Facile detection of pesticides using atmospheric pressure matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry with multi-walled carbon nanotubes-based matrix
Sijin Chen,Hunxi Zho,Lili Jio,Zhenhun Wng,Mengy Zho,Lu Tin,Yng Xiu,*,Shuying Liu,b,*
a Jilin Ginseng Academy,Changchun University of Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130117,China
b Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry,Chinese Academy of Science,Changchun 130022,China
Keywords:Atmospheric pressure MALDI Pesticides MWCNTs-based matrix Ambient ionization
ABSTRACT A novel atmospheric pressure matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry (AP-MALDIMS) method was established for the facile detection of pesticides in ambient environment.Four kinds of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs)-based matrix were synthesized and utilized to enhance the ionization efficiency of pesticides.Organophosphorus,anilinopyrimidine,carbamate,triazine,triazole and benzimidazole pesticides were directly desorbed and ionized from MWCNTs-based matrix in ambient environment,showing clear background and good sensitivity.In a comparison,Fe3O4-doped MWCNTs improved the intensity of pesticide ions more than the other three matrices.Moreover,MWCNTs-based matrix exhibited better performance than organic matrix.Quantitative analysis of pesticides using APMALDI-MS was validated to be adequate linearity,repeatability and sensitivity.Overall,AP-MALDI-MS combined with MWCNTs-based matrix enables the directly qualitative and quantitative analysis of pesticides in ambient environment.
Pesticide refers to a general term for a wide variety of products designed to control and manage pests.It could be classified as insecticides,herbicides,fungicides and algicides,according to its primary target that intended to disrupt [1].Pesticide plays an important role in agricultural production for increasing the yield and value of agricultural products [2].However,the biological effects that make pest control products valuable may also result in unwanted effects that pose threats to human and environmental health.For this reason,there is demand for analytical techniques which are able to determine as many kinds of pesticides as possible with high sensitivity and throughput.Most of the methods proposed for the determination of pesticides use gas chromatography (GC) and liquid chromatography (LC) coupled with triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (MS) [3–6].Due to their high cost and complex analysis process,the application of these methods is limited.Nevertheless,MS is preferred as a time-saving and laborsaving approach [7].
Atmospheric pressure matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (AP-MALDI) is an ambient ionization method,introduced for the analysis of volatile molecules as a possible alternative to the ionization technique under reduced pressure [8].Its combination with MS not only enables the direct study of peptides [9–11],oligosaccharides [12,13] and bacterial identification [14],but also is capable of performing imaging experiments [15–17].However,APMALDI suffers from matrix problem in analysis of small molecules.Conventional organic matrix used in MALDI,such asα-cyano-4–hydroxy-cinnamic acid (CHCA),provides proton to the analyte for ionization through their cocrystallization [18].The interference in the low mass region and detector saturation are inevitable,which hinders the accurate analysis of small molecules.Much effort has been devoted to resolve this problem.Yang introduced magnetic silica nanoparticles as matrix for the analysis of oligosaccharides,amino,peptides,nucleosides,and ginsenosides.This nanoparticlebased matrix has better surface homogeneity,salt tolerance,and signal to noise (S/N) than conventional organic matrices,resulting in a good performance in the analysis of biomolecules [19].Hani analyzed biomolecules through desorption and ionization on graphene-coated silica,which reduced the chemical background significantly [20].
Multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) have been developed as the matrix for MALDI MS analysis of small molecules [21].As MWCNTs do not readily ionize under moderate laser energy,it succeeds in eliminating ion interference and offers a clear background.But,because of its poor dispersion in water and organic solvent,MWCNTs was hard to be attached tightly to the sample target and hence to form homogeneous matrix layer,which lead to the reduced repeatability and resolution of MALDI MS analysis [22].In addition,the loosely attached MWCNTs tended to fly into the ion source,also raising a contamination problem.Therefore,MWCNTs was further functionalized to overcome these disadvantages [23–25].The functionalization procedure increased the solubility of MWCNTs in water by introducing carboxylic groups on its structure and cutting it into shortened tubes.Compared with raw MWCNTs,functionalized MWCNTs provide a homogenous and steady matrix layer,which makes them alternative matrices for MALDI-TOF MS analysis [26–28].For example,the Cd2+-doped carbon nanotubes with CdS nanoparticles could be used as matrix to efficiently ionize and analyze the microwave enzymatic digestion product of peptide mixtures and proteins [29].Polystyrene/oxidized carbon nanotubes film also showed good stability as sorbent and matrix to analyze small molecular compounds in urine samples [30].However,there is little research on the application of functionalized MWCNTs as the matrix of AP-MALDI-MS for the analysis of small molecules.AP-MALDI employs much lower laser energy and generates much shorter mean free path of ions in ambient environment than those of MALDI in closed circumstance and/or reduced pressure [31].Although they have been reported as the alternative matrices of MALDI MS,the feasibility and performance of functionalized MWCNTs used as AP-MALDI matrix are lack of comprehensive study,especially on the analysis of pesticides in ambient environment.
In this contribution,AP-MALDI-MS combined with functionalized MWCNTs-based matrix was utilized to detect nine pesticides of six classes in ambient environment (Table S1 in Supporting information).Three kinds of functionalized MWCNTs,that is Fe3O4-doped (Fe-),oxidized (o-),andβ-cyclodextrin-coated (β-) MWCNTs,were synthesized and used as matrix together with intrinsic (in-) MWCNTs to enhance the efficiency and repeatability of the ambient ionization.Organic matrices were employed to compare and evaluate the performance of MWCNTs-based matrix.Under optimized conditions,the quantitation of pesticides was also performed and validated.The present work aims to study the feasibility of AP-MALDI-MS for the detection of small molecules,and to raise the possibility of directly qualitative and quantitative analysis of pesticides in ambient environment.
The prepared in-MWCNTs,Fe-MWCNTs,o-MWCNTs andβ-MWCNTs are characterized by FTIR spectroscopy.As shown in Fig.S1a (Supporting information),there appear characteristic adsorption bands of in-MWCNTs at 3455 cm-1,1595 cm-1,1447 cm-1,1091 cm-1and 780 cm-1,which are assignable to the stretching vibrations of O-H and C=O bonds,asymmetric in-plane bending vibrations of C-H bond,stretching vibrations of C-O bond in tertiary alcohol group,and out-of-plane bending vibrations of C-H bond in aldehyde group,respectively.The bands at 2916 cm-1and 2851 cm-1are associated with C-H asymmetric and symmetric stretching vibrations of methylene group,respectively [32].The bands at 2409 cm-1and 2257 cm-1are resulted from unsaturated bonds.Because of the presence of functional groups,disordered or defect regions are supposed to be present in the in-MWCNTs.In Fig.S1b (Supporting information),the characteristic MWCNTs bands are observed with the appearance of a new band at 610 cm-1,which is assignable to the Fe-O out-of-plane bending vibrations,indicating that oxidized ferric species is introduced into MWCNTs framework with its integrity being maintained [33].The slight decrease of the 3455 cm-1band is attributed to the neutralization reaction after the addition of NaOH.For o-MWCNTs,the stretching vibration band of O-H at 3455 cm-1is enhanced with the appearance of two bands at 1249 cm-1and 1084 cm-1,which are associated with C-O-C asymmetric and symmetric stretching vibrations in ester group,confirming the successful oxidation of MWCNTs [34].Excessiveβ-cyclodextrin is mixed with MWCNTs to prepareβ-MWCNTs.Therefore,the spectrum of the resultingβ-MWCNTs is dominated by the characteristic adsorption bands ofβcyclodextrin,such as the asymmetric and symmetric stretching vibration of C-O bond in ether group at 1157 cm-1and 1034 cm-1,respectively,as well as the characteristic bands ofα-(1,4) glucopyranose between 1000 cm-1to 500 cm-1[35].
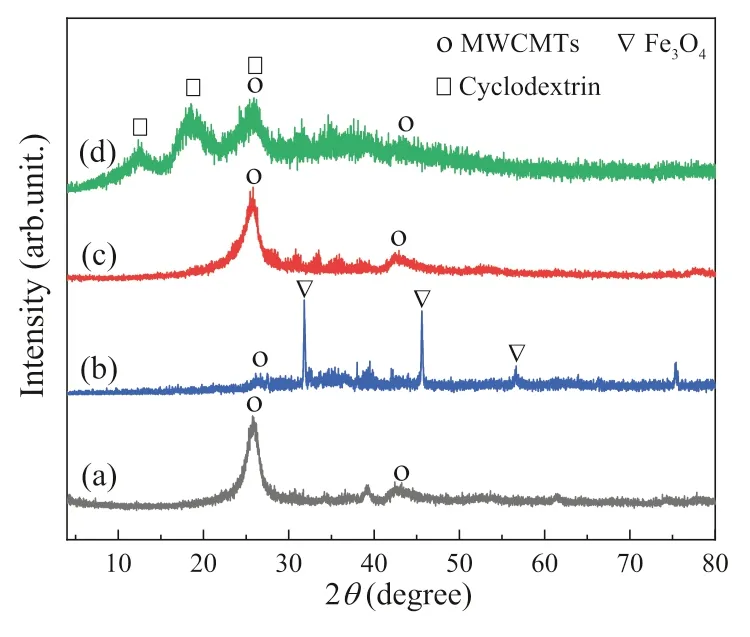
Fig.1.X-ray diffraction patterns of in-MWCNTs (a),Fe-MWCNTs (b),o-MWCNTs (c)and β-MWCNTs (d).
The X-ray diffraction patterns of in-MWCNTs,Fe-MWCNTs,o-MWCNTs andβ-MWCNTs are presented in Fig.1.These matrices show two broad diffraction peaks centered at 25.77° and 42.66°,which are in good agreement with the standard data of MWCNTs[32].In the pattern of Fe-MWCNTs,the peaks at 31.78°,45.54° and 56.67° are indicative of the presence of crystallized Fe3O4in Fe-MWCNTs (JCPDS No.21–0920).The pattern of o-MWCNTs is similar to that of in-MWCNTs,suggesting the oxidation treatment has little effect on the crystallinity of MWCNTs,but to introduce the oxygen-containing functional groups.These functional groups are beneficial to the dispersion of MWCNTs in methanol/water solvent which could increase the adhesion of MWCNTs to sample target so as to improve the repeatability and stability of AP-MALDI-MS analysis.Forβ-MWCNTs,its pattern is dominated by the diffraction peaks ofβ-cyclodextrin at 12.51°,18.46° and 26.40° with poor crystallization (JCPDS No.32–1627),which is similar to the FTIR results.
Laser energy has the direct impact on the ionization efficiency and hence the ion signal intensity of AP-MALDI-MS.In this work,the maximum pulse energy of the employed solid-state laser was 3 μJ,which is much lower than that of MALDI ion source [31].It was adjusted to determine the optimal energy for the ionization of pesticides.Typically,methomyl,cyprodinil,metolcarb and atrazine were analyzed using Fe-MWCNTs as matrix.And the absolute intensities of their protonated ion in base peak were recorded as a function of laser energy between 10% and 70% of the maximum energy with a stepwise of 10%.As shown in Fig.S2 (Supporting information),the pesticides could be ionized once the laser energy is over the threshold of 30%,showing a less reliance of MWCNTsbased matrix on optimal laser properties.The absolute intensities of monitored ions increase with laser energy,since higher incident laser energy could provide more energy to facilitate desorption and ionization of the analytes from matrix.When the laser energy is over 60%,the absolute intensities tend to be steady.Taking into account the energy attenuation of the laser devise when working at a constant high energy level,60% of the maximum energy is selected in further detection.Moreover,it is noted that,under the same conditions,the absolute intensities of these four pesticide ions exhibit different increase rate with incident laser energy,suggesting that the structure of analyte plays a key role in laser energy absorption and analyte desorption and ionization.
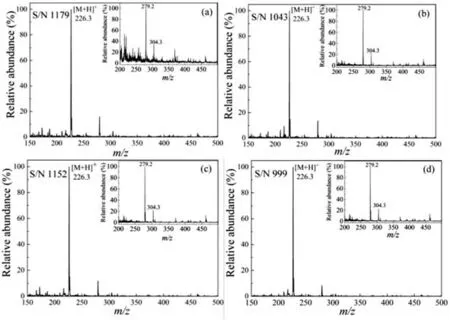
Fig.2.The mass spectra of cyprodinil analyzed by AP-MALDI-MS using in-MWCNTs (a),Fe-MWCNTs (b),o-MWCNTs (c) and β-MWCNTs (d) as matrix,respectively.
The sample preparation method decides the mixing of analyte and matrix,which has effect on the transfer of incident laser energy from matrix to analyte through the formation of co-crystalline or layered microstallites.Using Fe-MWCNTs as matrix,four sample preparation methods were evaluated for their effects on the absolute peak intensity of protonated pesticide ions.(1) Dried droplet method: the mixture of analyte solution and matrix in a certain mixing ratio was deposited onto the AP-MALDI target and left to air dry.(2) Thin layer method: a uniformly distributed thin layer of matrix was prepared with the assistance of gentle heating on top of which the analyte solution was deposited in a second step.(3) Sandwich method: another layer of matrix was deposited on top of a pre-deposited bilayered sample prepared by thin layer method.(4) Sample first method: Analyte solution was deposited onto the target and left to dry in air.Then,matrix was deposited onto the first layer.As shown in Fig.S3 (Supporting information),the dried droplet method exhibits the lowest signal intensity of pesticides.This is because the co-crystallization of matrix and analyte tended to yield comparatively large and unevenly distributed crystals,which were detrimental for the repeatability of MS detection.In contrast,the other three methods offered at least one interface between matrix and analyteviasuccessive deposition.The sandwich and the sample first method covered a matrix layer on top of the pesticide layer.As MWCNTs has marked adsorption to pesticides,the covered matrix layer may be unfavorable to the formation and desorption of pesticide ions from microstallites to gas phase,resulting in the relatively lower signal intensity.On the contrary,the thin layer method exposed pesticides to the direct laser irradiation.It is superior to the other three methods on the signal intensity of pesticides and therefore is used for the sample preparation in further AP-MALDI analysis.
Upon laser irradiation,the matrix in AP-MALDI functions as a mediator for laser energy absorption and transfer to assist the ionization of analyte molecules,which may also raise potential matrix effect to interfere MS analysis.The effect of MWCNTs-based matrix on the ionization of pesticides was typically evaluated using cyprodinil,one of anilinopyrimidine fungicides.As shown in Fig.2,each matrix demonstrates relatively clean spectrum with strong base peak centered atm/z226.3 and good S/N ratio.There are none of other addut,fragment,or matrix ions except for the protonated ion of cyprodinil.No distinctive difference in the four matrices is observed in these spectra.As a comparison,cyprodinil solution was directly deposited on the bare sample target and was irradiated by laser without matrix assisted.No peaks atm/z226.3 are observed,while the peaks atm/z279.2 and 304.3 are originated from sample target,as shown in the corresponding insets of Fig.2.This observation indicates that MWCNTs-based matrix are effective and essential in the direct detection of cyprodinil by AP MALDI.
To further confirm the possibility of MWCNTs-based matrix to assist the desorption and ionization of pesticides under atmospheric pressure by laser irradiation,another eight pesticides of six classes,including organophosphorus,carbamate,triazine,triazole and benzimidazole are analyzed by AP-MALDI with the use of in-MWCNTs,Fe-MWCNTs,o-MWCNTs andβ-MWCNTs as matrix.As shown in Figs.S4-S11 (Supporting information),all the pesticides could be ionized and detected by AP-MALDI using MWCNTsbased matrix in positive ion mode.The intact pesticide molecules are preserved in adduct ions without decomposition owing to the collisional cooling of the expanding plume,which suggests the soft ionization characteristics.Most of the detected pesticide ions are in their protonated form with some exceptions.The [M+H]+,[M+Na]+,and [M+K]+ions of dimethoate and methomyl are simultaneously detected when using in-MWCNTs as matrix (Figs.S5a and S7a in Supporting information),while only the [M+K]+ions are obtained for carbendazim in all the matrices (Fig.S6 in Supporting information).The ionization efficiency varies with pesticides and matrices.For example,cyprodinil and atrazine exhibit high ionization efficiency and low background signals with no interference to the analytes (Fig.2 and Fig.S4 in Supporting information).Triadimenol and diniconazole undergo relatively low efficient ionization process,resulting in abundant background interference(Figs.S8 and S10 in Supporting information).
Although the ambient enviroment of AP-MALDI inevitably brings background interference from atmosphere and sample target under high laser energy,using appropriate matrix could reduce the interference by improving the ionization efficiency of analytes.The four kinds of MWCNTs-based matrix exhibited different performance of assisted ionization for pesticides.The prepared Fe-MWCNTs,o-MWCNTs andβ-MWCNTs give relatively higher S/N ratios than in-MWCNTs when detecting metolcarb and diniconazole (Figs.S9 and S10 in Supporting information).On the other hand,in-MWCNTs shows a more clear spectrum than the other three matrices in the analysis of methomyl (Fig.S7 in Supportinginformation).As shown in Fig.3,Fe-MWCNTs improves the intensity of most pesticide ions more than the other three matrices.In combination with the S/N ratios as labeled in the corresponding mass spectra (Fig.2 and Figs.S4-S11 in Supporting information),MWCNTs-based matrix is suitable for the analysis of the nine pesticides.Moreover,the functionalization of MWCNTs could enhance the production of pesticide ions by AP-MALDI.And Fe-MWCNTs is superior to the other matrices in the detection of most of the nine pesticide ions.The introduction of Fe3O4particles into MWCNTs accounts for the results.
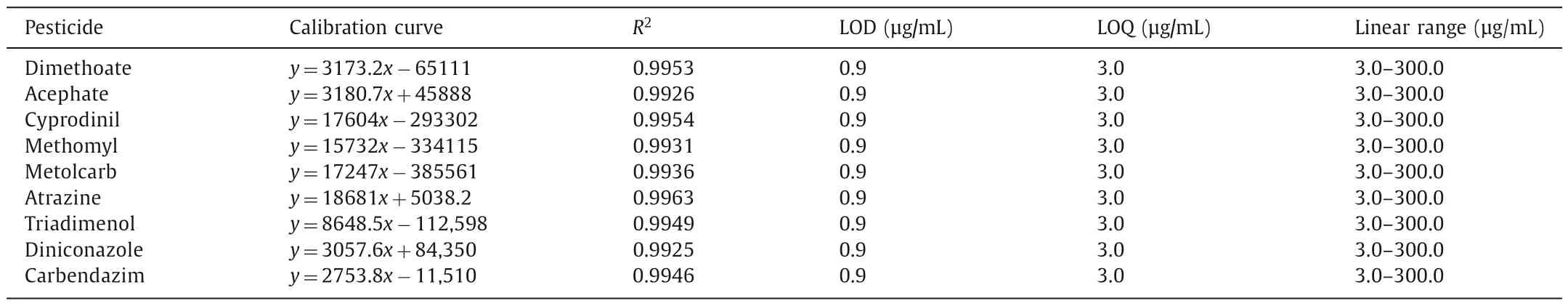
Table 1 The calibration curve, R2,LOD,LOQ and linearity range of pesticides analyzed by AP-MALDI-MS using Fe-MWCNTs as matrix.
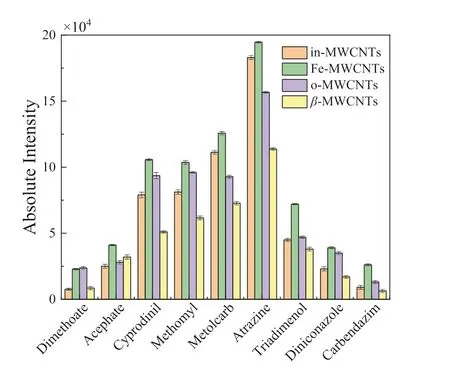
Fig.3.Peak intensities of nine pesticides detected by AP-MALDI using four kinds of MWCNTs-based matrix.
CHCA and THAP are two typical organic matrices with molecular weight of 189.2 and 168.2,respectively.They were employed to detect pesticides by using AP-MALDI-MS.As shown in Fig.S12 (Supporting information),cyprodinil and atrazine are ionized,showing the base peak atm/z226.3 andm/z216.1 of their respective [M+H]+ion and abundant interfering peaks.For other pesticides discussed above,there are no adduct ions present except for the [M+H]+ions when employing CHCA and THAP as matrix,indicating good protonating effect of CHCA and THAP on pesticides.This is attributed to their aromatic core and conjugated structures which are advantageous to the laser energy uptake and the resulting electronic excitation of the matrix.Moreover,CHCA and THAP do not give rise to obvious signals originating from thequasi-molecular ions of their own,which is due to the radiolytic decomposition of organic matrix under high laser fluence.However,the minor intensity of target pesticide ions and high level of background ions lead to the lower S/N ratios in comparison with those of MWCTNs-based matrix.This could be rationalized on the basis of detector saturation resulting from the series of cluster ions and some more abundant fragment ions of the largely used organic matrix [36].By contrast,MWCNTs-based matrix is more stable towards laser irradiation in ambient environment and has appropriate energy levels for the laser energy transfer to boost desorption and ionization of low molecular weight pesticides.Therefore,MWCNTs-based matrix is superior to the organic matrix in the facile detection of pesticides using AP-MALDI-MS.
The accuracy of ambient ionization in quantification is deeply affected by the measurement repeatability.Therefore,before developing quantitative method,the intra- and inter-spot repeatability of AP-MALDI-MS on the analysis of nine pesticides was investigated using MWCNTs-based matrix.As shown in Table S2 (Supporting information),the repeatability varies significantly with matrices and pesticides.The intra-spot repeatability ranges from 4.41%to 8.23%,while the inter-spot repeatability ranges from 2.81% to 29.34%.When using Fe-MWCNTs and o-MWCNTs as matrix,the repeatability is acceptable with RSDs less than 8.16% and 13.15%for intra- and inter-spot,respectively.This is due to their homogeneous dispersion in solvent and enhanced ionization efficiency to pesticides.As for CHCA and THAP,the intra- and inter-spot repeatability is unsatisfactory with RSDs over than 6.61% and 11.83%,which are higher than that of Fe-MWCNTs and o-MWCNTs for each pesticide and not suitable for the quantification of pesticides using AP-MALDI.Therefore,calibration curves for nine pesticides were obtained using Fe-MWCNTs and o-MWCNTs as matrix on APMALDI-MS.As shown in Table 1 and Table S3 (Supporting information),the correlation coefficient (R2) of each pesticide is above 0.99,indicating a good linearity between the concentration and MS peak intensity.The linearity could be remained in the range of 3.0–300.0 μg/mL.Based on the slopes of the calibration curves,diniconazole exhibits the lowest sensitivity,which is owing to its low ionization efficiency in both of Fe-MWCNTs and o-MWCNTs as discussed above.The LOD and LOQ are below 0.9 μg/mL and 3.0 μg/mL,respectively.Thus,it is possible for AP-MALDI-MS to quantify pesticides by using Fe-MWCNTs and o-MWCNTs as matrix.
In this study,we proposed an AP-MALDI-MS method for the facile detection of pesticides.Four kinds of MWCNTs-based materials were employed as matrices.As a proof of concept,the nine pesticides of six classes were successfully detected in ambient environment.MWCNTs-based matrix enables AP-MALDI to detect small molecule compoundsviasoft ionization with no decomposition of the pesticides during ionization.In comparison with organic matrix,MWCNTs-based matrix alleviates the background signals and improves the efficiency of desorption/ionization process.Additionally,MWCNTs-based matrix is simple in preparation.Among the employed matrix,Fe-MWCNTs shows the best performance in the assistance of pesticide ionization.Moreover,the quantitative method of pesticides based on AP-MALDI-MS was validated to be good linearity and repeatability when using Fe-MWCNTs and o-MWCNTs as matrix.In comparison with LC MS and GC MS,the developed method simplifies the sample introduction from the autosampler injections to the direct high-density spotting of pesticides on sample target in parallel and gets rid of the time-consuming chromatographic separation stage by using highfrequency lasers for sampling,which takes no more than a few minutes.It can be also used to detect polar,thermally unstable or low volatility pesticides that are not suitable for GC–MS analysis.Overall,AP-MALDI-MS combined with MWCNTs-based matrix has simple introduction and facile detection of the pesticides,and is of great potential for real-time monitoring and facile detection of pesticides in food and traditional Chinese medicine samples,that is what our lab is studying.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr.Chunsheng Liu of the ASPEC Technologies (Beijing) Limited for providing the AP-MALDI UHR ion source.This work was financially supported by the Science and Technology Development Plan Project of Jilin Province (Nos.20210204098YY,20200201093JC).
Supplementary materials
Supplementary material associated with this article can be found,in the online version,at doi:10.1016/j.cclet.2022.03.009.
 Chinese Chemical Letters2023年1期
Chinese Chemical Letters2023年1期
- Chinese Chemical Letters的其它文章
- Diabetic wound healing activated by supramolecular cascade reaction
- MBenes: Two-dimensional transition-metal borides with ordered metal vacancies
- Wet-adhesive materials of oral and maxillofacial region: From design to application
- Diverse catalytic systems for nitrogen-heterocycle formation from O-acyl ketoximes
- Fluorine-containing drugs approved by the FDA in 2021
- The development and application of dual-comb spectroscopy in analytical chemistry
