Undetected traumatic cardiac herniation like playing hide-and-seekdelayed incidental findings during surgical stabilization of flail chest:A case report
Su Young Yoon, Jin-Bong Ye, Junepill Seok
Su Young Yoon, Junepill Seok, Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Cheongju 28644, South Korea
Jin-Bong Ye, Department of Trauma Surgery, Chungbuk National University Hospital,Cheongju 28644, South Korea
Abstract BACKGROUND Post-traumatic blunt pericardial injury is a rare condition with only a few reported cases which were generally diagnosed during initial examinations upon admission. However, pericardial injuries not bad enough to dislocate the heart may only cause intermittent electrocardiogram (ECG) changes or be asymptomatic.CASE SUMMARY In this case, we report a blunt pericardial injury undetected on preoperative transthoracic echocardiography and chest computed tomography. We misjudged intermittent ECG changes and blood pressure fluctuations as minor symptoms resulting from cardiac contusion and did not provide intensive treatment. The pericardial injury was found incidentally during surgical stabilization of rib fractures and was successfully repaired.CONCLUSION Post-traumatic blunt pericardial ruptures should be considered in patients with blunt chest trauma showing abnormal vital signs and ECG changes.
Key Words: Cardiac herniation; Flail chest; Multiple rib fractures; Pericardial rupture;Surgical stabilization of rib fractures; Case report
INTRODUCTION
Post-traumatic blunt pericardial injury is rare but has occasionally been reported[1-4]. Once diagnosed, surgical repair is mandatory as this condition can trigger devastating complications[5,6]. However, in some cases, cardiac herniations may be misdiagnosed or masked by concomitant injury. In this case report, we share our experience with a blunt pericardial rupture with no specific symptoms apart from intermittent electrocardiogram (ECG) changes; the case was undiagnosed even after chest computed tomography (CT) and transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) in the preoperative period.
CASE PRESENTATION
Chief complaints
A 46-year-old male patient who was involved in a motor vehicle accident presented with a left abdominal wall injury and severe chest pain.
History of present illness
The patient had no specific history of present illness.
History of past illness
The patient had no specific history of past illness.
Personal and family history
The patient had no personal or familial disease.
Physical examination
Tenderness and rebound tenderness were observed in the lower left quadrant of the abdomen. Crepitus and tenderness were present in the left chest wall, accompanied by decreased breath sounds. Symmetrical chest wall expansion during breathing was observed with no initial flail motion.
Laboratory examinations
Initial arterial blood gas analysis showed a pH of 7.4, PO2of 80.3 mmHg, and PCO2of 34.0 mmHg on room air. Cardiac enzymes were elevated at troponin T 244 ng/L (normal range: < 14 ng/L), CK-MB 23.32 ng/L (normal range: < 4.94 ng/L), and CPK 4176 U/L (normal range: 58–348 U/L).
Imaging examinations
Chest CT revealed multiple rib fractures with hemopneumothorax in the left hemithorax. No abnormalities were observed in the mediastinum. Abdominal CT revealed a bowel herniation through an abdominal wall defect. The initial ECG showed an elevated ST segment in the anterior leads; however, it was deemed to be insignificant (Figure 1).
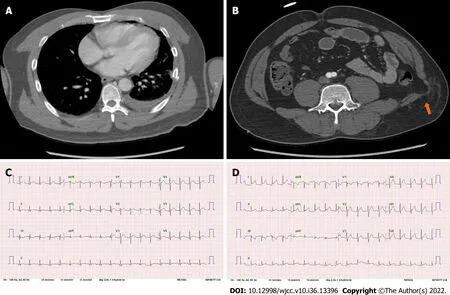
Figure 1 Computed tomography scan. A: Initial chest contrast computed tomography (CT) showing traumatic hemothorax, with no evidence of heart injury; B:Initial abdominal contrast CT showing visceral herniation through an abdominal wall defect (orange arrow); C: The initial electrocardiogram (ECG) showed widespread abnormal findings, but did not meet the criteria for myocardial infarction (MI); D: ECG performed later when the patient showed fluctuating systolic blood pressure. The ECG showed prominent ST changes with depressions at the lead III, aVR, and V1, which are not the classical reciprocal ECG changes seen in MI.
Diagnosis at initial presentation
The patient was initially diagnosed with multiple rib fractures and hemopneumothorax in the left chest. Panperitonitis due to bowel perforation was suspected, and blunt cardiac contusion was considered highly likely.
Initial treatment
A 24-French thoracic drainage catheter was placed, and the hemothorax was confirmed to be minor. Despite the perioperative risks associated with cardiac contusions, the patient underwent emergent surgery to rule out abdominal organ injuries. The peritoneum was intact, and no significant findings were observed except for several pelvic muscle tears.
Postoperative care in the surgical intensive care unit (SICU) was provided as usual. Blood tests for elevated cardiac enzymes were repeated every 4 h and showed gradual improvement. The patient did not complain of worsening chest pain, which was successfully controlled with analgesics. However, the patient’s systolic blood pressure fluctuated intermittently with prominent ECG changes. Although the changes were not the classical reciprocal findings observed for the myocardial infarction (MI), we still found it necessary to confirm the patient’s cardiac condition (Figure 1).
On Day 2 of hospitalization, TTE was performed to check for cardiac conditions. The patient was confirmed to have neither pericardial fluid collection nor abnormal cardiac movements. The patient’s ECG remained variable, fluctuating from normal to prominent ST elevations, and we regarded these findings as non-meaningful and indicative of the usual transient changes after cardiac contusion.
On Day 3 of hospitalization, the patient complained of dyspnea and difficulty with expectoration. Paradoxical asymmetric chest wall motion was newly observed on the left anterior chest wall to the extent where the chest wall moved in rhythm with the patient’s heartbeat. Despite proper support, including higher oxygen supplementationviaa high-flow nasal cannula, the patient’s condition gradually deteriorated. Follow-up chest CT revealed a worsening lung condition. However, the mediastinum was relatively clear (Figure 2). After thoroughly discussing the risks associated with cardiac contusions with anesthesiologists, we decided to perform surgical stabilization of rib fractures (SSRF).
Additional diagnosis during hospitalization and current problem list
A flail chest due to multiple rib fractures and blunt cardiac contusion were considered as additionally diagnosed conditions.
Additional treatment
The patient underwent SSRF on Day four of hospitalization. The surgery was performed routinely under general anesthesia with a single endotracheal intubation, with the patient placed in the 45-degree semi-lateral right decubitus position. An anterolateral thoracotomy was performed in the fifth intercostal space from the median border of the left pectoralis major muscle to the mid-axillary line. After opening the fifth intercostal space, a large hole was identified in the pericardium (Figure 3). The inferolateral left ventricular wall was visible through the hole and was covered by a thin whitish fibrin clot. We explored the pericardial space with an index finger and confirmed no apparent abnormalities.
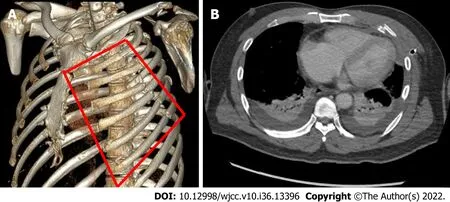
Figure 2 3-dimensional contrast chest computed tomography. A: A 3-dimensional (3D) contrast chest computed tomography (CT) with rib rendering. The anterolateral flail segment (indicated by the red lines) was located on the left rib cage; B: An axial cut of the 3D chest CT showing bilateral pleural effusion with collapsed lungs, with no evidence of heart injury.
FINAL DIAGNOSIS
Post-traumatic pericardial rupture with a flail chest by multiple rib fractures.
TREATMENT
The pericardium was subsequently repaired with 4-0 Prolene sutures. After stabilizing the fractured ribs with plates and screws and closing the wound, the patient was transferred to the SICU in stable condition.
OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP
The patient was successfully weaned off the mechanical ventilator two days following the operation (Day 5 of hospitalization). The postoperative ECG findings were still abnormal but had improved (Figure 3), and the patient was transferred to the general ward on Day 7 of hospitalization.
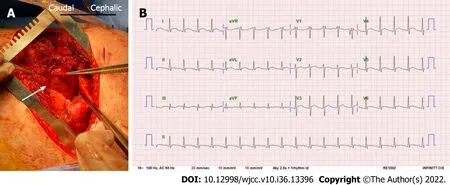
Figure 3 Rib examination. A: The operation field during surgical stabilization of rib fractures. We routinely performed a thoracic cavity exploration before fixing the rib fractures. The white arrow indicates that the left ventricle was visible through the 4 cm × 4 cm pericardial rupture, which was an incidental finding; B: The postoperative electrocardiogram with the resolution of all ST depressions and lower ST elevations than that present in the preoperative period.
DISCUSSION
In most cases, pericardial ruptures are diagnosed or suspected on chest CT on admission. Pneumo- or hemopericardium strongly suggests heart damage; therefore, these are considered strong indicators that intensive treatment, such as surgery, will be required. However, in the classification of traumatic cardiac dislocations proposed by Graefet al[3], grade I pericardial rupture without dislocation of the heart can barely be detected on CT scans, and entirely secondary findings in patients with a diaphragm with intrathoracic herniation of abdominal organs can be diagnosed by chest radiography or CT[7]. Similarly, in our case, no preoperative examination suggested pericardial rupture. In cases of silent pericardial rupture accompanied by intermittent symptomatic cardiac herniation, as in our patient, it was almost impossible to suspect pericardial rupture until a thoracotomy was performed. If the patient had not worsened due to a flail chest, the probability of finding pericardial rupture would have been extremely low.
Mottoet al[8] reported that cardiac herniation could be intermittent; therefore, sequential evaluation is recommended. We performed serial laboratory follow-ups for elevated cardiac enzyme levels, consecutive chest CTs, and preoperative TTE. In our case, however, the pericardial hole was only 4 cm × 4 cm and was too narrow to cause a severe symptomatic cardiac herniation. Instead, we hypothesized that it may have caused intermittent ECG changes and vital instability, resembling MI. In addition, pain from the patient’s rib fractures may have masked chest discomfort due to cardiac herniation. Many patients with cardiac contusions show elevated cardiac enzyme levels and abnormal ECG findings[9]. Finally, we deemed these findings to be typical of cardiac contusions, which do not require treatment. However, we believe that this case may not be unique, and such a mistake is common in practice.
CONCLUSION
Post-traumatic blunt pericardial rupture is a rare but fatal injury that is usually diagnosed by CT upon admission but may be asymptomatic and misdiagnosed. If a patient with blunt chest trauma shows fluctuating vital signs and accompanying ECG abnormalities, pericardial rupture and cardiac herniation should be considered.
FOOTNOTES
Author contributions:Seok J and Yoon SY wrote and revised the manuscript; Seok J, Yoon SY, and Ye JB contributed the patient care and management; Ye JB performed the initial emergency operation to rule out abdominal organ injuries; Seok J and Yoon SY performed thoracic surgery, including the pericardial repair and surgical rib fixations.
Informed consent statement:All study participants or their legal guardian provided informed written consent about personal and medical data collection prior to study enrolment.
Conflict-of-interest statement:All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
CARE Checklist (2016) statement:The authors have read the CARE Checklist (2016), and the manuscript was prepared and revised according to the CARE Checklist (2016).
Open-Access:This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BYNC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is noncommercial. See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Country/Territory of origin:South Korea
ORCID number:Su Young Yoon 0000-0001-9264-1371; Jin-Bong Ye 0000-0002-5597-4502; Junepill Seok 0000-0002-9010-6495.
S-Editor:Fan JR
L-Editor:A
P-Editor:Fan JR
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年36期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年36期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Liver injury in COVID-19: Holds ferritinophagy-mediated ferroptosis accountable
- Amebic liver abscess by Entamoeba histolytica
- Living with liver disease in the era of COVID-19-the impact of the epidemic and the threat to high-risk populations
- Cortical bone trajectory screws in the treatment of lumbar degenerative disc disease in patients with osteoporosis
- Probiotics for preventing gestational diabetes in overweight or obese pregnant women: A review
- Effectiveness of microwave endometrial ablation combined with hysteroscopic transcervical resection in treating submucous uterine myomas
