miRNA-107、肿瘤坏死因子α及血清胃蛋白酶原Ⅰ/Ⅱ联合检查对胃癌的诊断价值

[摘要]目的研究肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)、miRNA-107和血清胃蛋白酶原(PG)Ⅰ/Ⅱ联合检测对胃癌的诊断价值。方法选取2018年6月~2019年6月确诊为胃癌的患者51例为胃癌组(早期胃癌23例、进展期胃癌28例),并选取同期就诊的60例良性胃病患者(良性胃病组)及60例健康体检者(健康组)。检测三组miRNA-107、TNF-α和PGⅠ、PGⅡ水平,以miRNA-107、TNF-α和PGⅠ/Ⅱ为自变量,以是否发生胃癌为因变量进行多因素logistic分析,建立联合检测的预测模型,以ROC曲线评估各指标对胃癌的诊断效能。结果各组miRNA-107、TNF-α及PGⅠ/Ⅱ比较,差异均有统计学意义(Plt;0.05)。胃癌组PGⅠ/Ⅱ水平低于健康组和良性胃病组(Plt;0.05),miRNA-107、TNF-α水平高于健康组和良性胃病组(Plt;0.05);良性胃病组PGⅠ/Ⅱ水平低于健康组(Plt;0.05),miRNA-107、TNF-α水平高于健康组(Plt;0.05)。胃癌进展期PGⅠ/Ⅱ水平低于胃癌早期(Plt;0.05),miRNA-107与TNF-α水平高于胃癌早期(Plt;0.05)。ROC分析结果显示:三者联合诊断的曲线下面积最高,其诊断效能高于各指标的单独检测(Plt;0.05)。结论PGⅠ/Ⅱ指标降低和miRNA-107、TNF-α水平升高均与胃癌的发生发展存在密切关联,三者联合检测可有效提高胃癌诊断的准确度和灵敏度,对早期胃癌诊断具有重要临床价值。
[关键词]肿瘤标志物;胃癌;联合检测;诊断
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-7593.2023.05.017
the Value of Combined Detection of miRNA-107,TNF-α and Serum PepsinogenⅠ/Ⅱ in the Diagnosis of Gastric Cancer
Li Jianfeng1,Jiang Junlin2
1Linpu Community Healthcare Center,Xiaoshan District,Hangzhou,Hangzhou311215;2Xiaoshan First People's Hospital,Hangzhou,Hangzhou311215
[Abstract]ObjectiveTo investigate the diagnostic value of combined detection of tumor necrosis factor-α(TNF-α),miRNA-107 and serum pepsinogen(PG)Ⅰ/Ⅱ in gastric cancer.Methods51 patients diagnosed with gastric cancer from June 2018 to June 2019 were selected as gastric cancer group(23 cases of early gastric cancer and 28 cases of advanced gastric cancer),and 60 patients with benign gastric disease(benign gastric disease group) and 60 healthy subjects(healthy group) who visited the hospital during the same period were selected.The levels of miRNA-107,TNF-α,PGⅠ and PGⅡ in the three groups were measured,and multivariate logistic analysis was performed with miRNA-107,TNF-α and PGⅠ/Ⅱ as independent variables and the presence or absence of gastric cancer as dependent variable to establish a prediction model for combined detection,and ROC curves were used to assess the diagnostic efficacy of each index for gastric cancer.ResultsThere were significant differences in miRNA-107,TNF-α and PGⅠ/Ⅱ among the groups(Plt;0.05).In gastric cancer group,the levels of PGⅠ/Ⅱ were lower than those in healthy group and benign gastropathy group(Plt;0.05),and the levels of miRNA-107 and TNF-α were higher than those in healthy group and benign gastropathy group(Plt;0.05);the levels of PGⅠ/Ⅱ in benign gastropathy group were lower than those in healthy group(Plt;0.05),and the levels of miRNA-107 and TNF-α were higher than those in healthy group(Plt;0.05).PG Ⅰ/Ⅱ levels in advanced gastric cancer were lower than those in early gastric cancer(Plt;0.05),and miRNA-107 and TNF-α levels were higher than those in early gastric cancer(Plt;0.05).ROC analysis showed that the area under the curve of the combined diagnosis of the three was the highest,and its diagnostic efficacy was higher than that of the single detection method of each index(Plt;0.05).ConclusionDecreased PGⅠ/Ⅱ index and increased levels of miRNA-107 and TNF-α are closely related to the occurrence and development of gastric cancer,and the combined detection of the three can effectively improve the accuracy and sensitivity of gastric cancer diagnosis and has important clinical value for the diagnosis of early gastric cancer.
[Key words]Tumor markers;Gastric cancer;Combined detection;Diagnosis
胃癌属临床常见恶性肿瘤,其发病机制与个人生活习惯、遗传因素及幽门螺杆菌等因素有关,但目前已有研究证实东部沿海地区和西北地区胃癌发生率明显高于南方[1]。研究发现,在我国胃癌多好发于50岁以上人群,发病早期治愈率较高,但晚期5年生存率仅为20%[2]。有效的肿瘤标志物检查可提高临床确诊率,因此早期寻找到有效的防治和诊断方案可增加患者生存率,还可降低患者痛苦增加胃癌筛查敏感性[3]。miRNA-107、肿瘤坏死因子α(Tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)、血清胃蛋白酶原(Pepsinogen,PG)Ⅰ/Ⅱ这3个指标单独检测均被证实可用于胃癌的诊断[4]。但三者联合检测能否提高诊断效能目前尚无定论,本研究旨在通过分析miRNA-107、TNF-α、PGⅠ/Ⅱ联合检测对胃癌诊断效能的影响,以期为胃癌的诊断提供新的思路。
1对象与方法
1.1研究对象
选取2018年6月~2019年6月收治的51例胃癌患者为胃癌组(早期胃癌23例、进展期胃癌28例),并选取同期就诊的良性胃病患者60例为良性胃病组,健康体检者60例为健康组。胃癌组男32例,女19例,年龄61~77岁,平均(67.08±8.11)岁;良性胃病组男34例,女26例,年龄62~75岁,平均(67.13±7.82)岁;健康组男33例,女27例,年龄60~75岁,平均(66.37±9.25)岁。三组临床一般资料比较,差异均无统计学意义(Pgt;0.05)。纳入标准:①胃癌患者经病理学检查确诊;②良性胃病组患者经胃镜检查确诊;③患者意识清醒,可配合相关检查与治疗;④签署知情同意书。排除标准:①入组前接受过相关治疗;②合并有心、肝、肾等其他重要脏器疾病;③合并有其他恶性肿瘤。本研究经医学伦理委员会批准。
1.2方法
1.2.1材料ELISA试剂盒由北京美康生物技术研究中心提供、酶标仪由奥地利Anthos公司提供。TNF-α采用酶联免疫吸附法,试剂盒由Genzyme公司提供。PGⅠ、Ⅱ测定采用罗氏cobas e411电化学发光分析仪及配套试剂、配套校准品和质控品。
1.2.2检测方法所有对象空腹抽取静脉血3 mL,肝素抗凝,30 min内常规离心,血清标本于-80℃冰箱保存待用,操作步骤均按试剂说明书进行。采用双抗体夹心ELISA法测定TNF-α水平,利用化学发光分析法测定PGⅠ、PGⅡ水平。使用RT-PCR荧光定量聚合酶链式反应检测miRNA-107水平,根据GenBank设计引物(a:正义引物;b:反义引物),miRNA-107-Fa:GTGAAATGTTTAGGACCACTAGAA,miRNA-107-Rb:GCTGTCAACGATACGCTACGT;U6 RNA-Fa:CGCTTCGGCAGCACATATAC,U6 RNA-Rb:TTCACGAATTTGCGTGTCAT。
1.3统计学方法
应用SPSS15.0统计学软件进行数据分析。正态分布计量资料采用±s表示,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析(任意两组比较采用LSD-t检验);计数资料采用χ2检验;采用多因素logistic回归分析建立联合检测模型,以ROC曲线评估各指标对胃癌的诊断效能,曲线下面积之比行Z检验,Plt;0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2结果
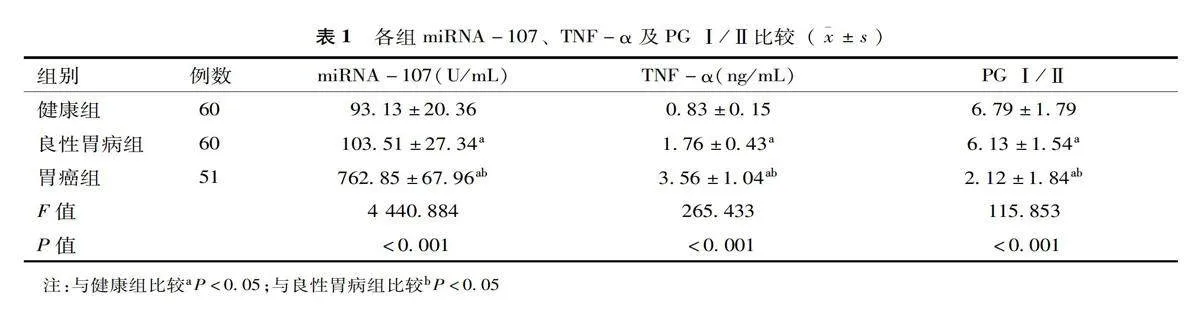
2.1各组miRNA-107、TNF-α及PGⅠ/Ⅱ比较
各组miRNA-107、TNF-α及PGⅠ/Ⅱ比较,差异均有统计学意义(Plt;0.05)。胃癌组PGⅠ/Ⅱ低于健康组和良性胃病组(Plt;0.05),miRNA-107、TNF-α水平高于健康组和良性胃病组(Plt;0.05);良性胃病组PGⅠ/Ⅱ低于健康组(Plt;0.05),miRNA-107、TNF-α水平高于健康组(Plt;0.05),见表1。
2.2胃癌组早期与进展期miRNA-107、TNF-α及PGⅠ/Ⅱ比较
胃癌进展期PGⅠ/Ⅱ低于胃癌早期,miRNA-107与TNF-α高于胃癌早期,差异均有统计学意义(Plt;0.05),见表2。
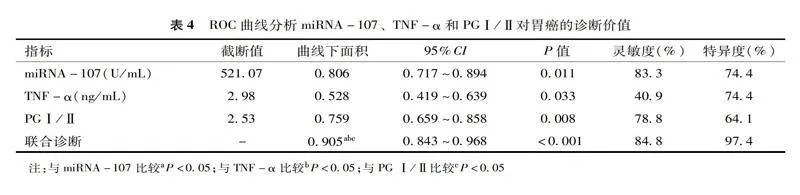
2.3miRNA-107、TNF-α和PGⅠ/Ⅱ对胃癌的诊断价值
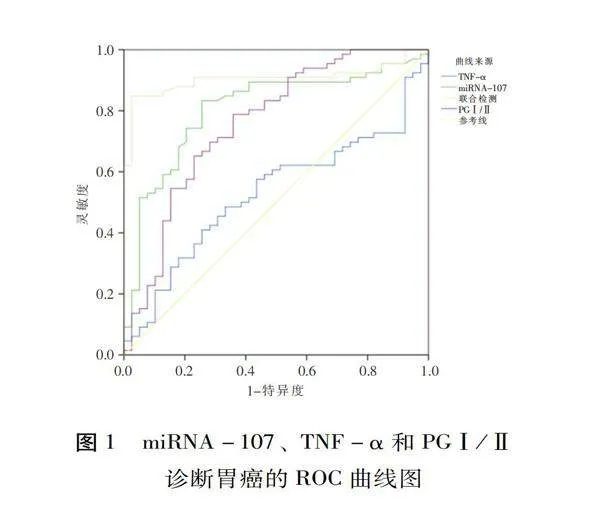
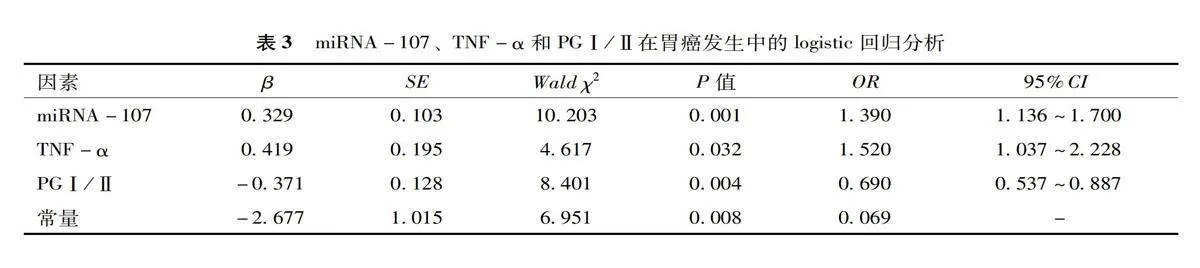
以miRNA-107、TNF-α和PGⅠ/Ⅱ为自变量,以是否发生胃癌为因变量进行多因素logistic分析,建立联合检测的预测模型,见表3。miRNA-107、TNF-α和PGⅠ/Ⅱ联合检测使用logistic回归分析预测概率作为预测值,ROC分析结果显示:三者联合诊断的曲线下面积最高,其诊断效能均高于各指标的单独检测,见表4、图1。
3讨论
世界卫生组织报道2018年全球共计新发胃癌患者为100万例,在诸多癌症中胃癌发病率排第5,死亡率排第3,且男性发病率高于女性[5-6]。研究发现我国胃癌发病率占全球的40%以上,且仅2014年新发胃癌41万例,占诸多癌症的10.79%[7-8]。早期确诊胃癌治疗5~10年生存率高达95%,因此早期确诊可有效提高患者的生存率,且有效的肿瘤标志物对患者病情的判断和临床预后具有重要应用价值[9-10]。PG主要由胃底腺细胞合成,经胃酸或已存在活性PG直接作用于胃蛋白酶,PG在临床中分为PGⅠ和PGⅡ,其中PGⅠ可反映胃酸分泌是否升高,或胃黏膜腺体萎缩PGⅠ水平则开始逐渐下降,PGⅡ水平升高与异型增殖、胃上皮化生或胃底线管萎缩等存在密切关联,而PGⅠ/Ⅱ比值水平降低则与胃黏膜萎缩进展有关,当胃黏膜发生病理变化时,血清PG含量也随之改变,被称为胃黏膜的“血清学活检”[11-12]。近年来临床上胃癌的检测大多先采用PG检查,再依据所得结果进行胃镜检查,两者联合检查有效提高了患者的5年生存率[13]。本研究中胃癌组组PGⅠ/Ⅱ低于健康组和良性胃病组(Plt;0.05),证实胃癌发病与PGⅠ/Ⅱ水平含量存在明显关联。
研究表明,当胃癌患者胃底腺黏膜出现病变时会导致胃底腺主细胞减少,造成PGⅠ分泌能力降低[14]。有研究发现,PGⅠ降低时与致癌诱导因子有关,当基因发生突变时导致PGⅠ分泌能力丧失从而造成PGⅠ降低;而PGⅡ主要基于成熟腺细胞中所产生与癌细胞分化无明显相关性[15]。胃癌在早期初筛时应用PG检测具有重要的临床应用价值,但单独检测时其敏感性较低。有研究发现miRNA-107与胃癌的发生发展存在明显相关性,且随着病情的进展miRNA-107水平会出现异常表达[16-17]。TNF-α是由激活淋巴细胞和巨噬细胞分泌形成的,此指标具备广泛的生物学活性。TNF-α在机体内大量释放会严重破坏免疫平衡,且TNF-α可通过上调基质金属蛋白酶-9等起到促肿瘤生长和转移。为了提高早期胃癌诊断率,本实验将miRNA-107、TNF-α和PGⅠ/Ⅱ联合检测显示其三者联合有较高的灵敏度和准确性。曲线下面积明显高于单独检测结果。本研究中,胃癌进展期患者miRNA-107与TNF-α水平明显高于早期者,且PGⅠ/Ⅱ水平低于早期患者,说明3种肿瘤标志物与胃癌的发展存在明显关联,此3项标志物联合检测可起到互补作用,有效提高了胃癌的确诊率。因miRNA-107、TNF-α和PGⅠ/Ⅱ标志物缺乏对肿瘤分型和发生部位的特异性,因此应结合临床综合数据结果进行分析确诊。
参考文献
[1]杨梅,原丽莉.内镜下早期胃癌的诊疗进展分析[J].国际老年医学杂志,2022,43(5):627-630.
[2]Corso G,Magnoni F,Massari G,et al.CDH1 germline mutations in healthy individuals from families with the hereditary diffuse gastric cancer syndrome[J].J Med Genet,2022,59(4):313-317.
[3]Khan H,Johnston FM.Current role for cytoreduction and HIPEC for gastric cancer with peritoneal disease[J].J Surg Oncol,2022,125(7):1176-1182.
[4]Ni J,Jiang M,Chen Y,et al.Cadherin 11-mediated juxtacrine interaction of gastric cancer cells and fibroblasts promotes metastasis via YAP/tenascin-C signaling[J].Sci Bull(Beijing),2022,67(10):1026-1030.
[5]Wang J,Xiu J,Baca Y,et al.Large-scale analysis
of KMT2 mutations defines a distinctive molecular subset with treatment implication in gastric cancer[J].Oncogene,2021,40(30):4894-4905.
[6]胡鹏,朱长才,汪薇,等.血清胃蛋白酶原联合胃泌素-17对胃癌筛查的 价值研究[J].当代医学,2018,24(6):95-97.
[7]Tang Y,Chen YY,Liu YW,et al.Detection of gastric cancer-associated d-amino acids and carcinoembryonic antigen by colorimetric and immuno ecl sensing platform based on the catalysis of N/S-Doped carbon dots @ N-rich porous carbon nanoenzyme[J].Anal Chem,2022,94(51):17787-17794.
[8]钟华,吴雪艳,刘迪群.血清胃蛋白酶原Ⅰ、Ⅱ及比值联合Hp抗体检测对早期胃癌的诊断价值[J].重庆医学,2017,46(6):821-823.
[9]Mori M,Shuto K,Hirano A,et al.Preoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio may predict postoperative pneumonia in stage I-Ⅲ gastric cancer patients after curative gastrectomy:a retrospective study[J].World J Surg,2021,45(11):3359-3369.
[10]贺亮,黄凌杉.血清胃蛋白酶原Ⅰ、Ⅱ比值对胃癌病灶内恶性生物学行为的评价价值研究[J].海南医学院学报,2018,24(20):1838-1841.
[11]Zhu C,Sandilos G,Henry O,et al.Medicaid expansion is associated with earlier diagnosis of gastric cancer[J].Am J Surg,2022,224(1 Pt B):539-545.
[12]徐新生.血清胃蛋白酶原与再生基因Ⅳ联合检验对胃癌早期诊断的应用价值[J].现代诊断与治疗,2015,26(19):4348-4349.
[13]Yamasaki J,Hirata Y,Otsuki Y,et al.MEK inhibition suppresses metastatic progression of KRAS-mutated gastric cancer[J].Cancer Sci,2022,113(3):916-925.
[14]Xie F,Zhang K,Li F,et al.Diagnostic accuracy of convolutional neural network-based endoscopic image analysis in diagnosing gastric cancer and predicting its invasion depth:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J].Gastrointest Endosc,2022,95(4):599-609.e7.
[15]Schmidt CR.Innovations defining the future of gastric cancer:Summary[J].J Surg Oncol,2022,125(7):1183.
[16]殷立奎,徐广晓,朱新兴,等.miRNA-203联合TSGF、CEA检测在胃癌诊断中的应用[J].检验医学与临床,2018,15(6):821-824.
[17]Cheong JH,Wang SC,Park S,et al.Development and validation of a prognostic and predictive 32-gene signature for gastric cancer[J].Nat Commun,2022,13(1):774.
(2020-08-06收稿)

