脑梗死血管介入治疗后远端再闭塞超选动脉溶栓治疗效果评价
顾贵业


【摘要】目的:評价脑梗死血管介入治疗后远端再闭塞超选动脉溶栓治疗效果。方法:选取2019年1月—2022年12月期间,院内收治的脑梗死血管介入治疗后远端再闭塞患者40例进行研究。随机抽取其中20例实施静脉溶栓并命名为参比组,剩余20例患者实施远端再闭塞超选动脉溶栓治疗并命名为应用组。评价溶栓前后患者神经功能损伤、不良事件发生情况、尿激酶剂量和血管再通情况等指标。结果:溶栓前两组神经功能损伤、脑卒中评分比较无差异(P>0.05);溶栓后应用组神经功能损伤得分低于参比组;脑卒中评分高于参比组(P<0.05)。两组脑出血率、穿刺部位血肿、原支架移位率比较,应用组更低(P<0.05)。两组尿激酶用量、血管再通率比较,应用组优于参比组(P<0.05)。两组血脂水平(总胆固醇、甘油三酯、高密度脂蛋白、低密度脂蛋白)比较,应用组优于参比组(P<0.05)。结论:脑梗死血管介入治疗后接受远端再闭塞超选动脉溶栓能够减轻神经功能损伤,预防复发等不良事件发生,改善血脂水平,治疗效果显著。
【关键词】脑梗死;远端再闭塞;超选动脉溶栓;神经功能损伤;血脂水平
Evaluation of superselective intra-arterial thrombolysis for distal re-occlusion of cerebral infarction after interventional therapy
GU Guiye
Department of Neurosurgery, Peoples Hospital, Qiandongnan Miao and Dong Autonomous Prefecture, Guizhou Province, Qiandongnan, Guizhou 556000, China
【Abstract】Objective to evaluate the efficacy of superselective intra-arterial thrombolysis for distal re-occlusion of cerebral infarction after interventional therapy. Methods: from January 2019 to December 2022,40 patients with distal re-occlusion of cerebral infarction after interventional therapy were selected. 20 patients were randomly selected and treated with intravenous thrombolysis and named as the reference group. The remaining 20 patients were treated with distal superselective arterial thrombolysis and named as the application group. The neurologic impairment, adverse events, urokinase dose and vascular recanalization were evaluated before and after thrombolysis. Results: there was no significant difference in the scores of neurological impairment and stroke between the two groups before thrombolytic therapy (P>0.05). The scores of neurological impairment and stroke in the treatment group after thrombolytic therapy were lower than those in the control group, and the scores of stroke were higher than those in the control group(P<0.05). The rate of cerebral hemorrhage, hematoma at puncture site and original stent displacement were lower in the treatment group than those in the control group(P<0.05). The dosage of urokinase and the recanalization rate in the treatment group were better than those in the control group (P<0.05). Compared with the control group, the application group was better in the level of blood lipids (total cholesterol, triglyceride, high-density lipoprotein and Low-density lipoprotein) (P<0.05). Conclusion: superselective intra-arterial thrombolysis with distal re-occlusion after interventional therapy for cerebral infarction can alleviate neurological function injury, prevent recurrence and other adverse events, and improve the level of blood lipids.
【Key Words】Cerebral infarction; Distal re-occlusion; Superselective arterial thrombolysis; Neurological impairment; Blood lipid level
脑梗死是脑血管堵塞,造成脑功能受损,患者临床表现为肢体无力、交流困难,甚至出现昏迷、头晕[1-2]。一旦患者发病需立即入院溶栓治疗,使血管再通,恢复缺血半暗带的供血,减轻神经功能损伤,提高预后效果。研究显示[3-4]:溶栓时间越早,血管再通率越高。临床治疗中,采用超选动脉溶栓有直达病灶的优势,对脑血管、侧支循环有更好的掌握。实践证明,脑梗死患病位置血管药物浓度,动脉溶栓是常规治疗的9倍。故采用动脉溶栓具有剂量少、不良反应小、复发率低的特点。但是,目前关于超选动脉溶栓在脑梗死患者效果的研究较少,缺乏可靠依据,临床应用受限[5-6]。鉴于此,为进一步验证超选动脉溶栓治疗,特选取40例脑梗死血管介入治疗后远端再闭塞患者为研究样本,现报告如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选取2019年1月—2022年12月期间院内收治的脑梗死血管介入治疗患者40例进行研究。随机抽取其中20例实施静脉溶栓并命名为参比组,剩余20例患者实施远端再闭塞超选动脉溶栓治疗并命名为应用组。参比组20例,男12例,女8例,年龄59~79岁,平均年龄(64.50±4.50)岁,病程2~7h,平均病程(2.5±0.3)h,格拉斯哥昏迷得分(GCS):<8分 12例、>8分 8例;应用组20例,男13例,女7例,年龄58~78岁,平均年龄(65.24±4.46)岁,病程1~5h,平均病程(2.3±0.2)h。格拉斯哥昏迷得分(GCS):<8分 11例、>8分 9例。纳入标准:①经影像学(MRI、CT)诊断为脑梗死;②自愿参与或经家属同意入组,已签订同意书;③年龄<80岁者。排除标准:①颅内出血史或出血倾向疾病;②遵医行为差,研究期间失访;③重要脏器功能疾病;④合并慢性病者。40例患者临床资料比较无差异(P>0.05),试验可行。
1.2 方法
参比组:静脉溶栓:阿替普酶(生产企业:Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co. KG;国药准字:S20110051)0.9mg/kg,以静推。
应用组:超选动脉溶栓:创建静脉通道,甘露醇(生产企业:上海百特医疗用品有限公司;国药准字:H20023078)250mL,快速滴入。地塞米松(生产企业:西安国康瑞金制药有限公司;国药准字:H20053754)10mg,静推,经右侧股动脉穿刺,全脑血管造影,明确病灶部位。经透视将多孔微导管与微导丝经介入治疗并获得远端闭塞血管的血栓位置。随后,推出微导丝,经导管治疗把尿激酶(生产企业:青岛康原药业有限公司;国药准字:H20054010)、生理盐水(生产企业:华润双鹤药业股份有限公司;国药准字:H20023300)融合泵入,每5h1次脑血管造影。如果没有实现再通则持续用尿激酶,但总剂量不可超过180萬单位。与此同时监测凝血状态,如果凝血功能异常,即超出标准范围1.5倍则停止注入尿激酶,暂停治疗。
1.3 评价指标
(1)使用神经功能缺损评分量表(National Institute of Health Stroke Scale,NIHSS)和脑卒中评分量表(The European Stroke Scale,ESS)评价溶栓前后两组神经功能缺损情况和脑卒中得分。其中,NIHSS评价标准:共15个条目,每项0~3分,以得分低者为佳。ESS评分标准:百分制,以得分高者为佳。(2)不良事件发生率:评价两组脑出血率、穿刺部位血肿、原支架移位率。(3)评价并记录患者尿激酶用量、血管再通率。(4)血脂水平:评价两组总胆固醇(Total cholesterol,TC)、甘油三酯(Triglyceride,TG)、高密度脂蛋白(High-density lipoprotein,HDL-C)、低密度脂蛋白(low density lipoprotein,LDL-C)变化情况。
1.4 统计学方法
采用SPSS 25.0统计学软件进行数据分析。计数资料采用(%)表示,进行x2检验,计量资料采用(x±s)表示,进行t检验,P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
2 结果
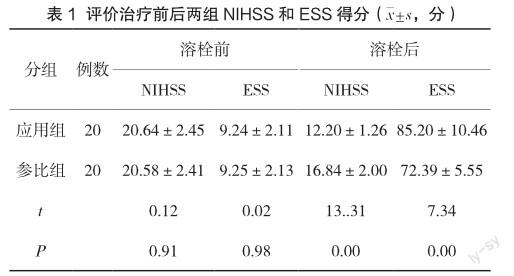
2.1 评价治疗前后两组NIHSS和ESS得分
溶栓前两组神经功能损伤、脑卒中评分比较无差异(P>0.05);溶栓后应用组神经功能损伤(12.20±1.26)得分低于参比组(16.84±2.00);脑卒中评分(85.20±10.46)高于参比组(72.39± 5.55)(P<0.05),见表1。

2.2 评价两组不良事件发生率
应用组脑出血率(0%)、穿刺部位血肿率(5.00%)、原支架移位率(5.00%)低于参比组(15.00%、15.00%、20.00%)(P<0.05),见表2。
2.3 评价两组尿激酶用量、血管再通率
应用组尿激酶用量(94.21±10.46)低于参比组(130.20±20.87);血管再通率(95.00%)高于参比组(80.00%)(P<0.05),见表3。


