Reliability analysis for wireless communication networks via dynamic Bayesian network
YANG Shunqi ,ZENG Ying ,LI Xiang ,LI Yanfeng ,and HUANG Hongzhong
1.School of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering,Huazhong University of Science and Technology,Wuhan 430074,China;2.School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering,University of Electronic Science and Technology of China,Chengdu 611731,China;3.China University of Petroleum at Karamay,Karamay 834000,China
Abstract: The dynamic wireless communication network is a complex network that needs to consider various influence factors including communication devices,radio propagation,network topology,and dynamic behaviors.Existing works focus on suggesting simplified reliability analysis methods for these dynamic networks.As one of the most popular modeling methodologies,the dynamic Bayesian network (DBN) is proposed.However,it is insufficient for the wireless communication network which contains temporal and non-temporal events.To this end,we present a modeling methodology for a generalized continuous time Bayesian network (CTBN) with a 2-state conditional probability table (CPT).Moreover,a comprehensive reliability analysis method for communication devices and radio propagation is suggested.The proposed methodology is verified by a reliability analysis of a real wireless communication network.
Keywords: dynamic Bayesian network (DBN),wireless communication network,continuous time Bayesian network (CTBN),network reliability.
1.Introduction
With the rapid development of radio-frequency technology,wireless communication turns to be an essential technology in business,transportation,and daily life [1].As the transmission rate of communication increases,its defects such as disconnecting from the internet appear gradually.A reliable wireless communication network becomes more and more important,and more research is devoted to reliability analysis of wireless communication networks [2-4].Radio propagation reliability [5],communication device reliability [6],and wireless communication network reliability [7] are three of the hottest issues in communication reliability analysis.Sufficient scientific achievements are applied to the former two topics,but wireless communication network reliability analysis is still a difficult problem.How to quantify the impacts of devices and radio propagation reliability on the full networks is one of the most important questions that need to be solved urgently.
For radio propagation reliability,one of the most popular analytical methods is to evaluate the path loss [8],which is the most effective factor in radio communication.Research on path loss released by international communication sectors provides influence factors of communication scenarios [9],line-of-sight (LOS) probability[10],and antennas [11].Path loss models provide an empirical model to describe a linear proportionality between the communication distance and path loss under different scenarios.Existing radio propagation reliability models [12] adopt the lognormal distribution to fit the distribution of communication distance and derive the probability distribution function (PDF) of path loss,which can be applied to evaluate the radio propagation reliability via the threshold of path loss value.
The communication station is an infrastructural device for wireless communication networks.It includes several electronic components such as the voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO),the band-pass filter (BPF),and the lownoise amplifier (LNA) [13].For a single component,there are many methods to evaluate the reliability such as finite element simulation [14].However,if these components are integrated into one device,the complex logical structure and dynamic characteristics make it difficult to analyze the reliability of this device.Particularly,in a wireless communication network,there are several failure distributions for each node,including discrete distributions and continuous distributions.Therefore,further research is required for analyzing this station.
Existing studies on dynamic network reliability analysis have proposed several methods including the Markov regenerative process [15],the dynamic fault tree [16],and the dynamic Bayesian network (DBN) [17].Among these methods,DBN is one of the most efficient tools to evaluate the dynamic impact on the system.Existing algorithms for DBN include the discrete-time Bayesian network (DTBN) [18] and the continuous-time Bayesian network (CTBN) [19].The DTBN has been sufficiently studied and applied to dynamic network reliability analysis with components following different failure distributions,but it needs high memory cost and cannot be applied to non-temporal variables.CTBN,however,provides a closed-form solution that can be applied to reliability and sensitivity analysis.
For a wireless communication network,its device failure is a temporal event,however,radio propagation failure is affected by non-temporal factors such as communication distance,terrain shading,and LOS [12].Therefore,reliability analysis for a wireless communication network should consider different dynamic elements.CTBN is one of the suitable methods for multiple heterogeneous nodes and provides a closed-form solution that can integrate the binary discrete events into a temporal system expediently.Therefore,this paper proposes a generalized CTBN with a 2-state conditional probability table (CPT) which can be applied to DBN with mixed failure distributions.
2.DBN
The failure process of complex systems always has complex dynamic characteristics related to failure time and sequence.Motivated by this complexity,DBN is proposed to overcome the deficiencies of static Bayesian network (BN) in dynamic reliability analysis.Different from static BN,DBN extends its model for temporal system analysis issues.Meanwhile,DBN considers more logic gates including a warm spare (WSP) gate.Events in DBN have a temporal distribution associated with them.According to different temporal representations,two main modeling methods (DTBN and CTBN) for DBN have been proposed.
As one of the most popular approaches,DTBN provides a standard inference engine for DBN,which can be applied to various kinds of system reliability analysis.In a DTBN,mission time is divided into serval intervals,and the marginal probability density (MPD) &conditional probability density (CPD) of each node is replaced by the marginal probability table (MPT) and CPT.However,as the state space of a DTBN is discrete,it can only get an approximate solution in a specific time interval.The size of CPT will increase exponentially with the increasing number of nodes and time intervals.For a complex system such as the wireless communication network,DTBN modeling is time-consuming and inapplicable.Thus,as an optimized algorithm,CTBN is proposed.Events in CTBN are following continuous failure distributions.All of the MPD &CPD are presented in forms of functions.For example,the conditional PDFfT|A,B(T|A,B) of AND nodeTin Fig.1(a) with a CTBN formalism [19] is shown as
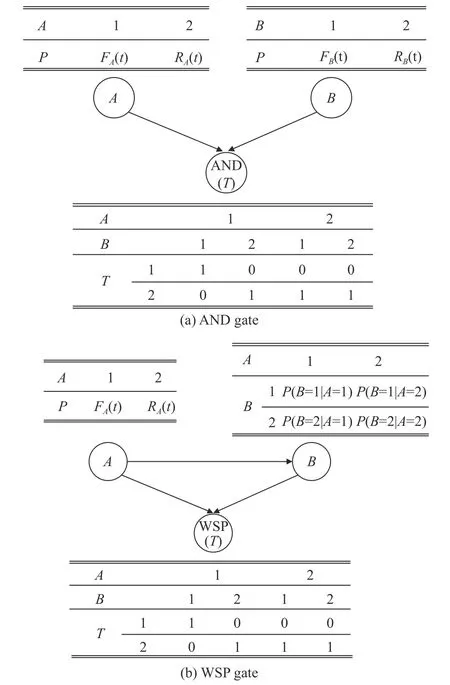
Fig.1 MPT and CPT for the logic gates
ThroughfT|A,B(T|A,B),FT(t)=FA(t)FB(t) can be derived.With the closed-form solution of PDF,CTBN can get precise reliability at an instant time.However,there is no CTBN inference engine for general distribution.For these problems,this paper proposes a CTBN formalism with a 2-state CPT,as shown in Fig.1.
In Fig.1(a),P(A=1)=FA(t) denotes the failure probability of nodeA,whileP(A=2)=RA(t)=1-FA(t)denotes the reliability of nodeA.
For AND gate,
For OR gate,
where Pa(Ti) is the parent node of nodeT,piandhdenote the state of each node and are equal to 1 or 2.Based on this fundamental theory,the CPT for dynamic logic gate in the DBN can be derived.
WSP [19] is a typical dynamic logic gate in the DBN which defines a dormant node and a primary node.As shown in Fig.1(b),nodeBis a standby node of nodeA.When nodeAis working,nodeBworks in a dormant condition,and its hazard rate λBis reduced by a dormancy factor α,0 ≤α ≤1.NodeBwill change into working condition after nodeAfails.
Assume thatfB(t) andfαB(t) are the PDFs of nodeBin working condition and dormant condition respectively.tAandtBdenote the failure time of nodesAandB.
Typically,when the failure time distributions of nodesAandBfollow the exponential distribution,i.e.,givenfA(tA)=fB(t)=λe-λtandfαB(t)=αλe-αλt,the CPT of nodeBcan be presented in Table 1.
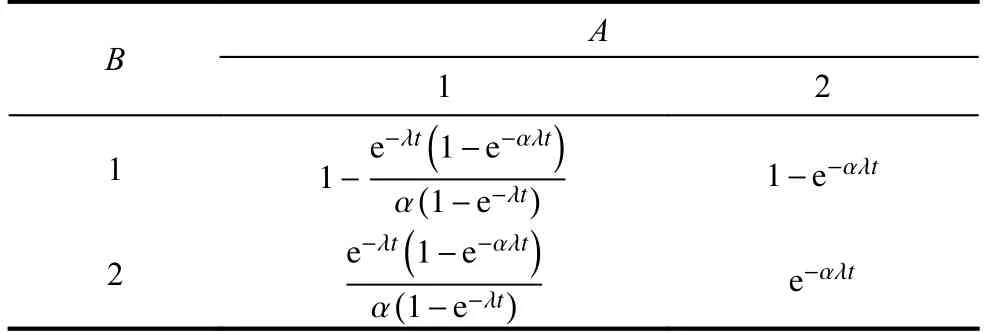
Table 1 CPT of node B in Fig.1(b)
Via CPT of nodeB,we can obtain the marginal probabilityFB(t) andRB(t) through (2) and (3).
The marginal probability of nodeBis the same as the CTBN results in [19],however,with the modeling method of CPT,this methodology can be conveniently applied to system reliability analysis via Bayesian network toolbox (BNT) for Matlab [20].
3.Methodology
3.1 Radio propagation reliability evaluation
As introduced in Section 1,radio propagation reliability[21-24] is influenced by shadow fading and communication distance.In our previous work [12],Okumura-Hata model [8] and the lognormal distribution were used to model the closed-form solution of the PDF of path loss valueL,which denotes the signal attenuation under different communication scenarios,and can be applied to radio propagation reliability evaluation.According to previous research,Lfollows the normal distribution,and its thresholdLTis given by [12],the reliability of radio propagation can be obtained as
whereddenotes the communication distance,and lnd~N.hbandhredenote the effective height of the base station and the receiving station;Ccell,Cterrainand α(hre) are the correction factors for communication cell type,terrain andhre.
3.2 Devices reliability analysis
In reliability analysis of a wireless communication network,devices’ failures are typical temporal events that follow an exponential distribution [25-27].It is worth noting that the proposed method is also applicable to the non-exponential case.However,the failure life of electronic products usually follows an exponential distribution,which is adopted in this paper.The radio station is the main device in this network.As shown in Fig.2(a),the communication-related components in a radio station are provided.According to this structure,DBN for communication function can be modeled and shown in Fig.2(b),and the description for each node is shown in Table 2.
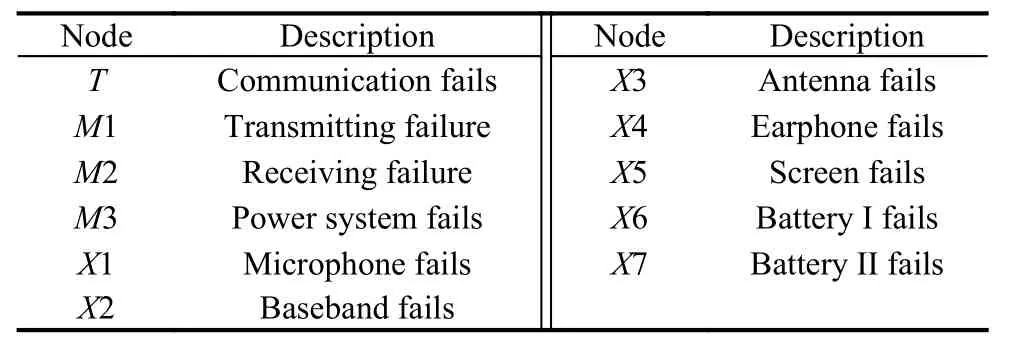
Table 2 Description for each node in Fig.2(b)
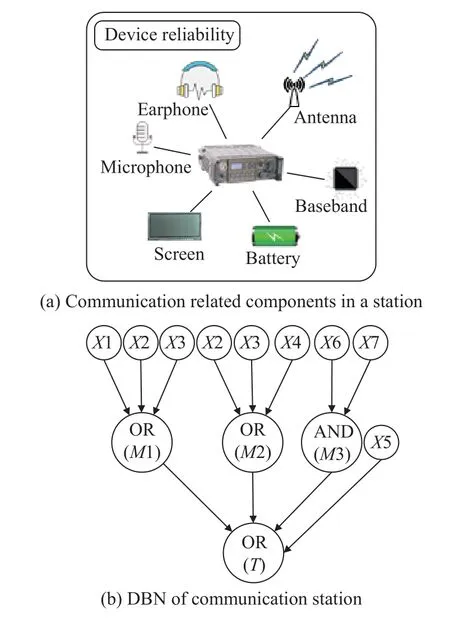
Fig.2 Communication station
As shown in Fig.2(b) and Table 2,nodesX2 (baseband fails) andX3 (antenna fails) are the common failures of nodesM1 (transmitting failure) andM2 (receiving failure).There are two batteries (X6,X7) for the power system (M3),i.e.,M3 is the AND of nodesX6 andX7.
For the OR nodes in this DBN (M1,M2,T),the algorithm to calculate the CPT of OR nodes withiparent nodes can be proposed in Algorithm 1.
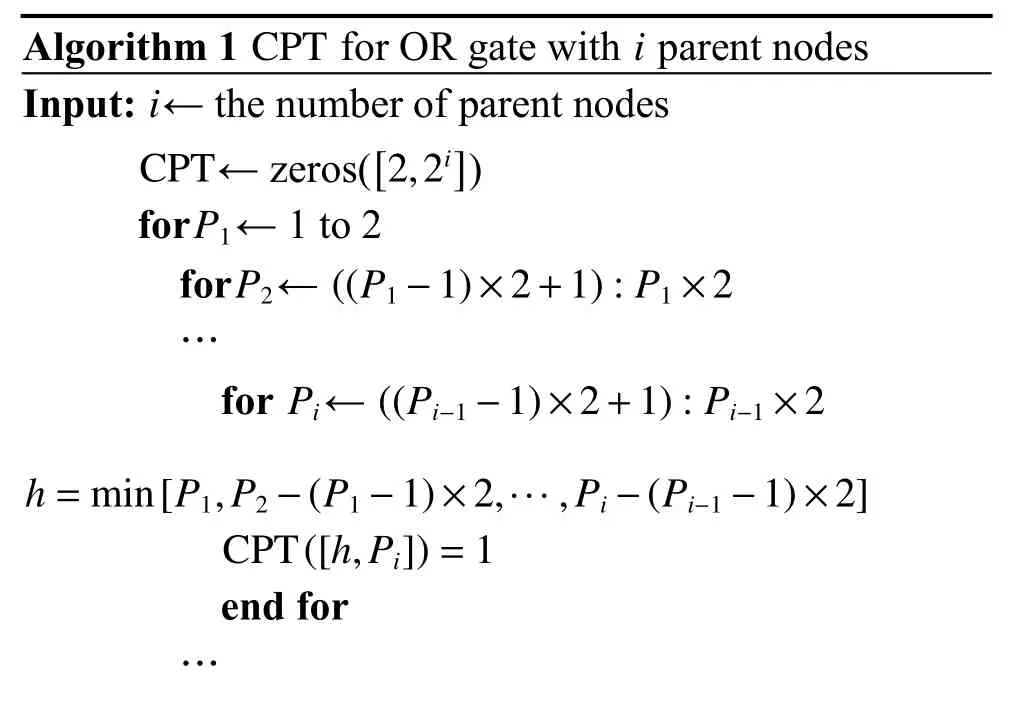
Typically,the reliability of node power systemTcan be obtained as
whereRXi(t) is the reliability of nodeXi(i=1,2,···,5);RM3(t) represents the reliability of the power systemM3.
3.3 Network reliability analysis
Wireless communication network reliability analysis[28-30] needs to consider the reliability of each device and radio propagation.However,these two events follow temporal and non-temporal failure distributions.For this problem,a solution of CTBN formalism with a 2-state CPT is proposed.As shown in Fig.3,a simple wireless communication network is provided,where station I connects to station II via a certain frequency.The DBN of this communication mission is constructed.As shown in Fig.4,nodesAandBrepresent the temporal failure events of corresponding stations,while nodeWrepresents the non-temporal failure event of radio propagation.As one of these three node fails,nodeTfails,i.e.,nodeTis the OR gate of nodesA,B,andW.The MPTs &CPTs are also provided in Fig.4.
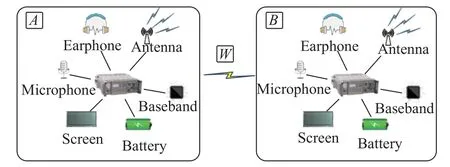
Fig.3 Wireless communication network
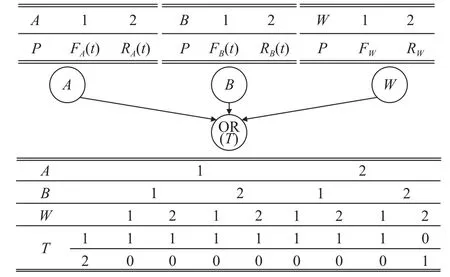
Fig.4 DBN for network in Fig.3
4.Case study
In this section,an application example of a wireless communication network is provided.As shown in Fig.5,this network consists of five nodes (A,B,C,D,andE).The mission of nodeAconnecting nodeDneeds to pass through corresponding communication stations and radio bands.NodeAhas three communication stations (A1,A2,andA3),stationsA1 andA2 are working in parallel while stationA3 is the cold spare station of them.W2 is the cold spare band of bandW1 which these stations work on.NodeBhas two communication stations (B1 andB2),stationB1 is responsible for connecting nodeAwhile stationB2 connects nodeCvia bandW3.NodeChas three stations (C1,C2,andC3) which connect nodesB,D,andErespectively.In nodeD,D2 is cold spare station of stationD1.
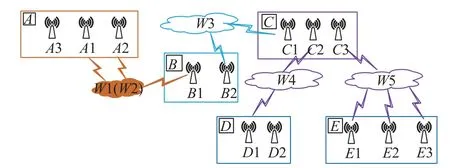
Fig.5 Wireless communication network topology
The DBN of communication between nodesAandDis constructed and shown in Fig.6.
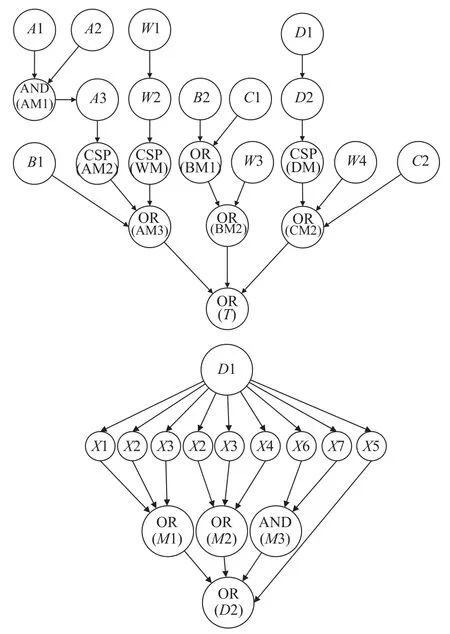
Fig.6 DBN for a wireless communication network in Fig.5
There are three types of logic gates in this DBN including AND,OR,and cold spare (CSP) gates,among them three CSP nodes (A3,W2,D2) are included.Although the three nodes are all CSP nodes but not the same,nodesD2 andA3 represent spare communication stations which are temporal events,according to the DBN in Fig.7,when these stations are in a dormant state,their base events are also in a dormant state.For instance,the DBN of nodesD1 toD2 will change to the structure shown in Fig.6.The CPTs of nodesX1-X7 can be modeled as Table 3.The failure distributions of these nodes all follow the exponential distribution and λiis the hazard rate of nodeXi(i=1,2,···,7) listed in Table 4.fD1(tD1) is the PDF of failure time whiletD1is the failure time of nodeD1.
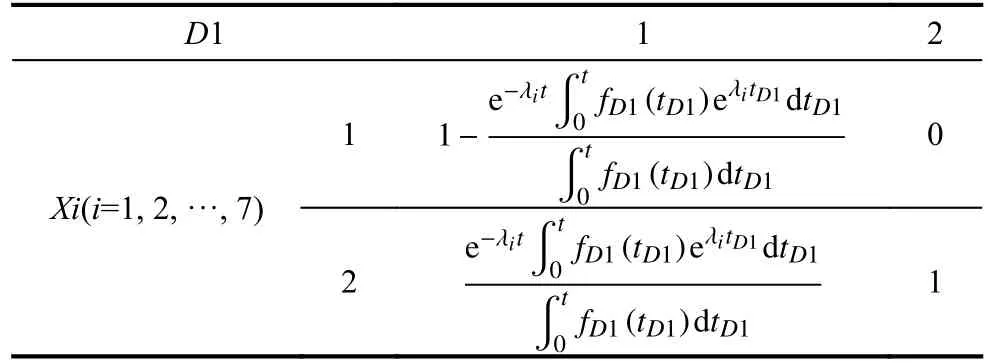
Table 3 CPT of node W1
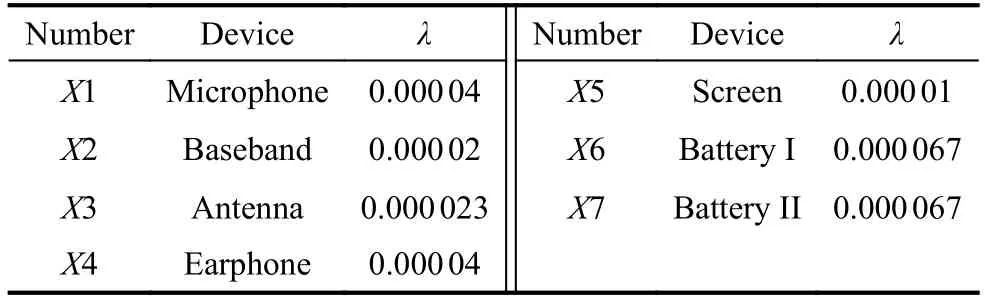
Table 4 Hazard rate of node Xi (i=1,2,···,7)
NodeW2 represents the failure of spare communication frequency,which is a non-temporal event.The CPT of nodeW1 can be calculated through Table 5.The reliability of each communication frequency under the suburban scenario is shown in Fig.7(a) [12].

Table 5 CPT of node W1
As shown in Fig.6,four nodes in this DBN represent different communication missions,i.e.,T(nodeAconnects nodeD),AM3 (nodeAconnects nodeB),BM2(nodeBconnects nodeC),and CM2 (nodeCconnects nodeD).Based on the reliabilities of communication devices and radio propagation,the reliability of communication between each node can be calculated through Algorithm 2,where the states of these four nodes are both equal to 2.
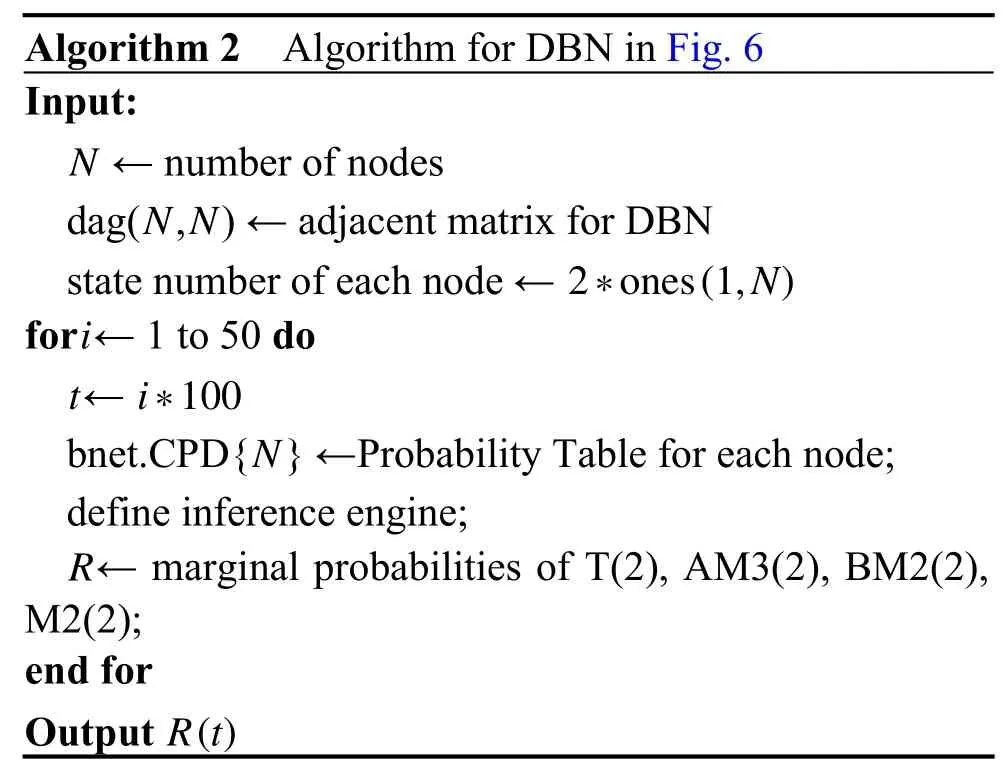
Based on Algorithm 2 and BNT toolbox for Matlab[24],the communication reliability of each node in this network can be calculated as shown in Fig.7(b).This methodology can comprehensively analyze the posterior probability of query nodes,which can be applied to marginal probability evaluation of each communication mission in this network.
5.Conclusions
This paper proposes a generalized CTBN with a 2-state CPT and derives the algorithms for logic gates including AND,OR,and WSP gates in DBN.Subsequently,reliability analysis methodologies for radio propagation,communication devices,and networks are presented.Moreover,a case study of reliability analysis for a wireless communication network is accomplished via this method.Overall,some conclusions are listed as follows.
(i) For the WSP gate,this generalized CTBN with a 2-state CPT can get the same closed-form solution of marginal probability as traditional CTBN.Furthermore,combined with the BNT toolbox for Matlab,reliability of such a wireless communication network with temporal and non-temporal events can be analyzed sufficiently.
(ii) A novel DBN structure for a wireless communication network is proposed.Simultaneously,different communication missions between each node are considered,and the posterior probability for these nodes can be analyzed directly through this DBN.
 Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics2023年5期
Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics2023年5期
- Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics的其它文章
- Attention mechanism based multi-scale feature extraction of bearing fault diagnosis
- LSTM-DPPO based deep reinforcement learning controller for path following optimization of unmanned surface vehicle
- Anti-interference self-alignment algorithm by attitude optimization estimation for SINS on a rocking base
- TOA positioning algorithm of LBL system for underwater target based on PSO
- Scene image recognition with knowledge transfer for drone navigation
- Leader trajectory planning method considering constraints of formation controller
