三相永磁同步电机单电流传感器矢量控制策略
许观达,肖 飞,连传强,刘计龙
三相永磁同步电机单电流传感器矢量控制策略
许观达,肖 飞,连传强,刘计龙
(海军工程大学舰船综合电力技术国防科技重点实验室,湖北 武汉 430033)
为提高三相永磁同步电机单电流传感器条件下的控制性能,提出了一种基于全阶滑模观测器和准比例谐振调节器的电流重构方法。该方法首先在两相静止坐标系下以电流和扩展反电动势为观测量,建立了全阶滑模观测器的数学模型。然后利用准PR调节器对未知相电流误差进行重构,以获得全阶滑模观测器所需要的电流误差信息。最后利用观测器估计的电流信息实现高性能的闭环矢量控制,并给出了观测器和准PR调节器的参数设计方法。相较于传统的低通滤波器与PI调节器的控制方法,所提方法实现简单并且避免了低通滤波器造成的相位滞后和幅值衰减问题。半实物实时仿真结果表明,新方法在不同工况下的轴电流谐波减小10%~20%,并且具有更高的转矩控制精度和更好的动态性能。
永磁同步电机;单电流传感器;全阶滑模观测器;准比例谐振调节器;矢量控制
0 引言
永磁同步电机(permanent magnet synchronous motor, PMSM)因其结构简单、运行可靠、体积小、质量轻、功率密度高和运行效率高等优点,广泛应用于工业驱动、船舶推进和精密数控机床等领域[1-4]。
三相永磁同步电机驱动系统通常采用电流环和速度环的双闭环控制。电流环控制通常需要2~3个相电流传感器来获得完整的相电流信息[5]。然而,受制于制造工艺以及运行条件等因素的影响,如受到振动、冲击、高温高湿等恶劣环境影响,电流传感器容易出现损坏现象。对于实际驱动系统,所有相电流传感器同时损坏的概率非常小。单电流传感器控制方法就是通过设计电流重构算法,根据1个相电流传感器和电机其他参数信息获得完整的电流信息,从而实现电流环闭环控制。
目前单电流传感器矢量控制方法主要有:基于状态观测器法[6]、基于直流母线电流检测法[7]、基于神经网络或模糊控制等智能算法[8]以及基于坐标变换法[9]。基于直流母线电流检测法通常存在重构电流盲区,导致重构电流包含谐波较大,重构精度不高。文献[10]提出了一种基于母线电流信息进行相电流重构的方案,该方案通过改变电流传感器位置,利用矢量脉冲插入法来消除重构电流盲区,但是该方法存在开关损耗过大的问题。基于智能算法[11]的电流重构方法需要实时的数据更新,通常计算量大、应用困难。基于坐标变换法通常依赖系统参数的准确性,对于参数扰动的鲁棒性不高。基于状态观测器法根据模型状态方程构造各类观测器,对电流进行估计,该方法面对参数扰动时具有较强的鲁棒性,但是存在系统抖振的问题。文献[12]设计了一个Luenberger观测器,利用剩余无故障电流传感器信息来获取故障电流传感器的估计值。文献[13]提出了一种基于卡尔曼滤波器的电流观测方法,但是控制性能不佳,电机转矩存在非周期性脉冲尖峰。
为了提高单电流传感器矢量控制策略在各类工况运行时的稳态性能和抗干扰能力,本文将准比例谐振(PR)调节器应用在基于全阶滑模观测器的单电流传感器控制中,利用准PR调节器在谐振频率点的大增益特性,对电流信号进行无静差跟踪。同时利用FPGA和DSP芯片搭建了半实物实时仿真平台,实现了三相永磁同步电机单电流传感器条件下的矢量控制。仿真结果证明,与已有的基于PI调节器的方法相比较,本文所提的矢量控制方案的轴电流所含谐波更小,转矩控制精度更高,在全转速工况下的控制性能更优。
1 PMSM数学模型
在旋转坐标系下,PMSM的电压方程[14]为
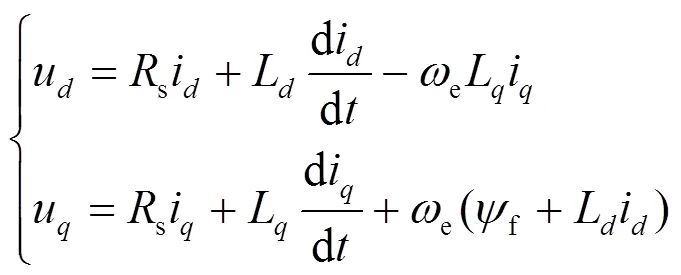
电磁转矩方程[15]为
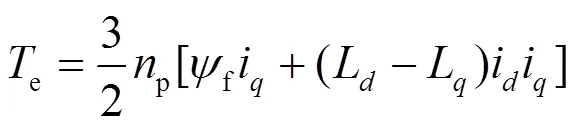
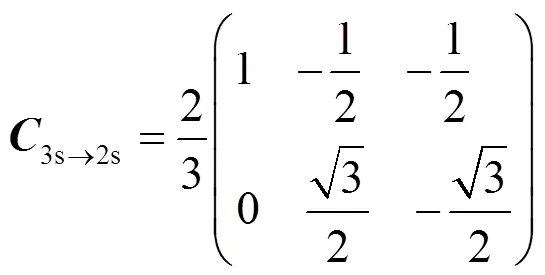
2 单电流传感器控制算法
2.1 PMSM单电流传感器控制基本原理
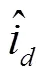
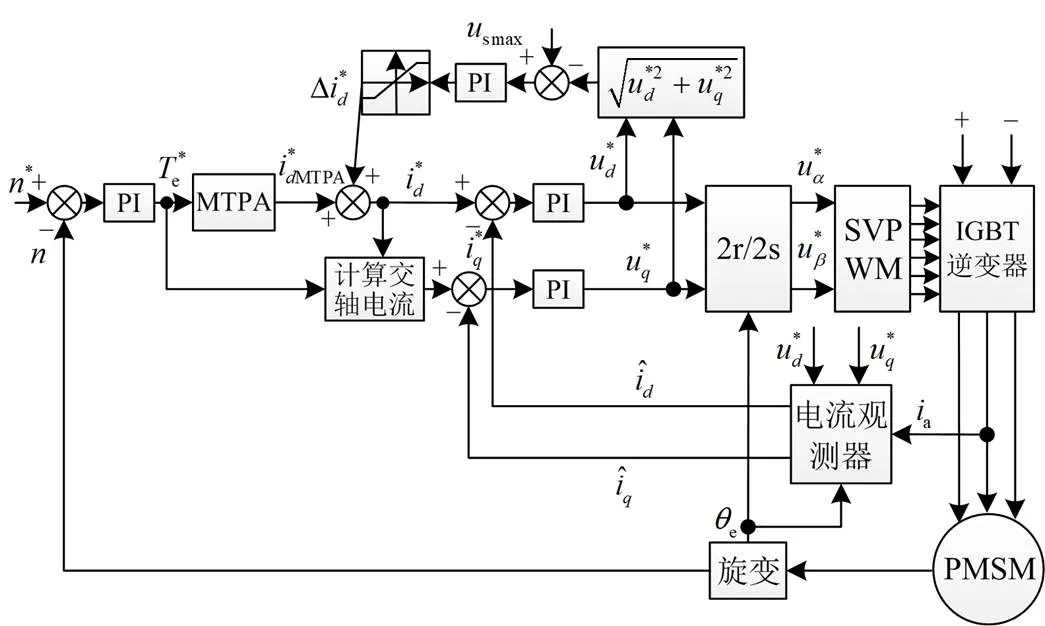
图1 PMSM单电流传感器矢量控制框图
2.2 电流重构策略
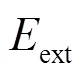
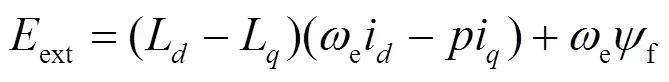
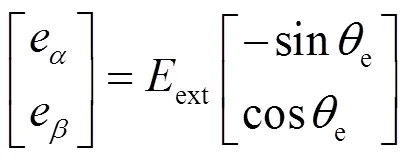
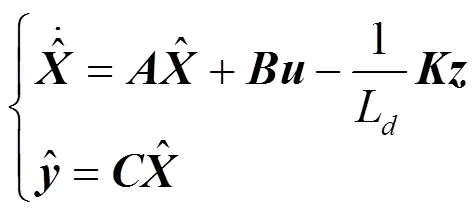
其中:
式中:为反馈增益矩阵;、均为正常数。
选择电流误差构建滑模面如式(7)。
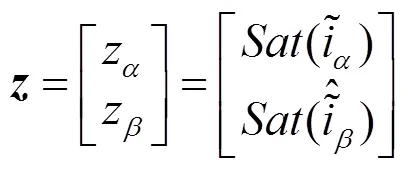
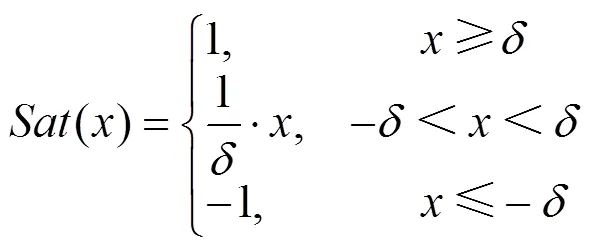
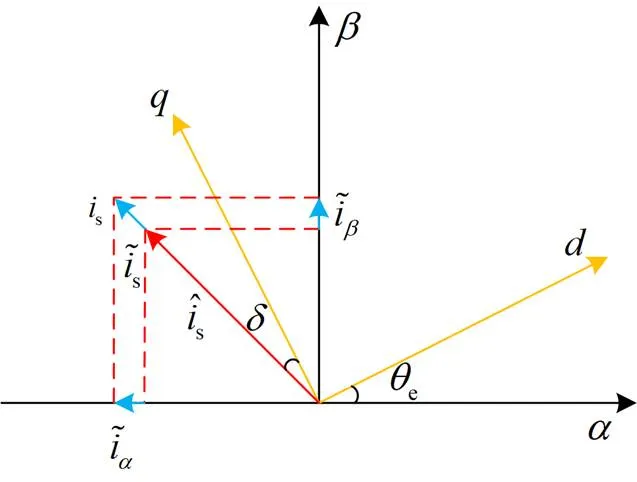
图2 电流矢量关系
由电流空间矢量估计误差在静止坐标系内的投影关系,可以得到
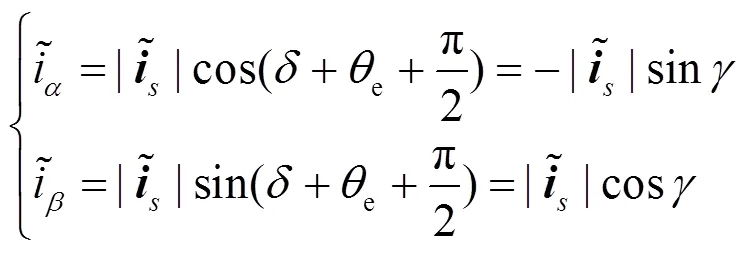
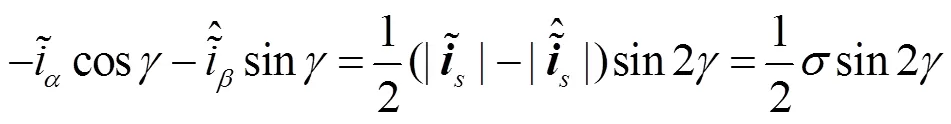
通过提取并控制误差量收敛为零,可获得电流空间矢量误差,随后通过式(9)可获得重构轴电流误差。传统方法是使用低通滤波器消除交流谐波,再利用PI调节器提取直流误差。此方法对低通滤波器参数要求很高,因为滤波时间常数太大会引起相位滞后,导致动态性能差;时间常数太小则无法消除交流谐波。因此本文提出了一种新的基于准比例谐振调节器的相电流误差重构方法。此方法利用准PR调节器对谐振频率的交流谐波具备大增益特性,直接调控和跟踪电流空间矢量误差,从而获得准确的轴重构电流误差。图3给出了基于PI的传统方法和基于准PR的本文方法的β轴电流误差重构框图。
2.3 参数设计
2.3.1滑模观测器参数设计
文献[19]通过Lyapunov稳定性分析,推导了全阶滑模观测器反馈增益矩阵参数与自然振荡角频率和阻尼比的关系表达式,具体如式(11)所示。
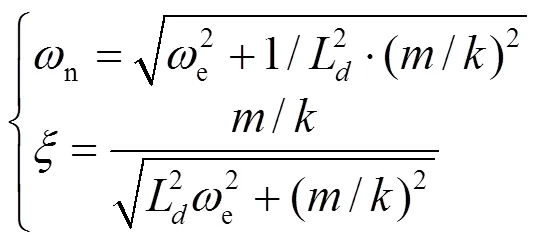
此外,边界层厚度越大,抑制抖振效果越好;但边界层厚度过大,会影响滑模观测器响应速度,降低系统鲁棒性[20],具体取值可通过调试获得。
2.3.2准PR调节器参数设计
PR调节器利用其在谐振频率点的高增益特性,可以对特定频率交流信号实现无静差跟踪控制[21-22]。PR调节器的传递函数为[23]
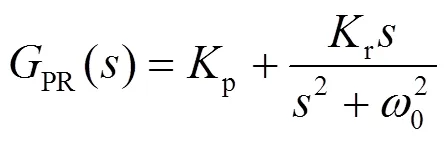
文献[24]表明,以上PR调节器只能对单一频率起作用。为增大系统带宽,提高PR控制器的适用性和稳定性,需对其进行改进。改进后的准PR调节器传递函数为

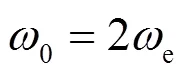
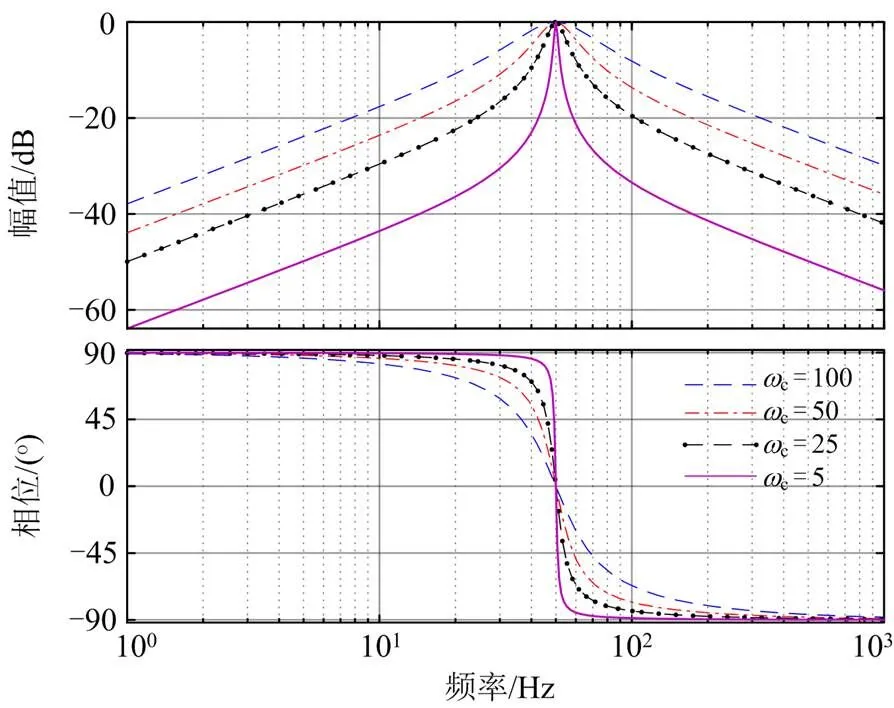
图4 变化时准PR控制器Bode图
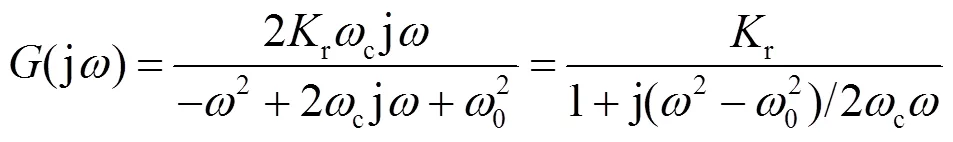
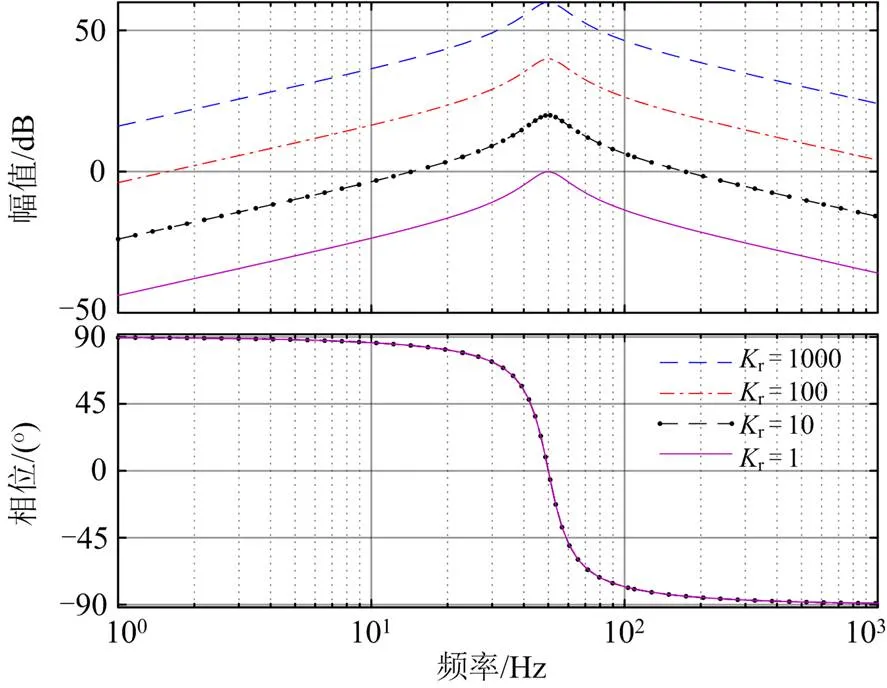
图5 变化时准PR控制器Bode图
3 半实物实时仿真验证
本文对所提的单电流传感器矢量控制策略进行了半实物实时仿真验证。半实物实时仿真平台包含了TI公司的DSP芯片TMS320F28335和FPGA芯片Cyclone Ⅳ E系列EP4CE115F2317,如图7所示。
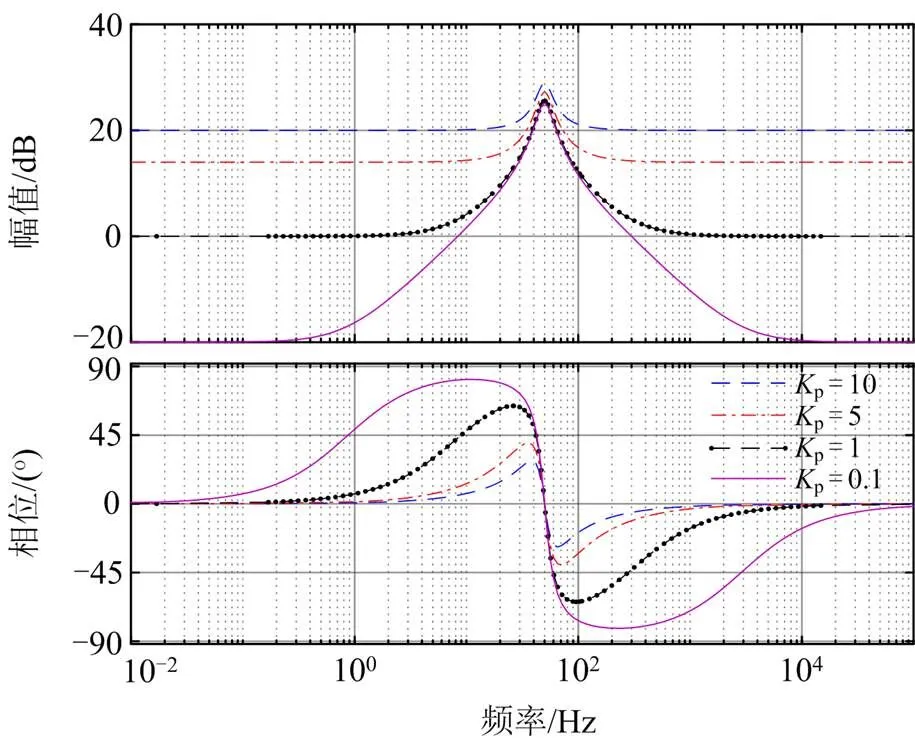
图6 变化时准PR控制器Bode图
图7 半实物实时仿真平台
Fig. 7 Hardware-in-the-loop real-time simulation platform
仿真平台首先利用Matlab搭建逆变器和PMSM的Simulink模型,利用HDL coder工具箱生成相应的HDL语言,并将其抄写到FPGA芯片。DSP实现的主要功能包括电流观测器、矢量控制、PWM调制策略。DSP芯片通过CAN卡连接上位机,实现上位机控制。本文对两种单电流传感器矢量控制策略进行了对比,一是传统PI调节器方案,二是本文提出的准PR调节器方案。
PMSM模型参数如表1所示。仿真条件设置:直流侧电压DC= 900 V,SVPWM开关频率为5 kHz,滑模观测器增益= 10,= 10。
本文波形图纵坐标均为相应量的标幺值,基准值为额定值。
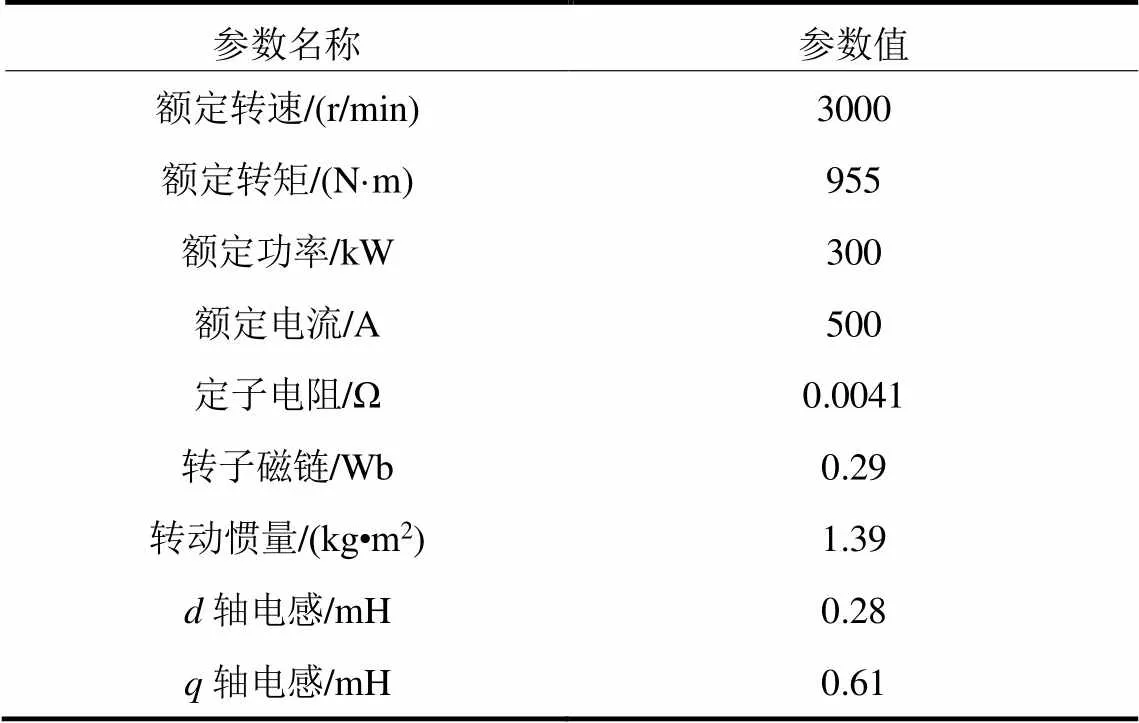
表1 PMSM参数设计
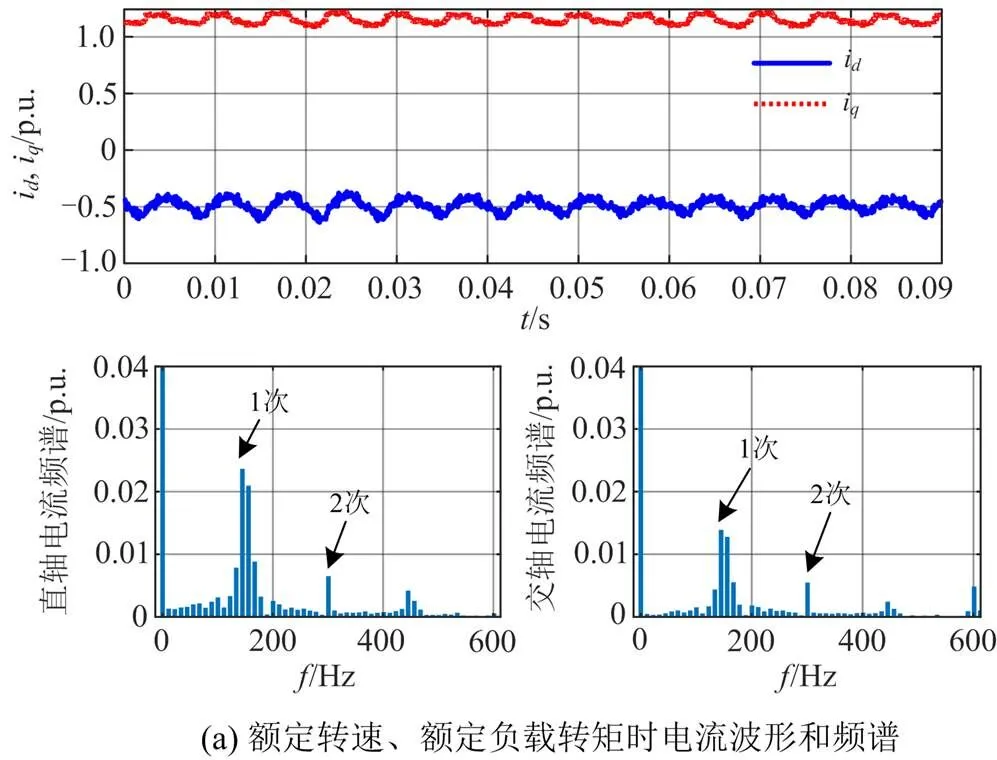
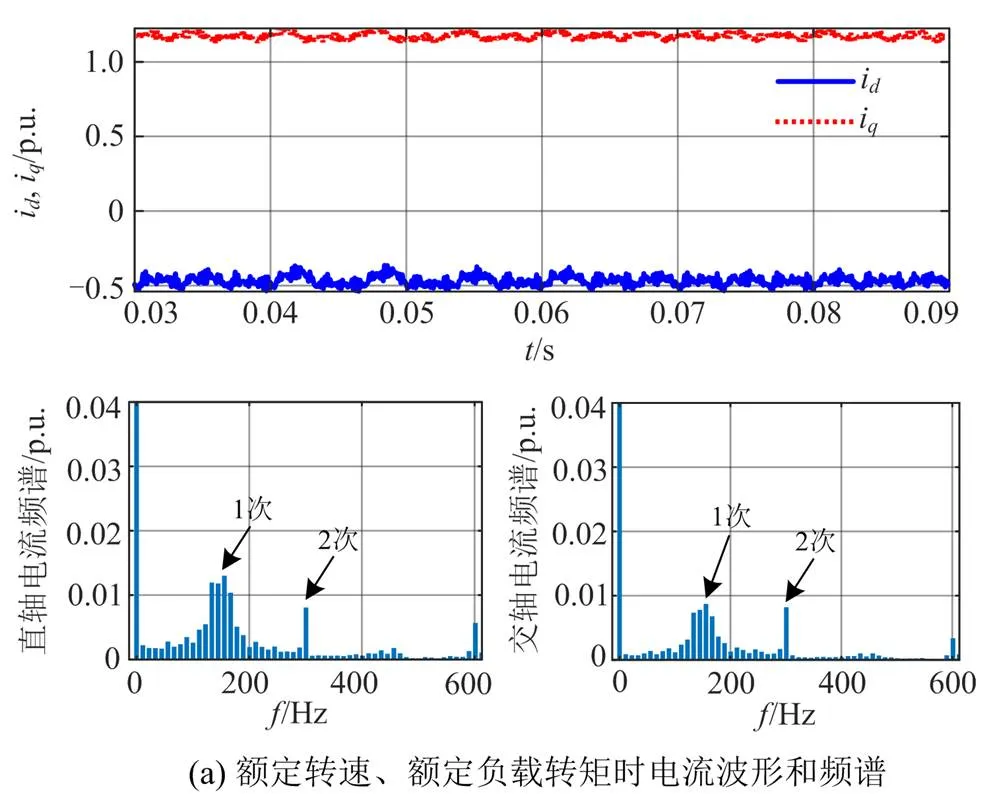
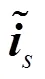
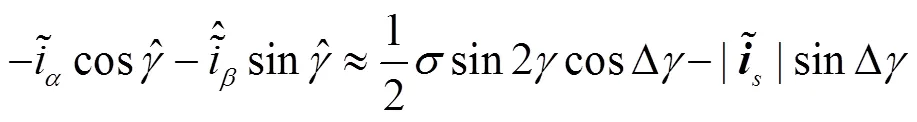
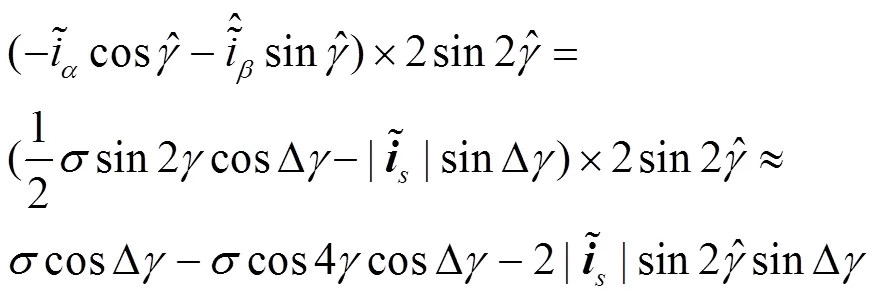
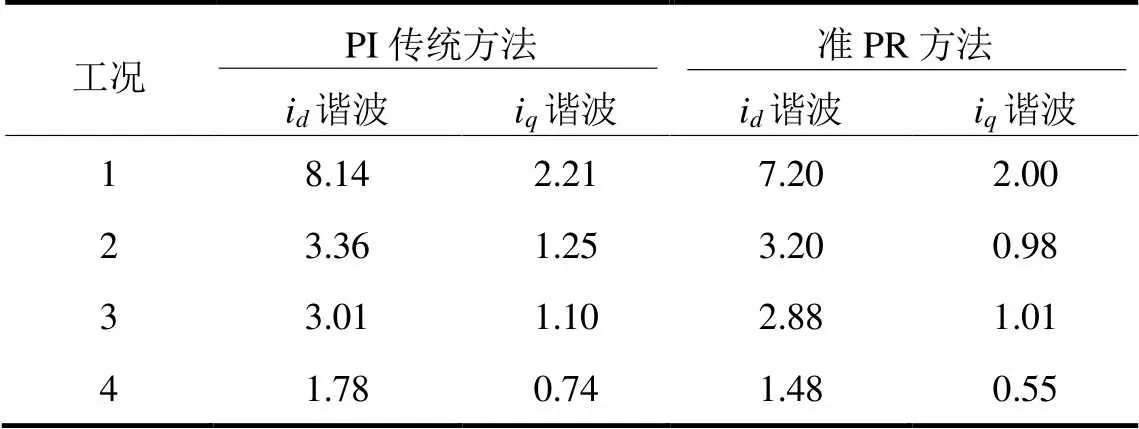
表2 不同工况下dq轴电流谐波含量
图10为固定转矩为30%额定转矩时,从10 r/min到额定转速再降到10 r/min(全转速)运行时的轴电流和转速波形图。由波形图对比看出,传统PI方法在低速(10 r/min)运行时轴电流波动大,准PR方法在此工况下的轴电流变化平滑,控制性能更加稳定。
图11给出了额定负载转矩下,两种控制方法在不同转速稳态时的转矩平均相对误差。此转矩相对误差为电流观测器观测的转矩值与实际电机转矩的相对误差,计算公式为

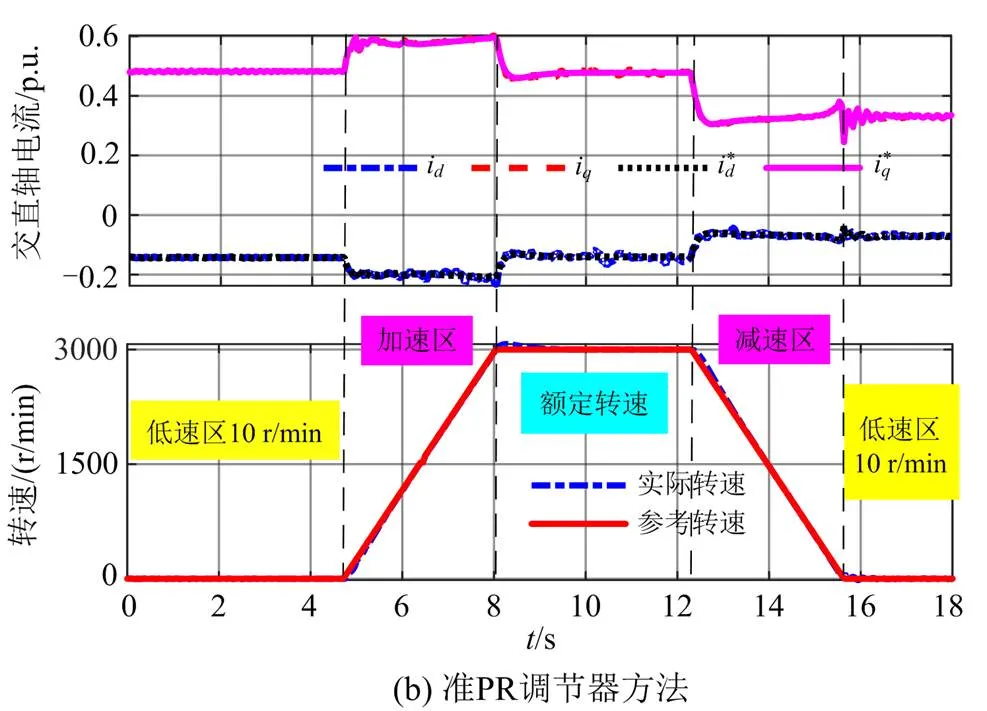
图10 两种控制方法在全转速工况下的仿真结果
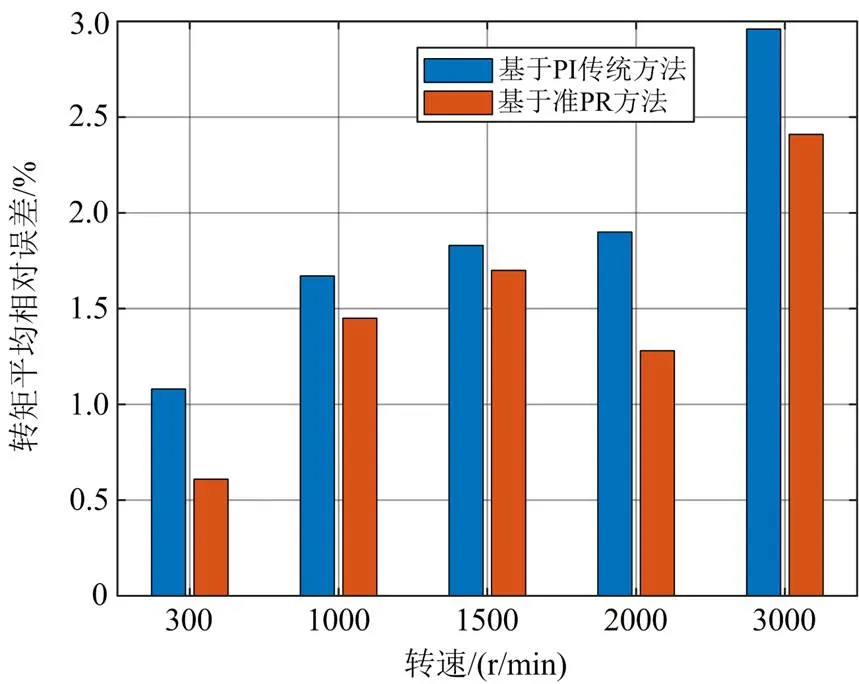
图11 不同转速工况下的转矩平均相对误差
4 结论
本文基于全阶滑模观测器和准PR调节器,提出了一种新的单电流传感器矢量控制策略。并利用FPGA和DSP实现了半实物实时仿真。与现有的基于低通滤波器和PI调节器的方法相比较,提出的准PR方法矢量控制时轴电流所含谐波更小,THD值减小10%~20%,所含1次、2次、4次主谐波成分的幅值均更低,在全速范围内稳态运行时控制转矩的平均相对误差更小,控制精度更高。在转速变化的动态过程中,准PR方法矢量控制时的轴电流变化平滑,改善了传统方法在低速范围内电流波动大的情况。半实物实时仿真结果表明,本文所提出的单电流传感器矢量控制策略可行且有效。
[1] 俞沛宙, 王澍, 杨继辉, 等. 基于灰狼优化的永磁同步电机自适应反推鲁棒控制策略[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49(2): 39-46.
YU Peizhou, WANG Shu, YANG Jihui, et al. Adaptive backstepping robust control strategy of PMSM based on grey wolf optimization[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49(2): 39-46.
[2] 王金兵, 沈艳霞. 基于增量模型的永磁同步直线电机鲁棒预测电流控制[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2020, 48(8): 69-77.
WANG Jinbing, SHEN Yanxia. Robust predictive current control for a permanent magnet synchronous linear motor based on an incremental model[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2020, 48(8): 69-77.
[3] 曹亚丽, 曹竣奥, 宋昕, 等. 一种改进滑模观测器的PMSM矢量控制研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49(16): 104-111.
CAO Yali, CAO Jun'ao, SONG Xin, et al. Research on vector control of PMSM based on an improved sliding mode observer[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49(16): 104-111.
[4] Soukaina E D, Loubna L. Comparison between PI-DTC-SPWM and fuzzy logic for a sensorless asynchronous motor drive[J]. Protection and Control of Modern Power Systems, 2021, 6(4): 430-442.
[5] 王国鑫. 永磁电机驱动系统传感器故障诊断与容错控制[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2018.
WANG Guoxin. Sensor fault diagnosis fault tolerant control permanent magnet motor drives[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018.
[6] Huang Gang, Luo Yiping, Zhang Changfan, et al. Current sensor fault diagnosis based on a sliding mode observer for PMSM driven systems[J]. Sensors, 2015, 15(5): 11027-11049.
[7] Adzic E, Porobic V, Adzic M, et al. Advanced induction motor drive control with single current sensor[J]. Thermal Science, 2016, 20(2): 421-436.
[8] GOU Bin, XU Yan, XIA Yang, et al. An intelligent time- adaptive data-driven method for sensor fault diagnosis in induction motor drive system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 66(12): 9817-9827.
[9] 李英强. 永磁同步电机单电流传感器电流预测控制技术研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2018.
LI Yingqiang. A novel predictive current control method for PMSM drive with single current sensor[J]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018.
[10] 卢伟. 基于单电流传感器的PMSM宽运行范围相电流重构算法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2018.
LU Wei. Research on phase current reconstruction algorithms for PMSM wide operating range based on single current sensor[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018.
[11] 崔宏伟. 永磁同步电机控制系统无电流传感器技术的研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州交通大学, 2018.
CUI Hongwei. Research on current sensorless technology for permanent magnet synchronous motors control system[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou Jiaotong University, 2018.
[12] Wang Zhiqiang, Shi Xiaojie, Tolbert L M, et al. A di/dt feedback-based active gate driver for smart switching and fast overcurrent protection of IGBT modules[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2014, 29(7): 3720-3732.
[13]Beng G , Zhang Xinan, Vilathgamuwa D M. Sensor fault-resilient control of interior permanent- magnet synchronous motor drives[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2014, 20(2): 855-864.
[14] 连传强, 肖飞, 高山, 等. 基于实验标定及双时间尺度随机逼近理论的内置式永磁同步电机参数辨识[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39(16): 4892-4898, 4991.
LIAN Chuanqiang, XIAO Fei, GAO Shan, et al. Parameter identification for interior permanent magnet synchronous motor based on experimental calibration and stochastic approximation theory with two time scales[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39(16): 4892-4898, 4991.
[15] 王龙, 郭寅远, 杨博, 等. 永磁同步发电机自适应分数阶变桨距角控制[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49(20): 92-103.
Wang Long, Guo Yinyuan, Yang Bo, et al. Adaptive fractional-order variable-pitch control for a permanent magnetic synchronous generator[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49(20): 92-103.
[16] 杨蕾, 李胜男, 黄伟, 等. 永磁同步发电机自适应分数阶PID控制设计[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2020, 48(9): 49-58.
Yang Lei, Li Shengnan, Huang Wei, et al. Adaptive fractional-order PID control design of permanent magnetic synchronous generator[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2020, 48(9): 49-58.
[17] 周洪雷. 内置式永磁电机驱动系统电流传感器故障容错控制[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019.
ZHOU Honglei. Research on current sensor fault tolerant control of encoderless IPMSM drive system[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019.
[18] 金鸿章, 罗延明, 肖真, 等. 抑制滑模抖振的新型饱和函数法研究[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2007, 28(3): 288-291.
JIN Hongzhang, LUO Yanming, XIAO Zhen, et al. Investigation of a novel method of saturation function for chattering reduction of sliding mode control[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2007, 28(3): 288-291.
[19] 张国强. 基于全阶滑模观测器的IPMSM无位置传感器控制策略研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2013.
ZHANG Guoqiang. Full-order sliding mode observer based position sensorless IPMSM control strategy[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2013.
[20] 王要强, 冯玉涛, 秦明, 等. 表贴式永磁同步电机全阶滑模观测与控制策略[J]. 电工技术学报, 2018, 33(24): 5688-5699.
WANG Yaoqiang, FENG Yutao, QIN Ming, et al. Full-order sliding mode observation and control strategy of surface- mounted permanent magnet synchronous motor[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2018, 33(24): 5688-5699.
[21] 周锦荣, 骆婉红, 周慰君, 等. 基于PR调节器的双闭环控制单相逆变器[J]. 现代电子技术, 2019, 42(4): 125-128, 133.
ZHOU Jinrong, LUO Wanhong, ZHOU Weijun, et al. Double closed-loop control single-phase inverter based on PR regulator[J]. Modern Electronics Technique, 2019, 42(4): 125-128, 133.
[22] 雷亚雄, 李建文, 李永刚. 基于准PR调节器电流双闭环LCL三相并网逆变器控制[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2014, 42(12): 44-50.
Lei Yaxiong, Li Jianwen, LI Yonggang. Control strategy of three-phase LCL grid-connected inverter based on quasi-PR adjuster[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2014, 42(12): 44-50.
[23] Yepes A G, Freijedo F D, Doval-Gandoy J, et al. Effects of discretization methods on the performance of resonant controllers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2010, 25(7): 1692-1712.
[24] 张赛鹏, 郭荣欢, 刘赫. 基于PI与准PR调节的并网逆变器控制参数设计[J]. 黑龙江电力, 2017, 39(1): 40-44, 84.
Zhang Saipeng, Guo Ronghuan, Liu He. Control parameter design of grid-connected inverter based on PI and quasi-PR regulation[J]. Heilongjiang Electric Power, 2017, 39(1): 40-44, 84.
A vector control strategy using a single current sensor for a three-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor
XU Guanda, XIAO Fei, LIAN Chuanqiang, LIU Jilong
(National Key Laboratory of Science and Technology on Vessel Integrated Power System, Naval University of Engineering, Wuhan 430033, China)
To improve the control performance of a three-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor with a single current sensor, a current reconstruction method based on full-order sliding mode observer and a quasi-proportional resonant regulator is proposed. First, the mathematical model of the full-order sliding mode observer is established in the two-phase stationary coordinate frame with the current and extended back electromotive force as the observed quantities. Then the unknown phase current error is reconstructed using a quasi-proportional resonant (quasi-PR) regulator to obtain the current error information required by the full-order sliding mode observer. Finally, the current information estimated by the observer is used to realize high-performance closed-loop vector control, and the parameter design methods of the observer and quasi-PR regulator are also provided. Compared with the traditional control method using a low-pass filter and a PI regulator, the proposed method is simple to implement and avoids the problems of phase lag and amplitude attenuation caused by the low-pass filter. The ‘hardware-in-the-loop’ real-time simulation results show that the new method reduces the-axis current harmonics by 10%~20% under a variety of working conditions, and has higher torque control accuracy and better dynamic performance.
permanent magnet synchronous motor; single current sensor; full-order sliding mode observer; quasi- proportional resonant regulator;vector control
10.19783/j.cnki.pspc.220211
国家自然科学基金面上项目资助(52177202)
This work is supported by the General Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52177202).
2022-02-22;
2022-04-02
许观达(1998—),男,硕士,研究方向为永磁电机系统及其控制;E-mail: 1985556356@qq.com
连传强(1986—),男,通信作者,博士,副研究员,研究方向为电机系统及其控制、人工智能。E-mail: wzdslcq@ 163.com
(编辑 许威)

