Research on the Impact of Independent R&D and Collaborative Innovation on Economic Performance in China’s pharmaceutical Industry
Li Wanting,Qiao Jiahui,Wang Su,Chen Yuwen
(School of Business Administration,Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,Shenyang 110016,China)
Abstract Objective To study the impact of independent R&D and collaborative innovation on economic performance in the pharmaceutical industry.Methods A panel regression model was established by selecting the panel data of China’s pharmaceutical industry from 2009 to 2019.Results and Conclusion Independent R&D and collaborative innovation of the pharmaceutical industry in eastern,central and western regions of China had a positive effect on economic performance.Besides,the promotion effect of independent R&D was greater than that of collaborative innovation.The positive driving effect of economic performance is the largest among the three regions,followed by the central and western regions.The collaborative innovation has the greatest positive effect on economic performance in the central region,followed by the eastern and western regions.
Keywords: independent R&D;collaborative innovation;economic performance;pharmaceutical industry
“The 14th Five-Year Plan for the National Economic and Social Development of the People’s Republic of China and the Outline of the Vision for 2035” (referred to as the “14th Five-Year Plan”) emphasizes “adhering to the core position of innovation in the overall situation of China’s modernization drive”.In addition,in terms of improving the technological innovation capabilities of enterprises,the plan proposes to encourage enterprises to increase investment in R&D,support the R&D of industrial common basic technologies,and improve the enterprise innovation service system[1].Pharmaceutical industry is closely related to public health.At the same time,as one of the high-tech industries,pharmaceutical industry is also the knowledge intensive industry,which is the forefront of innovation-driven development.Besides,it plays a significant role in China’s economic development in the future.There are two modes for pharmaceutical industries to achieve innovation.One is independent R&D,that is,enterprises invest human,financial and material resources to establish their own R&D innovation team to carry out innovation.The other is collaborative innovation,that is,enterprises rely on external resources such as universities,scientific research institutions and other units to carry out innovative activities together[2].Pharmaceutical industries usually choose one of the modes or a combination of the two modes.Independent R&D is conducive to enterprises to gain advantages in products and technologies,which help them enjoy knowledge achievements and economic benefits.However,while improving their core competitiveness,they must face problems such as high R&D risks and insufficient technological innovation resources.Through collaborative innovation,the cooperation with universities,scientific research institutions and other units,enterprises can make up for the shortcomings of independent R&D to a certain extent.Based on the perspective of the whole country and different regions,this paper studies the contribution of independent R&D and collaborative innovation to the economic performance of China’s pharmaceutical industry,analyzing the role and problems of the two innovation modes to provide suggestions for the government to formulate relevant policies.It has important theoretical and practical significance for relevant decision-making and selection of the two innovation modes for pharmaceutical industry.
1 Literature review
Independent R&D and collaborative innovation are two common ways for enterprises to innovate.Scholars at home and abroad have also conducted some research on their impact on economic performance.
In terms of the impact of independent R&D on economic performance,ML Yeh,et al.(2010)[3]adopted the panel threshold regression model to analyze the impact of R&D intensity on the performance of listed information technology and electronics companies in Taiwan,and the results confirmed that there was an inverted U-shaped relationship between R&D intensity and corporate performance.Yue Xiyou(2021)[4]studied the impact of capital input and labor input on innovation performance of high-tech industry based on panel data of 26 provinces from 2010 to 2016.He found that the contribution of capital input in R&D was much larger than that of labor input.Wang Lianghu,et al.(2021)[5]based on micro enterprise data and using threshold regression model,analyzed the influence on innovation performance under the different enterprise scale level.The results showed that there was a U-shaped relationship between R&D investment and innovation performance.It meant R&D investment of both small enterprises and large enterprises had a more obvious promoting effect on innovation performance.Zhao Ying,et al.(2021)[6]selected China’s (growth enterprise market) GEM technology-based enterprises from 2015 to 2019 as the research object to analyze the intermediary effect of R&D investment on the impact of government subsidies on their innovation performance.The results showed that R&D investment had a significant positive effect on innovation performance,and this effect had a certain lag.
Meanwhile,some other scholars analyzed the impact of collaborative innovation on economic performance.Dong Zuojun,et al.(2021)[7]believed that innovation in the pharmaceutical industry through R&D cooperation could improve technical standards and product competitiveness.Wu Weihong,et al.(2021)[8]conducted a questionnaire survey on 226 high-tech listed companies.They used the SEM model and hierarchical regression analysis method to find that six common types of collaborative innovation risks had a significant negative impact on innovation performance.The negative effect of collaborative risk was the most obvious,and the negative effect of moral hazard was the smallest.He Wei,et al.(2021)[9]analyzed the impact of collaborative innovation on corporate performance based on the 2012 World Bank survey data on Chinese enterprises and found that collaborative innovation had a positive pulling effect,and the influencing way were through improving product quality,production flexibility and increasing human capital.Yang Haochang,et al.(2019)[10]studied the regional impact of collaborative innovation on economic performance based on the panel data of the provincial manufacturing industry from 2001 to 2015.They found that collaborative innovation in the eastern region was conducive to improving economic performance,but collaborative innovation in the central and western regions was not.It would have a crowding-out effect on the economic performance of the manufacturing industry.
Other scholars studied the impact of independent R&D and collaborative innovation on economic performance.M Ramsza,et al.(2020)[11]investigated the behavior of firms in product R&D with enhanced demand,compared corporate and non-cooperative R&D investments.They found that firms under cooperative R&D were more profitable than noncooperative R&D.Guo Qianghua (2019)[12]used the face number regression model and impulse response function to analyze the impact of independent R&D and collaborative innovation on the innovation speed.Then he found that the elasticity coefficient of independent R&D (1.224) was much larger than that of collaborative innovation (0.227).Jiang Kaidong,et al.(2015)[13]used panel data and an unexpected output efficiency model to measure the performance of independent R&D and collaborative innovation based on the technology input and output data of high-tech industries.They found that the elasticity coefficient of independent R&D on technology output was significantly positive,while the elasticity coefficient of collaborative innovation was negative.
From the studies on the impact of independent R&D and collaborative innovation on economic performance,we can see that few scholars conducted in-depth studies on a specific industry segment.Besides,they did not make comparative studies on independent R&D and collaborative innovation at the same time.Therefore,the conclusions about the impact of independent R&D and collaborative innovation on economic performance were also inconsistent.The pharmaceutical industry is characterized by a large amount of capital investment.How to allocate funds to the innovation mode plays a crucial role in improving the economic performance of enterprises and promoting their long-term development.However,there is almost no literature on the impact of independent R&D and collaborative innovation on economic performance of pharmaceutical industry.The research in this paper can make some contribution to this field.
2 Empirical study design
2.1 Variable selection and model building
The explained variable in this paper is the economic performance of pharmaceutical industry,which is measured by the sales revenue of new products[14,15].The core explanatory variables are independent R&D and collaborative innovation,which are measured by internal R&D expenditure[12]and external R&D expenditure[13]of pharmaceutical industry respectively.Previous studies[16-18]show that human capital and competition degree also have an impact on economic performance,so human capital and competition degree are selected as control variables and measured by full-time equivalent of R&D personnel in pharmaceutical industry and number of pharmaceutical industries respectively.
lnSRit=C+β1lnIRDit+β2lnERDit+α1lnLit+α2lnQit+ui+εit
Among them,SRitrefers to sales revenue of new products.C refers to a constant term.IRDitrefers to the internal expenditure of R&D funds.ERDitrefers to the external expenditure of R&D funds.Litrefers to the full-time equivalent of R&D personnel.Qitrefers to number of companies.uirefers to unobservable individual effects.εitrefers to random disturbance term.
Due to the long history of data,in order to reduce the impact of data fluctuation on the follow-up empirical research and eliminate heteroscedasticity,the sales revenue of new products,internal expenditure of R&D expenditure,external expenditure of R&D expenditure,full-time equivalent of R&D equivalent personnel and number of enterprises in the pharmaceutical industry are logarithmically processed.
2.2 Data source and descriptions
In this paper,provincial panel data of pharmaceutical industry from 2009 to 2019 were selected.Considering the continuity of data,provinces such as Tibet,Qinghai,Ningxia and Xinjiang with more data missing were removed,and a small number of missing values in other provinces,municipalities and autonomous regions were replaced by average values.Finally,the relevant data of 27 provinces,municipalities and autonomous regions from 2009 to 2019 were retained,with a total of 297 observed values.All data are from “Statistical Yearbook of China’s High-tech Industry (2010-2020)”.
3 An empirical analysis of independent R&D,collaborative innovation and economic performance
The following is an empirical analysis of independent R&D,collaborative innovation and economic performance based on national and regional perspectives.
3.1 National perspective
3.1.1 Descriptive statistical analysis
A descriptive statistical analysis was conducted for each variable.The descriptive statistical results of relevant variables in the national pharmaceutical industry was shown in Table 1.
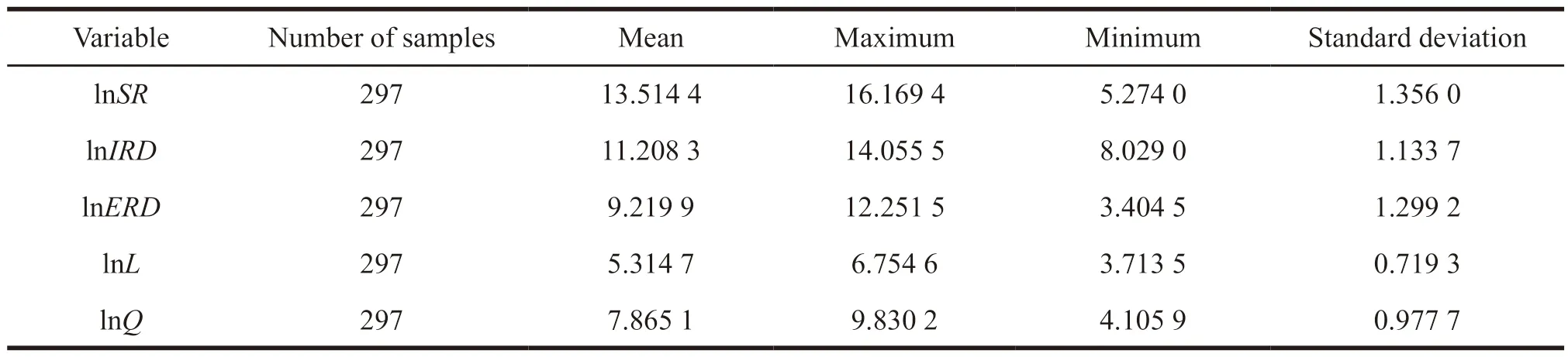
Table 1 Descriptive statistical results of relevant variables in China’s pharmaceutical industry
It can be seen from Table 1 that the standard deviation of the internal expenditure of R&D funds,the external expenditure of R&D funds and the sales revenue of new products in the national pharmaceutical industry is relatively large,and the gap between the maximum value and the minimum value is also large,indicating the level of independent R&D in different regions,the level of collaborative innovation and economic performance are quite different.
3.1.2 National regression model test of independent R&D,collaborative innovation and economic performance
Firstly,the fixed effect model and random effect model are established respectively.Secondly,the null hypothesis is rejected,showing that both fixed effect model and random effect model are superior to mixed regression.Thirdly,the Hausman test is used to determine the final choice of fixed effect model or random effect model.Hausman test results show that thePvalue is 0.139 3,so the random effect model should be used.The regression results are shown in Table 2.

Table 2 National regression results of independent R&D,collaborative innovation and economic performance
It can be seen from the results that both the internal expenditure of R&D funds and the external expenditure of R&D funds have a significant positive effect on the sales revenue of new products.The elasticity coefficient of the sales revenue of new products with respect to the internal expenditure of R&D funds (0.607 9) is greater than the external expenditure of R&D funds (0.270 4),indicating that R&D Internal expenditure of funds has a greater positive effect on sales revenue of new products.Therefore,the improvement of the economic performance of the pharmaceutical industry mainly comes from the contribution of independent R&D.Independent R&D is beneficial for enterprises to possess core technologies,build product advantages and maintain their competitiveness.Once the independent R&D is successful,the enterprise can enjoy the economic benefits alone,and the economic benefits brought by an innovative drug with good therapeutic effect are huge.In addition to independent R&D,enterprises can effectively make up for the lack of innovation resources and reduce the cost through collaborative innovation.The strong innovation capabilities of universities and scientific research institutions can also provide enterprises with more advanced and cutting-edge innovation achievements,which can improve the economic performance of enterprises[19].
The number of enterprises has a positive effect on the sales revenue of new products,indicating that an appropriate increase in the market competition of pharmaceutical industries can effectively improve their economic performance.This is because the competition among enterprises will enhance the innovation awareness of enterprises.Enterprises will try to improve their competitiveness and occupy more markets through product innovation or product upgrades,which can continue to promote more innovative drugs or higher-quality drugs.When the high quality of generic drugs are produced,the economic performance of the entire pharmaceutical industry will be improved.The full-time equivalent of R&D personnel also has a positive effect on the sales revenue of new products,but this effect is not significant.The pharmaceutical industry is a technology-and knowledge-intensive industry,which has a high demand for R&D talents.High-level R&D talents can improve the R&D efficiency of enterprises,create more achievements,and bring more economic benefits.However,many pharmaceutical industries in China do not give sufficient incentives to talents,nor do they pay enough attention to the cultivation of talents.The insufficient R&D talents leads to few R&D achievements.In addition,the enthusiasm of many talents to innovate has not been stimulated.Many talents would like to go to foreign-funded enterprises.For various reasons,the positive effect of human capital on economic performance is not obvious.
3.1.3 Robustness test
This paper also carries out robustness testing to verify the reliability of the results.Increasing or decreasing control variables is one of the methods of robustness testing[20-22].This paper adopts the method of reducing the control variables and observing the sign and significance of the explanatory variables to test the robustness of the model.The test results are shown in Table 3.
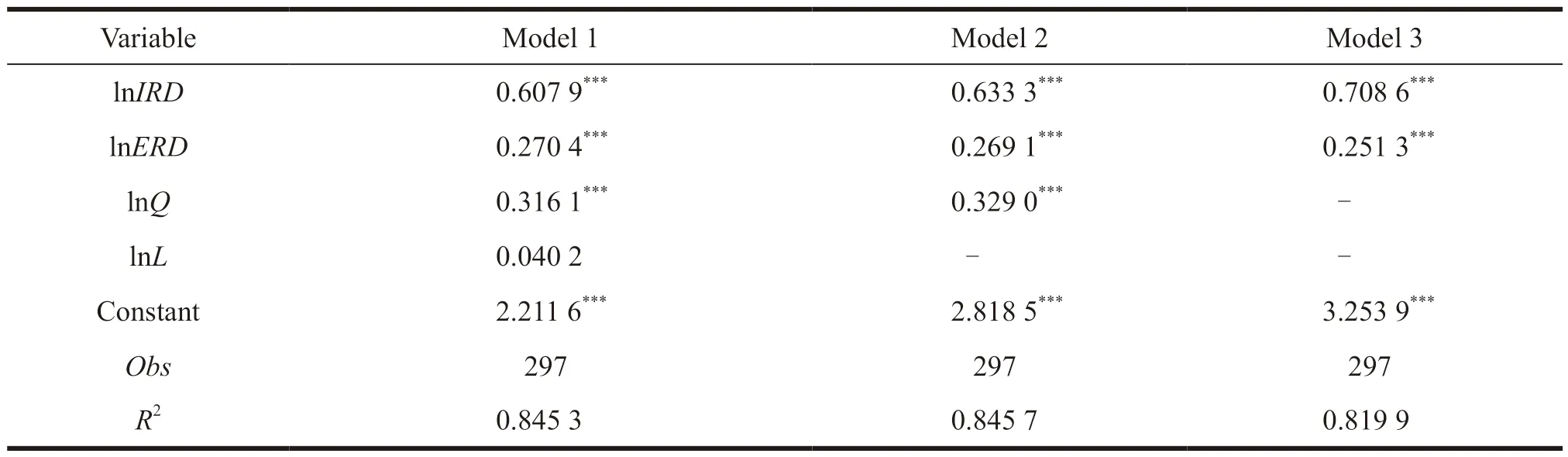
Table 3 Robustness test
The results of the robustness test show that in the process of gradually reducing the control variables,the sign and significance of the core explanatory variables in the three models do not change.Therefore,the empirical results based on national-level independent R&D,collaborative innovation,and sales revenue of new products in the pharmaceutical industry are robust and valid.
3.2 Regional perspective
3.2.1 Descriptive statistical analysis
Firstly,a descriptive statistical analysis is carried out on the variables related to the pharmaceutical industry in the eastern,central and western regions.The descriptive statistical results are shown in Table 4.

Table 4 Descriptive statistics of variables related to pharmaceutical industry in different regions
From the results in Table 4,the sales revenue of new products in the pharmaceutical industry in the eastern region,the internal expenditure of R&D funds,the external expenditure of R&D funds,the full-time equivalent of R&D personnel,and the number of enterprises,whether it is the mean or the maximum value,are larger than those in the central and western regions.Therefore,the pharmaceutical industry in the eastern region has a relatively large investment in R&D funds and R&D manpower,indicating the competition is relatively fierce,and the overall performance level is high.
3.2.2 Regional regression model test of independent R&D,collaborative innovation and economic performance
Firstly,the fixed effect model and random effect model of the eastern,central and western regions are established.The results show that both the fixed effect model and the random effect model are better than mixed regression.Then,the Hausman test is performed,and the results show that the fixed-effects model should be selected for the eastern region,while the random-effects model should be selected for the central and western regions.The regression results for each region are shown in Table 5.

Table 5 Regional regression results of independent R&D,collaborative innovation and economic performance
From the regression results by region,the internal expenditures of pharmaceutical R&D funds in the eastern,central and western regions all play a significant positive role in promoting the sales revenue of new products,and the order of the positive role is eastern>central >western.The pharmaceutical g industry in the eastern region has more advanced technology,strong economic strength,large scale of development,obvious advantages in technological innovation,the highest level of independent R&D,and the greatest driving effect on economic performance.Due to the weak innovation capability,insufficient human capital,weak R&D foundation,and lack of funds in the western region[23],the independent R&D of the pharmaceutical industry in the western region is low.
The external expenditures of pharmaceutical R&D funds in the eastern,central and western regions all play a positive role in promoting the sales revenue of new products,and the order of the positive role is central >eastern >western.The pharmaceutical industry in the central region has taken shape,but compared with the eastern region,its independent R&D strength is still weak.In product R&D,major technology research,technology incubation and achievement transformation,pharmaceutical companies in the central region often choose collaborative innovation[24].Therefore,the collaborative innovation of the pharmaceutical industry in the central region has a greater effect on economic performance.In terms of the significance of the effect,only the western region is not significant.Due to the weak economic foundation in the western region and the low level of innovation of enterprises and scientific research institutions,their collaborative innovation is not active,and the effect of improving economic performance is not obvious.
Regardless of the location of the pharmaceutical industry,the positive effect of internal R&D expenditure on new product sales revenue is greater than that of external R&D expenditure.If pharmaceutical companies want to achieve long-term development,occupy a larger market,and maintain long-term core competitiveness,they must depend on independent R&D.
The number of pharmaceutical industries in the eastern region has a significant negative inhibitory effect on the sales revenue of new products.Meanwhile,it plays a positive role in promoting the sales revenue in the central and western regions.Since the market competition of pharmaceutical industries in the eastern region becomes fierce,and the number of enterprises has also become saturated,if the competition increases,it may lead to vicious competition among enterprises,which will lower the economic performance of the entire region.In contrast,the market competition in the central and western regions is small as it has big market,and the sensitivity to market competition is stronger[25].Appropriately increasing the competition in the central and western regions is conducive to the development of new products and new technologies by pharmaceutical companies and to obtain more economic benefits[2].
The full-time equivalent of R&D personnel only shows a significant positive effect on the sales revenue of new products in the western region.This may be due to the excessive investment of R&D personnel in pharmaceutical industries in the eastern and central regions,resulting in redundant personnel and unreasonable organizational structure of R&D personnel[26].The human capital of the pharmaceutical industry in the western region plays a large role in economic performance.This may be because the government has carried out the policy to stimulate the western development in recent years and provided strong support for talents,which has increased the number and quality of R&D personnel.It effectively improves the economic performance[27].
3.2.3 Robustness test
After the regression model test,the robustness of the model should also be tested to ensure that the model is robust and effective.The robustness results of the model in the eastern,central and western regions are shown in Table 6.
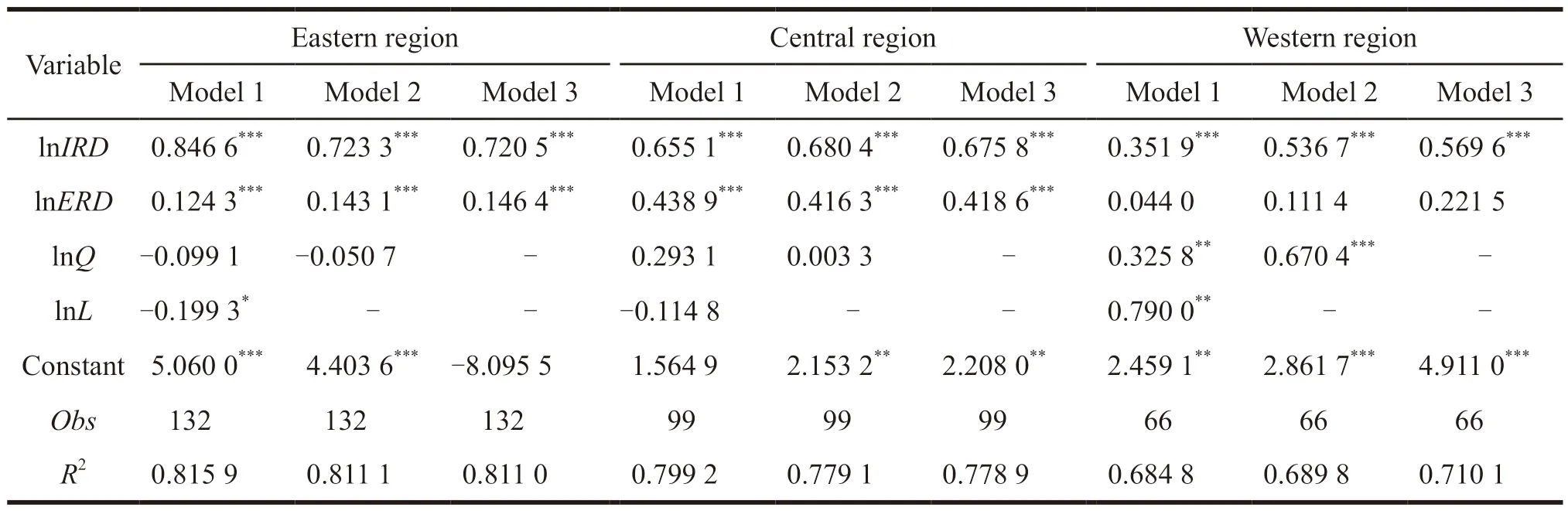
Table 6 Robustness test in different regions
The results of the robustness test show that in the process of gradually reducing the control variables,the sign and significance of the three core explanatory variables of the three models in each region have not changed.Although the significance of the control variables is different from the original regression results,the coefficients symbols are the same.Therefore,the empirical results based on different regions are robust and valid.
4 Conclusion and suggestions
4.1 Conclusion
Based on the national regression results,both independent R&D and collaborative innovation in the pharmaceutical industry play a significant positive role in promoting economic performance.Besides,the positive role of independent R&D is greater.From the regional regression results,the contribution of independent R&D in the pharmaceutical industry in the eastern,central and western regions to economic performance is greater than that of collaborative innovation.However,the contribution of collaborative innovation in the pharmaceutical industry in the western region to economic performance is not significant.
4.2 Suggestions
4.2.1 Increasing the investment in R&D and expanding funding channels
Innovation is the key for pharmaceutical companies to achieve long-term development.The research in this paper also confirms that independent R&D and collaborative innovation have a positive effect on the economic performance of the pharmaceutical industry.Therefore,pharmaceutical companies should attach importance to R&D innovation and increase capital investment in independent R&D and collaborative innovation activities.The profit of pharmaceutical companies is an important source of R&D investment.However,relying on their own profit is usually not enough.Companies must broaden the channels for raising funds.For example,they can get loan from banks,attract venture capital,and apply for national priorities for innovation projects to increase funds[28].
4.2.2 Strengthening the awareness of independent R&D and developing high-quality innovative products
Compared with collaborative innovation,independent R&D has a greater role in promoting economic performance.So pharmaceutical companies should strengthen the awareness of independent R&D.Pharmaceutical companies in the eastern region should continue to maintain their technology advantages,increase investment in independent R&D,and leverage economies of scale.At the same time,they should rationally cultivate R&D talents.In addition,they should also strive to develop innovative drugs,patented drugs and other high value-added products.Pharmaceutical companies in the central and western regions should actively obtain advanced technologies,introduce R&D talents,make full use of the rich resources of traditional Chinese medicine for independent R&D,and create unique advantages in pharmaceutical products.
4.2.3 Improving the level of collaborative innovation and seeking long-term and stable cooperation
Collaborative innovation plays an important role in improving economic performance.Collaborative innovation is crucial for the innovation activities and long-term development of some pharmaceutical industries with weak R&D strength.In collaborative innovation,pharmaceutical industries should firstly select partners from the aspects of R&D professionalism,talent quality and transformation ability.Secondly,we should take market demand as the guidance to establish common R&D goals with partners,which can avoid the derailment of R&D results.In addition,timely communication with partners should be made to establish long-term cooperative relations and improve the efficiency of collaborative innovation.Scientific research institutions,universities and enterprises should also strive to improve their scientific research level and serve the R&D goals set by enterprises.Besides,they should establish professional SOP,and use their advanced scientific research information and research personnel to develop high-quality products for enterprises.
4.2.4 Establishing market-oriented awareness and improving the efficiency of achievement transformation
Enterprises should not only focus on the results of R&D,but also on the transformation of the results,which can truly enhance economic performance.Firstly,pharmaceutical companies should be guided by market demand to conduct their R&D.Secondly,pharmaceutical companies should vigorously cultivate talents in the achievement transformation by providing them incentives,which will accelerate the transformation of achievements.In addition,pharmaceutical companies can cooperate with universities,scientific research institutions and other enterprises to make full use of their information,talents,technology and other resources to transform the results,thereby improving economic performance.
4.2.5 Providing relevant support and creating a favorable environment for innovation
As an important external force for pharmaceutical industries to carry out innovation activities,the government should make some support polices.First,the government should provide financial support to enterprises,especially pharmaceutical industries in underdeveloped areas such as the central and western regions.For example,the government can offer financial support for enterprise R&D through tax incentives,bank loan,and the establishment of key funds.Second,the government should guide pharmaceutical companies to compete in an orderly manner.When the government can effectively supervise the market,it will promote the continuous product R&D of pharmaceutical companies.Thirdly,the government should guide enterprises to expand their scale and develop in clusters.When leading enterprises are cultivated,it can improve their independent R&D level.Fourthly,science and technology intermediary service institutions should be set up,which can integrate the resources of enterprises,universities,and scientific research institutions.Lastly,pharmaceutical industries should actively cooperate with scientific research institutions,key laboratories,and universities to improve the level of collaborative innovation.
- 亚洲社会药学杂志的其它文章
- Investigation and Countermeasures of the Development of Chinese Pharmaceutical E-commerce in the B2C Model Based on PEST-SWOT Analysis
- Research on the Construction of Evaluation Model for the Development of Biopharmaceutical Park in China
- Current Situation and Prospect of the Application of Real-World Evidence in Health Care
- Study on Public Health Behavior against the Background of COVID-19 Pandemic -Based on Bandura Reciprocal Determinism
- Foreign Experience and Enlightenment of Reimbursement Management of Multi-indication Drugs
- The Status Quo and Enlightenment of the Foreign Extended Clinical Trial System

