Radiomics in the diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
Chun Jiang , Yi-Qi Cai , Jia-JiYang , Can-Yu M, Jia-Xi Chen , Lan Huang ,Ze Xiang , Jian Wu , *
a Department of Clinical Laboratory, The Affiliated Suzhou Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Suzhou Municipal Hospital, Gusu School, Nanjing Medical University, Suzhou 215008, China
b Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310030, China
c Department of Infection Management, The Affiliated Suzhou Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Suzhou Municipal Hospital, Gusu School, Nanjing Medical University, Suzhou 215008, China
Keywords:Hepatocellular carcinoma Radiomics Diagnosis Prognosis Treatment
ABSTRACT
Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most frequent malignant tumors worldwide, with more than 800 000 new cases each year.HCC accounts for 8.2% of all cancer-related deaths in the world, only second to lung cancer [1-3].Early-stage HCC often has no obvious symptoms while middle- and late-stage HCC may lead to epigastric pain, jaundice, ascites, etc., which adds difficulties to the early diagnosis and treatment.There are limited treatment approaches for HCC, and surgery is considered the only curative treatment for patients with early HCC [4].As for emerging immunotherapeutic strategies, few trials have been conducted and the results are not optimistic [5].
Conventional imaging technologies include computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), positron emission tomography (PET), ultrasound (US), and X-ray, etc., which recognize the images of the internal structures of organs and help evaluate the physiological function and pathology change of human organs.These images are essential nowadays for the diagnosis and treatment of HCC.Radiomics refers to extracting image features from the region of interest (ROI) of radiological images with high throughput for automatic analysis, extracting key information through machine learning methods, and obtaining accurate quantitative evaluation of lesions [ 6 , 7 ].Radiomics is noninvasive and reproducible, provides diagnosis and stages of cancer, helps plan the treatment, and predicts the therapeutic outcomes.
In order to improve the accuracy of early diagnosis of HCC and explore new therapeutic strategies, we reviewed the roles of imaging technology and radiomics in the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of HCC.
Radiomics is an important auxiliary tool for HCC diagnosis
In general, the prediction of HCC by radiomics can be divided into three main aspects.The first is to distinguish HCC from other solid lesions and to classify them according to risk factors [8].The second is to predict microvascular invasion (MVI) [9].The third is to predict early recurrence, overall survival, recurrence-free survival and acute liver failure after hepatectomy [10-12].
Radiomics analysis based on multimodal US images is helpful for comprehensive evaluation of HCC, including differential diagnosis and clinical prognosis [13].Pathological indicators and special biomarkers are important for diagnosis of several diseases [14-16], including HCC.Radiomics also plays a role in this process.For example, alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is considered the most useful biomarker for HCC diagnosis [17].AFP in fetal serum reaches a maximum concentration of 300 μg/L between 12 and16 weeks of gestation [18], then drops rapidly.If the cut-off value of AFP is defined to>20 μg/L as positive, the sensitivity ranges from 41% to 65%, and the specificity ranges from 80% to 94% [19].Using the combination of apparent diffusion coefficient and AFP,radiomics features can be extracted and used to diagnose welldifferentiated HCC [20].Ki-67 is a biomarker of tumor proliferation.CT-based radiomics features predict the level of Ki-67 in HCC patients, which may enable noninvasive measurement of cell proliferation [21].Preoperative identification of cytokeratin19 (CK19)status in HCC, a useful marker in differentiating malignant from benign conditions, can also be achieved by radiomics.Radiomics can be used to detect multiple related indicators, which more comprehensively reflect the preoperative situation of patients [22].In addition, glypican 3 (GPC3) expression has been shown to be a key risk factor associated with prognosis in patients with HCC.Combined nomograms and radiomics characteristics may provide an effective means for noninvasive prediction of GPC3 positivity in HCC patients [23].
Radiomics is valuable to predict the state of MVI in patients with HCC.Radiomics based fusion models are a promising tool that produces accurate and reproducible results in predicting MVI status of HCC [24].The preoperative line map integrating clinical radiological risk factors and MRI-based radiomics features also shows good prediction efficacy in predicting MVI in patients with HCC.Compared with clinical radiology, radiomics models that evaluate the radiological characteristics and clinical radiological factors related to MVI are more valuable to predict MVI [25].
Radiomics helps extract imaging features that cannot be detected by the naked eye from high-throughput quantitative images.These radiomics features are used for risk stratification of HCC patients.MRI-based radiomics features can be used as noninvasive predictors of immune oncology features and tumor recurrence of HCC, and thus may help achieve treatment stratification of HCC patients [26].In differentiating low-grade and high-grade HCC, MRI-based radiomics features and clinical models differentiate patients with poorly differentiated HCC from other patients,with the accuracy up to 70%, which is helpful for planning personalized medicine [27].In addition, machine learning based radiomics demonstrates good evaluation performance and is valuable in preoperative differentiation of low-grade and high-grade HCC [28].Through machine learning, the radiomics features of contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT) can be used to predict the pathological grade of HCC [29].After the risk stratification of HCC patients in the above way, corresponding therapeutic strategies can be adopted according to the actual situation of the patients to achieve accurate treatment on an individual basis and facilitate the management of the patient’s condition.
Radiomics helps clinicians improve the diagnostic accuracy and distinguish the types of diseases, and achieve accurate treatment( Fig.1 ).HCC is the most common type of primary liver cancer with poor prognosis.In addition, liver diseases also include focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH), hepatic hemangioma (HH), pyogenic liver abscess (PLA), hepatocellular adenoma (HCA), and hepatic epithelioid angiomyolipoma (HEAML), etc.It is difficult to distinguish these diseases in the diagnosis process.As an auxiliary diagnostic method, radiomics is helpful in this respect.A radiomics model using gadolinium diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid (Gd-DTPA)contrast-enhanced MRI can successfully distinguish HCC from FNH,which reduces the diagnostic difficulty of clinicians and assist clinical decision-making [30].Radiomics is used as an auxiliary modality to differentiate HCC from HH.Furthermore, some CT-based radiomics models can distinguish between necrotic hepatocellular carcinoma (nHCC) and PLA, HCC and HCA [ 31 , 32 ].Using machine learning based on MRI and CT radiomics features, it is possible to distinguish combined hepatocellular cholangiocarcinoma (cHCCCC) from cholangiocarcinoma (CC) and HCC [33].After testing, two radiomics models from CT and MRI perform well in differentiating HEAML, HCC and FNH [ 34 , 35 ].Distinguishing different types of disease is the basic requirement for accurate diagnosis.With the help of imaging technology and radiomics, it is more accurate than the diagnosis based on experience, which also provides evidence for the selection of treatment plans and follow-up.Young radiologists (2 years of experience) obtain almost equivalent accuracy of HCC diagnosis with the help of radiomics compared with those of experienced radiologists (10 years of experience) [36].Application of radiomics in the diagnosis of HCC is shown in Table 1.
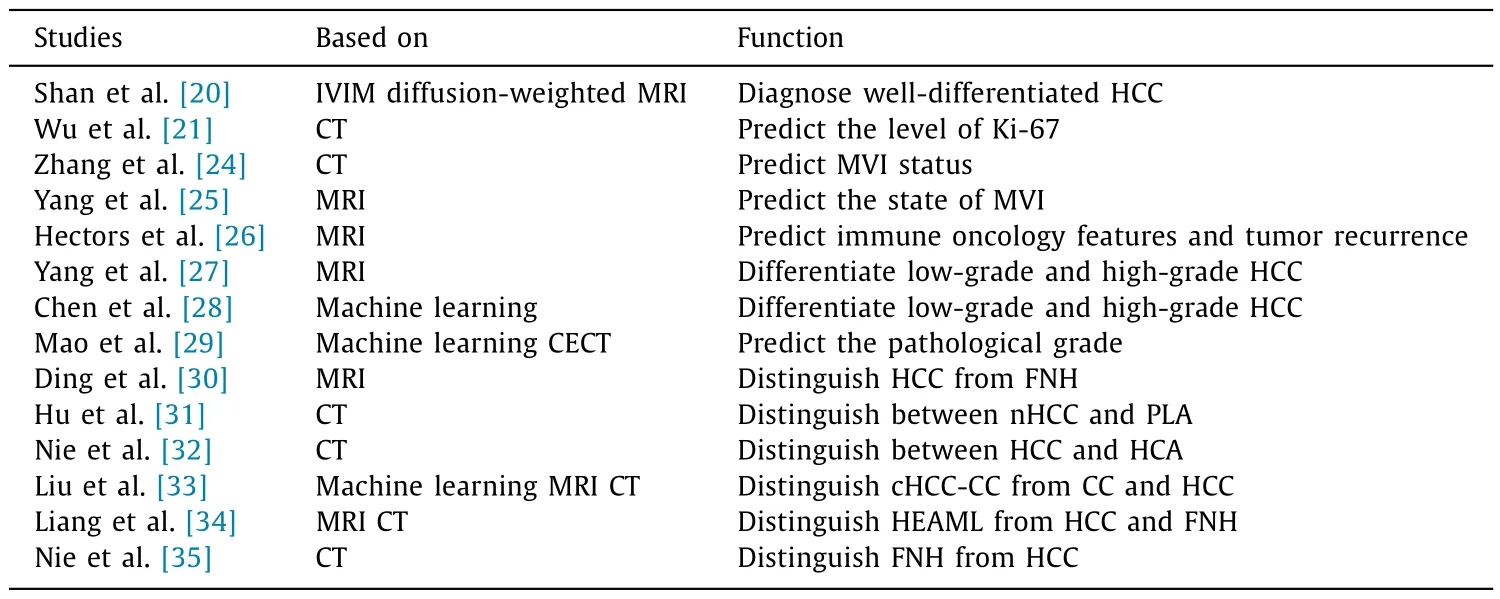
Table 1Application of radiomics in diagnosis of HCC.
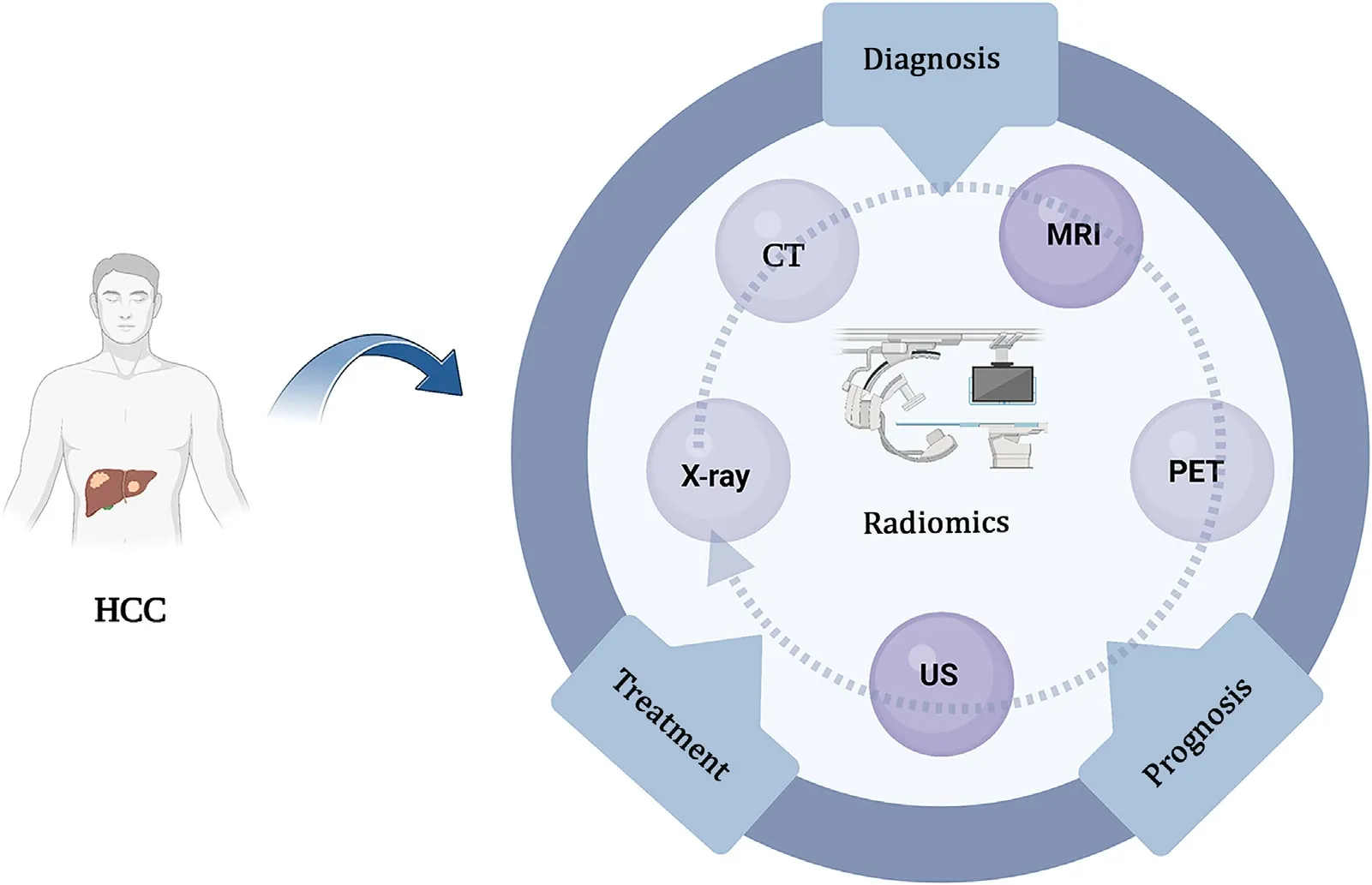
Fig.1.The role of radiomics in the diagnosis and treatment of HCC.HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; CT: computed tomography; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging; PET:positron emission tomography; US: ultrasound.
Radiomics promotes individualized treatment
The current guidelines still recommend surgical resection as the best choice for HCC patients at early-stage.Radiomics is helpful for clinicians to accurately understand the tumor status before the operation to avoid adverse events during and after operation.For example, preoperative assessment of MVI status in patients with HCC helps select a more reasonable surgical procedure.Radiomics has become a new method that helps identify imaging information related to tumor pathophysiology, and its clinical utility is being gradually accepted [37].Radiomics based on medical image data has broad application prospects in preoperative prediction and provides quantifiable image features [38].A radiomics scoring model based on US has been proven to be able to predict the preoperative MVI of HCC.Compared with clinical nomograms,radiomics nomograms have superior predictive performance [10].The radiomics nomogram based on contrast-enhanced ultrasound(CEUS) can be used to assess the MVI of patients with HCC preoperatively.Compared with the non-radiomics preoperative clinical prediction model, radiomics has a higher score in terms of calibration, differentiation and clinical utility [39].Combined with machine learning model, preoperative prediction of MVI in HCC can also be obtained by biphasic enhanced CT, CECT and radiomics [ 40 , 41 ].In addition, CT- and MRI-based radiomics have a considerable predictive performance for MVI of HCC.The proposal of a variety of radiomics models implies that prospective, largescale and multi-center studies can be conducted in the future, to improve the diagnostic ability of MVI [42].
Radiomics help clinicians predict the postoperative outcome of patients with HCC and adjust the surgical plan, and therefore, put the precision medicine into practice.It is well-known that the postoperative recurrence after hepatectomy is still high.In preoperative evaluation, the combination of multiple predictors, radiomics nomography, and machine learning algorithm effectively improve the prediction accuracy of HCC recurrence, and help evaluate the surgical plan and make personalized adjustment [ 43 , 44 ].
Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) is the first choice for the treatment of advanced HCC.However, due to the high heterogeneity of HCC, some patients have the possibility of extrahepatic metastasis or vascular invasion after treatment.Therefore, prediction of patient response after TACE treatment plays an important role in the selection of treatment regimen [45].Some researchers have demonstrated that a compound model generated by non-contrast CT radiomics and clinical features directly predict TACE response and overall survival [46].Similarly,CT-based radiomics nomograms can be used to predict the response before TACE treatment.These may provide better guidance for further TACE treatment decisions [47].In addition to CT, contrast-enhanced MRI (CE-MRI) radiomics analysis is another noninvasive tool to predict the response of HCC patients to TACE treatment [48].The prediction of the postoperative response of patients by radiomics helps measure the suitability of the treatment plan.If postoperative side effect is predictable, treatment strategy can be adjusted in time to achieve the best therapeutic outcome.
In addition to TACE therapy, radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is also one of the important treatment methods for HCC.Radiomics models and nomograms achieve accurate preoperative prediction of progression for RFA, which helps optimize the treatment options for patients with early HCC [49]( Fig.2 ).
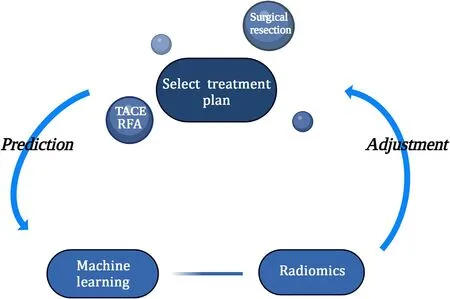
Fig.2.Radiomics promotes personalized therapy.TACE: transcatheter arterial chemoembolization; RFA: radiofrequency ablation.
Radiomics improves the accuracy of prognostic prediction
MVI is one of the most important factors for HCC recurrence and poor prognosis.Accurate preoperative identification of MVI is very significant for predicting the prognosis of patients with HCC [50].MVI has a momentous impact on the prognosis of HCC.The most effective treatment for HCC is surgical resection, but recurrence rate is high, partially because of the presence of MVI [51].It has been suggested that the use of random forest to predict MVI by nomogram before operation has achieved considerable accuracy in MVI stratification [52].The application of radiomics in this process is explored.The radiomics features extracted from medical images can be used to predict MVI [53].For example, the limit gradient lifting (XGBoost) and the deep learning prediction model based on CT images may be used to predict MVI status before surgery [54].In addition to CT, radiomics analysis of MRI is also used to predict MVI in patients with HCC.By comparing the different parameter settings of radiomics, one study points out that the 15 minutes model of hepatobiliary phase has the best differential diagnosis ability [55].
The prediction of macrovascular invasion also has prognostic significance, and quantitative radiomics analysis based on CT predicts the development of macrovascular invasion in HCC patients with high accuracy [56].
Radiomics nomogram is a noninvasive preoperative biomarker that can be used to predict early recurrence of HCC [57].Wen et al.showed that patients with HCC (3 cm) still have poor prognosis.For patients with small size HCC who underwent surgical resection or RFA, radiomics nomogram can be used for preoperative prediction of early recurrence [58].For the prediction of recurrencerisk, a radiomics based model gives three risk levels, with different characteristics of high, medium and low recurrence risk and the number of recurrent tumors, which is helpful to predict the early recurrence of HCC [59].CT-based radiomics features can be conveniently used to predict early recurrence in patients with HCC [60].Specifically, the radiomics features extracted from CT images may be potential imaging biomarkers for HCC invasion, which can predict recurrence after liver transplantation [61].In addition, the dynamic CEUS radiomics model and the radiomics method combining multiphase CT images with deep learning have certain potential in predicting early recurrence of HCC [ 62 , 63 ].
In addition to the prediction of recurrence, survival prediction is also one of the important applications for radiomics.The new type of deep radiological analysis can be used to predict the overall survival of HCC patients receiving stereotactic body radiotherapy [64].Also, an MRI-based radiomics model is an effective method to predict the 5-year survival of patients with HCC.A more standard assessment of the prognosis will help clinicians select patients for additional treatment [65].In contrast, the radiomics nomogram integrating radiomics features provides more accurate overall survival estimation than the clinicopathological nomogram for HCC patients after hepatectomy [66].
The radiomics nomogram integrating clinicopathological and radiomics features can be used to predict the early recurrence of HCC patients after curative ablation, which is crucial for the following managements [67].The combination of radiomics characteristics based on MRI and clinical factors predicts the recurrence-free survival of HCC patients who received surgical resection [68].In addition, predicting the possibility of post-hepatectomy liver failure in patients with HCC before hepatectomy is of great significance.A radiomics clinical model based on enhanced MRI has a predictive value of post-hepatectomy liver failure and its severity preoperatively [69], which is helpful for planning hepatectomy [70].
Prognosis prediction with risk assessment and stratification of HCC patients before operation are helpful for patient management and precision medicine.Radiomics analysis based on MRI has the potential to predict early recurrence of HCC patients after hepatectomy, which can increase support for individualized treatment plans [71].Generally, radiomics improves the accuracy of prognostic prediction ( Table 2 ).
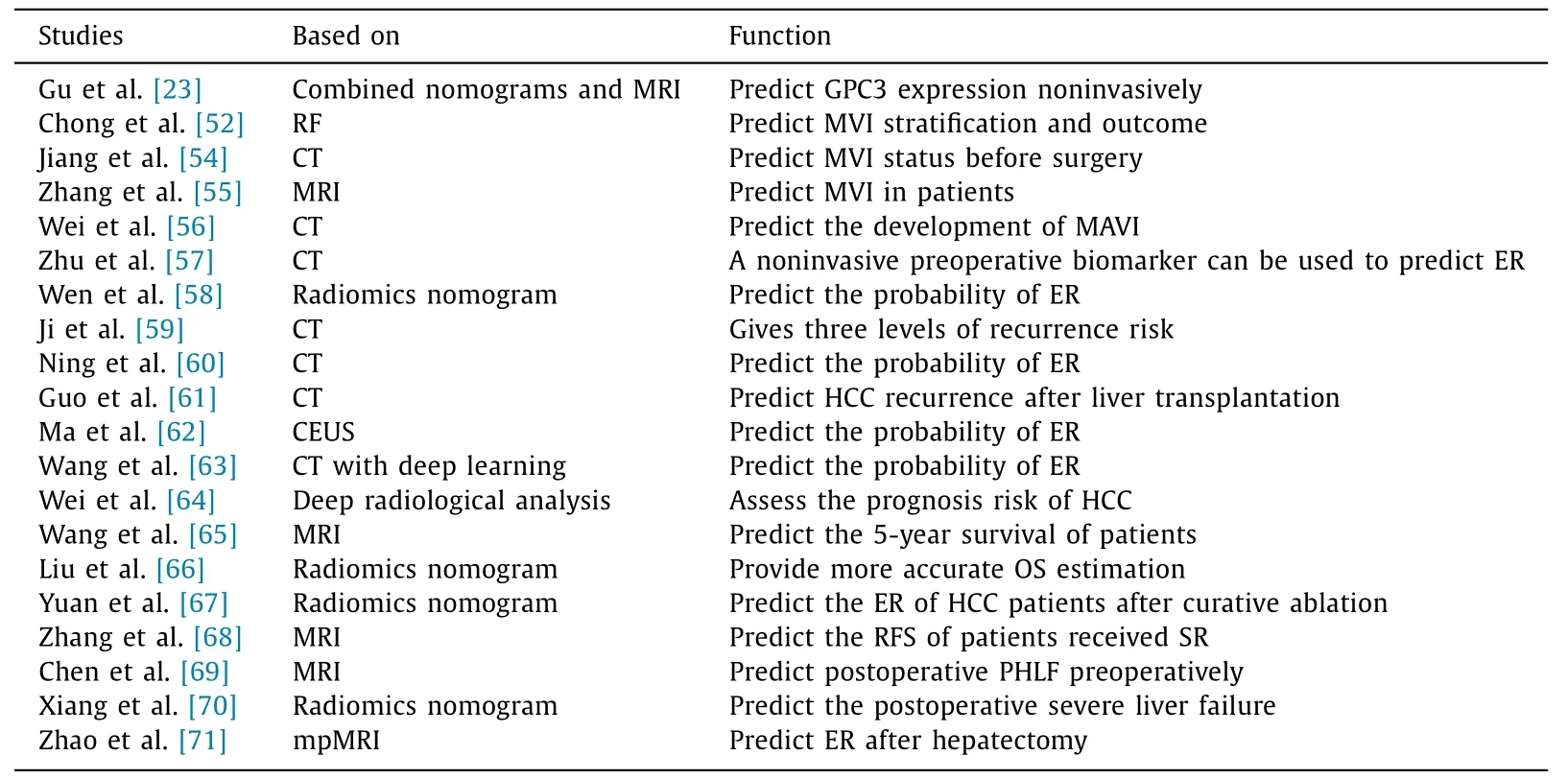
Table 2Application of radiomics in prognosis of HCC.
Summary and prospect
With increasing studies on the application of radiomics in liver cancer, the good prediction performance of radiomics has been gradually explored [72].Of course, compared with traditional methods, radiomics also has some disadvantages.The diagnostic accuracy of radiomics needs to be improved.For example, CT-based radiomics has poor reproducibility among different centers, and image heterogeneity (such as slice thickness) may be an important factor [73].Radiomics can be used for detection of MVI preoperatively, but different dimensionality reduction modeling methods will affect the diagnostic performance of the final model [74].The MRI-based radiomics function has repeatability when using the same MRI system, but it has poor repeatability when using different MRI platforms.Therefore, the data must be interpreted carefully when conducting multi-platform radiomics studies [75].
Radiomics is a method for mining a large number of quantitative imaging features and developing prediction models [76].Radiomics based on various imaging technologies can be widely used in the diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of HCC, specifically including the prognostic prediction of HCC, distinguishing different disease types and grading according to disease risk, preoperative diagnosis, treatment response prediction, postoperative recurrence prediction, and many other aspects.Radiomics plays an important role from early detection to HCC management and prediction of treatment outcomes.
Acknowledgements
None.
CRediT authorship contribution statement
Chun Jiang :Conceptualization, Writing - original draft.Yi-Qi Cai :Conceptualization, Writing - original draft.Jia-Jia Yang :Data curation, Writing - original draft.Can-Yu Ma :Data curation.Jia-Xi Chen :Formal analysis.Lan Huang :Formal analysis.Ze Xiang :Conceptualization, Writing - review & editing.Jian Wu :Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing - review & editing.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China ( 82272396 ), and Suzhou Medical and Health Science and Technology Innovation Project ( SKY2022057 ).
Ethical approval
Not needed.
Competing interest
No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
 Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International2023年4期
Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International2023年4期
- Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International的其它文章
- Novel re-intervention device for occluded multiple uncovered self-expandable metal stent (with video)
- Hepatopancreatoduodenectomy for the treatment of extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma ✩
- Microbiological cultures and antimicrobial prophylaxis in patients undergoing total pancreatectomy with islet cell autotransplantation
- Risk factors for posttransplant diabetes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
- The role of targeting protein for Xklp2 in tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Isolated IgG4-associated autoimmune hepatitis or the first manifestation of IgG4-related disease?
