Host-guest interactions based supramolecular complexes self-assemblies for amplified chemodynamic therapy with H2O2 elevation and GSH consumption properties
Yng Bi,Yujie Pn,N An,Hito Zhng,Cho Wng,Wei Tin,To Hung
a Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Chemical Additives for Industry,College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,Shaanxi University of Science and Technology,Xi’an 710021,China
b School of Light Industry Science and Engineering,Qilu University of Technology,Shandong Academy of Sciences,Ji’nan 250353,China
c MOE Key Laboratory of Material Physics and Chemistry under Extraordinary Conditions,School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,Northwestern Polytechnical University,Xi’an 710072,China
Keywords:Cyclodextrin Host-guest inclusion interactions Chemodynamic therapy
ABSTRACT Although endogenous H2O2 is overexpressed in tumor tissue,the amount of endogenous H2O2 is still insufficient for chemodynamic therapy (CDT).In addition,the abundant cellular glutathione (GSH) could also consume ·OH for reduced CDT.Thus,the elevation of H2O2 and the consumption of GSH in tumor tissue are essential for the increased ·OH yield and amplified CDT efficacy.In this paper,hostguest interactions based supramolecular complexes self-assemblies (SCSAs) were fabricated by incorporating cinnamaldehyde (CA) and PEG-modified cyclodextrin host units (mPEG-CD-CA) with ferrocene-(phenylboronic acid pinacol ester) conjugates (Fc-BE) on the basis of CD-induced host-guest interactions.After being internalized by cancer cells,CA can be released from SCSAs through the pH-responsive acetal linkage,elevating the H2O2 level by activating NADPH oxidase.Then,Fc can catalyze the H2O2 to higher cytotoxic hydroxyl radicals (·OH).Moreover,quinone methide (QM) can be produced through H2O2-induced aryl boronic ester rearrangement and further consume the antioxidant GSH. In vitro and in vivo experiments demonstrate that SCSAs can be provided as potential amplified CDT nanoagents.
As an innovative class of therapeutic strategies,chemodynamic therapy (CDT) has emerged as a promising modality for cancer treatment due to its tumor-specific properties [1,2].The weak acidity and overexpressed H2O2in the tumor microenvironment could provide Fenton/Fenton-like reaction conditions and reactants respectively,to generate hydroxyl radicals (·OH) for the initiation of cell apoptosis [3–5].Due to the higher redox potential and cytotoxicity of·OH over other reactive oxygen species (ROS),such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) or singlet oxygen (1O2),nanoagents for CDT have drawn wide interest in the cancer therapy field [6–8].However,some barriers have restricted their further application and could be summarized in two aspects.One barrier is therapeutic efficacy,which is highly dependent on endogenous H2O2levels in cancer cells.Although the intrinsic concentration of H2O2in cancer tissue (50–100 μmol/L) is higher than the intrinsic concentration of H2O2in normal tissues (20 nmol/L),endogenous H2O2is still insufficient and unsatisfactory for the catalytic efficacy of the intracellular Fenton reaction [9–14].The other barrier is that the overexpressed antioxidant GSH could consume the·OH to reduce the CDT performance.Hence,the upregulation of H2O2and the downregulation of GSH in tumor tissue are essential for increased·OH yield and amplified CDT efficacy.
Benefitting from recent progress in ROS-mediated therapy,some functional molecules,such as cinnamaldehyde,vitamin C and glucose oxidase,which could selectively elevate H2O2levels and cause damage to some biological molecules related to the proliferation of cancer cells,have already been discovered and utilized in the design and construction of nanotherapeutic agents.Notably,as a major component of cinnamon,cinnamaldehyde (CA) which contains the Michael pharmacophore,has been proven to be an effective agent to elevate intracellular H2O2levels and disrupt redox homeostasis in cancer cells [15–17].The upregulation of H2O2levels can provide sufficient reactant for amplified CDT efficacy.Moreover,to maximize CDT efficiency,ROS scavengers such as GSH should be downregulated to decrease antioxidant capacity and amplify oxidative stress.Thus,the inhibition of antioxidant capacity can be combined with the augmenting of ROS stress levels to disrupt the redox balance.Quinone methide (QM) is a harmful antioxidant that can rapidly alkylate GSH and destroy the redox balance[18].Therefore,the combination of CDT and QM provides an ideal therapeutic companion for CDT by self-supplying H2O2and selfconsuming GSH,suggesting more efficient and continuous cancer cell death [19].
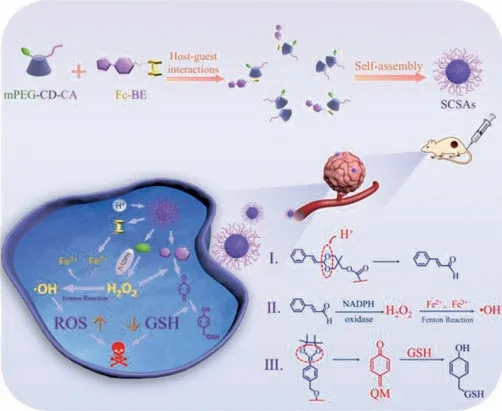
Fig.1.Construction of supramolecular complex based self-assemblies (SCSAs) for amplified chemodynamic therapy.
Iron-based nanoparticles have been widely utilized as catalysts for CDT,however,slow iron release in the tumor microenvironment may weaken their therapeutic efficacy.In contrast to inorganic iron sources,ferrocene (Fc) is an iron-containing organometallic molecule which is preferable for CDT and exhibits unparalleled advantages,including molecular stability,excellent biocompatibility and biodegradability [20,21].In addition,Fc could be included by the cavity ofβ-cyclodextrin (β-CD) to construct supramolecular complexes with ROS-responsive properties[22,23].These host-guest interaction-based self-assemblies have been widely utilized in the chemotherapy,photodynamic therapy and photothermal therapy fields due to their simplified modular construction strategy [24–31].
Thus,it is extremely worthwhile but challenging to fabricate CDT nanoagents which can be activated by specific stimuli in the tumor microenvironment for amplified oxidative stress.Here,in this work,we fabricate host-guest interaction-based supramolecular complex based self-assemblies (SCSAs) by incorporating cinnamaldehyde and PEG-modified cyclodextrin (mPEG-CD-CA) with ferrocene-(phenylboronic acid pinacol ester) conjugates (Fc-BE) on the basis of host-guest interactions.The corresponding mechanism is shown in Fig.1.After being internalized by cancer cells,hostguest inclusions can be dissociated under cancer cellular redox conditions.CA can be released through the pH-responsive acetal linkage to elevate the H2O2level by the activation of NADPH oxidase.Then,the ferrocene can catalyze the endogenous and exogenous H2O2to higher cytotoxic hydroxyl radicals (·OH).In addition,QM can be produced through H2O2-induced aryl boronic ester rearrangement to consume the antioxidant GSH.The SCSAs can be utilized as potential amplified CDT nanoagents with up-regulation of H2O2and down-resgulation of GSH properties.
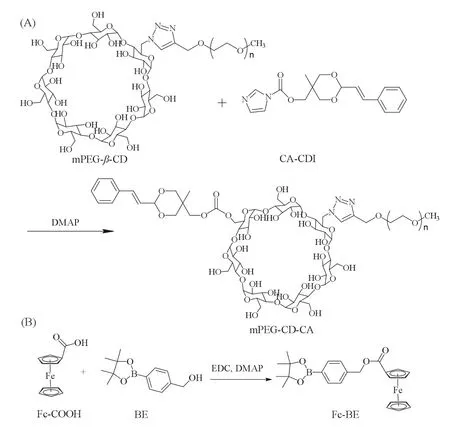
Fig.2.Synthesis routes of (a) mPEG-CD-CA and (b) Fc-BE.
Firstly,in order to obtain host-guest interaction based supramolecular complexes (SCs),host and guest building blocks,including mPEG-CD-CA and Fc-BE,were synthesized according to the methods shown in Fig.2 and Scheme S1 (Supporting information).The products were carefully characterized by1H NMR spectroscopy,FTIR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry.The corresponding data are provided in Figs.S1-S14 (Supporting information).Briefly,mPEG-CD was synthesized through the click reaction between mPEG-Alk (Mn=1000) andβ-CD-N3(Figs.S1–S6).CA-OH and CA-CDI were synthesized according to the literature with the introduction of pH-responsive acetal linkages (Figs.S7–S9).Then,mPEG-CD-CA was obtained through the esterification reaction (Figs.S10 and S11).Through the integral ratio of benzene group in CA and 2,3-OH inβ-CD,the average number of CA linked on CD was determined as approximately one according to the NMR results.As another building block,Fc-BE was obtained through the esterification reaction between Fc-COOH and BE (Figs.S12-S14).The molecular weight of Fc-BE (Fig.S14) measured by ESI-MS was 469.11 [M+Na]+,which was consistent with the theoretical weight(469.14 [M+Na]+).All these results demonstrated that mPEG-CDCA and Fc-BE were successfully prepared.
Subsequently,supramolecular complexes (SCs) were constructed through host-guest inclusion between mPEG-CD-CA and Fc-BE in aqueous solution [32,33].To avoid the overlap with UV–vis spectra,mPEG-CD,Fc and CA were chosen as the model molecules to further prove their host-guest inclusion behaviors.As shown in Figs.3A-D,when the concentration of Fc or CA was fixed to 4×10-5mol/L,the absorbance of Fc and CA at 290 nm and 259 nm showed a clear enhancement with the stepwise addition of mPEG-CD.This phenomenon suggested the inclusion behavior of mPEG-CD/Fc and mPEG-CD/CA,which increased the water solubility of the Fc and CA molecules.To determine and verify the inclusion constants between CA and Fc withβ-CD,a double-reciprocal plot was fitted by the modified Benesi-Hildebrand equation as follows [34,35]:
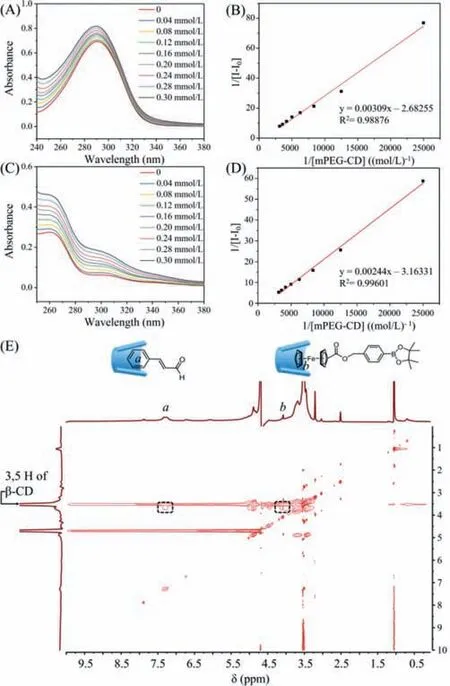
Fig.3.(A) UV–vis absorption spectra of CA upon the stepwise addition of mPEGCD.(B) Linear fitting of the UV–vis absorption changes at 290 nm of CA as a function of the mPEG-CD concentration.(C) UV–vis absorption spectra of Fc upon the stepwise addition of mPEG-CD.(D) Linear fitting of the UV–vis absorption changes at 259 nm of Fc as a function of the mPEG-CD concentration.The concentration of CA and Fc was kept at 4×10-5 mol/L.(E) 2D NOESY NMR spectra of supramolecular complexes based on mPEG-CD-CA and Fc-BE in D2O/DMSO–d6 (10:1) at a concentration of 10 mg/mL.
Obviously,the relationship betweenΔAand 1/[mPEG-CD] is a straight line,and the inclusion constantsR2are equal to 0.989 and 0.996 respectively,indicating that the stoichiometric ratio between CA and Fc-OH and mPEG-CD is 1:1.The inclusion constant of CD/CA and CD/Fc was determined as 868 0 K-1and 1296 K-1,respectively.In addition,the UV–vis spectra of mPEG-CD-CA,Fc-BE and their mixture in aqueous solution (Fig.S15 in Supporting information) were also measured to prove their host-guest interaction based on the obvious redshift of the Fc-BE moiety.Moreover,the 2D NOESY NMR spectra of host/guest mixtures were utilized to investigate the association of host-guest interactions between mPEG-CD-CA and Fc-BE.As shown in Fig.3E,an intermolecular correlation cross-peak appeared between the internal 3-H and 5-H protons in the cavity ofβ-CD and the protons in the CA and Fc moieties,indicating the formation of SCs due to the host-guest interactions betweenβ-CD and CA and the Fc moieties in the two segments.These results suggested the formation of host-guest interactions based supramolecular complexes mPEG-CD-CA@Fc-BE.
Due to the amphiphilic nature of host-guest interactions based mPEG-CD-CA@Fc-BE,supramolecular complexes based selfassemblies (SCSAs) can be further formed.An obvious tyndall effect of SCSAs was observed in Fig.4,proving the existence of nanoparticles.Then the critical aggregation concentration (CAC) of SCSAs was investigated to confirm the formation of self-assemblies.Utilizing pyrene as the fluorescent probe,the CAC of the SCSAs was determined to be 5.5×10-6mol/L (Fig.4A).Subsequently,SCSAs (1 mg/mL) at pH 7.4 were characterized by dynamic light scattering (DLS),transmission electron microscopy (TEM),and atomic force microscopy (AFM),and the morphology and size of SCSAs were confirmed.DLS showed that SCSAs with an average hydrodynamic diameter of 230 nm and a narrow PDI can be obtained(Fig.4B),indicating their potential to apply in the nano-carriers field.Moreover,the size and polydispersibility (PDI) were tested at time intervals to prove the stability of SCSAs.As shown in Fig.4C,no obvious change in the size and PDI of SCSAs was observed for one week.Furthermore,as shown in Figs.4D and E,spherical micelles were clearly seen with an average diameter of approximately 200 nm in the TEM.The element mapping images indicated the existence of C,O,Fe and B element which was ascribed to Fc-BE in SCSAs.The AFM results for SCSAs (Fig.S16 in Supporting information) were agreed with the TEM results.Notably,in order to realize the excellent anti-tumor outcomes,the SCSAs should respond to the tumor microenvironment,such as lower pH and overexpressed H2O2level.In our designed systems,the introduction of the pHresponsive acetal linkage,H2O2-responsive CD/Fc dissociation and phenylboronic acid pinacol ester linkage could be utilized for the SCSAs to achieve the tumor therapy.Thus,in order to investigate the responsive properties of SCSAs,SCSAs at pH 7.4 with H2O2,and pH 5.0 with/without H2O2were further investigated.As shown in Figs.S17 and S18 (Supporting information),the TEM and DLS results of the above samples showed the formation of large irregular aggregates due to the partial disassembly of SCSAs.These results indicated the disassembly behavior of SCSAs in acid pH and overexpressed H2O2conditions which are consistent with tumor microenvironment.
Due to introduction of acetal linkage and aryl boronic esters in the systems,SCSAs could exhibit pH- and H2O2-dually responsive behaviors.The UV–vis spectra at time intervals were conducted to monitor SCSAs (1 mg/mL) at different pH and redox conditions.At pH 7.4,the SCSAs showed stable status (Fig.S19 in Supporting information).As displayed in Fig.5B,after the addition of H2O2,the detachment of the boron acid group increased the acidity of the systems,accelerating the breakage of the acetal linkage.Compared with the above results,the wavelength of CA exhibited red-shift from 252 nm to 291 nm in Figs.5A–C.This result indicated that the acetal bond can be broken rapidly at pH 5.0 regardless of whether H2O2is added to the system through,suggesting its potential application in the tumor microenvironment.Then,the responsive release of CA was monitored by UV–vis spectroscopy to investigate the absorbance at 291 nm using the dialysis method under different pH and H2O2conditions.As shown in Fig.5D,the results show only 18% of CA can be released at pH 7.4,suggesting that the SCSAs are stable in a normal physiological environment.Meanwhile,the release rate of CA was faster at pH 5.0 than at pH 7.4,which was ascribed to the accelerated hydrolysis of the responsive acetal linkage.Furthermore,the existence of H2O2facilitates the detachment of the boron acid group,which could accelerate the hydrolysis of acetal bonds and the release of CA.In addition,nearly 90% of the total amount of CA could be released from SCSAs in 48 h at pH 5.0 with 10 mmol/L H2O2.
The effective conversion of H2O2to·OH through the Fenton reaction by Fc plays a key role to amplify the intracellular oxidation stress in our designed systems.Here,the generation of·OH was investigated by using methylene blue (MB) as an indicator.When MB was degraded by·OH,the blue color weakened.As shown in Figs.5E and F,when MB was incubated with H2O2in the presence of SCSA at a concentration of 1 mg/mL,a significant decrease in absorbance at 664 nm was observed,while no obvious changes were observed for MB solution cultured with SCSAs alone (Fig.S20 in Supporting information).Unlike traditional iron-based inorganic nanoparticles,which exhibit strong dependence on acid reaction conditions (pH 2–4) for effective Fenton reactions [36],SCSAs possess a high catalysis rate even at neutral pH due to the sufficient ferrous ions in the systems.
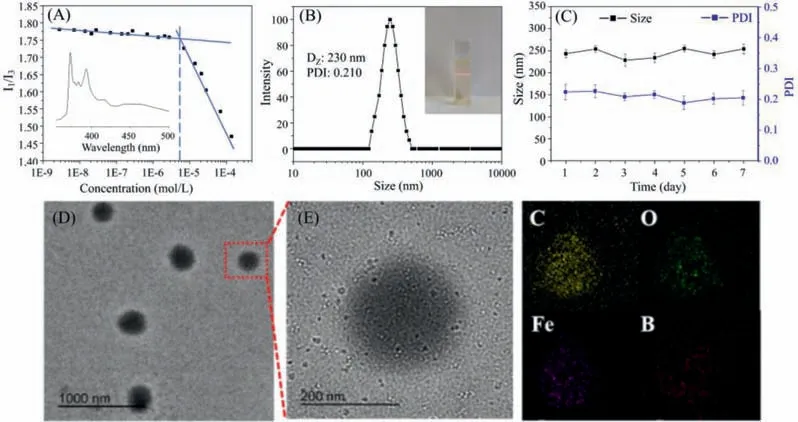
Fig.4.(A) The critical aggregation concentration (CAC) of SCSAs measured with pyrene as a fluorescent probe.(B) DLS results and (C) stability of SCSAs (1 mg/mL) at pH 7.4.(D,E) Typical TEM images and their element mapping of SCSAs at pH 7.4.
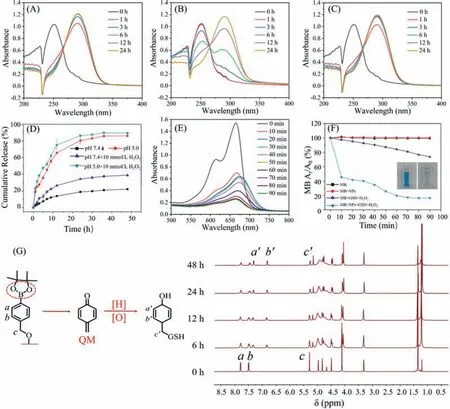
Fig.5.UV–vis absorption spectra of SCSAs (1 mg/mL) in (A) pH 5.0,(B) H2O2,(C) pH 5.0+H2O2 condition.(D) Cumulative release curves of CA from SCSAs in PBS (pH 7.4 and 5.0 with/without H2O2) at 37 °C; (E) Time-dependent UV–vis spectra of MB degradation behavior in the presence of SCSAs.(F) Time-dependent degradation of MB caused by ·OH generated from SCSAs in the presence or absence of GSH (10 mmol/L) and H2O2 (1 mmol/L).(G) H2O2-responsive release of QM in Fc-BE monitored by 1H NMR.
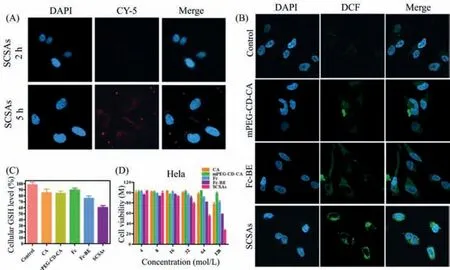
Fig.6.(A) CLSM images of HeLa cells incubated with Cy5-loaded SCSAs at a concentration of 64 μmol/mL.(B) ROS generation of HeLa cells incubated with PBS,mPEG-CDCA,Fc-BE,and SCSAs using DCFH-DA as a fluorescent probe after 6 h.(C) Quantitative cellular GSH level analysis measured in HeLa cells treated with CA,mPEG-CD-CA,Fc,Fc-BE,and SCSAs for 24 h.(D) In vitro cytotoxicity of HeLa cells incubated with CA,mPEG-CD-CA,Fc,Fc-BE,and SCSAs for 48 h.
Furthermore,upon the addition of H2O2,the aryl boronic esters can be rearranged,accompanied by the production of quinone methide (QM) from SCSAs.The generation of QM was monitored by1H NMR,as QM could easily transform into phenols in the presence of water [37,38].As described in Fig.5G,Fc-BE was utilized as a modal molecule to verify QM production at time intervals with 1 mmol/L H2O2.The H proton resonance signals of a at 7.77–7.81 ppm and b at 7.48–7.51 ppm gradually reduced and shifted to a’at 7.32–7.36 ppm and b’at 6.83–6.87 ppm,as well as the appearance of new peaks c’at 5.15 ppm,which was ascribed to the -CH2-OH of phenol,suggesting the generation of QM and the potential of SCSAs to consume intracellular GSH at the tumor site.Since tumor cells possess higher H2O2levels and acidic pH than normal cells,SCSAs might be utilized as potential nanoagents for cancer therapy according to the abovementioned results.
To verify whether the SCSAs could be utilized to realize the amplified CDT,anin vitrocell experiment was performed to investigate the interactions between SCSAs and cancer cells.In this work,HeLa cells were chosen as the model cells and incubated with Cy5-loaded SCSAs to investigate their cellular uptake behaviours through CLSM observation.As shown in Fig.6A,the red fluorescence intensity of Cy5-loaded SCSAs was enhanced with continuous treatment time from 2 h to 5 h.The quantitative analysis results (Fig.S21 in Supporting information) also agreed with that SCSAs had effective cellular uptake property.
Moreover,the generation of·OH could enhance intracellular ROS levels and is crucial for CDT.Thus,intracellular ROS production was investigated through a DCFH-DA assay.As depicted in Fig.6B,after treatment with mPEG-CD-CA and Fc-BE,the green fluorescence intensity,which represented ROS levels in HeLa cells,was obviously enhanced compared to the green fluorescence intensity of the control group.More importantly,ROS production in SCSAs was significantly enhanced compared to the ROS production in other groups at the same concentration,suggesting the enhanced oxidative stress through self-supplying H2O2and effective Fenton reaction.In addition,GSH overexpression plays a key role in ROS consumption during the therapy process.Therefore,to verify the QM-mediated GSH consumption property of SCSAs,the effects of CA,mPEG-CD-CA,Fc,Fc-BE and SCSAs on HeLa cellular GSH levels were further investigated.As displayed in Fig.6C,the cells treated with Fc-BE exhibited obvious GSH downregulation behaviours,and no obvious change appeared after incubation with the CA,mPEG-CD-CA and Fc groups,confirming that QM produced through aryl boronic ester rearrangement could effectively decrease the intracellular GSH content.Meanwhile,a significant downregulation of GSH was observed in the SCSAs group,suggesting the self-consuming GSH property of SCSAs and the potential application for amplified CDT.Finally,to verify the hypothesis that SCSAs could be utilized for amplified CDT,thein vitrocellular cytotoxicity of HeLa cells was evaluated by CCK-8 assay.As shown in Fig.6D,the viability of HeLa cells after treatment for 48 h was significantly decreased in the Fc-BE and SCSAs groups compared with the CA,mPEG-CD-CA and Fc groups as a function of concentration.Fc-BE possessed mild cytotoxicity due to the insufficient H2O2for Fenton reaction and the generation of·OH.In addition,the SCSA groups exhibited higher toxicity than the Fc-BE groups,which might be caused by the effective cellular uptake and sufficient H2O2of SCSAs for CDT,suggesting the significant inhibition of HeLa cell proliferation.All these results proved that SCSAs could be utilized as typical nanoagents and achieve amplified CDT efficacy through self-supplying H2O2and self-consuming GSH behaviours.
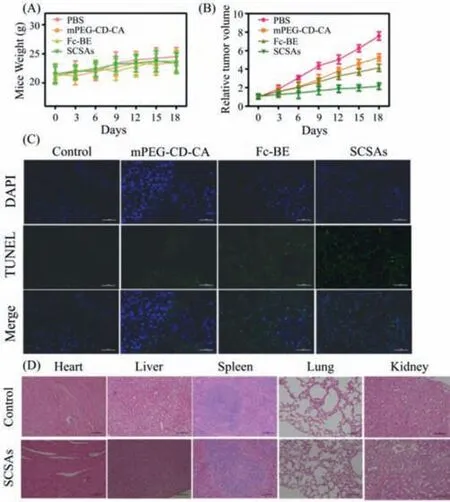
Fig.7.(A) Bodyweight growth as a function of time,and (B) tumor relative volume growth curves of different groups of nude mice after treatment with PBS,mPEGCD-CA,Fc,Fc-BE,and SCSAs.(C) TUNEL staining of tumor (Scale bar: 50 μm).(D)Biosafety evaluation by the H&E staining study (Scale bar: 100 μm).
Finally,in vivoanti-tumor effect was conducted on nude mice bearing HeLa tumors.PBS,mPEG-CD-CA,Fc-BE and SCSAs were intravenously injected on days 0,4 and 9.The body weight and tumor growth relative volume were monitored for 18 days (Figs.7A and B).Compared with the PBS-treated group,the mPEG-CDCA-treated group exhibited slight tumor inhibition,and the Fc-BEtreated group exhibited slightly better tumor inhibition,whereas the nude mice treated with SCSAs exhibited the best therapeutic tumor inhibition,indicating an excellent antitumor effect.At the same time,the negligible differences in the mouse weights in different groups were observed,suggesting no significant systemic toxicity of SCSAs.These results proved that SCSAs are potential CDT nanoagents for cancer treatmentin vivo.In addition,the TUNEL assay was further performed to investigate the cellular death induced by the proapoptotic activity of SCSAs (Fig.7C).Notably,compared with the mPEG-CD-CA and Fc-BE groups,the green color in the tumor was enhanced in the SCSA group,proving the effective proapoptotic events of SCSAs.Finally,in order to evaluate thein vivobiosafety of SCSAs,H&E staining was conducted.As depicted in Fig.7D,compared with control group,no visible tissue damage and side effect presented in normal organ,such as heart,liver,spleen,lung and kidney in SCSAs groups,suggesting the potential security of SCSAs during the therapy process.These results revealed that our designed SCSAs could provide promising nanoagents for CDT.
In conclusion,host-guest interaction-based supramolecular selfassemblies (SCSAs) based on mPEG-CD-CA and Fc-BE were constructed.The target SCSAs were stable under physiological conditions and possessed stimuli-responsive drug release properties.Importantly,after cellular internalization,the SCSAs can release CA to self-supply H2O2as the reactant for CDT and self-consume GSH through QM,achieving amplified CDT.In vivoinvestigations confirmed their excellent CDT performance.Overall,in view of the excellent antitumor efficacy,it is worthwhile to believe that the development of SCSAs will provide promising prospective results in the field of cancer treatment.
Declaration of competing interest
All the authors declare that they have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work reported in this paper.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos.21801162,22071197,22022107),Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China (No.2020JC-20).
Supplementary materials
Supplementary material associated with this article can be found,in the online version,at doi:10.1016/j.cclet.2022.05.066.
 Chinese Chemical Letters2023年1期
Chinese Chemical Letters2023年1期
- Chinese Chemical Letters的其它文章
- Diabetic wound healing activated by supramolecular cascade reaction
- MBenes: Two-dimensional transition-metal borides with ordered metal vacancies
- Wet-adhesive materials of oral and maxillofacial region: From design to application
- Diverse catalytic systems for nitrogen-heterocycle formation from O-acyl ketoximes
- Fluorine-containing drugs approved by the FDA in 2021
- The development and application of dual-comb spectroscopy in analytical chemistry
