Structural design of the fluted shaped charge liner using multi-section optimization method
Shengjie Sun ,Jinwei Jing ,Shuyou Wng ,* ,Jinbing Men ,b ,Mei Li
a State Key Laboratory of Explosion Science and Technology, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, PR China
b Tangshan Research Institute, Beijing Institute of Technology, Tangshan 063000, Hebei, PR China
Keywords:Fluted liner Spin-compensation SPH Structural optimization
ABSTRACT Spin effect of the small diameter shaped charge results in the centrifugal stress during the jet stretching process.Consequently,the jet scatters,which deceases the jet penetration capability.In the present study,a multi-section method was proposed to design the spin-compensation liner.The spincompensation rate (SCR) of the liner was defined as the specific angular velocity that a fluted liner can offset.Based on the plain stress theory,SPH numerical method was applied to study the converging process of the 2D fluted structure.The spin-compensation mechanism of the fluted structure was illustrated.Then,nine cross sections were chosen along the liner axis equidistantly.On each of the section,a 2D fluted structure was designed to offset a given initial angular velocity.After,the optimized fluted structures were integrated into a 3D fluted liner.Jet appearances of the normal liner and the fluted liners under different initial angular velocities were compared,which verifies the practicality of the multi-sectional method.The multi-section optimization method provides a new efficient method of designing the shaped charge liner for a specific usage.
1.Introduction
Shaped charge liner is an effective device to defeat heavy armor or fortifications [1].Usually,shaped charge liner with small diameter(like Φ=30 mm)are often spin-stabilized to prevent tumbling during the flight to the target.However,spinning a shaped charge results in the rotation of the liner material,which decreases the penetrating capability of the formed jet[2].Therefore,several types of spin-compensation liner structures,including fluted liners [3],shear-formed liners [4] and wide-angle liners [5],have been employed to offset the spin effect [6].Shear forming introduces crystalline anisotropy of the metallic grains and residual stresses to compensate spin [7,8].Wide-angle liners produce large diameter projectiles with relatively slow moving speed which are not sensitive to spin [9].Fluted liner is able to compensate higher rate of spin than the shear-formed liners and the wide-angle liners [10]with the help of a‘thick-thin’structure[11,12].Experimental study showed the validity of the fluted liner in reducing the influence of the spin on jet forming performance [13].The fluted liner has a slope premade at both inner and outer circumference of the liner,which induces tangential impulse to offset the spin.Theoretical and experimental studies have been made to explore the mechanism of the spin-compensation phenomenon[14-16].Stress contour of the spun jet was also studied[17].Since nowadays the shaped charges with large charge diameter are often equipped with good aerodynamic shape to maintain a stable flight with rocket being used as the propelling source,so the initial spin is less needed to keep stable while flying to the target.As for the shaped charges with small charge diameter,it is less economic to equip the charge with rocket propelling system,since the shaped charges with small diameter are often used with large demand,and the initial spin is still needed to keep stable during the flight.Therefore,the present study focuses on optimizing the spin-compensation structure of the liner with small charge diameter.
Among the effective spin-compensation structure,the two-side fluted structure displays outstanding spin-compensation ability[13].However,the two-side fluted structure also has some drawbacks.Since the liner surface interacting with the charge (outer surface) is also equipped with the fluted structure,the charge is often melted and casted rather than pressed into the designed shape.This makes the density of the casted charge lower than the pressed charge,so that the energy released by the charge is limited,considering that the detonation speed and the pressure of the explosive production is related to the charge density[18].The meltcast technique also induces cracks inside the charge,especially at the un-smoothed surface like the fluted surface,due to the heating and cooling effect.Consequently,when the charge undertakes compression loading during the propelling process in a barrel,stress concentrates at the crack and “hot spot” appears inside the explosive,which initiates the charge detonation.So that the application safety of the charge decreases.Additionally,the crack also leads to the fluctuation of detonation pressure when the detonation wave propagates inside the charge.Therefore,the jet forming process will be affected and becomes no longer consistent.Therefore,an inner fluted structure with a smoothed outer surface was chosen in the present work to design the spin-compensation liner.
Usually,2D axisymmetric algorithm is an efficient method to design the liner structure [19,20].However,the fluted liner structure is not axisymmetric.Thus,a new method is required in the present study.Although 3D full scale [21,22] or half-scale [23]model has already been applied to analyze the asymmetric shaped charge problems,the designing process is quite time-consuming and requires large quantity of computing resources.Therefore,the 3D full scale or half-scale model is not the best choice while designing the fluted liner.Inspired by the additive manufacturing technology[24],a multi-section method was proposed to optimize the fluted liner structure.Based on the plain stress theory,the fluted structure on each of the section was designed to offset a given initial angular velocity.Then all the sections were integrated into a 3D fluted liner structure.This method improves the efficiency of the fluted liner designing work.
Among the existing simulation methods,the Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics(SPH)method was chosen to implement the multisection designing work.Smoothed particle hydrodynamics(SPH)is a mesh-free numerical method to simulate high speed impact and explosive loading phenomenon [25].Previous studies have shown that the SPH method is suitable in analyzing the collapsing process of the shaped charge liners [26,27].During the SPH simulation process,the computational domain is discretized with a set of particles.Field variables and the corresponding derivatives are approximated as weighted summations over surrounding particles within the support domain of the smoothing function [25].Previous study has shown that SPH is also an attractive method in designing a shaped charge liner [28].
Based on the reviewed references,we proposed a multi-section method to study the spin-compensation ability of the fluted liner with a “thick-thin” inner structure and a smoothed outer surface,which is a novel idea of applying SPH method to study the fluted liner.Firstly,the spin-compensation mechanism of the 2D fluted structure was studied.Initial angular velocity was given to the fluted structure,which imitates the liner spin effect.The spincompensation rate (SCR) was defined as the specific angular velocity that a fluted structure can offset.After the spincompensation process,the angular velocity of the whole fluted structure decreases to zero.Based on plain stress theory,the converging process of the fluted structure was studied,which illustrates the spin-compensation mechanism.The relationship between the SCR and the structural parameters was revealed.Then,nine cross sections were chosen along the charge axis equidistantly.The fluted structures on each of the surfaces were optimized to offset a given angular velocity.Then the fluted structures were integrated into a 3D fluted liner before discretizing into SPH model.Jet performances of normal liner and the designed fluted liners were compared under different initial angular velocities.The results indicate the practicality of the multi-sectional method,which provides a new idea in designing the shaped charge liner for a specific usage.
2.Multi-section optimization method
The multi-section optimization method proposed in the present study is illustrated in Fig.1.Spin-compensation structure on each cross section along the charge axis was designed to offset a given angular velocity.Then the sectional structures were integrated into a 3D spin-compensation liner.

Fig.1.Schematic diagram of multi-section optimization method.
2.1.2D sectional fluted structure
Firstly,a fluted inner structure with a smoothed outline was designed as shown in Fig.2.The geometric parameters include deflecting angle (θ),tip offset radius (Rt),inner curvature radius(Rc),and period angle (α).All the parameters were normalized referring to the charge diameter(CD).In order to control the variable quantity,the radius of the fluted structure outline and the charge outline were fixed as 0.200 CD and 0.500 CD.The curvature radius on both sides of the fluted tip were equal.Rliis the original inner radius of the un-fluted structure.In order to control the variable quantity,Rliwas also set as constant(0.167 CD)during the simulation process.
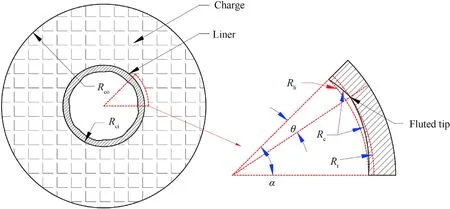
Fig.2.Geometric diagram of the sectional liner with a fluted inner structure and a smoothed outline.

Fig.3.2D sectional SPH models for result convergence analysis with the distance between particles of (a) 6e-3 CD,(b) 4.5e-3 CD,(c) 3e-3 CD and (d) 1.5e-3 CD.
2.2.SPH numerical method
The explicit and nonlinear LS-DYNA program is commonly used to simulate explosion and dynamic impact [29],which was employed in the present section.Specifically,the smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) processor was adopted.In the SPH method,the continuum volume is discretized by a number of particles[25].Each of the particle carries material information like velocity,mass,temperature,etc.The external forces and internal interactions between particles are calculated by the governing equations using a specified smoothing kernel function.A continuous functionf(x)can be discretized as follows:
whereWijis the smoothed function of a pair of particlesiandj,ρ and m are density and mass respectively.A variable smoothing length was used in the SPH processor.Time integration type for the smoothing length follows Eq.(3) [29].
whereh(t) is the smoothing length at momentt,Drepresents the dimension of the analysis,vis the variable being studied.The parameters of the algorithms referred to the previous work[27].
2.3.Material properties
The fluted liner material was oxygen-free high-conductivity copper (OFHC).In 1985,Gordon Johnson and William Cook proposed the famous Johnson-Cook strength model to quantify the effect of strain rate and temperature on the material behavior[30],which is thereby adopted in the present simulation work.The stress-strain relation of Johnson-Cook model is illustrated in Eq.(4).
whereA,B,n,Candmare material constants determined by experiments.σ is von Mises tensile flow stress at certain equivalent plastic strain εeq.is the dimensionless plastic strain rate at a reference strain rate of=1/s,T*=(T-Tr)/(Tm-Tr)is the homologous temperature,Tis the current material temperature,andTmis the melting temperature of the material.When material undertake dynamic loading,failure criterion is applied to determine the failure strain of the material.In Gordon Johnson and William Cook’s study,the material failure behavior was described by Eq.(5).
whereD1…D5are material constants fitted by experiments.Eq.(5)reveals the influence of stress triaxiality,strain rate and temperature on the failure strain of the material,which is adaptable in simulating jet forming performance.Therefore,Johnson-Cook failure criterion is adopted in the present study and the material constants refer to Johnson and Cook’s study [30].
The charge was made of Composition B.Jones-Wilkins-Lee(JWL) equation of state was used to describe the properties of the explosive products [31].The relationship of JWL function is expressed as Eq.(6).
wherePbis the blast pressure (GPa),Eis the internal energy per initial volume,υ is the initial relative volume.ω,C1,C2,r1andr2are material constants.The parameters of OFHC and composition B are cited from the material data base[32],which are listed in Tables 1 and 2 respectively.
2.4.Result convergence analysis
Based on plain stress theory,the 2D sectional fluted structure was discretized into SPH model.Result convergence was analyzed before simulation study.Take α=45°,θ=5.625°,Rc=0.167 CD,Rt=0.180 CD as an example.The distance between particles were set as 6.0e-3 CD,4.5e-3 CD,3.0e-3 CD and 1.5e-3 CD respectively,as shown in Fig.3.Python scripts were written to evenly initiate 720 detonation points at the outer circumference of the charge.All of the detonation points were ignited simultaneously.
Fig.4 shows the angular velocity histories of the fluted structure with various distance between particles.Angular velocity was initialized representing the shaped charge rotation at explosion.The right-hand rule was used to determine the sign of the angular velocity.Positive sign represents clockwise direction,vice versa.

Table 1 Parameters of OFHC in the Johnson-Cook model.
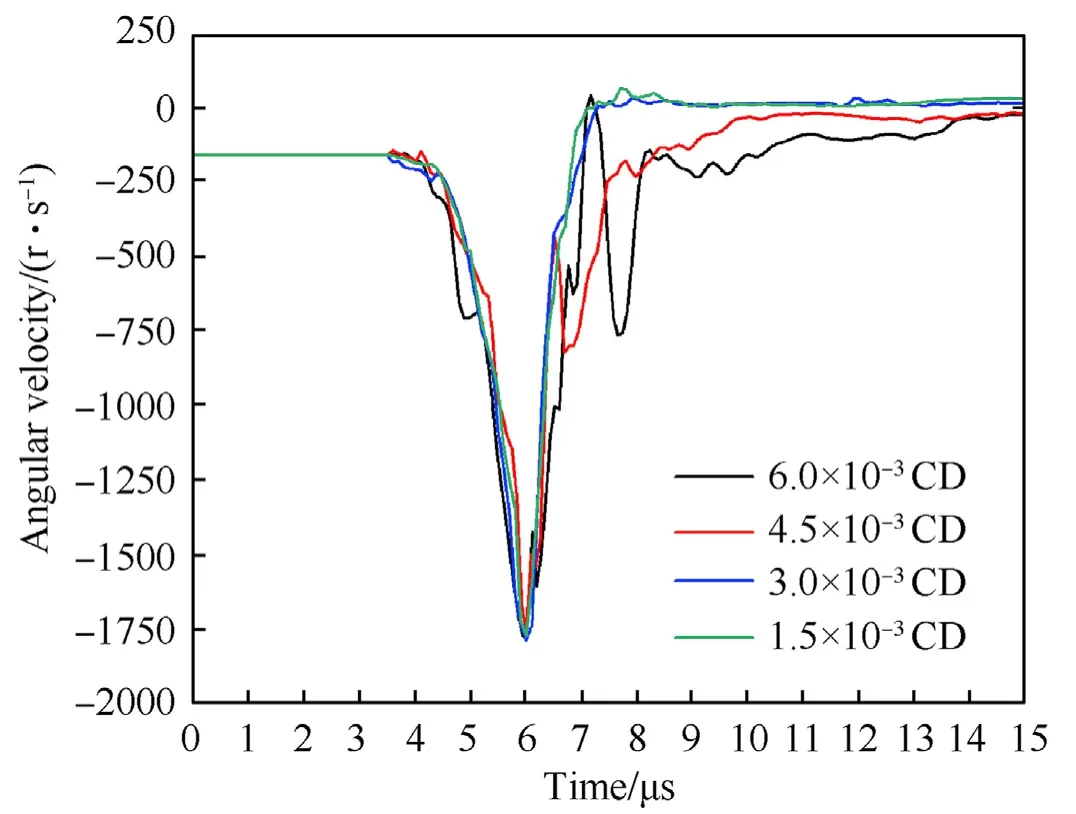
Fig.4.Angular velocity histories of the fluted structure with various distance between particles.

Fig.5.Schematic diagram of the deformation process of the sectional fluted structure.

Table 2 Parameters of composition B in the JWL model.
After around 3 μs,explosive product interacts with the fluted structure and the radius decreases.LetLi0be the initial angular momentum of each liner particle,which can be expressed as follows:
wheremiis the mass of particlei,riis the distance between particleiand the liner center,ωi0is the initial angular velocity of particlei.Considering the conservation of angular momentum,angular velocity of particleiat momentt,ωitcan be derived.
Therefore,the increase of angular velocity between 3 and 6 μs is caused by the decrease of structure radius.After 6 μs,the effect of spin-compensation prevails due to the collapsing of the liner material,which induces net tangential impulse to offset the spin.Consequently,the angular velocity drops to 0 r/s after 7.5 μs? The black line and the red line in Fig.4 indicate that large distance between particles results in result fluctuation.The blue line and the green line show the result converges as the distance between particles decreases.Thus,the distance between particles was taken as 3.0e-3 CD to balance the accuracy and the economy of calculation.
2.5.Spin-compensation effect of the fluted structure
The spin-compensation effect is caused by the circumferential interaction between the explosive product and the liner,which is called the ‘thick-thin’ effect [11].The thickness of the designed fluted liner is not even.Thus,the liner part with minimal thickness gains the maximum radial converging velocity during the collapsing process of the liner.
Figs.5(a)-5(c) shows the converging process of the sectional fluted structure.The periodically repeating structures are separated with black solid lines to capture the details of the deformation process of the fluted liners noted as process (a)-(c).The deformation process of one individual repeated part was analyzed and illustrated in Fig.6.
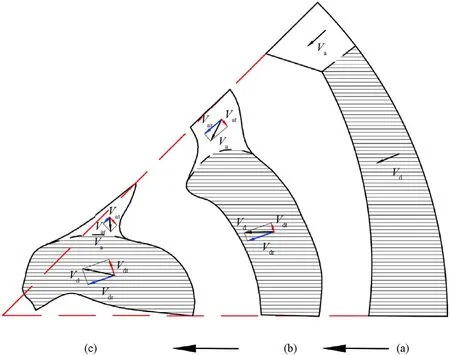
Fig.6.Deformation process of one individual repeating part of the fluted liner.

Fig.7.Relationship between SCR of the fluted structure and Rt with different θ and Rc: (a) Rc=0.133 CD;(b) Rc=0.167 CD;(c) Rc=0.200 CD;(d) Rc=0.233 CD.
By tracking the dividing line (black dashed) of the dominant region (shadowed) and the affiliated region (non-shadowed),the material flow trend was captured and recorded.VdandVarepresent the converging velocity of the dominant part and the affiliated part respectively.Subscripttandrrepresent the tangential component and radial component.In situation (a) where the detonation production starts to interact with the liner,VaandVdbegin to increase directing to the center point of the liner.Then the tangential velocity component appears both at the dominant part and the affiliated part,due to the “thick-thin” effect [11,12],as seen in situation (b).The tangential component of the dominant region makes contribution to offsetting the spin,while the tangential component of the affiliated region has the opposite influence.As the fluted liner continues to converge,Vdtoverwhelms Vatdue to the difference of the region area,as shown in situation (c).Consequently,the spin influence can be reduced.The SCR of the sectional fluted structure is related to the geometric parameters mentioned in subsection 2.1,which is thereby studied and discussed in the following section.
2.6.Influence of the fluted geometry on SCR
In this section,α is set as 45°to control the variable quantity.Figs.7(a)-7(d) shows the relationship between SCR of the fluted structure and Rtwith different θ and Rc.θ was taken as 5.625°,11.25°and 16.875°.Rcwas taken as 0.133 CD,0.167 CD,0.200 CD and 0.233 CD.In the case of Rtlarger than 0.187 CD,the fluted structure scatters at the thinnest part during the converging process.Therefore,the result with Rtlarger than 0.187 CD is not recorded.
One common ground that can be observed in four of the pictures is that,when θ equals to 5.625°,the trend of SCR varies with Rtis relatively smooth.Additionally,when θ equals to 16.875°,the maximum value of SCR is smaller than the case of θ equals to 5.625°and 11.25°.Notably,when Rcequals to 0.167 CD and 0.200 CD with θ of 5.625°,the maximum value of SCR is higher than the case of Rcequals to 0.133 CD and 0.233 CD,which means a wider adjustable range of SCR.Additionally,when Rcequals to 0.167 CD,less fluctuation is observed among the results.
Fig.8 shows the converging process of the fluted structure with different θ.One of the repeating parts in each case was picked out and taken into comparison.The dividing lines of the dominant part and the affiliated part,as explained in subsection 2.5,were tracked,so that the forming performances of each repeating part can be illustrated.As observed from Fig.8,with the increase of θ,the dominant region shrinks,together with the expansion of the affiliated region.This means that the net tangential impulse tocompensate spin decreases.

Fig.8.Converging process of the fluted liner with different θ and the forming performances of each repeating part.
An exponent trend can be observed between liner SCR andRcwith differentRcand θ,which is described by Eq.(9).The values of coefficient a,b and c of each case were fitted and listed in Table 3.

Table 3 Coefficient values of the exponent Eq.(8).
2.7.Influence of period angle on SCR
Based on the results of subsection 2.4.1,RtandRcare taken as 0.187 CD and 0.167 CD respectively to study the influence of α on SCR.Fig.8 shows the sectional fluted structures with period angle α equals to 90°,60°,45°,36°,30°,25.71°and 22.5°.The deflecting angle θ of each model shown in Fig.9 was calculated by keeping the ratio of θ/α equals to 0.125.Therefore,the deflecting angles of each model were 11.25°,7.5°,5.625°,4.5°,3.75°,3.21°and 2.8125°,respectively.
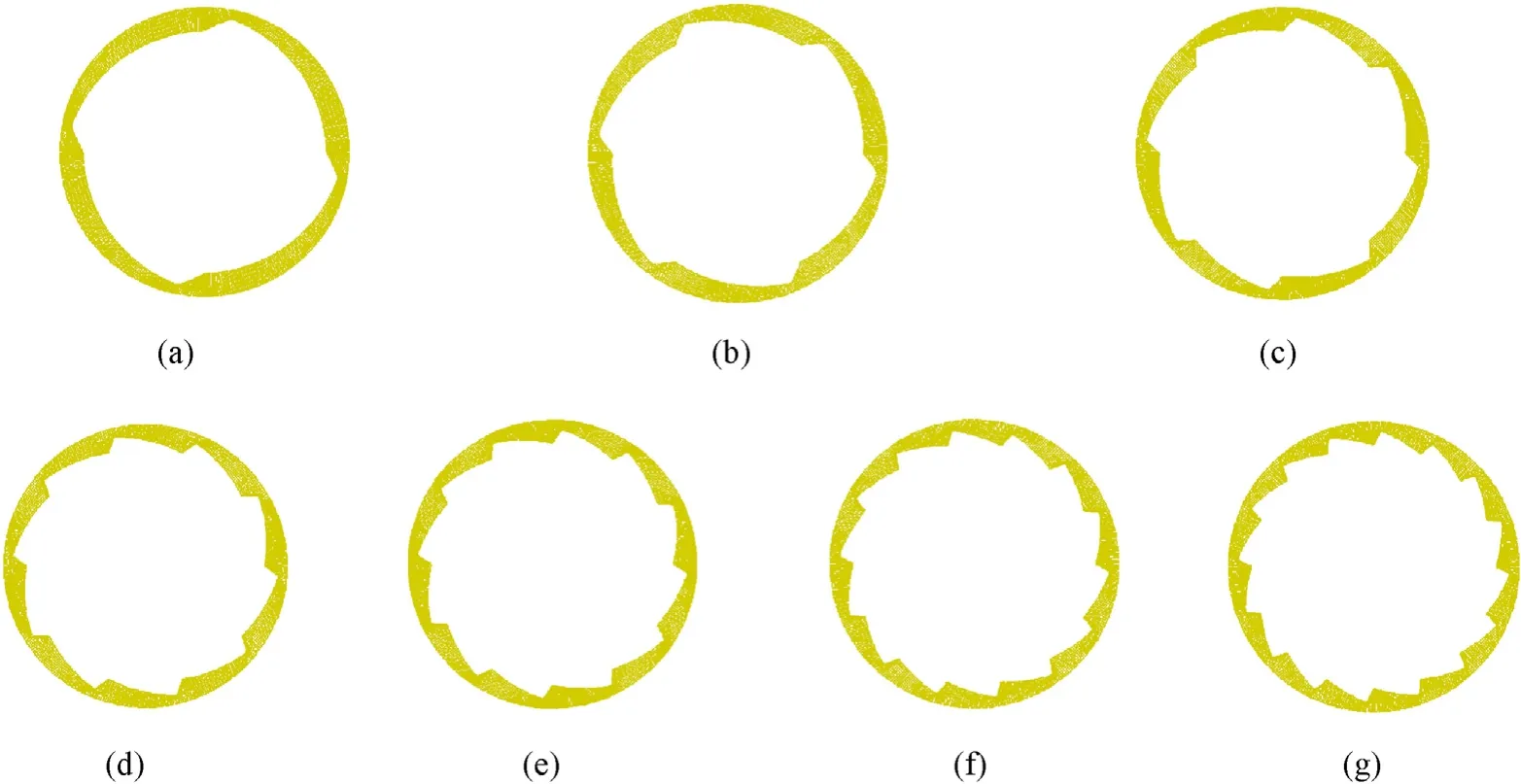
Fig.9.Sectional fluted structures with α equals to (a) 90°,(b) 60°,(c) 45°,(d) 36°,(e) 30°,(f) 25.71° and (g) 22.5°.
Fig.10 shows the SCR of the sectional fluted structures in Fig.9.Obviously,fluted structure with α equals to 90°has the maximum SCR.With the decrease of α,the arc interval between two adjacent fluted tips decreases.The longer arc interval leads to smaller affiliated region of the whole structure during the liner converging process,which results in larger net tangential impulse to offset spin,as illustrated in Fig.6.With a smaller arc interval,the affiliated region of the whole structure becomes lager.Therefore,less net tangential impulse is induced and the SCR decreases.

Fig.10.SCR of the sectional fluted structure with α equals to 90°,60°,36°,30°,25.71°and 22.5° respectively.
However,SCR is not the only factor that taken into consideration while designing a fluted liner.Liners with α equals to 90°,60°and 45°were divided into 4,6 and 8 repeating parts.The converging process of the liners are illustrated in Fig.11.
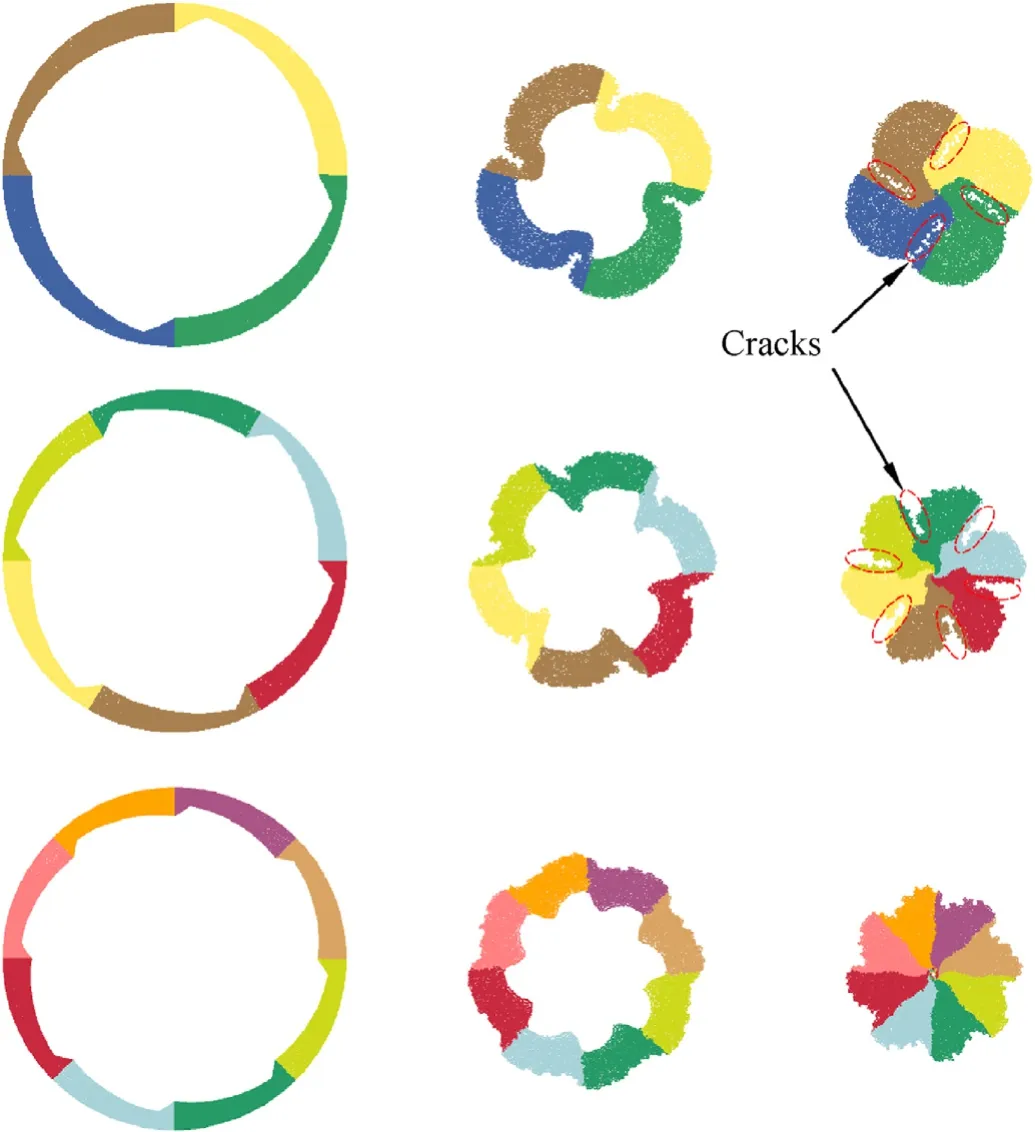
Fig.11.Converging process of fluted liners with α equals to 90°,60° and 45°.
During the forming process of the liner with α equals to 90°and 60°,cracks appear at the circumferential of the liners.Then the cracks propagate along the radial direction which decreases the diameter of the compact region of the jet to be formed.This phenomenon is caused by the large velocity gradient induced by the“thick-thin”structure[11,12].The decrease of the compact region of a jet during the converging process makes it easier for the appearance of necking while jet stretches.While in the case of liner with α equals to 45°,no crack is found around the liner during the converging process.Therefore,α equals to 45°is recommended for the following design work to guarantee a wider range of SCR adjustable based on the premise that a jet is able to form steadily.
3.Structural optimizations of 3D fluted liner
The multi-section optimization method proposed was applied to design the 3D fluted liners.As shown in Fig.12,nine cross sections were chosen with same interval distance alone the charge axis.Each of the cross section has a specific liner-charge proportion,based on which the fluted structure was designed.
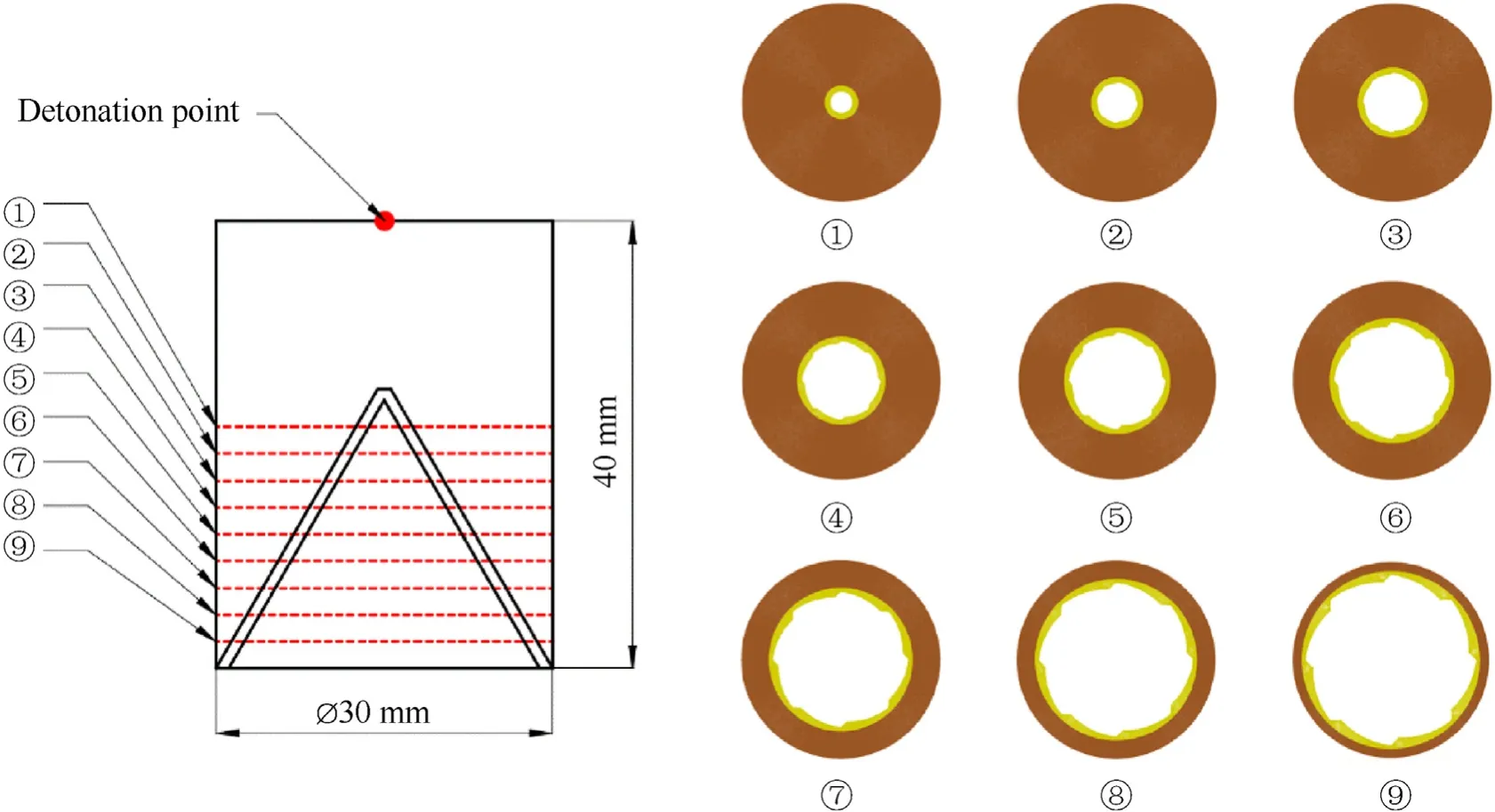
Fig.12.Schematic diagram of multi-section optimization method.
The detonation point was set at the top center of the charge and the detonation time of the charge was computed by dividing the straight-line path to the detonation point with the charge detonation speed.Therefore,the detonation wave was generated from the charge center to the peripheral on each of the sectional surface,and the detonation time was determined by the position of the designed sectional structure.In this way,the detonation propagating process of the integrated 3D model is similar to the designed sectional structures.The SCR on each of the cross section has a maximum value with the premise that the fluted structure does not fracture before converging at the axis.By adjusting the fluted structure on the cross section,the SCR upper limit on each of the cross section were calculated as shown in Fig.13.

Fig.13.The SCR upper limits on each of cross sections along the charge axis.
The SCR upper limit at the liner tip is zero due to the lack of space for liner converging.Consequently,the tangential impulse cannot be induced to offset the spin.As the position of the cross section moves from the tip to the middle,the converging space of liner increases,together with the decrease of charge proportion.The increasing converging space enables more tangential impulse induced to offset spin,and less charge proportion results in the decrease of driving energy.Therefore,the upper limit of SCR reaches the maximum value at position ④.After position ④,the liner converging space continues to increase while the charge proportion drops.This leads to the decrease of SCR upper limit from position ④to position ⑨.At the bottom of the liner,there is no charge to drive the liner.Thus,even with the largest converging space,the SCR upper limit still drops to zero.It is notice worthy that the upper limit of SCR at the middle part of the liner is relatively high.This means that the main contribution to offset the spin effect is made by the middle part of the fluted liner.
Later,fluted liners with SCR of 100 r/s,200 r/s and 300 r/s were designed using multi-section method.During the designing process,the required compensation rate was initialized on each of the sectional fluted structure individually.By adjusting the fluted structures,the final angular velocity on each of the cross section after material converging should be zero.If the required compensation rate is higher than the SCR upper limit on a cross section,the fluted structure related to the SCR upper limit is taken as the optimized structure.After the optimization of the 2D structures,the fluted structures were assembled into a 3D model using linear lofting method.The corresponding nodes of the sectional structure between the adjacent layers will be fitted along the liner axial direction,so that some guide lines were generated.Then an envelope surface was formed according to the fitted guide lines between the two layers.Consequently,a 3D model was assembled,as shown in Fig.14.
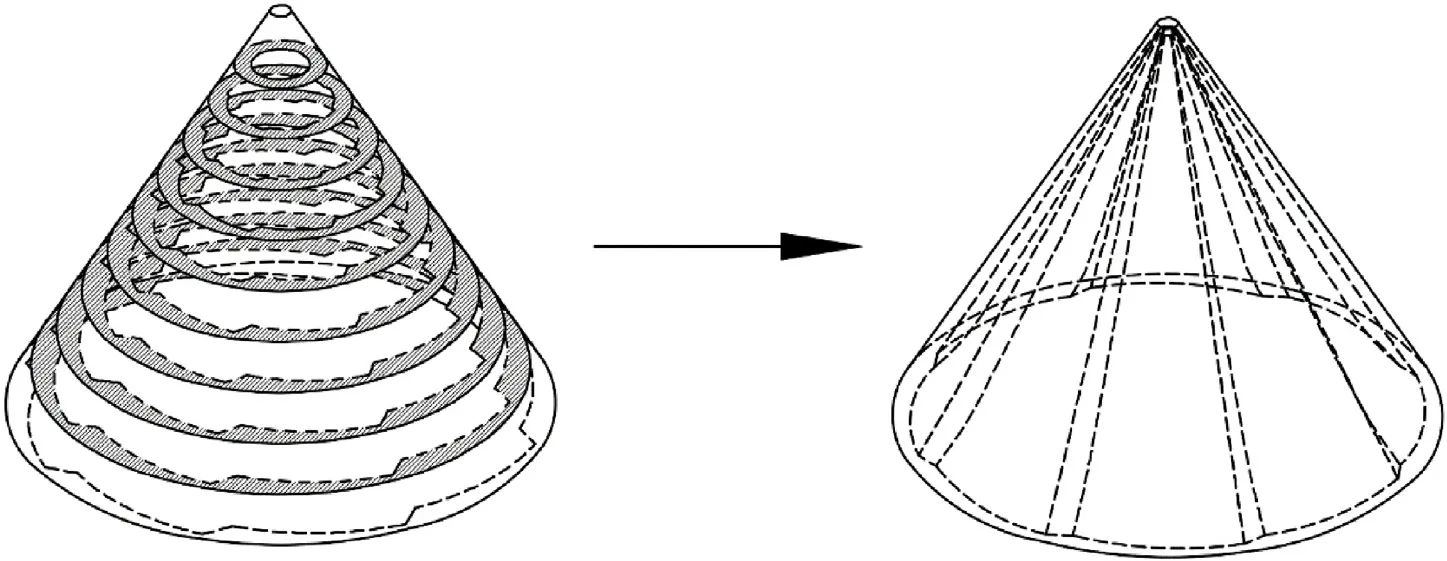
Fig.14.Integrate all the optimized sectional fluted structures into 3D fluted liner.

Fig.15.3D SPH models of the fluted liner and shaped charge.
The shaded area shown on the left represents the optimized sectional fluted structures.The right diagram shows the 3D perspective of the fluted liner.The fluted depth close to the liner tip is relatively small.As it getting closer to the liner bottom,fluted depth grows.As observed,the ridge of the 3D fluted structure is not linear distributed along the liner axis.
4.Numerical simulation of jet forming
The geometry models of 3D fluted liners were then discretized into 3D SPH models as shown in Fig.15.The distance between particles should be as small as possible to guarantee the accuracy of the simulation results.However,extremely small distance between particles makes the numerical process time-consuming.Previous studies have implemented the convergence test on the distance between particles while applying SPH method to simulate explosive loading and dynamic impact [33,34].According to which,the distance between particles was chosen as 0.375 mm while discretizing the liner model,which results in 121,904,110,416,103,432 and 96,632 particles respectively in the case of liner with SCR of 0 r/s,100 r/s,200 r/s and 300 r/s.The particle distance on the interaction surface between the charge and the liner was 0.375 mm and gradually increased to 0.5 mm to the rest part of the charge in order to keep the balance of computation time and accuracy of the results.So that the charge was composed of 784,536 particles.
The initial angular velocity direction and the spin-compensation direction are illustrated at the bottom view of the assembly.Jet forming processes of the liners with different SCR were simulated.The jet forming processes of the smoothed liner(with SCR of 0 r/s)was also studied to compare the spin influence on jet stretching process.Table 4 lists the jet performances at 25 μs after the detonation.

Table 4 Jet performances formed by liners with different SCR under initial angular velocity of 0 r/s,100 r/s,200 r/s,300 r/s,400 r/s and 500 r/s respectively.
The results of the first row in Table 4 shows that the spin affects the jet stretching process significantly.Higher initial angular velocity leads to severer lateral scattering phenomenon.This phenomenon was experimentally verified in Ref.[13].Jet scatters and breaks into fragments under the impact of the centrifugal stress induced by the spin,which undermines the effective jet mass[35].With the help of fluted structure,the spin effect can be relieved.The jet forming performance in Ref.[22] was similar to the present study,which implies the influence of the jet forming performance on the penetration capability.With the help of the spincompensation structure,jet penetration capability can be improved in a certain spin range [22].
Tables 5-8 records the axial velocity contour of jet with SCR of 0 r/s,100 r/s,200 r/s and 300 r/s at 15 μs,20 μs and 25 μs during the jet stretching process.
The axial jet tip velocities of each case are similar at around 7 km/s.Therefore,the spin effect on the jet stretching velocity along axial direction is not obvious.
Then the jet appearances were analyzed quantitatively.The effective jet length,L,and the maximum jet diameter,W,at 25 μs after the detonation were illustrated in Fig.16.An empirical method to determine the effective jet is based on the jet cutoff velocity[36].During the jet stretching process,the part with velocity higher than cutoff velocity is considered as the effective jet.As for the continuous jet,W is the maximum diameter of the effective jet.While for the scattered jet,W is the maximum diameter of the scattered part.

Fig.16.Schematic diagram of effective jet determined by the cutoff velocity of 2000 m/s.
By checking the axial velocity contour of the jet,2 km/s was taken as the cutoff velocity to evaluate jet properties,since the jet material in the present study is similar to that in M.Held’s study[36],W and L of each formed jet were measured and recorded in Figs.17(a) and 17(b).As seen in Fig.17(a),the effective jet lengths formed by the liners with different SCRs are almost the same.When the initial angular velocity equals to the liner SCR,the maximum radius of the jet reaches the minimum value.

Fig.17.(A) Effective jet length and (b) maximum diameter of the formed jets measured based on the cutoff velocity of 2000 m/s.
The fluted liner with SCR of 100 r/s keeps a continuous stretching process when the initial angular velocity equals to 100 r/s.However,as the initial angular velocity continues to increase,the middle part of the jet still scatters into fragments.Form Fig.17(b),it is observed that the jet forming performance is improved by comparing theWof the smoothed liner.When the initial angular velocity is larger than 200 r/s,the jet starts to scatter.
When the fluted liner is tailored with SCR of 200 r/s,the jet stretching performances under five different initial angular velocities are improved obviously.Wof the jet decreases a lot,and the jet begins to scatter when the initial angular velocity reaches 400 r/s.This means that the fluted liner with SCR of 200 r/s has a wider range of spin-compensation adjustable.
As for the fluted liner with SCR of 300 r/s,jet keeps good appearance when the initial angular velocity equals to 300 r/s,but the jet tip scatters with initial angular velocity larger than 300 r/s.As shown in Fig.13,only one sectional fluted structure meets the SCR requirement of 300 r/s.On other cross sections,the upper limits taken were smaller than the required SCR.Consequently,the jet forming process becomes unstable when the initial angular velocity is larger than SCR.However,when the initial angular velocity is lower than the tailored SCR,the middle part of the jet scatters.With a large SCR,the tangential impulse induced by the fluted structure leads to a higher compensation rate to offset the spin.Since the fluted structure is asymmetric,when the initial angular velocity is lower than the liner SCR,the tangential impulse also induces spin to the liner.As the initial angular velocity increases,the tangential impulse is offset by the initial spin,so that the centrifugal stress decreases and the liner forming performance is improved.This phenomenon is also observed in Ref.[19].Therefore,large SCR narrows the spin-compensation range.As for the fluted liner designed in the present study,the SCR lower than 300 r/s is recommended.

Table 5 Axial velocity contour during the stretching process of the spin-compensation jet with SCR of 0 r/s.

Table 6 Axial velocity contour during the stretching process of the spin-compensation jet with SCR of 100 r/s.
5.Conclusions
The multi-section optimization method proposed in the present study is well adapted in designing the fluted liner.Spincompensation mechanism was illustrated based on a fluted inner structure with a smoothed outline.During the converging process of the fluted structure,“thick-thin” effect results in the radial velocity gradient of the liner material,which leads to the appearance of the dominant region and the affiliated region.Net tangential impulse is induced to offset spin due to the difference of the region area.The deflecting angle (θ),is recommended to be 5.625°.The recommended fluted curvature radius,Rc,is 0.167 CD,which leads to a predictive exponential relationship between SCC and the tip offset radius,Rt.The coefficient of the empirical exponential formula was fitted.Periodic angle α is recommended to be 45°to balance the value of SCR and the stability of the jet forming.

Table 7 Axial velocity contour during the stretching process of the spin-compensation jet with SCR of 200 r/s.

Table 8 Axial velocity contour during the stretching process of the spin-compensation jet with SCR of 300 r/s.
The SCR at the tip and the bottom of a fluted liner is zero,due to the lack of converging space and enough driving energy respectively.The main contribution to offset the spin effect is made by the middle part of the fluted liner.When the initial angular velocity equals to the designed SCR,jet forming performance is improved compared to the case of normal smoothed liner.The fluted liner with SCR of 200 r/s has a wider range of spin-compensation adjustable.Large SCR narrows the spin-compensation range since the tangential impulse induced by the fluted liner also leads to the initial spin.Therefore,the SCR lower than 300 r/s is recommended.The effective jet length almost keeps the same during the stretching process of both the smoothed liner and the fluted liner.When the initial angular velocity equals to the liner SCR,the maximum radius of the jet reaches the minimum value.
In general,the multi-section optimization method provides a new efficient method to design liner for a specific usage.Later,the designed liners in the present study will be fabricated.Jet forming and penetration experiment will be implemented.Based on this,the influence of spin on jet penetration capability will be studied.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Acknowledgements
This research work is supported by the project of National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC,Grant No.12032006).
- Defence Technology的其它文章
- An aerial ammunition ad hoc network collaborative localizationalgorithm based on relative ranging and velocity measurement in a highly-dynamic topographic structure
- Molecular simulation study of the stabilization process of NEPE propellant
- Damage assessment of aircraft wing subjected to blast wave with finite element method and artificial neural network tool
- Experimental and numerical studies of titanium foil/steel explosively welded clad plate
- Effects of connection types and elevated temperature on the impact behaviour of restrained beam in portal steel frame
- Thermal and ignition properties of hexanitrostilbene (HNS)microspheres prepared by droplet microfluidics

