,Wang SH,Ling Y,et al.Association of C1q/TNF-related protein-1 (CTRP1) serum levels with coronary artery disease[J].J Int Med Res,2019,47(6):2571-2579.
[37]Zhang H,Zhang-Sun ZY,Xue CX,et al.CTRP family in diseases associated with inflammation and metabolism:molecular mechanisms and clinical implication[J].Acta Pharmacol Sin,2023,44(4):710-725.
[38]Choi KM,Hwang SY,Hong HC,et al.Implications of C1q/TNF-related protein-3 (CTRP-3) and progranulin in patients with acute coronary syndrome and stable angina pectoris[J].Cardiovasc Diabetol,2014,13:14.
[39]Dai YL,Zhou J,Niu LJ,et al.Increased serum C1q/TNF-related protein 4 concentration in patients with acute coronary syndrome[J].Clin Chim Acta,2022,524:187-191.
[40]Gao J,Lu J,Qiu JH,et al.C1q tumor necrosis factor-related protein 4 is associated with coronary artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes[J].J Diabetes Investig,2022,13(10):1723-1731.
[41]Liu YL,Wang XB,Wang T,et al.Retracted:relationship between coronary VH-IVUS plaque characteristics and CTRP9,SAA,and Hcy in patients with coronary heart disease (retracted article)[J].J Healthc Eng,2023,2023:9859038.
[42]Nahrkhalaji AS,Ahmadi R,Fadaei R,et al.Higher serum level of CTRP15 in patients with coronary artery disease is associated with disease severity,body mass index and insulin resistance[J].Arch Physiol Biochem,2022,128(1):276-280.
收稿日期:2023-09-27