Foreign Experience and Enlightenment of Reimbursement Management of Multi-indication Drugs
Wang Huiyan,Yu Hanshuang,Sun Lihua
(School of Business Administration,Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,Shenyang 110016,China)
Abstract Objective To provide reference for China’s medical insurance reimbursement plan of multi-indication drugs.Methods By referring to relevant foreign literature,the implementation process and conditions of different reimbursement management modes of multi-indication drugs were analyzed to provide suggestions for reimbursement of multi-indication drugs in China.Results and Conclusion It is suggested to further explore the suitable conditions and select the corresponding mode in China.Payment standards should be set according to value pricing and budget impact analysis.Besides,data collection and analysis mechanism must be improved.Lastly,reward and punishment mechanism can be adopted to improve management efficiency.
Keywords: multi-indication drug;medical insurance reimbursement;payment standard
In recent years,with the deepening of the research on the mechanism of drugs in treatment,more and more drugs have been proved to be effective in a variety of diseases[1].In addition,the continuous optimization of the drug review process for marketing registration has improved the approval efficiency of new drug indications.Therefore,there will be more multi-indication drugs facing medical insurance access.The value of multi-indication drugs may vary greatly because of the different treatment costs and health outcomes,usage and dosages,or combinations of medicines[2].However,China has a unified payment standard for drugs with the same generic name,which is not enough to reflect the value difference between drugs of different indications.Therefore,this paper aims to learn from foreign experience in drug reimbursement management of multiple indications,and to provide reference for relevant national policy formulation and regulatory decision-making.
1 Main modes of reimbursement management for multi-indication drugs
Reimbursement management of multi-indication drugs generally has three modes in international practice.
The first is to formulate different product names,different medical insurance codes,and different prices for various indications.Under this mode,when a drug is proved to have a new indication,the enterprise needs to apply to the drug approval department for a different trade name to be identified.After that,the medical insurance department will formulate different medical insurance codes and medical insurance payment standards for different indications of the drug[3].The main countries that use this mode are the United States and Sweden.
The second mode is the volume weighted average price[4].This mode takes each indication as an independent drug to formulate its payment standard and uses the percentage of the total market share of the drug for different indications as the weight,and then the volume and price are weighted.The specific calculation includes four steps: (1) Calculating the total annual expenditure of the drug in all indications;(2) Taking the percentage of expenditure of each indication t as the weight;(3) Multiplying the weight of each indication calculated in step 2 by its corresponding amount of each indication Price;(4)Adding up the prices of specific indications obtained for different indications in step 3 to obtain the payment standard of the drug.The main countries adopting this mode are Germany,France and Australia.
The third is to formulate a unified payment standard,and to sign different agreements at the same time to make the net price different[5].Under this mode,although the medical insurance department formulates uniform payment standards for drugs with the same generic name,the net prices for different indications are different by signing different agreements with enterprises.The agreement signed mainly includes three types,namely simple discount agreement,financial-based risk sharing agreement and result-based risk sharing agreement.Simple discount agreements are used for drug indications with no significant cost burden and clinical efficacy.Financial-based risk sharing agreements are suitable for drug indications with sufficient evidence of clinical efficacy but heavy cost burdens.Result-based risk sharing agreements are suitable for drug indications with insufficient evidence of clinical efficacy.Countries that adopt this mode mainly include Italy and the United Kingdom.
2 International implementation experience of different modes
The experience of the three different pricing models in different countries is shown below.
2.1 Different brands,different medical insurance codes,and different prices for different indications
2.1.1 America
In the United States,after the new drug indication is approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA),it will be given a new trade name,and then the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) will confirm whether the new drug indication is included in Medicare Part B.For the new indications included in the drug,CMS will give it a new healthcare common procedure coding system(HCPCS) code and establish the payment standard for this indication separately.Because the drug market in the United States is highly competitive,enterprises can freely set prices when drugs are sold on the market,so the payment standards for different indications are determined based on the average sales price(ASP) data of the indication.The specific calculation formula is shown in Table 1.This data is submitted by businesses to CMS within 30 days of the end of each quarter.In addition,to ensure the authenticity of ASP data,CMS stipulates that if companies report false data,they will be fined up to 10 000 US dollars per time[2].Based on the ASP data submitted by the enterprise,CMS will reimburse 1.06 times the ASP amount.If there is no historical ASP data,it will reimburse 1.06 times the wholesale price.
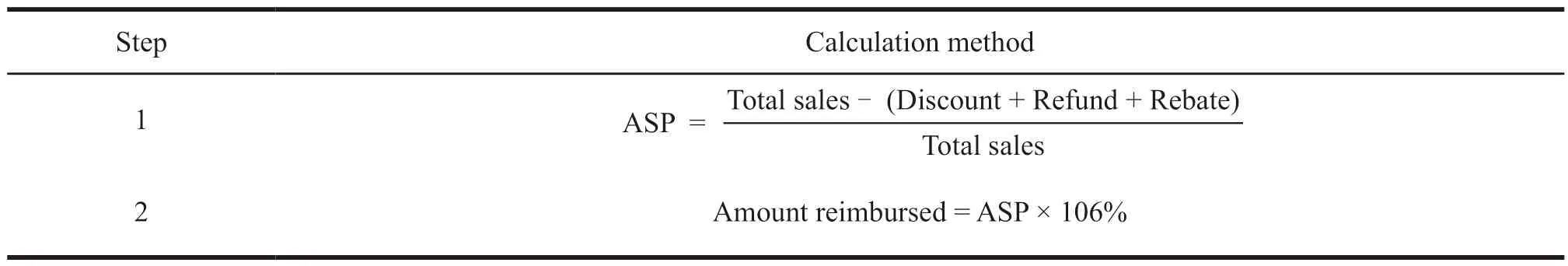
Table 1 The calculation steps of the US multi-indication drug payment standard
Since this mode sets different payment standards for drugs with the same generic name,there may be fraudulent insurance behaviors in which patients lie about their indications and purchase highvalue indication drugs at low prices.Therefore,the implementation of this mode requires a good regulatory environment.In the supervision of insurance fraud,the United States has mainly done three aspects of work[6]: (1) Passing legislation to restrict insurance fraud;(2) Establishing an investigation agency and an investigation team.The FBI is the primary investigative agency responsible for health insurance fraud,and its agency has established the Health Care Fraud Prevention and Enforcement Action Team;(3) Using information technology to detect fraudulent insurance behaviors.Based on the massive data provided by various medical information databases and electronic health records,CMS uses data modeling,mining and visualization tools to identify fraudulent behaviors.
2.1.2 Sweden
In Sweden,pricing and reimbursement planning is carried out by the Tandvårds-och läkemedelsförmåns verket (TLV).Sweden stipulates that those drugs with different indications are listed under different trade names.For new indications that have obtained marketing authorization,enterprises need to provide TLV with quotations for the indications,explanations of price rationality,and evidence of pharmacoeconomics.TLV will make decisions based on the following three points[7]: (1) Everyone should Treated and respected equally;(2) Prioritizing more serious diseases;(3) Cost-benefit principle.If the TLV accepts the price of the drug for that indication,the indication will be included in the Swedish Drug Benefit Scheme and paid for by value.The method for evaluating the value of drugs for different indications is as follows:
WTP is willingly to pay.Sweden does not explicitly stipulate the threshold of WTP,but the threshold of WTP generally accepted in the field of serious diseases such as oncology is 1 million kroner/QALY[8].QALYs means quality-adjusted life-years.Treatment costsocrepresents the cost of standard care.Treatment costnewrepresents the cost of new treatment.The cost of the treatment plan includes the cost of medicines,management costs,medical treatment costs,hospitalization costs,and adverse reaction costs.
2.2 Mode of the volume weighted average price
2.2.1 Germany
In Germany,companies are required to submit reimbursement applications for multi-indication drugs to the Gesetzliche Kranken Versicherung-Spitzenverband (GKV-SV).The Health Technology Assessment (HTA) Institute for Institutfür Qualitt und Wirtschaftlichkeit im Gesund-heitswesen (IQWIG)under the Gemeinsamer Bundesausschuss (G-BA) is responsible for evaluating the value of medicines for different indications.The value evaluation takes allcause mortality,morbidity,drug safety,health-related quality of life,patient satisfaction,and disease treatment time as the main judgment criteria,and divides the added value of drugs for different indications into six grades.The situation is directly linked to the formulation of the drug payment standard.The weights of different indications of a drug are calculated based on estimated or actual data.The estimated data are derived from prospective epidemiological data.The actual data are derived from real-world evidence (RWE)data.RWE data is generally available from payers and businesses.In addition,GKV-SV can obtain claim data provided by statutory health insurance.However,this mode has two limitations.First,claim data provided by statutory health insurance are only available after 9-12 months.Although drug data is linked to International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10),the classification of ICD-10 is not precise enough to accurately determine the indication of a drug[5].Second,the success of this mode depends on many factors,including the quality and timeliness of the data collected.
2.2.2 France
In France,the Haute Autorité de Santé (HAS) is responsible for evaluating the multi-indication drugs that apply for inclusion in the medical insurance list,and its Transparency Committee (TC) is responsible for evaluating the clinical benefit level (service médical rendu,SMR) and degree of improvement in clinical benefit (améliorationdu service médical rendu,ASMR)[9].Among them,the SMR grade focuses on reflecting the effectiveness,safety,severity of the disease treated,clinical manifestations (prevention,cure or alleviation of the disease) and the impact on public health for different indications of the drug.ASMR grade focuses on reflecting the degree of improvement in clinical efficacy of different indications of the drug compared with existing treatment regimens[10].Market share data of different indications of medicines can be obtained from hospital or outpatient prescriptions.TC obtains the preliminary price of the drug based on the SMR or ASMR rating results of different indications and the market share of the corresponding indications.CEPS will negotiate with companies to determine the payment standards for medicines.
2.2.3 Australia
In Australia,companies submit reimbursement applications for medicines of multi-indication to the Pharmaceutical Benefits Advisory Committee (PBAC).Then,PBAC,in collaboration with its Economic Subcommittee (ESC) and Drug Use Subcommittee(DUSC),will review the drug for different indications.Clinical research data,cost-effectiveness analysis,budget impact analysis and other materials are professionally evaluated,and the evaluation results are related to the price paid for the drug[11].The weight data of indications comes from the expected market share data predicted by the company,which is confirmed by DUSC.DUSC also compares actual usage data with forecasted usage data 24 months after the drug is marketed for different indications.Although DUSC will adjust the weighted average price based on the difference between the two data theoretically,it rarely happens in practice[5].
2.3 Mode of different net prices resulting from the establishment of uniform payment standards and the signing of different agreements
In Italy,companies submit drug access applications of multi-indication to the Drug Administration (Agenzia ltaliana del Farmaco,AIFA).The Committee for Technical Science (CTS) under AIFA is responsible for a comprehensive evaluation of different indications of drugs.The evaluation mainly examines the therapeutic value,degree of innovation,safety pharmacovigilance data,prices of medicines in similar or identical treatment groups,prices of medicines in other European member states,domestic market prospects,number of potential patients,and projected sales[12].After CTS expresses its opinion on reimbursement,the Committee for Pricing and Reimbursement (CPR) will negotiate with these companies.The negotiation will establish a unified and open nominal payment standard for generic drugs.Different agreements will be signed according to the characteristics of different indications.The types of agreement are shown in Table 2.The content of the agreement is confidential and will not be disclosed.

Table 2 Types of agreements signed in Italy
Obtaining data on patient-level efficacy and costs is a key difficulty in implementing the protocol.AIFA established a nationwide online registration system in 2006 to collect patient follow-up information.All drug indications of the enterprise can be registered in the system,and the enterprise needs to pay an annual management fee of 30 000 euros for the system after registration.For drugs registered for new indications,prescribers need to create a patient profile and upload relevant clinical data.Only after the patient file is submitted to the hospital pharmacy can the prescriber dispense the medication.When the patient’s condition has new progress,the prescriber needs to update the patient file.At the end of the session,the system automatically shuts down and sends the data to AIFA.AIFA will determine whether the reimbursement of the indication is reasonable based on the data.After AIFA confirms that the reimbursement is reasonable,the refund will be provided in the form of free merchandise or credit amount.This means that patients can only consume in the original hospital or pharmacy,thus making the medical institution or pharmacy profitable[13].
The Italian network registration system started early and is relatively mature.However,it has many deficiencies.First,it lacks data analysis and interregional data sharing capabilities.Second,the data update is not timely and in place.Prescribing information filing involves a lot of management work.AIFA does not manage the prescribers in place and the incentives are insufficient,resulting in the prescribers not completely updating the system data.Third,the management cost is high.Beginning in 2012,AIFA contracted the management of the agreement to an international consulting firm for up to 8.7 million euros[14].
3 Enlightenment
3.1 Further proving the conditions in China and choosing the corresponding mode
Different modes have different implementation conditions.The mode of “developing different trade names,different codes,and different prices for different indications” requires two conditions in the specific implementation process[3].Firstly,different trade names and codes need to be formulated for different indications of drugs.Secondly,to avoid the arbitrage behavior of patients,it is necessary to establish a data system related to drugs and indications and a sound supervision system.The volume weighted average price considers the market share of different indications in the process of formulating payment standards.Therefore,the implementation of this mode requires the medical insurance department to have the ability to collect data on the market share of drugs for different indications[5].In the mode of making a unified payment standard and signing different agreements at the same time to make the net price different,the simple discount agreement only requires the medical insurance department to determine the discount according to the value of the drug.Besides,the complex agreement requires the medical insurance department to collect the clinical efficacy of drugs of different indications and the use of medical fund[15].
The mode chosen in each country is usually influenced by the conditions of implementation.Taking the United States as an example,the level of refined management of medical insurance in the United States is high.CMS can separately code and manage different indications[3],which has the ability to collect data on the use and payment of prescription drugs in inpatient,outpatient hospitals and other suppliers[16].Secondly,the United States can effectively supervise insurance fraud through legislation,establishment of groups and information management methods[6],so it can formulate different trade names,different codes,and different prices for different indications of drugs.China needs to combine the specific implementation conditions of different modes,and choose an appropriate reimbursement management mode.
3.2 Paying attention to value pricing and budget impact analysis in the formulation of payment standards
The above countries apply value pricing and budgetary implications to the formulation of payment standards for drugs of multi-indication.Sweden measures the QALYs and incremental costeffectiveness ratios (ICERs) of different drugs of indications through Pharmacoeconomics and guides the formulation of payment standards.France and Germany have established clinical value assessments according to the system.Then,the clinical value of drugs of different indications is graded,and the grading results of different indications are related to the payment standard of drugs.Australia and Italy focus on the application of budget impact analysis.Australia will also apply the market share data from the budget impact analysis to the weight calculation of the volume weighted average price method.
At present,although pharmacoeconomic evaluation and budget impact analysis are used in the formulation of payment standards by China’s medical insurance departments,the payment standards cannot reflect the value of each indication in practice.Besides,the budget impact analysis is not mandatory for negotiation.It is suggested that when formulating payment standards for drugs with multiple indications,China should pay attention to drug value pricing,clarifying the framework and standards for value evaluation,and examining the impact of different indications on the budget of medical insurance funds.
3.3 Improving drug data information collection and analysis mechanism
The data collection and analysis mechanism are the core of the refined management of multi-indication drugs because they been explored by scholars in developed countries.According to the experience of the United States,Germany,France,and Australia,the medical insurance department can collect the price and market share data of drugs with different indications in three ways[5]: (1) Directly provided by enterprises;(2) From hospital data or outpatient prescriptions data acquisition;(3) From prospective epidemiological data.The data of clinical efficacy and medical insurance fund for different drug indications can be collected by establishing an independent data collection system.Italy collects follow-up information of patients by establishing a nationwide network registration system.When the patient’s condition has new progress,the prescriber needs to update the patient file.At the end of the course of treatment,the system is automatically closed,and the data is sent to AIFA[13].It is suggested that for the reimbursement management mode of selected multi-indication drugs,China should learn from foreign data collection methods,and vigorously improve the data collection and analysis mechanism for multi-indication drugs.
3.4 Adopting reward and punishment mechanism to improve management efficiency
Delicate management of multi-indication drugs means increasing the workload of clinical staff.However,the benefits of clinical staff from this management are minimal.The Italian AIFA had problems of inadequate management and insufficient incentives for prescribers,resulting in untimely and inadequate data updates.To alleviate this problem,AIFA gives hospitals an incentive to return refunds to patients in the form of free merchandise or credits.This means that patients can only consume in the original hospitals and pharmacies,thereby making medical institutions profitable and improving the enthusiasm of medical institutions[13].In the United States,the punishment method is adopted,too.If companies falsify regularly reported quarterly data,they will be fined 10 000 dollars per time[3].When implementing reimbursement management of multiindication drugs in China,it is recommended that medical insurance departments learn from foreign experience and take incentive or punishment measures for relevant parties who lack motivation to improve management efficiency.
- 亚洲社会药学杂志的其它文章
- Investigation and Countermeasures of the Development of Chinese Pharmaceutical E-commerce in the B2C Model Based on PEST-SWOT Analysis
- Research on the Construction of Evaluation Model for the Development of Biopharmaceutical Park in China
- Current Situation and Prospect of the Application of Real-World Evidence in Health Care
- Study on Public Health Behavior against the Background of COVID-19 Pandemic -Based on Bandura Reciprocal Determinism
- The Status Quo and Enlightenment of the Foreign Extended Clinical Trial System
- Research on the Effect of R&D lnvestment lntensity and Sales Expense on the Performance of Biomedical Enterprises

