Identification of cadmium containing metabolites in HepG2 cells after treatment with cadmium-selenium quantum dots
Beibei Chen,Lu Peng,Man He,Chuan Wang,Bin Hu
Department of Chemistry,Wuhan University,Wuhan 430072,China
Keywords:CdSe/ZnS quantum dots Cd speciation Metallothionein Cells High performance liquid chromatography Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry
ABSTRACT The transformation of quantum dots (QDs) by organisms has attracted broad attention but remains unclear.Understanding of the metabolites helps to reveal the transformation pathway of QDs.Cd containingmetallothionein (MT) are the main species formed by Cd released from CdSe QDs in HepG2 cells,while speciation analysis of Cd containing MTs remains a challenge because MTs has several subisoforms and can bind with several metals.Herein,we built a hyphenated platform for speciation analysis of QDs in HepG2 cells after treatment with CdSe/ZnS QDs.The Cd-containing MTs were separated in reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) and subsequently online detected by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) and electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (ESI-Q-TOF-MS) parallelly.Four groups of Cd-containing metabolites were found by detecting Cd in ICP-MS.Their structures were identified in ESI-Q-TOF-MS and further confirmed with standards of four subisoforms of MT,including N-terminal acetylation MT2a,N-terminal acetylation MT1e,N-terminal acetylation MT1g and MT1m.Each group of them contains various stoichiometry of Cd/Zn.The metabolites of QDs remain same while the concentrations of each metabolite and its stoichiometry of Cd/Zn vary for different incubation concentration/time.This work provides a new parallel hyphenation technique of HPLC-ICP-MS/ESI-MS with high separation resolution and powerful detection ability,and the obtained results provide detailed metabolism information of QDs in HepG2 cells after treatment of CdSe/ZnS QDs,contributing to deep exploration of the functional mechanisms of QDs in organisms.
Nanoparticles (NPs) have been widely used in bioimaging,biosensors,disease diagnosis and drug delivering [1–5],in which quantum dots (QDs) are a special kind of with unique fluorescence advantages [6].However,with the rapid development of QDs-related nanotechnology,the health effect of QDs to human being has become a non-ignorable issue,and the biosafety of QDs remains unclear because little is known about the functional mechanism of QDs.The recent mechanism studies of QDs toxicity found QDs-mediated reactive oxygen species (ROS) induction was an important pathway to generate cytotoxicity [7,8].Cd could be released from the QDs in living cells [9,10],which further induce oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage in cells [11].Thus,understanding the metabolism of QDs could reveal the basis of cytotoxicity of QDs.
The decomposition of Cd-QDs in living cells or organism was obtained by many researches [12–14].However,little is known about the existing species and the trans-formation of Cd after its release from QDs in cells,which significantly affect the transport,metabolism,accumulation and ultimate toxicity of QDs.In our previous study,the existing forms of CdSe/ZnS QDs in HepG2 cells after co-incubation was explored by hyphenated techniques;two species were found and identified as QD-like NPs and Cd containing-metallothionein fraction (MT-F),respectively [15].For the MT-F,it was assumed to be formed by Cd released from QDs with MTs in HepG2 cells; while more detailed information is required.
The hyphenation techniques combining high resolution separation tools such as high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)with high sensitivity detectors such as inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) are effective way for elemental speciation.And utilization of molecular MS is a good choice for identification of unknown species.However,speciation analysis of MTs is still difficult because MTs has several subisoforms with similar retention behavior and can bind with several metals with different molar ratio.Coupling HPLC with ICP-MS and electrospray ionization (ESI)-MS in parallel were shown to be an attractive technique to separate and identify individual MT isoforms [16,17].However,reports on online parallel connection of ICP-MS and ESI-MS as HPLC detectors are few,and the analytical performance should be further improved.
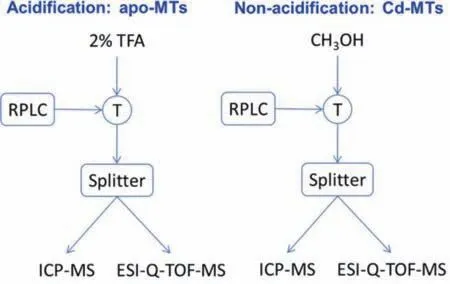
Fig.1.Schematic diagram of HPLC-ICP-MS/ESI-Q-TOF-MS analysis (operation conditions listed in Table S1 in Supporting information).
Herein,to reveal the transformation of Cd released from QDs in HepG2 cells,an on-line hyphenated technique of HPLC-ICP-MS/ESI- quadrupole time-of-flight (Q-TOF)-MS parallel measurement was developed for speciation of Cd containing-MTs,including the subisoforms of MTs and the Cd/MTs molar ratio.Four kinds of CdSe/ZnS QDs with different particle sizes (hydrodynamic diameter ofca.17–23 nm) and functional groups (carboxyl or amino functional group) (namely NH2-525,NH2-585,NH2-625,COOH-525)were used to incubated with HepG2 cells as the same in our previous studies [15,18],and the MT-F fraction after size exclusion chromatographic separation was collected for HPLC-ICP-MS/ESI-Q-TOFMS analysis.The analytical strategy was illustrated in Fig.1.After HPLC separation,the effluent with/without acidification was analyzed by ICP-MS and ESI-Q-TOF-MS simultaneously.Parallel measurement enabled monitoring elemental information of Cd by ICPMS and mass information of Cd-MTs in MT-F by ESI-Q-TOF-MS simultaneously.With post-column acidification,MTs subisoforms were demetallated as apo-MTs which facilitates identification of the involved MTs subisoforms by ESI-Q-TOF-MS.Without postcolumn acidification,mass spectra of metallated-metallothioneins(M-MTs) would be provided by ESI-Q-TOF-MS.Compared the mass to charge ratio of M-MTs to corresponding apo-MTs,the molar ratio of Cd binding on MTs could be obtained.
Taking MT-F of NH2–525 (termed as NH2-525-F) as the representative,the speciation results obtained for NH2-525-F were analyzed and specified as follows.Firstly,result obtained by ICP-MS detection without post-column acidification was analyzed to investigate the Cd containing species in NH2-525-F.As can be seen from the chromatogram for ICP-MS detection of Cd and total ion chromatogram (TIC) of ESI-Q-TOF-MS detection in Figs.2A and B,four chromatographic peaks were observed in NH2-525-F.These peaks with retention time at 1050,1420,1960 and 2240 s were named as Metabolite 1,2,3,and 4,respectively.
Secondly,result obtained by ESI-Q-TOF-MS detection with postcolumn acidification was analyzed to investigate the MS information of apo-MTs subisoforms in Metabolites 1–4.The mass result of apo-MTs in Metabolites 1–4 is shown in Fig.3A.To verify the MTs subisoforms in Metabolites 1–4,all the apo-MTs in human beings with possible post-modification sites (such as acetylation) from Uniprot database (http://www.uniprot.org/) were selected as candidates.The mass-charge ratio of the measured value(m/zmeasured,z=4) was compared with the mass-charge ratio of the theoretical value (m/ztheoretical,z=4) of the apo-MTs in human beings.Four subisoforms of apo-MTs,N-terminal acetylation MT2a (N Ac-MT2a),N-terminal acetylation MT1e (N Ac-MT1e),Nterminal acetylation MT1g (N Ac-MT1g) and MT1m (detailed properties listed in Table S2 in Supporting information),were obtained in corresponding retention time of Metabolites 1–4,respectively.The measured mass accuracies are all below 20 ppm and the detail results are listed in Table 1.Meanwhile,the extracted ion chromatogram (EIC) of the four apo-MTs was analyzed (Fig.3B).All the retention time of four apo-MTs in EIC were the same to the result of Metabolites 1–4 in ICP-MS,which further confirmed the one-toone correspondence between apo-MTs and Metabolites 1–4.
Thirdly,result obtained by ESI-Q-TOF-MS detection without post-column acidification was analyzed to investigate the MS information of Cd-MTs in Metabolites 1–4.The mass result of Cd-MTs in Metabolites 1–4 is shown in Figs.4A–C.After identification of the subisoforms of apo-MTs for Metabolites 1–4,corresponding Cd-MTs were selected as candidates for comparison,and the total molar ratio of Cd and Zn to MT was fixed as 7.The mass-charge ratio (m/z) of the measured value (m/zmeasured,z=5) was compared with them/zof the theoretical value (m/ztheoretical,z=5) of corresponding Cd-MTs candidates in human beings.The measured mass accuracies are all below 20 ppm and the detail results are listed in Table 1.As can be seen,Metabolites 1–4 are Cd,Zn-MTs complex which are formed by different molar ratio of Cd/Zn (3:4,4:3,5:2 and 6:1) with N Ac-MT2a,N Ac-MT1e,N Ac-MT1g and MT1m,respectively.Four group peaks with retention time at 1000,1400,2000 and 2200 s were also detected in MT-F for COOH-525,NH2-585 and NH2-625 QDs incubated cells,as shown in Figs.S1–S12(Supporting information).Components of COOH-525-F,NH2-585-F and NH2-625-F are presented in Tables S3–S5 (Supporting information).Similarly to that observed for NH2-525-F,Cd,Zn-MTs complex are formed by different molar ratio of Cd/Zn with N Ac-MT2a,N Ac-MT1e,N Ac-MT1g and MT1m for Metabolites 1–4,respectively.
The MT2a,MT1e,MT1g and MT1m related genes are considered to be highly expressed in HepG2 cells [19,20].Moreover,the expression protein of these MT-genes has high affinity for several heavy-metal ions including Cd and Zn.In this work,Metabolites 1–4 was separated by HPLC in order of the hydrophobicity properties of MTs subisoforms as predicted by grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY).When the value of GRAVY is positive,the larger the value is,the stronger the hydrophobicity is.The GRAVY value of MT2a,MT1e,MT1g and MT1m is increased from 0.131 to 0.269 in turn; it coincides the order in which Metabolites 1–4 was eluted in HPLC.Meanwhile,the information of M-MTs in Metabolites 1–4 obtained by HPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS without post-column acidification indicated the molar ratio between metals and MTs was 7:1;Cd and Zn,with the molar ratio of 2:5 to 7:0,were combined together with N Ac-MT2a,N Ac-MT1e,N Ac-MT1g and MT1m in Cd-MTs,respectively.Among them,molar ratio of 4:3 and 5:2 were the largest existing species,followed by molar ratio of 3:4 and 6:1,and the molar ratio of 2:5 and 7:0 were the least.MTs commonly consist of two subunits:α-domain (C-terminal) andβ-domain (Nterminal) [21].MTs can always incorporate with seven divalent metals (Cd,Zn,etc.) per molecule,providing a highly dynamic,regulated,and uniquely biological metal buffer [22].In vitroandin vivo,MTs exist mainly in Zn form or as mixed-metal proteins[21–23].Previous studies have demonstrated that Cd can displace Zn in MTs and form mixed Cd,Zn-MTs [24–27],because the binding constants for Cd with MTs is commonly two orders of magnitude more than that for Zn [21,23].Thus,in this work,the Cd released from QDs was combined with four MTs subisoforms,forming several different kinds of Cd,Zn-N Ac-MT2a,Cd,Zn-N Ac-MT1e,Cd,Zn-N Ac-MT1m and Cd,Zn-MT1m species in HepG2 cells.Meanwhile,the QDs used in this work consisted of ZnS shell and CdSe core,suggesting that a degradation of ZnS shell was a prerequisite for the decomposition of CdSe core.Thus,when Cd was released from QDs,Zn had been released from ZnS shell to a more extent.As a result,Cd,Zn-MTs with median molar ratio of Cd/Zn(4:3 and 5:2) were the main existing species in Metabolites 1–4,which is the evident that Cd(II) binds with stronger affinity than Zn(II) to MT,implying possible toxicity of the degraded Cd from QDs.
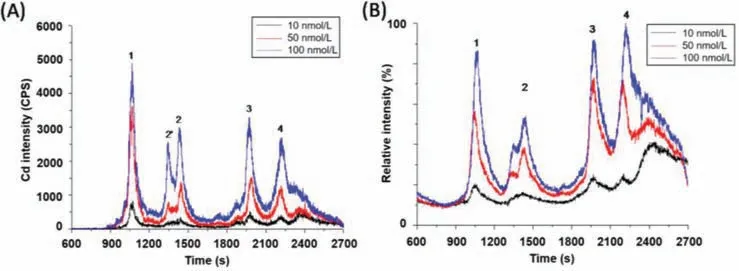
Fig.2.HPLC-ICP-MS/ESI-Q-TOF-MS analysis of NH2-525-F under different incubation concentrations without post-column acidification.(A) ICP-MS detection of Cd; (B) TIC of ESI-Q-TOF-MS detection.1–4 represent for Metabolites 1–4,respectively.
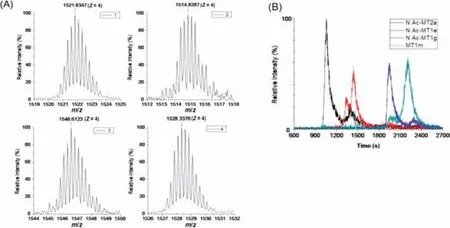
Fig.3.MS spectra (A) and EIC (B) of 1521.8347 (z=4),1514.8184 (z=4),1546.66086 (z=4) and 1528.3376 (z=4) for Metabolites 1–4 in NH2-525-F (100 nmol/L) with post-column acidification.1–4 represent for Metabolites 1–4,respectively.
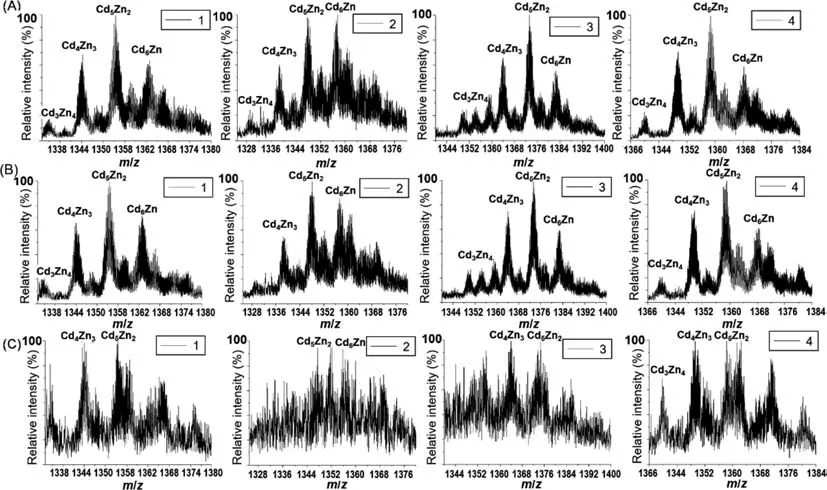
Fig.4.MS spectra of Metabolites 1–4 in NH2-525-F without post-column acidification under different incubation concentrations.(A) 100 nmol/L,(B) 50 nmol/L and (C)10 nmol/L.1–4 represent for Metabolites 1–4.
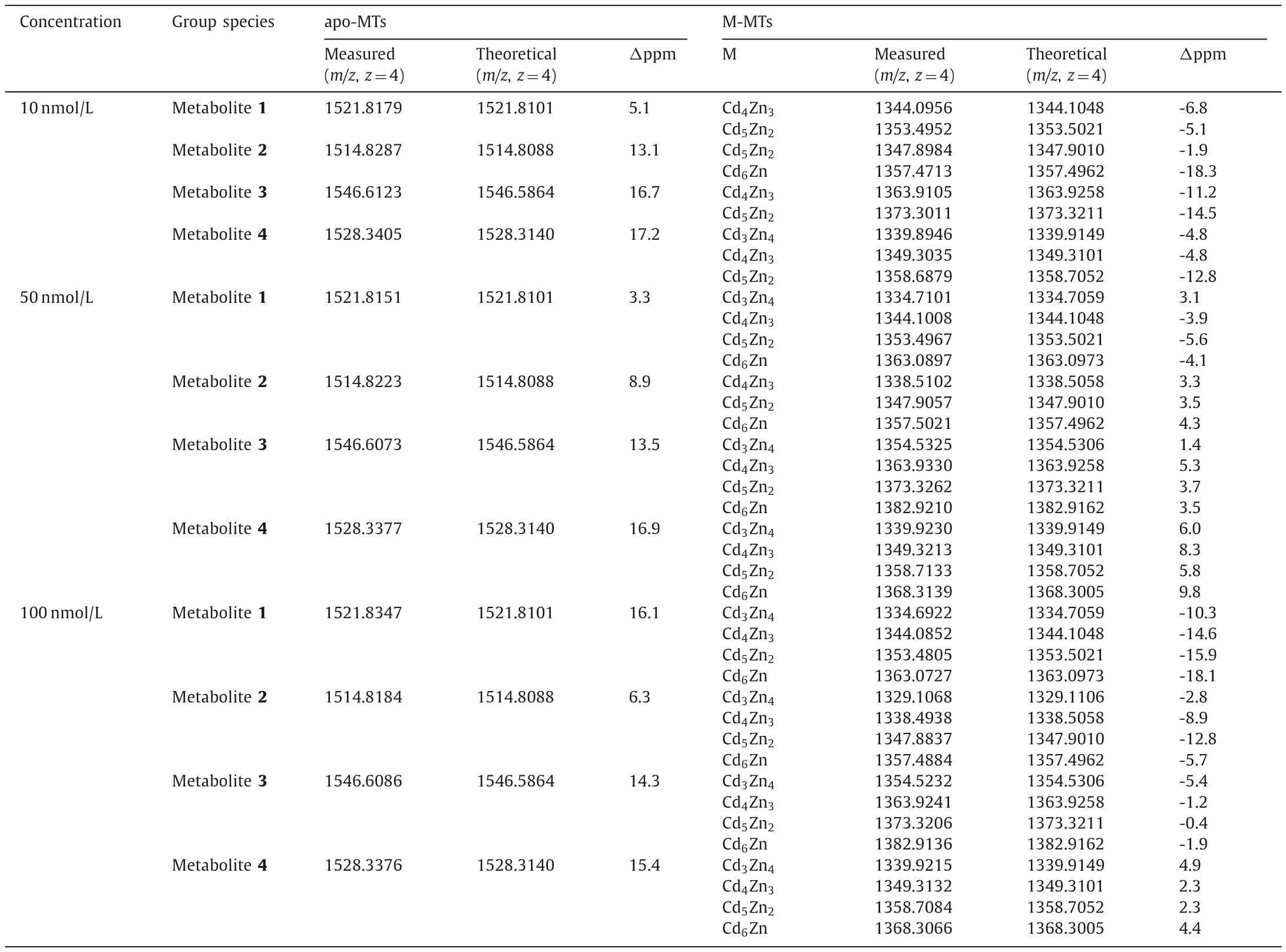
Table 1 MS information of NH2-525-F under different incubation concentrations.
The variation of Cd-MTs components in cells after incubating with different concentration /time and eliminating for different time was investigated (results shown in Figs.S13–S44 and Tables S6–S13 in Supporting information).Four species,Metabolites 1–4,occurred whichever concentration/time was employed; while,the intensity of Metabolites 1–4 is quite different when the incubation conditions was varied.For four QDs incubation,the intensity of Metabolites 1–4 all rose up when QDs incubation concentrations were increased,which was verified by ICP-MS and ESI-Q-TOF-MS measurement simultaneously.Meanwhile,larger numbers of Cd-MTs in Metabolites 1–4 were found with the increase of incubation concentrations.It was demonstrated that the amount of CdSe/ZnS QDs in cells increased with increasing the incubation concentrations and more Cd was released from QDs [15].Since MT-F was the sum of Metabolites 1–4,these results confirmed the variation tendency of MT-F amount under different incubation concentration in our previous study [15].Similar results were found under different incubation time.Metabolites 1–4 all increased and growing numbers of M-MTs species in Metabolites 1–4 were obtained when the incubation time was extended,due to the increasing release of Cd from original QDs in cell matrix.
Meanwhile,the analytical results,obtained for Cd-MTs components after eliminating for a certain time,showed that the intensity of Metabolites 1–4 in three MT-F groups (NH2-525-F,COOH-525-F,NH2-625-F) all increased firstly (0–12 h) and then decreased(12–48 h); a little difference was obtained for NH2-585-F,the intensity of Metabolites 1–4 decreased over all the time.It is probably ascribed to the relatively slow degradation rate for NH2-585 QDs [15],and the resulting slow Cd releasing from QDs in cells.The difference needs to be further investigated.The number of MMTs species in Metabolites 1–4 decreased with elimination time increasing from 0 h to 48 h.
In conclusion,we built an on-line parallel hyphenation technique of HPLC-ICP-MS/ESI-Q-TOF-MS for speciation analysis of Cd in MT-F fraction collected from HepG2 cells incubated with CdSe/ZnS QDs.Four group species,Metabolites 1–4,were obtained in MT-F and they were confirmed to be Cd,Zn-MTs complex formed by different molar ratio of Cd/Zn with N Ac-MT2a,N Ac-MT1e,N Ac-MT1g and MT1m,respectively.Meanwhile,Metabolites 1–4 was also observed in MT-F when different incubation concentration/time and elimination time was employed.The intensity of Metabolites 1–4 all increased and more Cd,Zn-MTs species in each peak were obtained with increasing the incubation concentration/time.This work proposed a MS-based hyphenated platform with improved performance for metallomics research,and the obtained results provided worthwhile information for the transformation of CdSe QDs in cells,greatly contributing to the elucidation of metabolism and toxicity of QDs.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Acknowledgments
The financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos.21575107,21775113,21575108),the Science Fund for Creative Research Groups of NSFC (No.20921062) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No.114009) are greatly acknowledged.
Supplementary materials
Supplementary material associated with this article can be found,in the online version,at doi:10.1016/j.cclet.2022.02.067.
 Chinese Chemical Letters2023年1期
Chinese Chemical Letters2023年1期
- Chinese Chemical Letters的其它文章
- Diabetic wound healing activated by supramolecular cascade reaction
- MBenes: Two-dimensional transition-metal borides with ordered metal vacancies
- Wet-adhesive materials of oral and maxillofacial region: From design to application
- Diverse catalytic systems for nitrogen-heterocycle formation from O-acyl ketoximes
- Fluorine-containing drugs approved by the FDA in 2021
- The development and application of dual-comb spectroscopy in analytical chemistry
