Metal phenolic network-stabilized nanocrystals of andrographolide to alleviate macrophage-mediated inflammation in-vitro
Kosheli Thp Mgr,George Frimpong Bofo,Mkhloufi Zoulikh,Xiohong Jing,Xiotong Li,Qingqing Xio,Xuyng Xing,Xiochun Wng,Lifng Fn,Zhenfeng Wu,Wei He,
a School of Pharmacy,China Pharmaceutical University,Nanjing 211198,China
b Jiangsu Aosaikang Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd.,Nanjing 211112,China
c Key Laboratory of Modern Preparation of TCM,Ministry of Education,Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine,Nanchang 330004,China
Keywords:Inflammation Macrophages Andrographolide Metal phenolic network Nanocrystals
ABSTRACT Macrophages play a crucial role in initiating,maintaining,and resolving inflammation through the phenotypic shift,inducing or inhibiting the production of inflammatory cytokines.Therefore,macrophages are potential targets for treating inflammatory diseases.Andrographolide (AND) is a potent anti-inflammatory drug that can reduce pro-inflammatory cytokines and suppress NF-κB /MAPK pathway in activated macrophages.Although AND has many medicinal properties,its lower water solubility and first-pass effect in the liver have hindered its clinical application.In this context,by using a metal phenolic network as a stabilizer,we designed and prepared highly stabilized AND nanocrystals (AND-MPN Ns) with high drug loading capacity to facilitate the clinical application of AND.Our findings showed that AND-MPN Ns could be used to enhance the anti-inflammation in-vitro via macrophage polarization,reducing proinflammatory cytokines IL-6 and TNF-α,and suppressing the NF-κB signaling pathway activation.The results demonstrated the potential of AND-MPN Ns to combat inflammatory diseases effectively.
Inflammation is an essential life process that protects the body from harmful agent infection; however,chronic inflammation often worsens various diseases,including atherosclerosis,cancer,and rheumatoid arthritis [1].Macrophages play a vital role in regulating inflammation through phenotypic shifting and the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines [2].
AND is a di-terpenoid lactone (molecular formula,C20H30O5;molecular weight,350.44 g/mol) isolated from roots and leavesAndrographis paniculate[3].It is a poorly water-soluble drug(74 μg/mL) that belongs to the BCS II class.Stability of AND is better at low temperature,stable at low pH conditions,and unstable at alkaline medium [4].It is reported to have beneficial effects with a variety of medicinal properties [5,6],such as antiviral,anti-inflammatory,anti-malarial,anti-platelet properties,and hepatoprotective [7–11].Moreover,it exhibits potent anti-inflammatory activityviareducing pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α,IL-6,and IL-1βand suppressing nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB)/MAPK signaling pathway [12] in LPS-stimulated macrophages (RAW264.7 cells).It can inhibit the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and enhance the expression of anti-inflammatory marker CD206 [13].Due to poor water solubility,first-pass metabolism,limited biodistribution,short biological half-life,and poor palatability,the traditional dosage forms of AND have a low oral bioavailability (2.67%) despite their extraordinary pharmacological activity [14].For enhancing AND solubility,many techniques have been used,including solid dispersions [15],dried nanosuspensions [16],solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) [17],nanoemulsions [18],and micelles [19].Even though AND solubility and hence bioavailability have increased to some amount,drug loading is still low.In particular,carrier-free AND nanocrystals (Ns)have shown a higher drug loading capacity than other nanosystems [20].In previous studies,it has been reported that drug Ns could release the drug in a controlled manner which is beneficial to macrophages targeting treatment of inflammation [21,22].However,AND Ns has not been implemented yet to treat macrophagemediated inflammation.In this study,we prepared AND-MPN Ns using a metal phenolic network (MPN) as a stabilizer to alleviate macrophage-mediated inflammation.
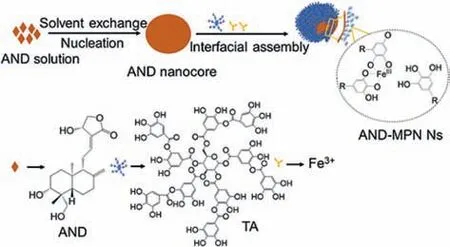
Fig.1.Schematic illustration of metal phenolic network-stabilized AND nanocrystals (AND-MPN Ns).
In preparing drug Ns,stabilizers are crucial in preventing the unstable particles from aggregation and Ostwald ripening [23,24].Recently,MPN,chelation of polyphenols and metal ions,has shown potential effect as a stabilizer or coating material [25] owing to its ability to suppress Ostwald ripening and prevent further particle growth of the nanocomplex resulting in improved bio-stability,prolonged circulation half-time,and controlled drug release.MPN exhibits biocompatibility,high drug loading capability,low immunogenicity,and negligible toxicity [26,27].The adhesive nature of MPNs enables their coating on various nanomaterials for multifunctionalities.In addition to adhesiveness,the coordination networks of MPNs provide favorable conditions for drug encapsulation,and multiple types of drugs can be incorporated into MPNsviacovalent/non-covalent interactions [28–30].Interestingly,multifunctional properties of MPN,including high mechanical [31,32]and selective permeability [33,34],have attracted widespread interest in present works [35,36].In our previous study,MPN was used as a stabilizer in preparing different drug nanocrystals [37].Therefore,we used MPN as a stabilizer to fabricate AND-Ns (ANDMPN Ns) to alleviate the macrophage-mediated inflammationin-vitro.
By determining hydrodynamic particle size distribution,we can estimate Ns’surface coating,hydration layer,and homogeneity or heterogeneity [38].Furthermore,the biological behavior of nanoparticles (NPs) can be predicted by analyzing their surface charge.The Ns’size and morphology are the essential factors to investigate thein-vitroandin-vivofate [39,40].Several studies have evidenced that the small size NPs is more likely to enhance the penetration on specific site of the disease [41].Moreover,reducing the particle size of NPs significantly affects cellular uptake of the drug [42].In this study,AND-MPN Ns were prepared to deliver hydrophobic anti-inflammatory drug and reduce inflammation efficiently.The significant anti-inflammatory effects of AND could be achieved by the highly stable and high DL capacity of AND-MPN Ns.The TA-Fe(III) complex (MPN) coats the drug particle and prepares stabilized AND-MPN Ns.First,the AND-MPN Ns were prepared by the general anti-solvent ultrasonication method (Fig.1).Formulations were optimized by changing the amount AND drug(2,5,10,20 mg) while maintaining the TA-Fe(III) at a constant value (approx.2:1 molar ratio).We obtained increased particle size and PDI with the increased amount of AND (Fig.2A).Then,we changed the molar concentration of TA to Fe(III) and kept a constant drug concentration (10 mg).Relatively small particle size and PDI of AND-MPN Ns were observed in the 2:1 TA to Fe(III) molar ratio compared to other TA to Fe(III) molar ratio containing ANDMPN Ns formulations (Fig.2B).Different ultrasonication power and time were used and observed a relatively small particle size at an ultrasonic power of 250 W in 10 min ultrasonication time compared to 200 W and 15 min (Fig.2C).After using various parameters to optimize the AND-MPN Ns,the parameter measured relatively small particle size,and less PDI value was utilized to prepare an optimized formulation.Small particle size and PDI value about 210.1 nm and PDI 0.161 were recorded using 10 mg drug loading,TA and Fe(III) molar ratio 2:1,and ultrasonication power 250 W and 10 min.Fig.2D showed the DLS particle size measurement of the optimized AND-MPN Ns.The TEM examination of the AND-MPN Ns confirmed the spherical morphology of optimized AND-MPN Ns with a 200–250 nm diameter (Fig.2E).The blue color of optimized AND-MPN Ns was observed due to the formation of TA and Fe(III)the complex (Fig.2F).After preparing AND-MPN Ns,free TA and Fe(III) present in AND-MPN Ns were removed by the ultracentrifugation method.These results demonstrated that the particle size is in the nano range,which is beneficial for targeting specific disease sites.And also,spherical morphology with a homogeneous distribution of drugs in nanosystems could improve the therapeutic effi-cacy of the drug in treating particular diseases.It has been demonstrated that Ns formulation compromises 100% drug particles in the nanosized range [15,43,44].However,the actual DL capacity of Ns should be known to confirm an optimal dosage regimen and reduce dose-related toxicities [41].The high DL capacity of Ns has shown a promising strategy to deliver insoluble drugs to the target sites.Furthermore,it is essential that anti-inflammatory agents successfully load into Ns to enhance the drug’s anti-inflammatory efficacy in the macrophages to treat inflammatory diseases.According to the UV-detector results,the DL capacity of the optimized formulation was approximately 87.6% ± 1.36%,with an EE of 99.2% ± 0.21%.The high EE% and DL% might be due to the robust intramolecular organization and adhesive properties of MPN and AND-MPN interactions.Interestingly,the DL capacity of ANDMPN Ns was significantly more than previously reported [45,46].
UV-spectrum results confirmed the formation of the TA and Fe(III) complex surrounding the AND Ns.As shown in Fig.S1A(Supporting information),optimized AND-MPN Ns and TA-Fe(III)complex showed a small peak at 556 nm,which proved that the strong interaction occurred between the TA and FeCl3·6H2O and confirmed the formation of MPN around the surface of Ns of AND.However,TA did not show any peak at 556 nm.This MPN formation onto the AND Ns prevented them from particle size growth and Ostwald ripening so that the AND-MPN Ns could be stable for the long term.PXRD experiment was performed to analyze the crystallinity of the drug in the AND-MPN Ns.The pure AND XRD pattern demonstrated sharp Bragg peaks at 2θequal to 9.88°,14.8°,19.86°,indicating the crystalline state of AND.In contrast,no noticeable peaks were appeared for the TA-Fe(III) complex,indicating the amorphous nature of the MPN.The freeze-dried AND-MPN Ns formulations showed peaks at 11.95° and 15.67° and a similar XRD pattern to pure AND powder but weakened intensity (Fig.S1B in Supporting information).Therefore,the PXRD record of the AND-MPN Ns preparations confirmed the microcrystalline state of AND in AND-MPN Ns.In the stability study,AND-MPN Ns were kept at 4 °C for a month,then particle size and PDI were examined at a pre-determined time interval.As seen in Fig.S1C (Supporting information),it was observed that particle size and PDI values of AND-MPN Ns were from 185.2±2.2 nm to 190±1.02 nm and 0.152±0.021 to 0.159±0.023,respectively after 28 days.These results demonstrated that the AND-MPN Ns were stable at 4 °C.In thein-vitrorelease study,the most widely used released media similar to physiological fluid 1% SDS containing PBS with different pH values were used.As shown in Fig.S1D (Supporting information),AND-MPN Ns reached release equilibrium after 48 h under different pH conditions.Approx.70.16%,86.1%,and 89.64% of AND were released within 48 h,at pH 5.5,6.8,and 7.4,respectively,with an initial burst of 39.2%,at pH 5.5,52.1% at pH 6.8,and 68.18%at pH 7.4 within 12 h.Additionally,the highest release of AND was recorded at 72 h with about 73.2%,86.12%,and 90.2% at pH 5.5,6.8,and 7.4,respectively.The results indicated that the drug release from AND-MPN Ns was pH-dependent due to the good solubility of AND at high pH compared to other low pH release media.
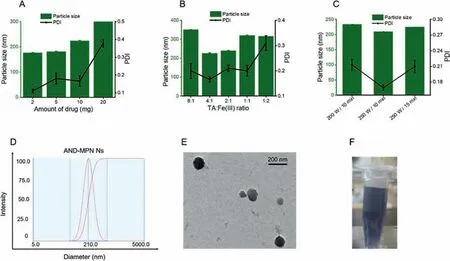
Fig.2.(A) Formulation optimization of AND-MPN Ns,the effect of drug concentration,(B) effect of TA and Fe(III) molar ratio and (C) effect of the ultrasonication time power on particle size and PDI (n=3).(D) Size distribution graph of optimized AND-MPN Ns.(E) TEM image of optimized AND-MPN Ns.(F) Optical image of AND-MPN Ns.
The cytotoxicity of MPN,free AND,and AND-MPN Ns against RAW264.7 cells was determined by MTT assay.AND-MPN Ns showed little cytotoxicity with a cell survival rate of 86.1% at 100 μg/mL AND concentration.The stabilizer TA-Fe(III) complex did not exhibit any cytotoxicity effect,indicating that the stabilizer is nontoxic to macrophages.While free drug AND showed a concentration-dependent cell cytotoxicity effect,i.e.,at 50 μg/mL and 100 μg/mL with cell viability rate 53.55% and 34.26%,respectively (Fig.S2A in Supporting information).The cellular uptake of FITC labeled AND-MPN Ns in RAW264.7 cells was observed quantitatively and qualitatively.Overall,FITC-AND-MPN Ns were taken up by the macrophages in a time- and concentration-dependent fashion.For time-dependent quantitative cellular uptake analysis,cells were incubated with FITC-AND-MPN Ns at fixed concentrations of FITC (7.5 μg/mL) for 0.5,1,2,4,6,and 8 h.For concentrations dependent uptake analysis,different concentrations (5,7.5,15,and 20 μg/mL) of FITC were added to the cultured cells and incubated for 4 h at 37 °C.Then,flow cytometry was used to determine the quantitative results of cellular uptake of ANDMPN Ns in cells.As shown in Figs.S2C and D (Supporting information),the uptake of AND-MPN Ns in cells was boosted within 1 h of treatment,and the uptake of AND-MPN Ns has reached equilibrium within 1–2 h.Figs.S2E and F (Supporting information) showed that the cellular uptake of prepared formulations in cells was depended on the FITC concentrations.Among all concentrations,the highest concentration of FITC containing ANDMPN Ns,i.e.,20 μg/mL,showed the highest cellular uptake effect,which confirmed the cellular uptake AND-MPN Ns was dependent on concentrations of the drug in AND-MPN Ns.CLSM assayed qualitative uptake of AND-MPN Ns in RAW264.7 cells.From the CLSM results,the robust intracellular green fluorescence around the round nuclei was observed within 1 h of treatment with ANDMPN Ns compared to 2 h and 4 h treatment (Fig.S2B in Supporting information).This result indicated that the AND-MPN Ns were quickly endocytosed into the macrophages.This fast intracellular uptake of AND-MPN Ns could be due to the small size and spherical shape of the AND-MPN Ns.Therefore,the significant efficacy of macrophages to FITC-AND MPN Ns uptake within a short period could enhance the drug’s therapeutic effectiveness for treating inflammation.
Two phenotypic proteins CD206 and INOS,are highly expressed in M2 and M1 phenotype macrophages,respectively [47].The phenotypic shift effect of AND-MPN Ns in macrophages was determined by IF assay.Quantitative and qualitative expression of two proteins CD206 and INOS,in macrophages were detected.As shown in Figs.3A and B,AND-MPN Ns produced the prior effects to increase the M2 phenotype CD206.In contrast,the PBStreated cell group showed low phenotype CD206 expression compared with both AND-MPN Ns and free AND treatment.AND-MPN Ns were enabled a ~2-fold increase in the expression of CD206 over free AND.Furthermore,inflammatory phenotype AND-MPN Ns significantly downregulated INOS expressions and free AND drug,compared with PBS treatment (Figs.3C and D).These results indicated that AND-MPN Ns exhibited potent anti-inflammatory activityviaa phenotypic shift from macrophage M1 to M2.
The AND drug has been approved as traditional Chinese medicine (TCM),exhibits a potent anti-inflammatory effect.Several pro-inflammatory cytokines,such as IL-6 and TNF-α,are released on the injured artery.Eventually,the large number of these cytokines leads to the progression of inflammatory diseases[48].The anti-inflammatory effects of AND-MPN Ns on reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and TNF-αlevels were observed by ELISA analysis.After treating different cell groups with ANDMPN Ns and free drug AND,IL-6 and TNF-αwere measured.The data in Figs.4A and B indicated that the IL-6 and TNF-αlevels were markedly decreased by high dose (50 μg/mL) and low dose(25 μg/mL) AND-MPN Ns compared to other treated groups,including high dose and low dose free drug.These results indicated that the AND-MPN Ns could inhibit IL-6 and TNF-αwith high efficacy and lease the inflammation effectively.These results could be due to the high DL capacity of AND-MPN Ns,enhanced cellular uptake by cells,and sustained drug release.AND has shown a significant anti-inflammatory property by inhibiting the activation of the NF-B signaling pathway [49].To examine the underlying mechanism associated with anti-inflammation induced by AND,we performed WB assay.Phospho-NF-κB-p65 protein expression in LPS induced RAW264.7 cells was measured.WB result demonstrated that the expression level of phospho-p65 was markedly downregulated in both high doses (50 μg/mL) and low doses (25 μg/mL)in AND-MPN Ns treated RAW264.7 cells (Figs.4C and D).In contrast,the phospho-NF-κB-p65 expression level was reduced at the deficient level in both high dose and low dose free drug-treated RAW264.7 cells.These results indicated that AND-MPN Ns could effectively block the NF-κB signal pathway activation by downregulating the overexpressed protein phospho-NF-kB p65 protein in LPS activated RAW264.7 cells.Overall,these results proved that the AND-MPN Ns showed potent anti-inflammatory activity over free AND drugs.This result could be due to the high DL capacity,good drug release effect of AND-MPN Ns in macrophages.The enhanced anti-inflammation could also be ascribed to the sustained drug release from drug nanocrystals after uptake.Previous intracellular fate studies demonstrated that drug nanocrystals could constantly release drug within several hours after cell entering and,as a result,improve the effectiveness of an anti-inflammatory drug[22,44,49].
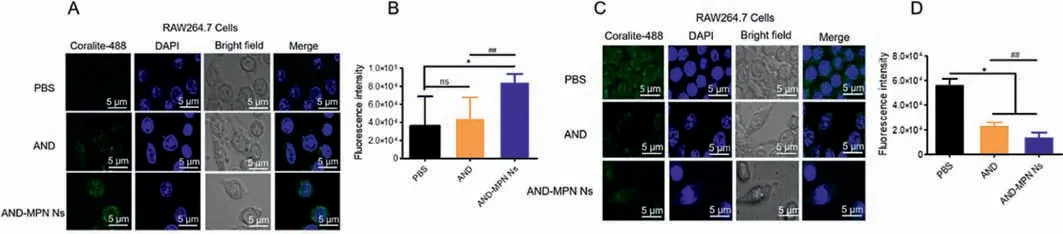
Fig.3.Phenotypic shift study in-vitro.IF and quantitative analysis of CD206 (A,B) and INOS (C,D) expression on RAW 264.7 cells after treatment (n=3,*P<0.05 compared to PBS group; ns,not significant; ##P<0.01 as compared to AND).DAPI (blue) was used to stain the nuclei,and CoraLite-488 conjugated antibody (green) stained CD206 and INOS.The scale bar is 5 μm.
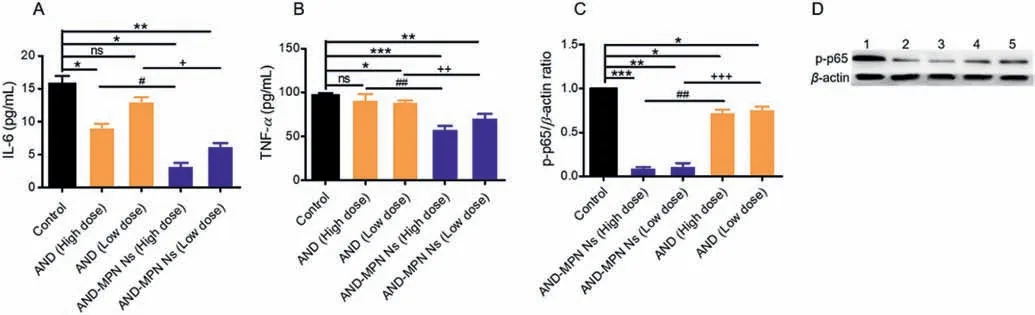
Fig.4. In-vitro anti-inflammatory activity.(A) IL-6 and (B) TNF-α concentration in RAW264.7 cells determined by ELISA assay.The LPS stimulated RAW264.7 cells were incubated with free drug (AND) and AND-MPN Ns at AND concentration of 25 μg/mL (low dose) and 50 μg/mL (high dose) for 12 h at 37 °C.Western blot assay (C,D)evaluating p65 phosphorylation in RAW264.7 cells after treatment with the drug formulations at AND concentration 25 μg/mL (low dose) and 50 μg/mL (high dose). n=3,*P<0.05,**P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 as compared to the control group; ns,not significant; #P<0.05,##P<0.01 as compared to AND high dose; +P<0.05,++P<0.01,+++P<0.001 as compared to AND low dose.The internal control for normalizing protein expression was β-actin.Formulations: 1,Control; 2,AND-MPN NS (50 μg/mL); 3,AND-MPN NS (25 μg/mL); 4,AND (50 μg/mL); 5,AND (25 μg/mL).
In this study,AND-MPN Ns were fabricated to deliver hydrophobic anti-inflammatory drug (AND) to treat macrophagemediated inflammation.The highly stable AND-MPN Ns were obtained by using MPN as a stabilizer.AND-MPN Ns were a blue in color and homogeneous nanosuspension with 210.1±0.77 nm particle size,0.161±0.001 with spherical morphology.Thein-vitroanti-inflammatory study results demonstrated the potent antiinflammation effect of AND-MPN Ns in LPS induced RAW264 cellsviamacrophage polarization and reduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6 and TNF-α) and suppression of NF-κB signal pathway activation.Consequently,AND-MPN Ns revealed excellent therapeutic effect by enhancing anti-inflammatory action,which proved to be a potential strategy for alleviating inflammation.
Declaration of competing interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos.81872823 and 82073782),the Shanghai Science and Technology Committee (No.19430741500),the Key Laboratory of Modern Chinese Medicine Preparation of Ministry of Education of Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,China(No.zdsys-202103).
Supplementary materials
Supplementary material associated with this article can be found,in the online version,at doi:10.1016/j.cclet.2022.04.051.
 Chinese Chemical Letters2023年1期
Chinese Chemical Letters2023年1期
- Chinese Chemical Letters的其它文章
- Diabetic wound healing activated by supramolecular cascade reaction
- MBenes: Two-dimensional transition-metal borides with ordered metal vacancies
- Wet-adhesive materials of oral and maxillofacial region: From design to application
- Diverse catalytic systems for nitrogen-heterocycle formation from O-acyl ketoximes
- Fluorine-containing drugs approved by the FDA in 2021
- The development and application of dual-comb spectroscopy in analytical chemistry
