Evaluation of macular choroidal and microvascular network changes by activity scores and serum antibodies in thyroid eye patients and healthy subjects
Mehmet Erkan Dogan, Ibrahim Basol, Hatice Deniz Ilhan, Yusuf Ayaz, Olgar Ocal
1Department of Ophthalmology, Akdeniz University, Konyaalti 07070, Antalya, Turkey
2Department of Ophthalmology, Kepez State Hospital, Antalya 07320, Turkey
3Department of Ophthalmology, Suruc State Hospital,Sanliurfa 63800, Turkey
Abstract
● KEYWORDS: thyroid eye disease; optic coherence tomography angiography; vascular density; choroidal thickness; foveal avascular zone area
INTRODUCTION
Graves’ disease is an organ specific autoimmune disease affecting the thyroid gland and orbit.Approximately 35%-47% of all patients with Graves’ disease have orbital manifestations described as thyroid eye disease (TED)[1].Possible risk factors include female gender, smoking and circulating antibodies against thyroid-stimulating hormone(TSH)[2-3].The inflammatory response involves ocular surface,orbital soft tissue, mainly orbital fat and extraocular muscles.Common clinical manifestations of TED include conjunctival redness and chemosis, orbital soft tissue swelling, eyelid retraction, lag exophthalmos, extraocular muscle involvement,corneal involvement, intraocular hypertension and optic neuropathy[4-5].The effects of the disease are mild in the majority of patients but about 3%-8% of the TED patients have sight-threatening dysthyroid optic neuropathy (DON)[6].
Orbital inflammation and mechanical compression in TED are known to affect the orbital vessels[7-8].Raised retrobulbar and episcleral venous pressure in TED patients may affect both retinal and choroidal vasculature.Besides, decreased orbital venous outflow detected using color doppler ultrasound may have a role in developing DON[9].However, color doppler ultrasound cannot adequately show the retinal microvascular network.Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is one of the biggest advancements in ophthalmic imaging.Built on that platform,OCT angiography (OCTA) is a new functional method that detects the motion contrast in the bloodstream and visualizes the capillary artery of the retina and choroid without using dye with a level of detail which is far beyond the one obtainedviaolder forms of imaging[10].In this study, we evaluated the choroidal thickness and the microvascular network changes around the macula in TED patients at different stages and the relationship of those changes with risk factors, serum antibodies and the severity of TED.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
Ethical ApprovalThe study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Akdeniz University Clinical Research Ethics Committee (protocol code KAEK 66 and date of approval 27.01.2021) for studies involving humans.Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Eighty-five TED patients admitted to the Akdeniz University hospital between 2021 and 2022 were registered in the study.Healthy controls were recruited during the same study period from among subjects who received annual eye examinations.Patients with retinal disease like diabetic macular edema or age-related macular degeneration and uveitis or glaucoma as well as systemic diseases like hypertension and diabetic retinopathy were excluded from this study.
Lid width, proptosis (in millimeters), best corrected visual acuity (BCVA), slit-lamp biomicroscopy, intraocular pressure(IOP), ophthalmoscopy examinations and OCTA images were recorded.The demographic data including age, sex, duration of hyperthyroidism, smoking status, therapy history (131I,thyroidectomy or medicine), any systemic disease was reported.Laboratory tests were conducted including free triiodothyronine(FT3), free thyroxine (FT4), TSH, autoantibodies [thyroid stimulating hormone-receptor autoantibodies (TRAB),anti-thyroid peroxidase (TPO) and human thyroglobulin autoantibodies (hTG)].The clinical activity scoring (CAS)[5]and European Group on Graves’ Orbitopathy Classification(EUGOGO)[11]was used to estimate TED activity.
凯迪拉克专卖店的老板见这么年轻的小伙子能凭自己的实力买凯迪拉克,决定把价格优惠到65万元,并握住他的手说:“一般来说,这么出色的车是不会与一个毫无背景的工薪族发生关系的,你一旦拥有了它,就是身份的象征。古人说:行天莫若龙,行地莫若马。这也符合凯迪拉克的精神,商标中冠和盾的图案,代表着金戈铁马,骁勇善战!但愿你拥有它后,能成为一个战无不胜的人!”
Subfoveal choroidal thickness (SFCT), foveal avascular zone(FAZ) area and macular vascular density measurements of the enrolled cases were performed with Topcon swept source OCT/OCTA DRI OCT Triton (Topcon Co.Japan).Fovea-centered 6×6 mm2OCTA images of the patients had better quality and higher reproducibility than 3×3 mm2images.6×6 mm2OCTA images were preferred to ensure adequate quality imaging and reproducibility.The scanning area centered on the fovea was 6×6 mm2with a signal strength index of >40 for each eye was selected.Any image with a double vessel pattern or motion artifacts of more than three lines was excluded.The superficial and deep retinal capillary plexuses were detected and separated automatically by the instrument.
Subfoveal Choroidal Thickness MeasurementsThe vertical distance from the hyperreflective line corresponding to the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) in the subfoveal area to the hyporeflective line of the choroido-scleral interface was measured manually using the OCT images by three different ophthalmologists.The average of the measured values was taken and compared with the values of the other patients and healthy controls group.All ophthalmologists were experts on OCT and also they were unaware of each other.
Foveal Avascular Zone MeasurementsThe FAZ boundaries in the superficial retina and deep retinal layer were marked on the images by two different ophthalmologists and the field was automatically measured by the device.The average of the measured values was taken and compared with those of the other patients and healthy controls group.
Macular Vascular Density MeasurementsBy selecting the“density map” measurement on the OCTA device, the capillary plexus of the superficial retinal layer and the deep retinal layer was measured automatically by the device.Superficial capillary plexus was segmented from 3 μm below the internal limiting membrane to 15 μm below the inner plexiform layer.Deep capillary plexus was segmented from 15 μm below the inner plexiform layer to 70 μm below the inner plexiform layer.These dimensions were placed on the macula with ETDRS Grid scale including 1 mm diameter of the central area and 3 mm diameter of the paracentral area.It was divided into separate quadrants as superior, temporal, inferior and nasal and the vascular densities of these quadrants were recorded separately.
Statistical AnalysisThe SAS version 9.4 was used to perform statistical analysis.While evaluating the study data, descriptive statistics including the means and standard deviations were obtained.The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test was conducted to check the normality distribution of the variables.Since the data was found to have non-normal distribution, the independent Mann-WhitneyUtest and Kruskal WallisHtest were used for the comparative analysis.APvalue of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
One hundred fifty-six eyes of 78 participants were analyzed after excluding 14 eyes of 85 participants because of poor segmentation and/or quality of images.Totally 78.2% of 78 TED patients were female and 48.6% were smokers.While 41 patients had hyperthyroidism, 37 patients had euthyroidism.TRAB, TPO and hTG antibody were measured in all patients.TRAB, TPO and hTG antibody were present in 53 patients(69.7%), 40 patients (60.6%) and in 32 patients (45%),respectively.Other patients had normal levels.
Patients were divided into two groups according to CAS, while 54 patients (69.2%) had CAS 0-3 and 24 patients (30.7%)had CAS 4-7.According to the EUGOGO classification, 22 patients (28.5%) were in the mild group, 45 patients (58.4%)were in the moderate to severe group and 10 patients (12.9%)were in the sight-threatening group.Fifteen patients (19.4%)had thyroid papillary carcinoma.

Table 1 All TED patients measurements
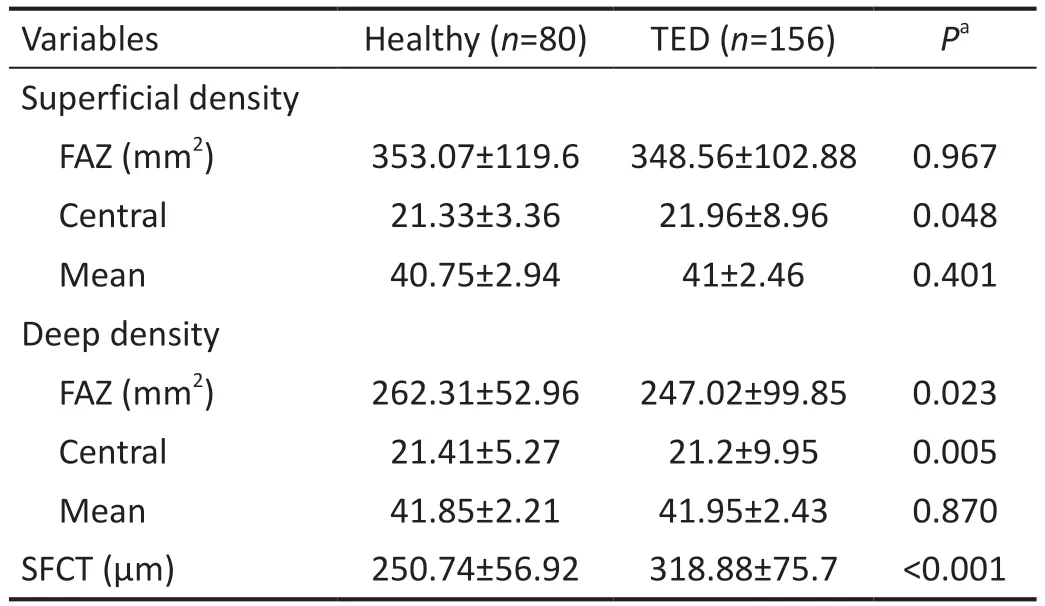
Table 2 Comparison of the TED patients and healthy subjects measurements mean±SD
Measurement results of all 78 TED patients and 40 healthy subjects from OCT and OCTA images including SFCT, mean superficial FAZ (s-FAZ) area, mean deep FAZ (d-FAZ), mean central superficial vascular density (c-SVD), mean superficial vascular density (m-SVD), mean central deep vascular density(c-DVD), mean deep vascular density (m-DVD) are shown in Tables 1 and 2.
As for OCT and OCTA measurements according to serum antibody levels, patients with high TRAB levels had increased SFCT (P=0.01), s-FAZ (P=0.02) and d-FAZ (P=0.01),decreased c-SVD (P=0.04) and m-SVD (P=0.03) but no difference was observed in c-DVD (P=0.58) and m-DVD(P=0.11) measurements.In patients with high TPO levels, only m-SVD (P=0.04) decreased but no difference was observed in other parameters.In patients with high hTG levels, SFCT(P=0.005) increased but no statistically significant difference was observed in FAZ area and vascular density measurements(Table 4).
According to the severity of the disease, those with a CAS score from 4 to 7 had higher c-DVD and m-DVD levels(P=0.02,P=0.03).There was no statistically significant difference in other parameters.When we evaluated the patients according to the EUGOGO classification, no statistically significant difference was found between the 3 groups in any parameters (Table 5).
DISCUSSION
TED is an autoimmune disease, but its pathogenesis is not still clearly understood.As we emphasized above, orbital inflammation and mechanical compression observed in TED are known to affect orbital vessels.Increased retrobulbar and episcleral venous pressure may affect both the retinal and choroidal vasculature.In our current study where we used OCT and OCTA, we compared the changes in choroidal thickness,FAZ area and retinal microvascular density in patients with TED according to clinical severity and serum antibody levels.We found that especially DVD increased in patients with high CAS score, and SVD decreased especially in patients with high serum antibodies such as TRAB and TPO.Moreover,patients with high TRAB were found to have increased SFCT and enlargement in the FAZ area.We suggest that these related factors may perhaps help us to better understand the pathogenesis of the disease.
Vascular DensityPrevious studies focused on the intraorbital blood flow in TED[8-9], whereas little attention has been paid to intraocular hemodynamic changes such as FAZ area and retinal vascular density.In a study with color Doppler ultrasonography, Alp[8]argued that orbital blood flow velocity was altered in patients with TED and increased blood flow velocity in arteries might be secondary to orbital inflammation.Konuket al[9]also showed that superior ophthalmic vein blood flow velocity decreased significantly in patients with DON.Wuet al[12]reported that the retinal microvascular density was significantly reduced in TED patients compared to healthy controls.Zenget al[13]reported that the macular microvascular density decreased significantly in the TED patients with chorioretinal folds compared to the TED patients with no chorioretinal folds.Ceylanogluet al[14]reported that no significant difference was observed in macular microvascular structure among pediatric TED patients compared to the healthy controls.In our study, demographic characteristics andOCTA parameters of the TED patients were compared with those of 40 healthy subjects.No significant difference was observed between their demographic characteristics.In the healthy subjects, c-SVD was measured as 21.33%±3.36% in OCTA parameters.It was considered to be reduced statistically significantly in the healthy group compared to the TED group (P=0.048).When the DVD of the healthy group and TED group was compared, c-DVD (P=0.005) values were found to be statistically reduced in the TED group.We tried to determine the association of retinal microvascular changes with serum antibody and clinical activity score.We found that especially SVD decreased in patients with high TRAB and high TPO levels, whereas DVD increased in patients with high CAS scores.Such increase in DVD might be due to the
fact that orbital inflammation was higher in patients with a high CAS score, and that inflammation caused an increase especially in DVD.There is some evidence that TRAB can increase inflammation through oxidative stress-induced apoptosis but its role in the pathogenesis of TED is still unclear.TRAB reflects the amount of antibodies depositing in the microvascular system.We think that the accumulation of these antibodies in the vascular system may impair circulation and reduce SVD in particular.

Table 3 Comparative measurements with sex, thyroid hormone, thyroid papillary carcinoma and smokers

Table 4 Comparative measurements with serum antibodies

Table 5 Comparative measurements with activity scores
Foveal Avascular Zone AreaThe FAZ area known as the most sensitive part of the retina is an area that does not contain capillaries in the fovea.It is known that the FAZ area expands in ischemic diseases such as diabetic retinopathy[15].Yuet al[16]argued that the FAZ area expanded in active TED patients.In our study, both the superficial and deep FAZ areas were observed to have expanded with decreased SVD only in TED patients with high TRAB.Furthermore, the d-FAZ area was also statistically significantly higher in TED patients compared to the healthy group (P=0.023).However, many factors such as age, gender, axial length can affect the size of the FAZ area[17].
Choroidal ThicknessThe choroid is the dense vascular network layer between the sclera and the retina that provides blood flow and nutrition to the RPE and outer retinal layers.Current literature suggests that it decreases in women,myopia, advanced age, cardiovascular diseases such as chronic hypertension, coronary artery disease, carotid artery stenosis[18], and the choroid of patients thickens in active phases of inflammatory diseases such as lupus, Behçet’s disease, systemic sclerosis and familial Mediterranean fever[19].Çalışkanet al[20]were the first ones to describe the changes in choroidal thickness in eyes with TED.They reported that the mean SFCT increased in eyes with active TED compared to the healthy control group.In our study, choroidal thickness was statistically higher in the healthy group compared to the TED group (P<0.001).Gulet al[21]compared choroidal thicknesses in active and stable TED patients and they found that SFCT was significantly higher in patients with TED at the active phase than in those at the stable phase of the disease.However,in our study including a larger patient group, we did not find a statistically significant difference in SFCT between active and stable TED patients by dividing the patients into groups according to CAS and EUGOGO severity classification.We think that increased blood flow velocity in the arteries during the active TED disease possibly caused primarily an increase in DVD.But it did not affect the SFCT.SFCT increased only in patients with high TRAB and hTG levels, who might perhaps have more severe inflammation.Additionally, it was observed that the SFCT was statistically thicker in active smokers group.It is still controversial, though.El-Shazlyet al[22]found that SFCT was significantly lower in active smokers compared to passive smokers.On the other hand, Ulaşet al[23]argued that SFCT significantly increased from baseline at 0 and 5min after smoking and then decreased until reaching baseline at 1h after smoking.
There were some limitations in our current study.This is a cross-sectional study and prevents us from associating vascular changes with disease progression.We only analyzed the hemodynamic changes in an area of approximately 6 mm diameter in the foveal region but did not analyze larger areas around the macula and optic disc.Perhaps more valuable information could be obtained in those regions.Moreover,dysthyroid patients in the absence of TED were not enrolled,which might also limit the interpretation of the results to some extent.
In conclusion, we used OCT and OCTA imaging to compare the macular choroidal and microvascular network changes in TED patients with different activity scores and the effect of serum antibodies.The results showed that both disease activation and serum antibodies had a different effect on both superficial and deep retinal vascular densities.High serum antibody levels were also demonstrated to affect choroidal thickness independent of disease activity.We believe that the ocular vascular network clearly plays an important role in the pathogenesis because of the hemodynamic changes that occur in eyes with TED.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to thank Prof.Dr.M.Ziya Fırat which performing the statistical analysis.
Authors’ contributions:Dogan ME and Basol I, acquisition of data, analysis of data, interpretation of data, and drafted the manuscript; İlhan HD contributed to the conception, design and analysis of data and critically revised the manuscript;Ayaz Y and Ocal O analysis of data, and critically revised the manuscript.All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest: Dogan ME,None;Basol I,None;Ilhan HD,None;Ayaz Y,None;Ocal O,None.
 International Journal of Ophthalmology2023年12期
International Journal of Ophthalmology2023年12期
- International Journal of Ophthalmology的其它文章
- Dynamic tear meniscus parameters in complete blinking:insights into dry eye assessment
- Effects of diquafosol sodium in povidone iodine-induced dry eye model
- Morroniside ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory damage in iris pigment epithelial cells through inhibition of TLR4/JAK2/STAT3 pathway
- Role of reactive oxygen species in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and apoptosis of human lens epithelial cells
- Electroacupuncture alleviates ciliary muscle cell apoptosis in lens-induced myopic guinea pigs through inhibiting the mitochondrial signaling pathway
- De novel heterozygous copy number deletion on 7q31.31-7q31.32 involving TSPAN12 gene with familial exudative vitreoretinopathy in a Chinese family
