一种基于滑模观测器的动车组整流器控制策略研究
王浩宇,张雨婷,2,张 乔,刘志刚
一种基于滑模观测器的动车组整流器控制策略研究
王浩宇1,张雨婷1,2,张 乔1,刘志刚1
(1.西南交通大学电气工程学院,四川 成都 611756;2.无锡市轨道建设设计咨询有限公司,江苏 无锡 214000)
为改善车网耦合系统在多工况运行下的直流电压抗干扰能力,提出了一种基于滑模观测器的动车组网侧整流器滑模控制策略(sliding mode control method based on sliding mode observer, SMO+SMC)。首先,通过建立CRH3型动车组在坐标系下的数学模型,推导了滑模观测器的设计方程。接着,利用滑模观测器实时观测牵引电机输出功率后间接得到整流器直流侧电流,将滑模观测器的输出提供给滑模控制的外环电压控制模块,实现滑模观测器和滑模控制的结合。最后,将PI、滑模控制和SMO+SMC策略分别应用于CRH3型动车组仿真模型,对多工况下整流侧直流电压控制效果进行分析验证,并基于HIL小步长实时仿真测试平台进行了半实物实验。仿真和实验结果表明,SMO+SMC策略可以提高动车组运行速度改变时的直流电压抗干扰能力和车网耦合运行时网侧电流的稳定性。
电气化铁路;动车组-牵引网耦合系统;多工况运行;滑模观测器
0 引言
随着高速铁路的飞速发展,交-直-交型动车组大量投入使用,使牵引供电系统具有强烈的非线性和冲击性,此外动车组在运行过程中还伴随着不同的工况(牵引、制动、惰行等),最终将导致牵引网-动车组耦合系统[1-4]供电电能质量问题,如启动超调量大、牵引网侧电流总谐波失真率增大、制动时直流侧电压波动大、负载突变时直流电压波动大等[2]。因此,如何提高动车组-牵引网耦合系统在不同运行工况下的电能质量,保障动车组在复杂路况中的安全高效运行具有重大意义。
不同网侧整流器(line side converter, LSC)控制策略对动车组-牵引网耦合系统的控制效果不同[5-7]。文献[8]将无源控制和传统解耦控制以及基于互连和阻尼分配的无源控制进行了对比分析,得出了基于互连和阻尼分配的无源控制时,网侧电流具有最小的总谐波失真率(total harmonic distortion, THD)、整流器直流输出电压波动最小且响应速度最快,实现了对升弓整备过程中,牵引网电压发生的低频振荡(low-frequency oscillation, LFO)现象的抑制等结论。文献[9]提出了一种基于扩张观测器(extended state observer, ESO)的非线性控制策略来抑制低频振荡,并与PI控制和滑模控制(sliding mode control, SMC)控制进行了比较,分析了其控制效果,并在车网耦合系统dSPACE半物理平台上验证了LFO的抑制效果。然而,以上研究成果的研究对象都是处于升弓整备状态时的动车组,且逆变器和电机被等效为一个纯电阻,没有考虑动车组在实际运行过程中的不同工况。
此外,车网耦合系统的性能与动车组运行工况也有一定关系,动车组发生再生制动时会对动车组整流器直流侧输出电压产生影响,严重情况下会出现过电压现象,对电网和动车组产生冲击。综合上述几点,本文尝试提出一种基于滑模观测器的动车组网侧整流器滑模控制策略来抑制车网耦合系统在不同工况下的电压和电流波动。
1 电力牵引传动单元建模
CRH3型动车组由4个牵引传动单元组成,牵引传动单元是由车载变压器、双重化四象限整流器、中间直流环节、逆变器以及4台三相异步电动机构成[10]。其中,两个整流器并联连接,并采用相同的控制方式和电气量参考值。CRH3型动车组整流器的控制策略一般采用传统比例积分(proportional integral, PI) 控制;牵引逆变器一般采用空间矢量调制和转子磁链定向控制策略[10-11]。
动车组4台牵引传动单元的等效拓扑结构如图1所示。在后文进行理论分析时,将逆变器和电机等效为一个电阻和非恒定直流电压源串联的电路[12-13]。


图1 CRH3型动车组单个牵引传动单元等效电路
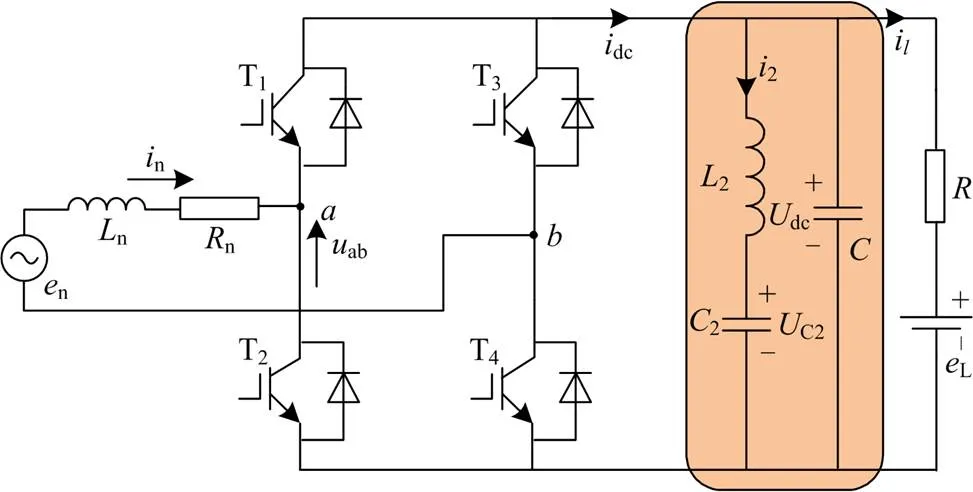
图2 CRH3型动车组拓扑结构图
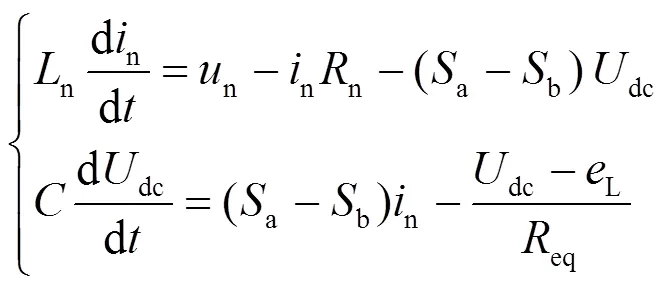
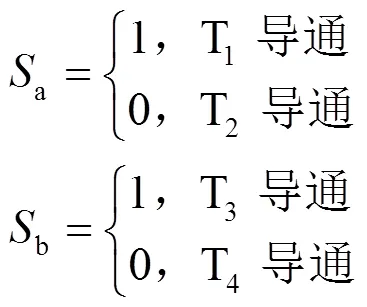
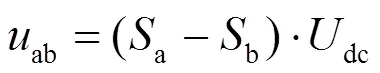

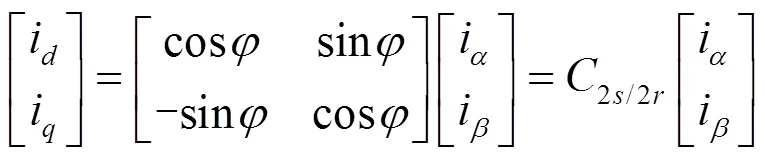
结合式(1)—式(5),可以得到旋转坐标系中动车组的数学模型为
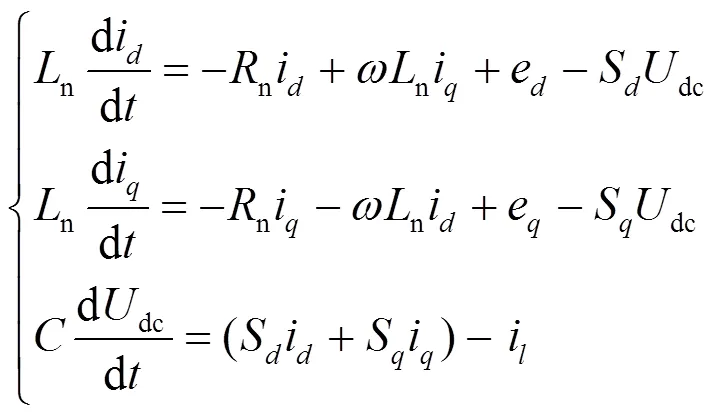
2 基于滑模观测器的滑模控制方法建模
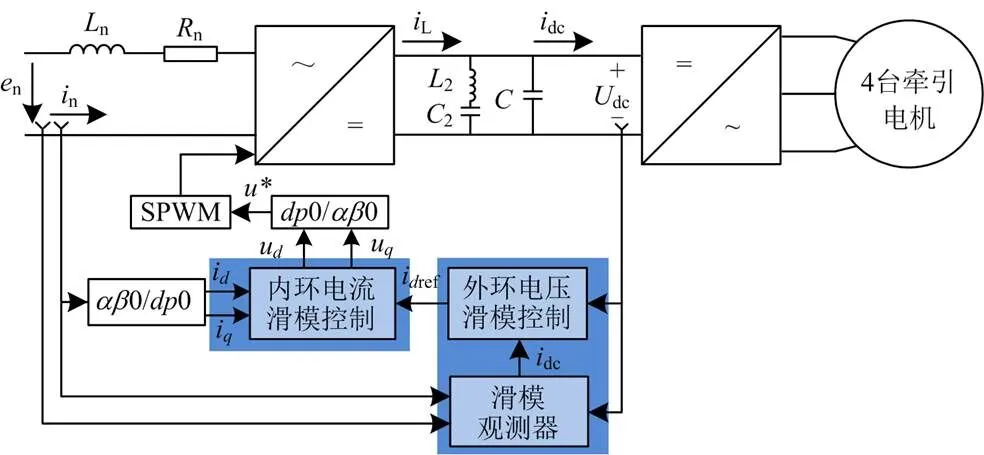
图3 基于SMC+SMO 4台牵引传动单元控制框图
3.1 外环电压模块设计

1) 首先,对滑模观测器进行数学建模。将式(6)中第3个式子等式两边分别乘以dc后可得

进一步化简可得
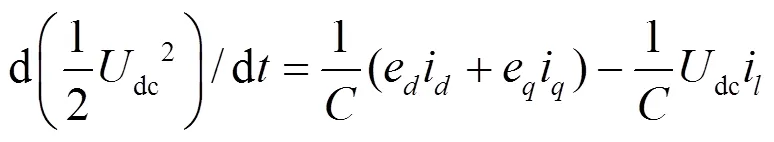
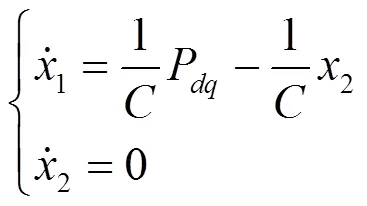

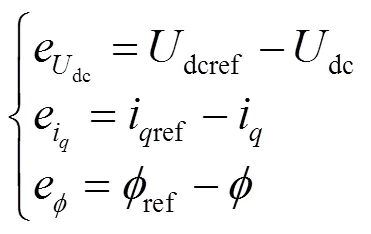

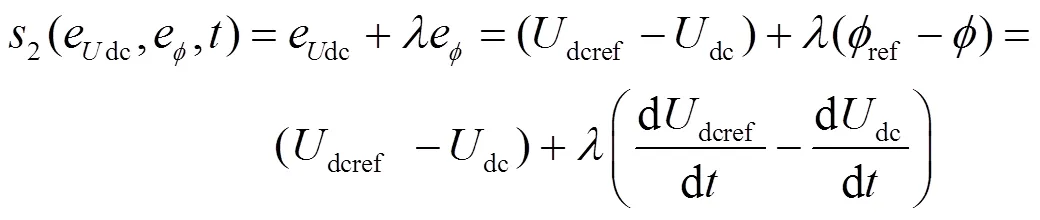

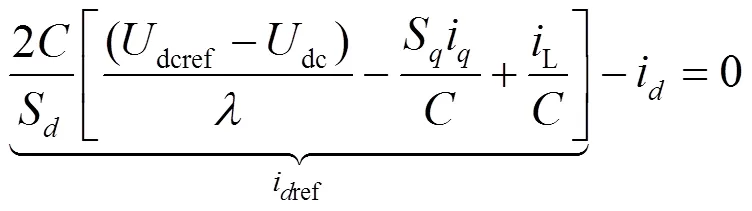
根据基尔霍夫电压定律定理可得
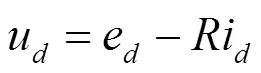

根据式(6)可得
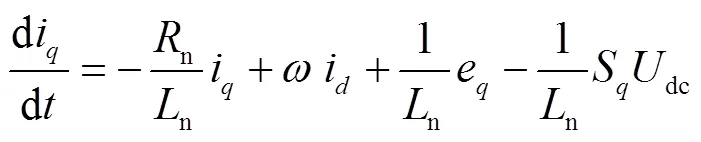
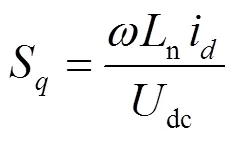
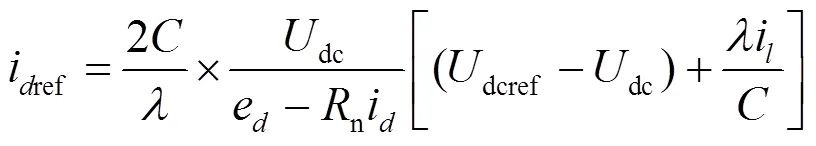

根据式(21)可搭建外环电压控制模块框图,如图5所示。
3.2 滑模观测器稳定性分析
将式(9)和式(10)相减,可以得到

定义李雅普诺夫函数为

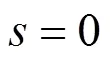
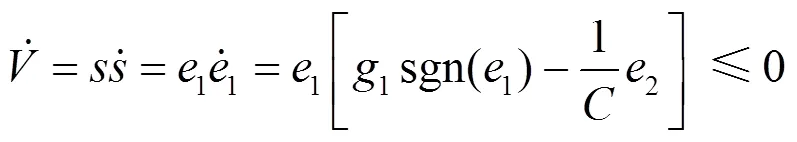
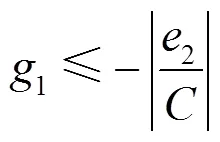

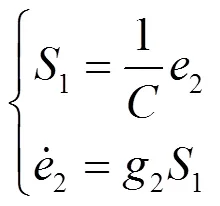
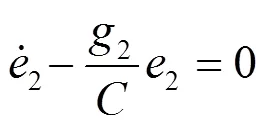
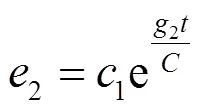
3.3 内环电流模块的设计
为保证车网系统具有较好的动、静态性能,本文选用指数控制律,如式(30)所示。
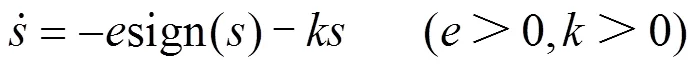
式中:项在系统状态远离滑模表面时起主要作用,它可使系统状态迅速接近滑模表面;sign()项在系统状态接近滑模表面时起主要作用,减慢系统状态的逼近速度,避免剧烈的颤动;和是常数,可在 600 ≤≤1000、≤105中取值;sign()为符号函数,如式(31)所示。
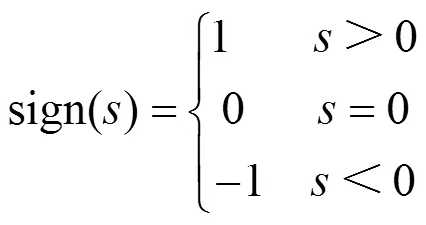

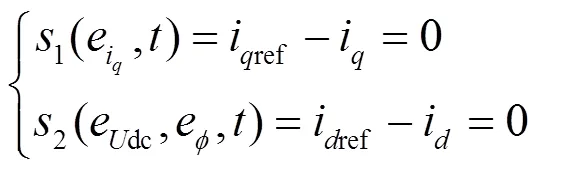
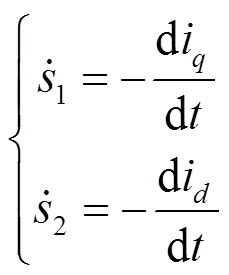
代入式(6)可得
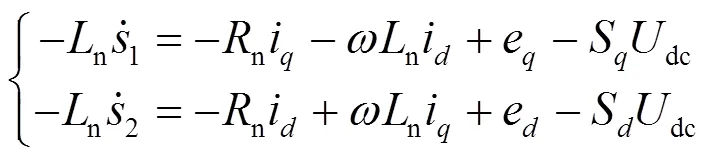
整理式(35)并将式(32)代入,可得开关函数的表达式,如式(36)所示。
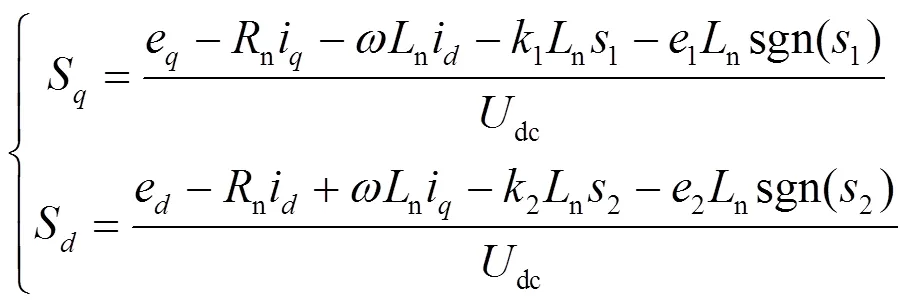
从而推导出输入到PWM模块的两个电量的表达式,如式(37)所示。
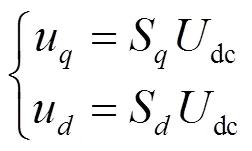
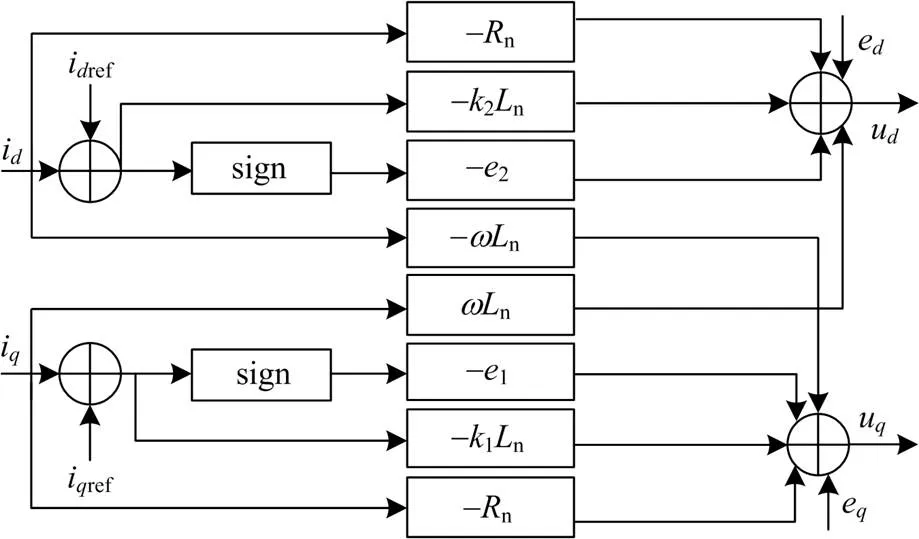
图6 内环电流控制模块框图
4 车网系统多工况运行性能仿真验证
4.1 牵引电机转速改变时的性能比较
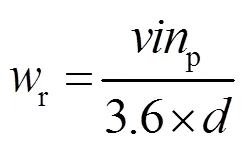
根据式(39)计算可得转动惯量的值为1000 kg·m2。
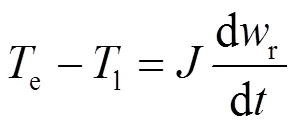

表1 整流器仿真模型主要参数

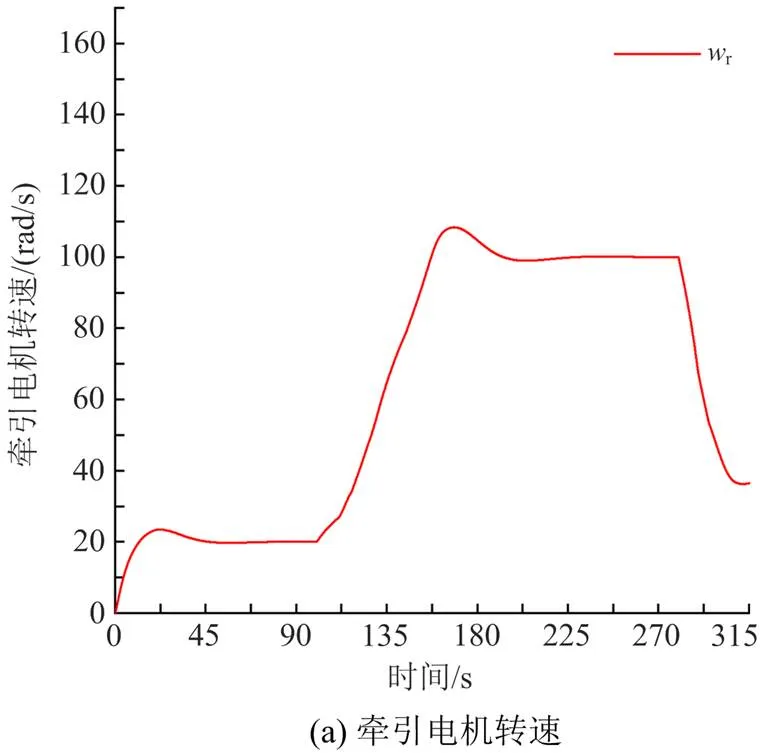

表2 SMO+SMC控制参数
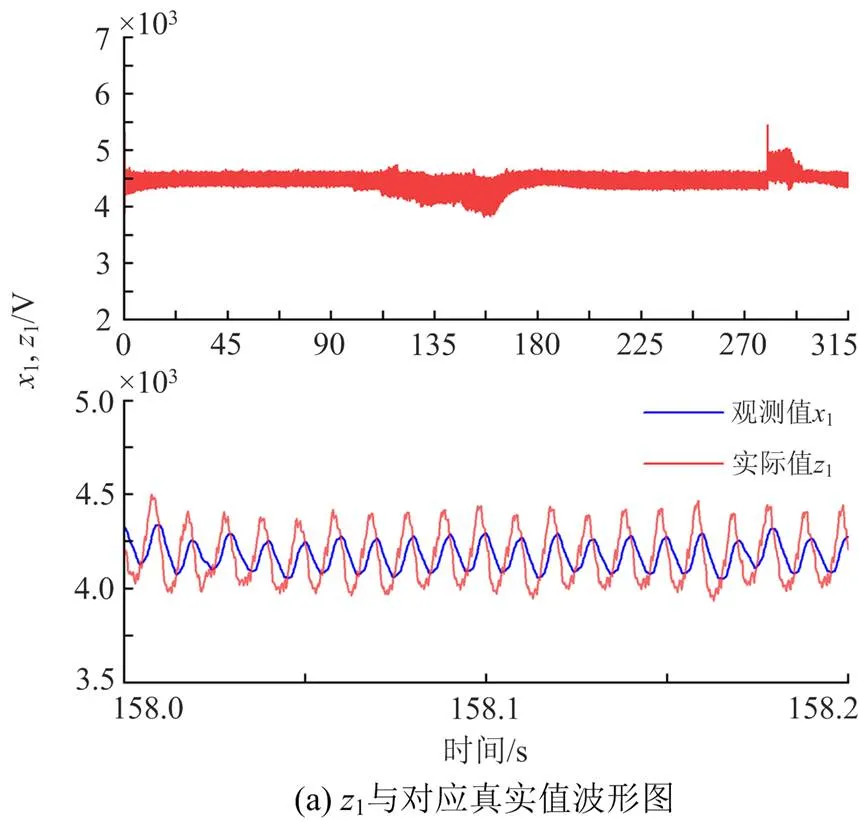
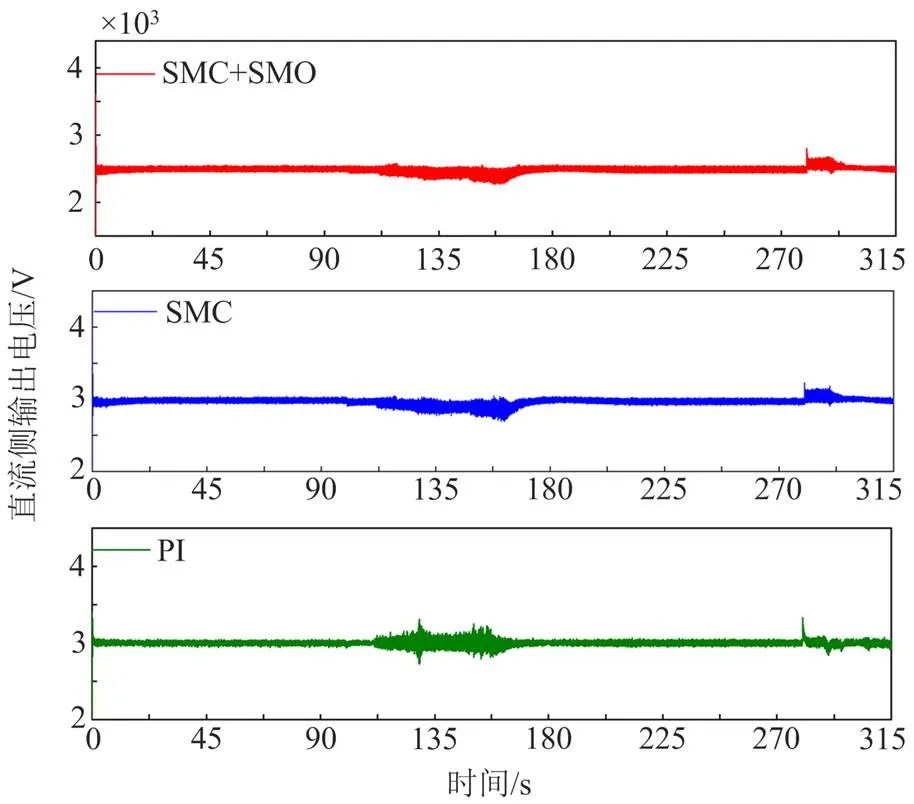
图9 列车运行速度改变3种控制策略下波形图
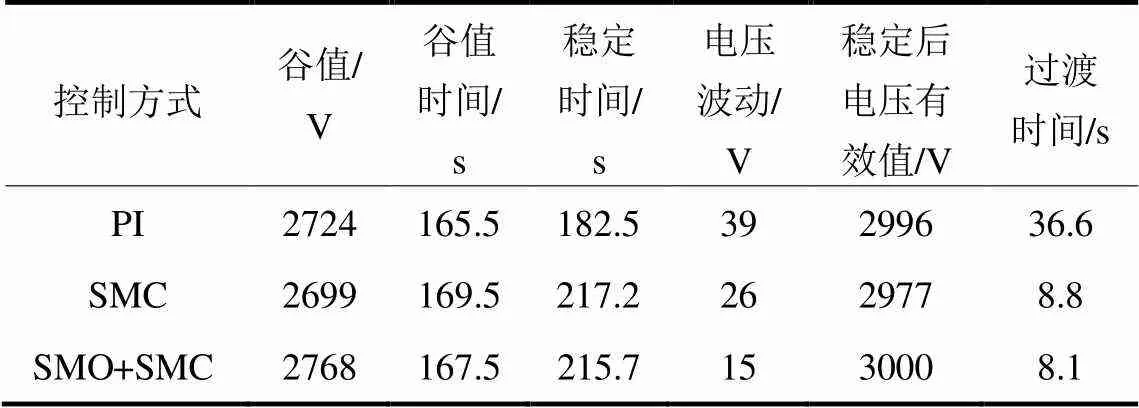
表3 列车增速时3种控制策略下直流侧电压性能指标

表4 列车减速时3种控制策略下直流侧电压性能指标

4.2 车网耦合模型网侧电流波动比较
为验证基于SMO+SMC控制的CRH3型动车组网侧单相整流器的控制策略抑制网侧电压电流波动的效果,采用降阶法建立25 km牵引网模型,与基于传统PI控制、SMC控制、SMO + SMC控制策略的4个牵引传动单元并联,构成相互耦合的级联系统。根据工程实际情况进行了仿真试验:列车在0 s时刻接入牵引网并以20 rad/s的速度匀速运行,在100 s时牵引电机转速由20 rad/s增加到100 rad/s、280 s时牵引电机转速减小到50 rad/s。
根据图10—图12、表5和表6可看出,在面对列车运行速度改变时,基于SMO+SMC控制的CRH3型车单相整流器的控制效果优于SMC控制或PI控制,网侧电流在车辆运行速度改变的瞬间,即100 s、280 s时产生了较小的波动,并迅速恢复稳定,以上对比说明SMO+SMC控制策略能够增加牵引网侧电流的稳定性,保证牵引网-动车组复杂耦合系统的稳定性且在3种策略中表现最佳。
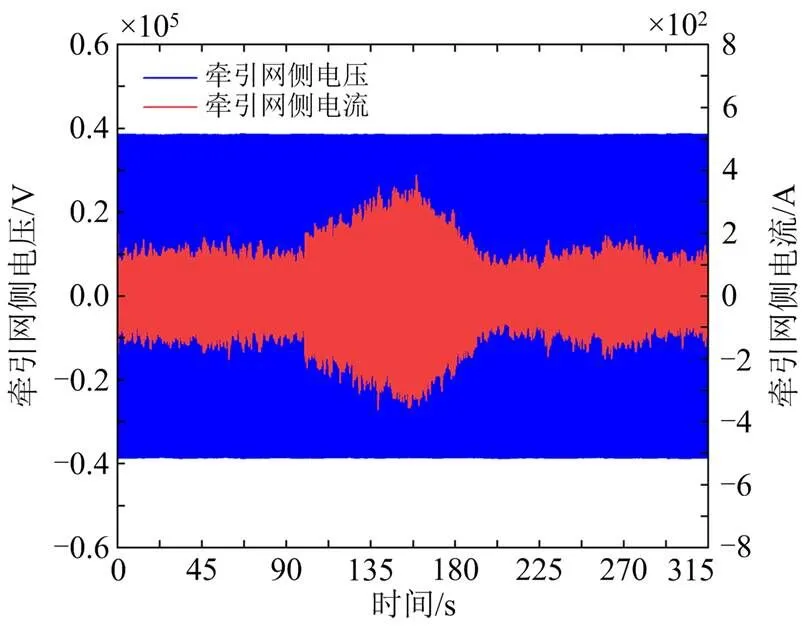
图10 车网耦合系统基于PI控制牵引网侧电压与电流仿真结果
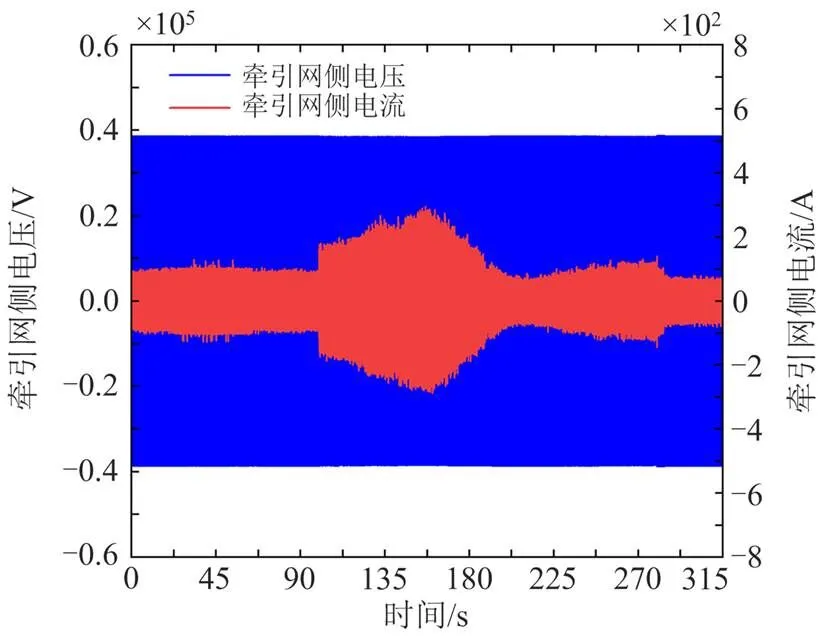
图11 车网耦合系统基于SMC控制牵引网侧电压与电流仿真结果
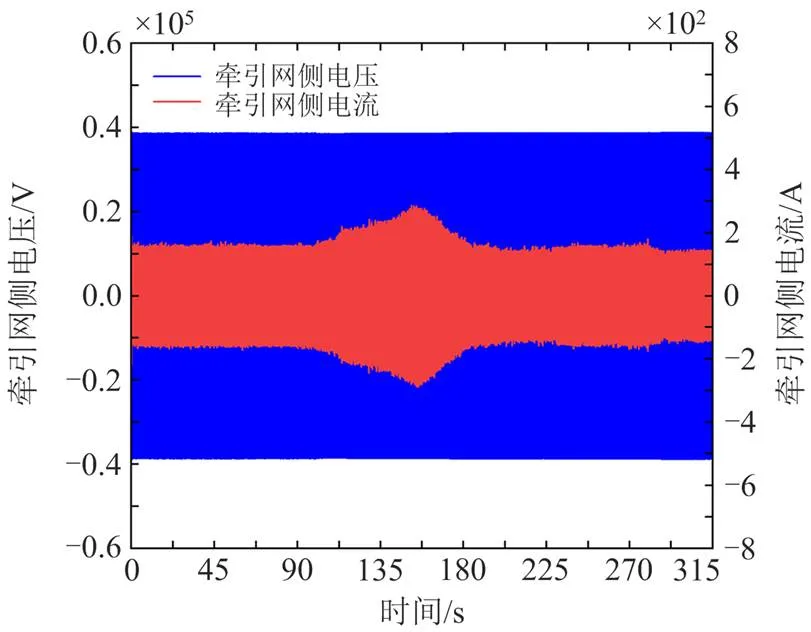
图12 车网耦合系统基于SMO+SMC控制牵引网侧电压与电流仿真结果

表5 列车速度增加时3种控制策略下牵引网侧电流性能指标

表6 列车速度降低时3种控制策略下直流侧电流性能指标
5 半实物验证
5.1 整流器直流侧输出电压实验验证
仿真测试平台上对仿真结果进行实验验证,测试平台示意图如图13所示。将CRH3型动车组4个牵引传动单元及车网耦合系统的仿真模型依次分为主电路和控制电路,主电路模型在基于NI-PXIe- FPGA-7868R的硬件在环测试系统HIL上运行,控制电路在CPU上运行。IO板包含许多IO通道,可以实现HIL和RCP之间的通信。示波器用于观测各电气量。主控机操作平台用于对整个平台进行操控。主电路和控制电路的相关参数都与Matlab/ Simulink平台上的仿真参数一致。
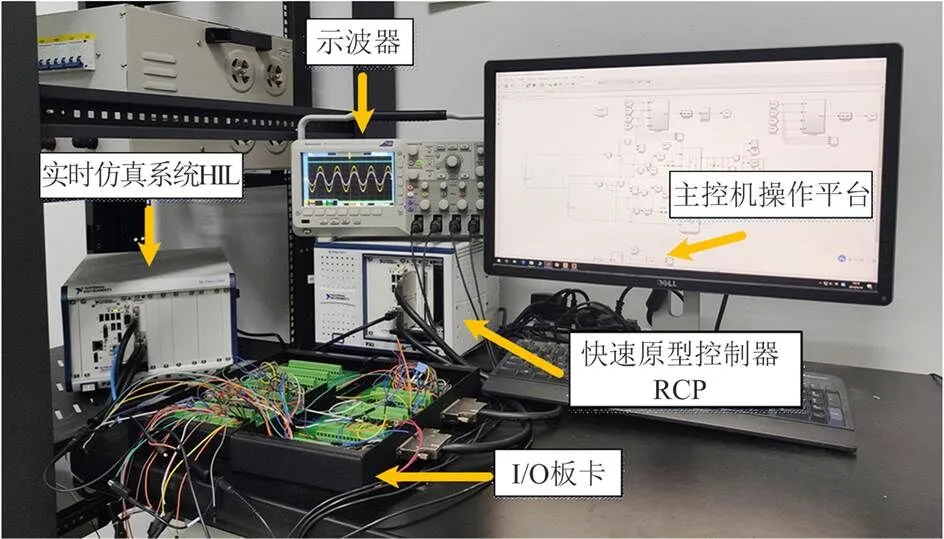
图13 半实物测试平台示意图

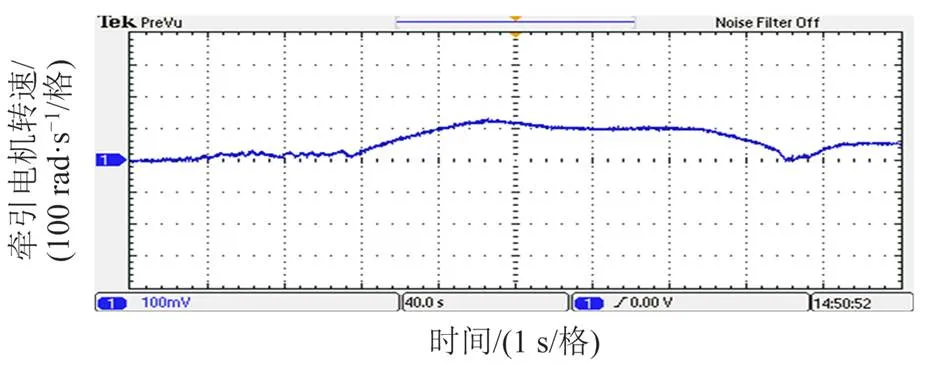
图14 牵引电机转速改变时半实物实验图
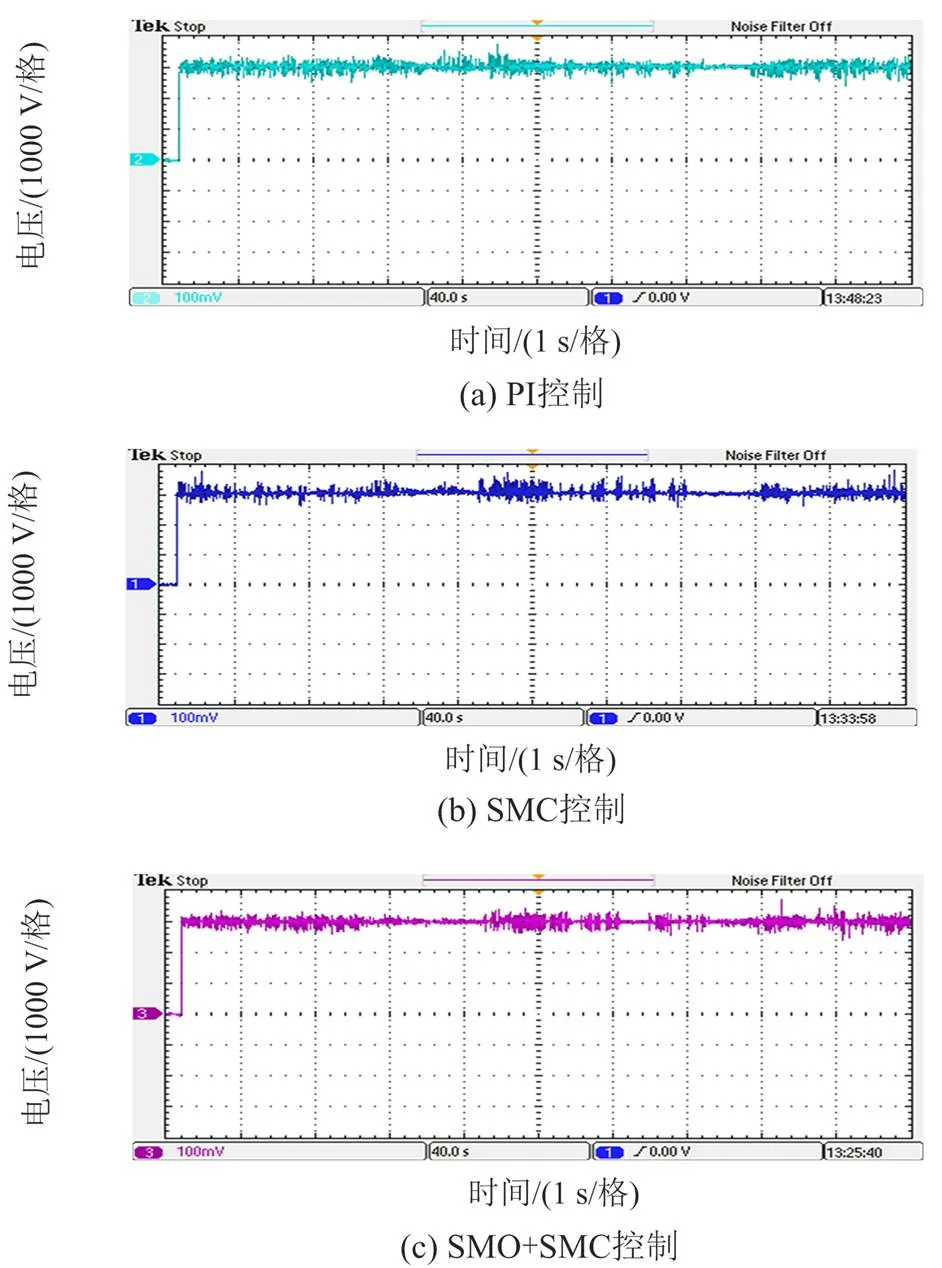
图15 基于不同控制策略牵引电机转速改变时实验图
5.3 车网耦合网侧电压电流实验验证
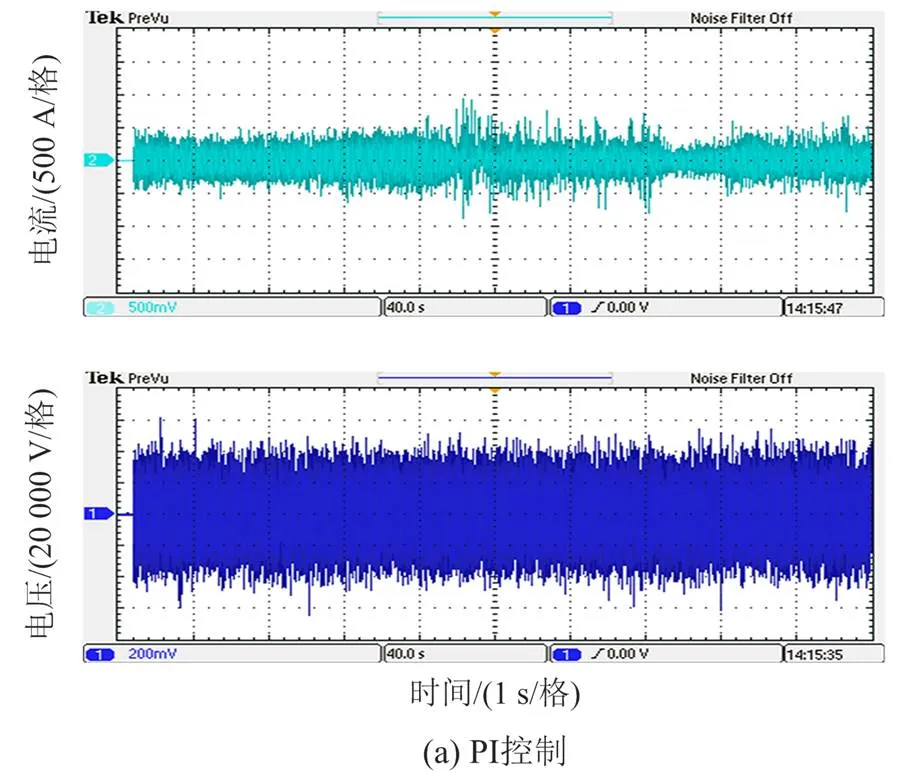
车网耦合模型的网侧电压电流的实验波形图如图16所示,实验结果表明PI、SMC、SMO控制下列车运行速度改变时,网侧电流波动明显SMC+ SMO控制策略下的网侧电流在列车运行速度改变时的幅值最小,这与仿真结果基本一致,实验可以说明在车网耦合模型中列车速度改变时SMO+SMC策略比PI控制和SMC控制的抗干扰能力更强。
6 结论
为提高车网耦合系统在多种运行工况下的电能质量,本文提出一种改善动车组整流器侧控制策略的方法。本文基于SMC和滑模观测器的相关理论知识,结合CRH3型动车组整车拓扑结构,设计了SMO+SMC控制策略,在Matlab/Simulink仿真平台、HIL半实物验证平台将两种控制策略和PI控制策略在多工况运行下的性能进行对比分析,主要结论如下:
1) 传统PI控制对系统多工况运行时动、静态性能的控制存在缺陷,例如启动时存在超调、响应速度慢、电压波动大以及负载变化时恢复至稳态的时间长等等。
2) 在列车运行速度发生变化时,基于SMC策略的CRH3动车组整流器输出直流电压波动较大,本文尝试将SMC算法与滑模观测器结合以改善SMC的控制缺陷,仿真和半实物结果表明SMO+SMC策略可以改善SMC在负载突变时鲁棒特性弱的缺点。
3) 在车网耦合系统中,列车运行速度发生变化时,仿真和半实物结果表明SMO+SMC策略可以有效改善牵引网侧电流在牵引电机转速改变时波动大的缺点。
[1] 欧阳森, 梁伟斌. 基于PSCAD/EMTDC的电气化铁路接入电网的电能质量评估方法[J]. 电工电能新技术, 2016, 35(12): 52-58.
OUYANG Sen, LIANG Weibin. An evaluation method of power quality about electrified railways connected to power grid based on PSCAD/EMTDC[J]. Advanced Technology of Electrical Engineering and Energy, 2016, 35(12): 52-58.
[2] LIU Z G, GENG Z Z, WU S Q, et al. A passivity-based control of Euler-Lagrange model for suppressing voltage low-frequency oscillation in high-speed railway[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2019, 15(10): 5551-5560.
[3] 赵宏程, 李再华, 梁海东, 等. 弱电网牵引变电所群电压不平衡预评估与治理研究[J]. 供用电, 2021, 38(12): 81-87.
ZHAO Hongcheng, LI Zaihua, LIANG Haidong, et al. Study on voltage unbalance pre-assessment and compensation for traction substation group connected to weak grid[J]. Distribution & Utilization, 2021, 38(12): 81-87.
[4]马喜欢, 陶顺, 徐永海, 等. 非线性负荷接入高压-超高压系统应用评估[J]. 中国电力, 2021, 54(12): 63-72.
MA Xihuan, TAO Shun, XU Yonghai, et al. Application evaluation of non-linear load connected to HV-EHV systems[J]. Electric Power, 2021, 54(12): 63-72.
[5] CHANG G W, LIN H W, CHEN S K. Modeling characteristics of harmonic current generated by high-speed railway traction drive converters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2004, 19(2): 766-773.
[6] BUSCO B, MARINO P, PORZIO M, et al. Digital control and simulation for power electronic apparatus in dual voltage railway locomotive[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2003, 18(5): 1146-1157.
[7] 张承烨, 汤赐, 曾云龙, 等. 再生制动工况下牵引变流器系统的稳定性分析[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2021, 36(4): 141-149.
ZHANG Chengye, TANG Ci, ZENG Yunlong, et al. The stability analysis of traction converter systems under regenerative braking conditions[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science and Technology, 2021, 36(4): 141-149.
[8] GENG Z Z, LIU Z G, HU X X, et al. Low-frequency oscillation suppression of the vehicle-grid system in high-speed railways based on H∞ control[J]. Energies, 2018, 11(6): 1594.
[9] LIU Zhigang, LIU Shuang, LI Zhiyuan, et al. A novel approach based on extended state observer sliding mode control to suppress voltage low frequency oscillation of traction network[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 52440-52454.
[10] 刘仕兵, 袁琳. 基于Simulink的高速铁路牵引供电系统仿真建模[J]. 华东交通大学学报, 2013, 30(6): 59-61.
LIU Shibing, YUAN Lin. Simulation and modeling of high speed railway traction power supply system based on Simulink[J]. Journal of East China Jiaotong University, 2013, 30(6): 59-61.
[11] 王晖, 吴命利. 电气化铁路低频振荡研究综述[J]. 电工技术学报, 2015, 30(17): 70-78.
WANG Hui, WU Mingli. Review of low-frequency oscillation in electric railways[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2015, 30(17): 70-78.
[12]冯晓云, 王利军, 葛兴来, 等. 高速动车组牵引传动控制系统的研究与仿真[J]. 电气传动, 2008, 38(11): 25-28.
FENG Xiaoyun, WANG Lijun, GE Xinglai, et al. Research and simulation on traction and drive control system of high-speed EMU[J]. Electric Drive, 2008, 38(11): 25-28.
[13]丁菊霞, 蒋奎. CRH3动车组牵引逆变器3种调制策略研究与仿真[J]. 电气传动, 2014, 44(6): 46-49.
DING Juxia, JIANG Kui. Research and simulation on three modulation strategies of traction inverter in CRH3 EMU[J]. Electric Drive, 2014, 44(6): 46-49.
[14]张加胜, 李浩光, 冯兴田. 四象限变流器的负载等效模型研究[J]. 电工技术学报, 2008, 23(1): 72-76.
ZHANG Jiasheng, LI Haoguang, FENG Xingtian. Research on load equivalent model of four-quadrant converters[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2008, 23(1): 72-76.
[15]TIAN X, LI X, ZHOU Z. Novel uninterruptible phase- separation passing and power quality compensation scheme based on modular multilevel converter for double-track electrified railway[J]. Energies, 2020, 13(3): 738-748.
[16]迟晓妮, 吴秋轩. 三相PWM并网换流器滑模控制策略研究[J]. 电力电子技术, 2020, 54(8): 120-123.
CHI Xiaoni, WU Qiuxuan. Study of three-phase PWM grid-connected converter based on the sliding mode control[J]. Power Electronics, 2020, 54(8): 120-123.
[17]刘爽, 刘志刚, 王亚绮, 等. 基于滑模控制的牵引网网压低频振荡抑制方法[J]. 电网技术, 2018, 42(9): 2999-3006.
LIU Shuang, LIU Zhigang, WANG Yaqi, et al. A novel approach to low frequency oscillation suppression of traction network voltage based on SMC[J]. Power System Technology, 2018, 42(9): 2999-3006.
[18]ZHANG Yuting, WU Siqi, LIU Zhigang, et al. An approach to improve system performance in the vehicle-grid system using sliding mode control under multiple operation conditions[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 11084-11095.
[19]刘宇博, 王旭东, 周凯. 基于滑模观测器的永磁同步电机电流偏差解耦控制[J]. 电工技术学报, 2020, 35(8): 1642-1652.
LIU Yubo, WANG Xudong, ZHOU Kai. Current deviation decoupling control with a sliding mode observer for permanent magnet synchronous motor[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2020, 35(8): 1642-1652.
[20]曹亚丽, 曹竣奥, 宋昕, 等. 一种改进滑模观测器的PMSM矢量控制研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49(16): 104-111.
CAO Yali, CAO Jun'ao, SONG Xin, et al. Research on vector control of PMSM based on an improved sliding mode observer[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49(16): 104-111.
[21]王家斌, 于永进, 阎振坤, 等. 基于自适应非奇异终端滑模控制的电力系统混沌抑制[J].电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49(7): 120-126.
WANG Jiabin, YU Yongjin, YAN Zhenkun, et al. Chaotic suppression of a power system based on adaptive non-singular terminal sliding mode control[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49(7): 120-126.
[22]孙立明, 杨博. 基于扰动观测器的电力系统鲁棒滑模控制器设计[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2020, 48(20): 124-132.
SUN Liming, YANG Bo. Design of perturbation observer-based sliding-mode controller for power systems[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2020, 48(20): 124-132.
[23]孙立明, 杨博. 超级电容储能系统的无源分数阶滑模控制设计[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2020, 48(16): 78-82.
SUN Liming, YANG Bo. Passive fractional order sliding mode control design of supercapacitor energy storage system[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2020, 48(16): 78-82.
[24]王金兵, 沈艳霞. 基于增量模型的永磁同步直线电机鲁棒预测电流控制[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2020, 48(8): 69-77.
WANG Jinbing, SHEN Yanxia.Robust predictive current control of permanent magnet synchronous linear motor based on incremental model[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2020, 48(8): 69-77.
[25]DAOUDI S E, LAZRAK L, LAFKIH M A. Sliding mode approach applied to sensorless direct torque control of cage asynchronous motor via multi-level inverter[J]. Protection and Control of Modern Power Systems, 2020, 5(2): 166-175.
[26]孙帮成. CRH380BL型动车组[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2014.
A control strategy for EMUs rectifier based on sliding mode observer
WANG Haoyu1, ZHANG Yuting1, 2, ZHANG Qiao1, LIU Zhigang1
(1. School of Electrical Engineering, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu 611756, China;2. Wuxi Rail Construction Design Consulting Co., Ltd., Wuxi 214000, China)
To improve the DC voltage anti-interference ability of a vehicle-grid coupling system under multi-operating conditions, a sliding mode control strategy of EMUs grid side rectifier based on a sliding mode observer (SMO+SMC) is proposed. First, through building the mathematical model of CRH3 EMUs in a dq coordinate system, the design equation of the sliding mode observer is derived. Then, the sliding mode observer is used to observe the output power of the traction motor in real time, and the voltage control module of the outer loop of the sliding mode control is supplied to realize the combination of the sliding mode observer and the sliding mode control. Finally, PI, sliding mode control and SMO+SMC are applied to the simulation model of CRH3 EMUs. In addition, the DC voltage control effect of the rectifier side under multiple working conditions is analyzed and verified, and then a semi-physical experiment is carried out based on the HIL small step real-time simulation test platform. The simulation and experimental results show that the SMO+SMC strategy can improve the DC voltage anti-interference ability and the stability of grid side voltage and current when multiple vehicles are connected to the grid.
electrified railway; EMUs-traction network coupling system; multi-condition operation; sliding mode observer
10.19783/j.cnki.pspc.220153
国家自然科学基金高铁联合基金重点项目资助 (U1434203)
This work is supported by the Key Project of High Speed Rail Joint Foundation of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U1434203).
2022-02-09;
2022-03-25
王浩宇(1998—),男,硕士,研究方向为轨道交通电气化与自动化;E-mail: 1102012570 @qq.com
张雨婷(1996—),女,硕士,研究方向为轨道交通电气化与自动化;E-mail: 1437149530 @qq.com
张 乔(1994—),男,通信作者,博士研究生,研究方向为轨道交通电气化与自动化。E-mail: zhangqiao_jq@ 163.com
(编辑 周金梅)

