Research on the Relationship between Cooperation lnnovation Expenditure and Economic Output of China’s Pharmaceutical lndustry
Wang Qiuli,Chen Yuwen
(School of Business Administration,Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,Shenyang 110016,China)
Abstract Objective To empirically analyze the relationship between cooperation innovation expenditure and economic output of China’s pharmaceutical industry,and provide a reference for improving its economic benefits and the capability of cooperation innovation in the future.Methods The relevant data of China’s pharmaceutical industry from 2000 to 2016 was selected as a sample.Based on the co-integration theory,an error correction model was established to conduct Granger test of causality to study the relationship between cooperation innovation expenditure and economic output of China’s pharmaceutical industry.Results and Conclusion The cooperation innovation expenditure of China’s pharmaceutical industry has a significant positive impact on economic output.If cooperation innovation expenditure increases 1%,its economic output will go up by 1.7%.At the same time,the long-term promotion effect of cooperation innovation expenditure on economic output is more significant than the short-term effect.
Keywords: pharmaceutical industry;cooperation innovation expenditure;economic output;co-integration test
As one of the six high tech industries in China,pharmaceutical industry is a knowledge-intensive industry integrating various advanced technologies.In recent years,with the support of the national policy and the increasing demand of the market,China’s pharmaceutical industry has developed rapidly.During the “12th Five-Year Plan” period,the “Guideline for the Development of Pharmaceutical Industry”,which was released in 2016,mentioned that the main business income of big pharmaceutical enterprises reached 2 688.5 billion yuan,and the total profit was 2 768.8 billion yuan in 2015.The average annual growth rate was 17.4% and 14.5%,respectively,ranking the top in various industries.In terms of innovation and development,big pharmaceutical enterprises spent about 45 billion yuan on R&D in 2015,quadrupling the amount spent in 2010.At the same time,the guideline also pointed out that China’s pharmaceutical industry still had some problems,such as weak original innovation capacity,weak transformation capacity,and few high-quality achievements.Therefore,strengthening the innovation capacity of China’s pharmaceutical industry is the top priority,which fully shows the key role of innovative R&D in the transformation and upgrading of China’s pharmaceutical industry[1].
There are two modes of innovation in pharmaceutical enterprises: independent innovation and cooperation innovation.Due to the characteristics of high investment,high risk and long cycle in pharmaceutical industry,many pharmaceutical enterprises no longer choose the traditional R&D innovation model,but actively cooperate with other scientific research units,institutions or universities in R&D and innovation outsourcing,thus allocating resources more reasonably and effectively,reducing the risk of R&D failure,bringing the good economic benefit and enhancing the core competitiveness of enterprises.The “Guideline for the Development of Pharmaceutical Industry”also proposed to build a number of pharmaceutical innovation centers,integrating government and social investment,R&D power of scientific research institutes and enterprises,clinical research resources of medical institutions,enterprises industrialization and other resources to promote innovation and development.Therefore,it is of great significance to explore the relationship between cooperation innovation expenditure and economic output,which can measure the cooperation innovation level of pharmaceutical enterprises.After summing up the relevant literature in recent years,it is found that most of the research focuses on the independent innovation of enterprises,while there is little research on the cooperation innovation and its impact on economic output.Based on the co-integration theory,the relationship between cooperation innovation expenditure and economic output in China’s pharmaceutical industry is analyzed empirically by using the data from 2000 to 2016,which can provide a reference for relevant policymaking departments to improve the economic benefit of pharmaceutical industry.
1 Literature review
1.1 Cooperation innovation expenditure has a positive effect on economic output
R Belderbos,et al.(2004)[2]used a large sample of data related to production statistics from innovative enterprises in the Netherlands in 1996 and 1998 to find that inter-university cooperation,as well as cooperation among competitors,helped create innovation and further promoted the sale of new products,and improved growth performance.Wang Longwei,et al.(2011)[3]investigated 400 enterprises selected randomly from the eastern,central and western regions of China,and concluded that cooperative R&D could significantly improve the product innovation performance of enterprises.Therefore,they suggested that enterprise managers should still attach importance to the role of cooperative R&D.Chu Shuzhen,et al.(2013)[4]selected the output value of new products and the sales revenue of new products as the measurement indexes of the economic output of the technical innovation efficiency in China’s pharmaceutical industry,and then they adopted DEA model to find that the external expenditure of R&D was one of the most important indexes that affected the efficiency of technological innovation in China’s pharmaceutical manufacturing industry.AG Frank,et al.(2016)[5]believed that managers continued to outsource R&D to other companies and their companies might gain knowledge created by other companies,which would help them innovate more.Yu Qian,et al.(2018)[6]used the data from 2004 to 2015 about industrial enterprises listed on small and medium-sized boards in Shenzhen Stock Exchange of China to carry out regression analysis based on the fixed effect model,finding that R&D input had a longterm positive effect on innovation output,and interfirm R&D cooperation had a short-term positive effect on innovation output.
1.2 Cooperation innovation expenditure has a negative impact on economic output
M Bruce and WG Biemans (1995)[7]pointed out some problems that might exist in cooperation innovation,such as enterprises would become more dependent on external technology,transaction costs would increase,the overall planning ability of managers would be in high demand,and core technology might flow out.These problems had a negative impact on firm performance.R Veugelers(1998)[8]believed that cooperative R&D might also have potential risks.And the information asymmetry with partners would pose a threat of opportunistic behavior,thus having a negative impact on firm performance.Luo Wei,et al.(2000)[9]pointed out that enterprises might encounter conflicts of values or corporate cultures when they cooperated with others,which led to the failure of R&D cooperation and hurt the performance of enterprises.
1.3 The effect of cooperation innovation expenditure on economic output is not significant
Gu Guoai (2013)[10]selected a total of 1 330 valid samples from 2006 to 2010 for whole regression analysis.Then,Cobb-Douglas production function was used to demonstrate that there were few provinces where external expenditure played a role in invention patents,and it had no significant impact on new product sales.Yang Tiantian (2015)[11]found there was no significant positive correlation between external R&D expenditure and innovation performance in both technology-intensive and non-technology-intensive industries by using the impulse response method.This might be due to the low efficiency of R&D cooperation between China’s enterprises,and the cooperation did not bring benefits to both parties.
2 Research design
2.1 Data sources and variable selection
2.1.1 Data sources
Based on the data of pharmaceutical industry in China from 2000 to 2016,the relationship between cooperation innovation expenditure and economic output is analyzed empirically in this paper.The relevant data in this paper are from “China Statistical Yearbook on High Technology Industry”[12-20]and“Statistics Yearbook on Science and Technology Activities of Industrial Enterprises”[21-25].The data sources are reliable,and the data are analyzed by Excel and Eviews10.0 software.
2.1.2 Selection of variables and indicators
(1) Independent variable.The independent variable in this paper is the cooperation innovation expenditure,which is measured by the external expenditure of R&D and recorded as RD.The external expenditure of R&D refers to the funds that the enterprises entrust or cooperate with the other units to carry out R&D activities.As to the availability of data,all the data from 2000 to 2016 are chosen.What needs to be explained is that the R&D expenditure data from 2000 to 2008 are replaced by the external expenditure for “Statistics Yearbook on Science and Technology Activities of Industrial Enterprises”[21-25].The data of R&D external spending from 2009 to 2016 come from “China Statistical Yearbook on High Technology Industry”[12-20].
(2) Dependent variable.The dependent variable in this paper is economic output,and the index is sales revenue of new products,which is recorded as SR.A new product is developed and produced by adopting new technological principles,new design,or an improvement over the original product,such as structure,material quality and technology.Therefore,the product performance is significantly improved or the function of the product is extended.The relevant data are all from “China Statistical Yearbook on High Technology Industry”[12-20]from 2000 to 2016.
To weaken the collinearity and heteroscedasticity of the model and improve the accuracy of the results,the relevant data are logarithmically processed in this paper.As RD is taken as lnRD and SR as lnSR,the logarithmic data does not change the correlation between variables.Relevant indicator data are shown in Table 1.

Table 1 R&D expenditure and sales revenue of new products in Chinese pharmaceutical industry from 2000 to 2016
2.2 Model construction and method selection
2.2.1 Unit root test
Most time series data are unstable variables,which can avoid the occurrence of false regression.Firstly,the stability of time series variables is tested by unit root test,and only when the time series variables satisfy the precondition of single integral of the same order can they be tested by co-integration test.The common unit root test method is ADF test,which is implemented by the following three models.

Whereαis a constant term,εtis a random term,Tis a time variable,and ΔXt-iis a delay term of ΔXt.Model (1) contains neither constant term nor trend term.Model (2) contains constant term but does not contain trend term.Model (3) takesTas a time variable,indicating that time series have certain trend.Therefore,it is a model that contains both constant and trend terms.The null hypothesis of these three models is that there is a unit root and the delayed term of ΔXt,which can eliminate the sequence correlation of the random interference term of the time series and ensure the random term is white noise.In the unit root test,AIC or BIC information criterion is used to get the lag order automatically.The test order is model(3),model (2) and model (1).Once the null hypothesis is rejected,there is no unit root,and then the time series variable becomes a stationary variable.
2.2.2 Co-integration tests
For the co-integration analysis of non-stationary time series,the two-step E-G method is usually used to verify the results.E Engel and P Granger proposed a two-step E-G test to test whether there is co-integration relationship between two time series variables of the same order of the first order.The cointegration relationship betweenXandYis represented by model (4).

Firstly,model (4) is regressed by OLS to get the regression equation (5) and the non-equilibrium error is calculated.


Then ADF unit root test is carried out on the stationarity of residual itemet,which can be tested by model (6).If the original sequence ofetis stable,thenYtandXtare (1,1) of the same order.
2.2.3 Error correction model (ECM)
ECM can reflect the short-term deviation of variables to correct the long-term equilibrium and make up for the shortcomings of the long-term model.According to Percy Granger’s representation theorem,it is necessary to carry out co-integration analysis on the variables before establishing the error correction model to obtain the long-term equilibrium relation among the variables,that is,the co-integration relation.Then the error correction term is formed,which is taken as one of the explanatory variables to establish the short-term model,the error correction model[26].If the two variables are cointegrated,their short-term disequilibrium relation can be expressed by an error correction model,as shown below.
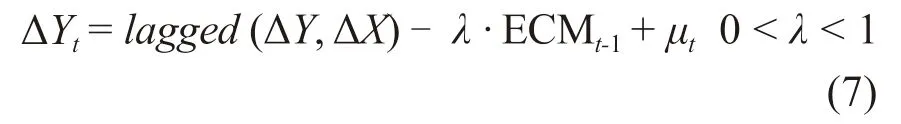
Among them,ECMtis a non-equilibrium error term andλis a short-term adjustment parameter.0 <λ< 1 indicates that the non-equilibrium error term in the previous period is a correction to theYvariable in the later period.Ifλ> 0,the model is wrong.
2.2.4 Granger test of causality
When two variables have a lead-lag relationship in time,it is necessary to examine whether their relationship is one-way or two-way.To solve this problem,in 1969,P Granger proposed an autoregressive model for both variables,called the Granger test of causality,which is a way of testing whether the lagging value of a variable can predict the information of the explained variable.Namely,variableXcan help explain the future change of variableY,and thisXis the Granger cause ofY.The following questions should be noted in the practical application of Granger test of causality.
(1) The result of Granger test of causality is sensitive to the choice of lag order.Generally speaking,different lag time length should be tested by Granger test of causality to observe its sensitivity.
(2) In theory,the Granger test of causality is only used for stationary time series,and it cannot be used directly for two single integral non-stationary time series variables of the same order.It is found that when the two sequences are transitioning from stationary to nonstationary processes,the probability of Granger test of causality between them is significantly increased.Therefore,results of the Granger test of causality for two unintegral nonstationary time series variables of the same order are reliable.
(3) The sample size of time series variables also can have great influence on the result.The larger the sample size of the time series variables,the more likely it has a Granger test of causality between the variables[26].
3 An empirical analysis
3.1 Unit root test
In this paper,ADF unit root test is used to test the stationarity of lnRD and lnSR.The results are shown in Table 2.
It can be seen from Table 2 that lnRD does not have unit root and it is stationary,lnSR has unit root and it is not stationary.So,these two variables do not have the same order unity.The unit root test of the first-order difference variables ΔlnRD and ΔlnSR shows that there is no unit root and they are stationary sequences.Therefore,these two variables have the same order and can be further tested for co-integration.
3.2 Co-integration tests
According to ADF test,both ΔlnRD and ΔlnSR have no unit root,which satisfies the premise of cointegration test.Therefore,E-G two-step method is used to test the co-integration relationship between the two variables and the estimated parameters.Firstly,the co-integration regression equation of R&D expenditure and new product sales revenue is established as follows.
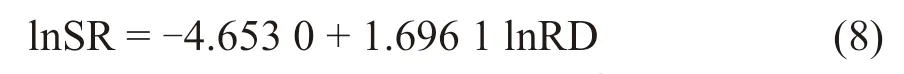
The adjustedR-squared figuresR2=0.916 3,close to 1,andF=176.234 4,which shows that the regression equation fits well.Then,residual item is made and resid=ECM,ECM=lnSR -1.696 1 lnRD+4.653 0.The unit root test of the residual ECM is performed.The results are shown in Table 3.
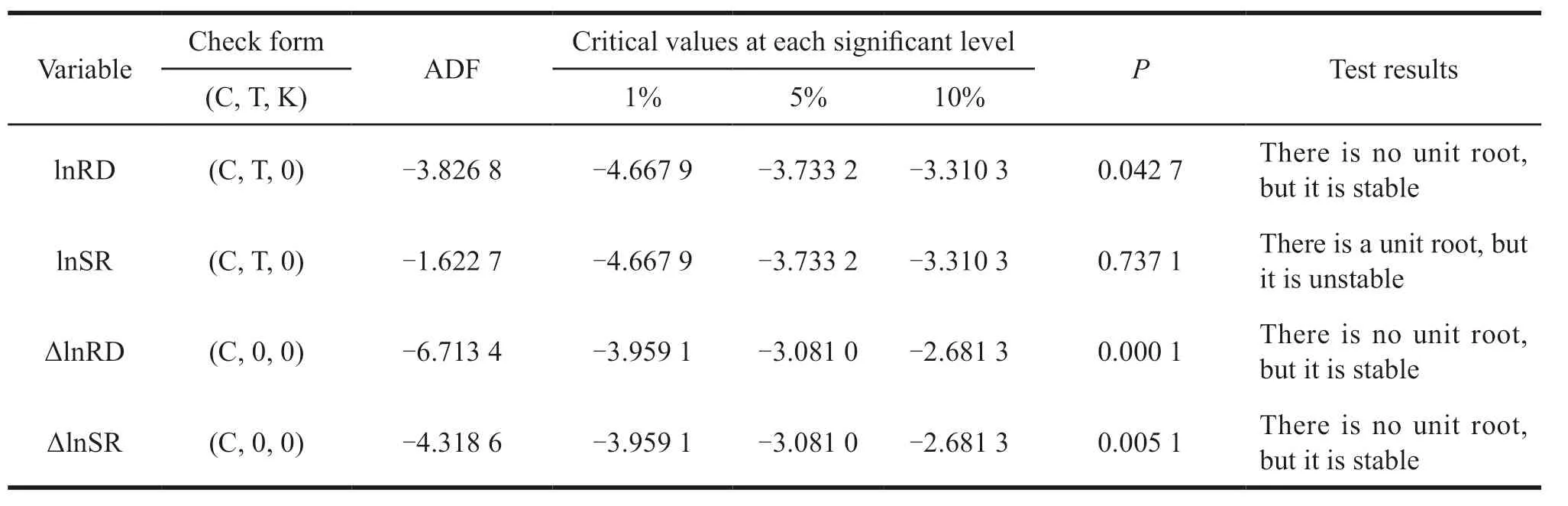
Table 2 The results of unit root test
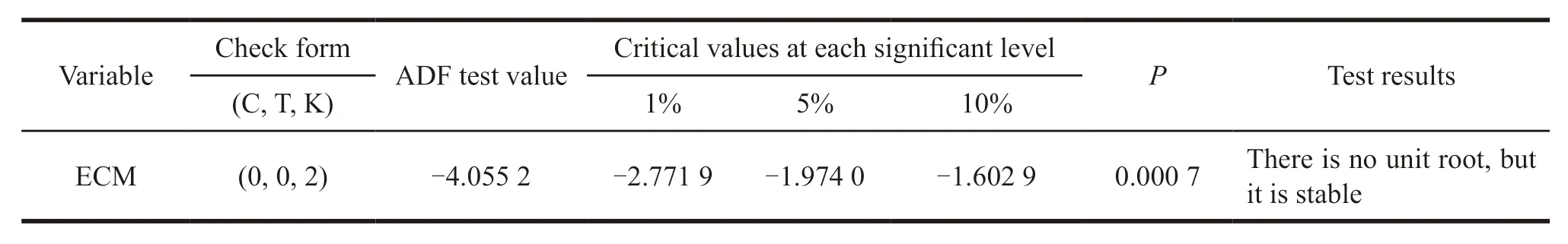
Table 3 ADF unit root test for residual series
From Table 3,we can see that there is no unit root of residual term ECM at 1% significance level,and it is a stationary sequence.So,there is a long-term equilibrium co-integration relationship between lnRD and lnSR.Among them,the elasticity of R&D expenditure to new product sales revenue is 1.696 1.It means that the new product sales revenue will increase 1.696 1 percent for one percent of R&D expenditure in Chinese pharmaceutical industry in the long run.
3.3 Constructing an error correction model
Based on co-integration test,an error correction model of R&D expenditure and new product sales revenue is constructed to illustrate the short-term dynamic relationship between the two variables.The ECM test results are shown in Table 4.
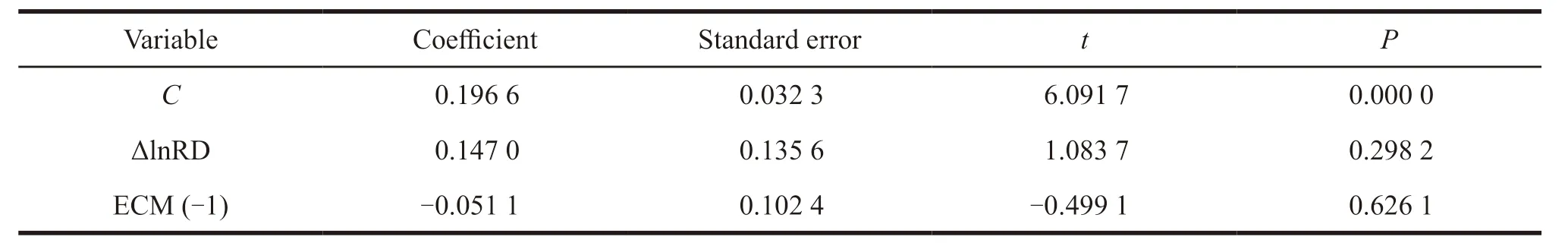
Table 4 ECM test results
The further error correction model equation is as follows.
ΔlnSR=0.196 6+0.147 0 ΔlnRD -0.051 1 ECM (-1) (9)
From equation (9),the coefficient of the error term is -0.051 1,less than 0,which is in line with the reverse correction mechanism.The short-term elasticity coefficient is 0.147 0,which indicates that the revenue of new products will increase by 0.147 0 percent for every percent of external expenditure of R&D in China’s pharmaceutical industry.
3.4 Granger test of causality
As can be seen from the above,the external expenditure of R&D funds has a long-term equilibrium relationship with the sales revenue of new products,and the variables lnRD and lnSR need to be tested by Granger test of causality.The results are shown in Table 5.
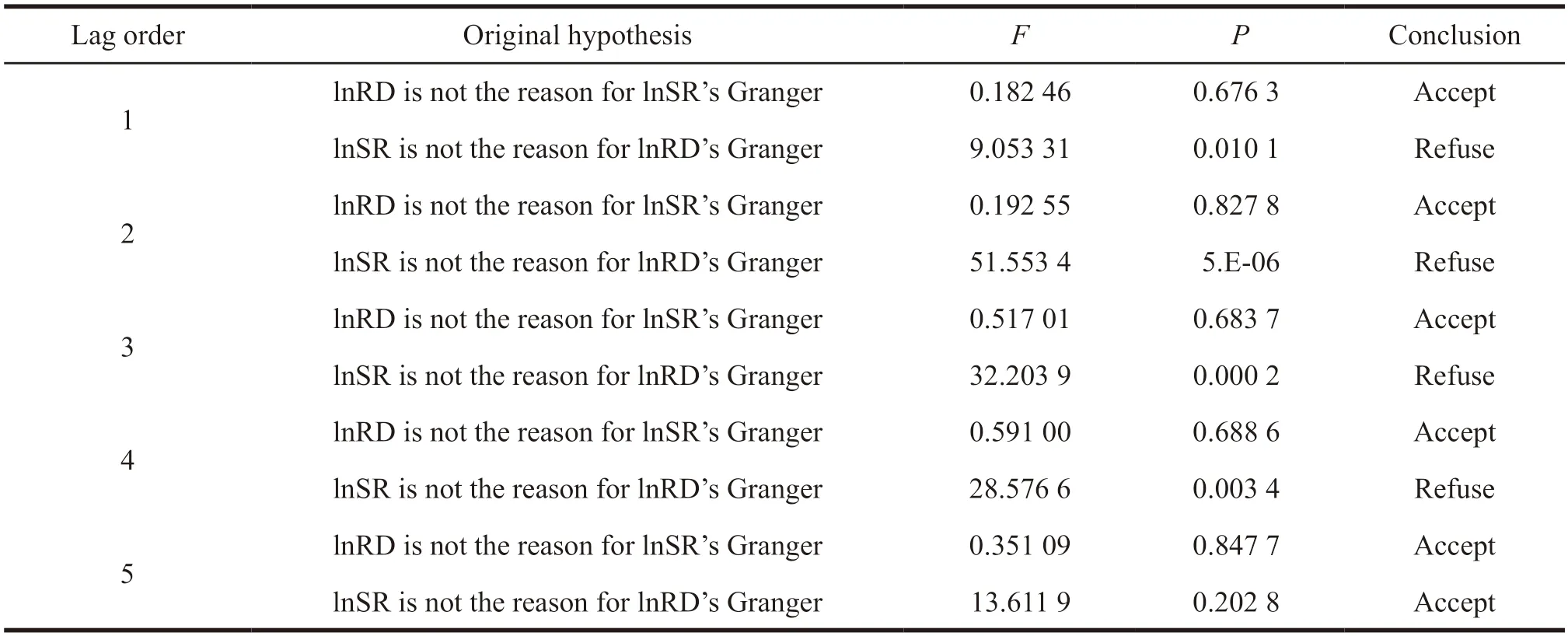
Table 5 Results of Granger test of causality
It can be seen from Table 5 that when the lag order is 1,2,3,4,the original assumption that “lnRD is not the Granger cause of lnSR” is accepted,and“lnSR is not the Granger cause of lnRD” is rejected.It means that lnRD is not the Granger reason of lnSR,but lnSR is the Granger reason of lnRD,indicating that the lag period of sales revenue of new products can correctly forecast the external expenditure of R&D.Otherwise,it is not tenable.When the lag order is 5,the original assumption that “lnRD is not the Granger cause of lnSR” and “lnSR is not the Granger cause of lnRD” is accepted,which means that there is no Granger causality between lnRD and lnSR.
3.5 Results and discussion
(1) Co-integration test shows that there is a longterm equilibrium co-integration relationship between R&D expenditure and sales revenue of new products.The elasticity coefficient of R&D expenditure to sales revenue of new products is 1.70.It means that R&D expenditure increases one percent,the sales revenue of new products will increase by 1.70 percent.This indicates that the increase in external R&D expenditure can increase the sales revenue of new products.In the long run,the cooperation innovation expenditure of China’s pharmaceutical industry has a significant positive impact on economic output,that is,the increase of the cooperation innovation expenditure is conducive to promoting its economic output.When the cooperation innovation expenditure increases by 1%,economic output will rise by 1.7%.
(2) The error correction model shows that the deviation of the long-term equilibrium relationship between R&D expenditure and sales revenue of new products will be corrected by 5.11% in the next period.The short-term elasticity coefficient of R&D expenditure to the sales revenue of new products is 0.15%.Therefore,for one percent increase in R&D expenditure in a short term,the sales revenue of new products will increase by 0.15 percent.The shortterm elasticity coefficient 0.15 is less than the longterm elasticity coefficient 1.70.It means that the longterm effect of the external expenditure of R&D funds on the sales revenue of new products is stronger than that of the short-term effect.It also means the longterm effect of cooperation innovation expenditure on economic output is more significant than the shortterm effect.
(3) Granger test of causality shows that the change of sales revenue of new products is the Granger cause for the change of external expenditure of R&D when the lag period is 1 to 4.Whereas the change of R&D expenditure is not the Granger cause for the change of sales revenue of new products.It shows that most pharmaceutical enterprises have a strong desire to put the sales revenue of new products into cooperation innovation activities,but the input cannot be effectively converted into output for some time.This may be due to the threshold effect of R&D innovation.Only when the cooperation innovation expenditure reaches a certain scale,it can be further transformed into economic output.This shows that the cooperation innovation expenditure of Chinese pharmaceutical industry is still low.It usually takes a long time for the cooperation innovation expenditure of China’s pharmaceutical industry to be transformed into economic output.However,the economic output of China’s pharmaceutical industry has a significant effect on the cooperation innovation expenditure which lags about 1 to 4 years.
4 Research recommendations
4.1 Pharmaceutical enterprises should actively expand cooperation innovation resources and enhance innovation capability
Innovation ability is an important criterion to measure the strength of pharmaceutical enterprises,which is the core driving force for the sustainable and healthy development of pharmaceutical enterprises with strong competitiveness.As the main body of innovation,enterprises should have the awareness of open innovation,and increase the expenditure of cooperation innovation to strengthen external R&D cooperation.Since the co-innovation expenditure is closely related to the innovation capability,the coinnovation channels should be expanded.For example,the co-R&D with universities,institutions and CRO companies should be strengthened.In particular,for projects with more R&D difficulties,it is necessary to make good use of the scientific and technological resources of other units such as universities and R&D institutions.Besides,a long-term cooperative partnership with other units can be established and some R&D centers should be set up,which will keep track of the progress of the project.Such cooperation can not only reduce the risk of R&D,but also greatly increase the chance of transforming scientific and technological achievements into economic output.
4.2 Cooperation innovation expenditure should be planned according to strategic objectives and R&D input should be allocated in time
The strategic objectives of an enterprise can guide the direction and level of its short-term,medium-term and long-term business activities.The overall operation of an enterprise will be carried out around the strategic objectives of business and capital investment plan.When carrying out cooperation innovation,enterprises need to make a careful business layout according to different situation of market and their own life cycle.The research shows that compared with the short-term,the cooperation innovation expenditure has an obvious long-term promotion effect on the economic output of China’s pharmaceutical industry.Therefore,enterprises should not pursue short-term benefits and blindly spend much cooperative innovation expenditure.It is necessary for them to find the right development opportunity according to the life cycle and stage target of enterprise,which will be more beneficial to the promotion of economic output.At the same time,enterprises should properly invest the revenue brought by economic output in the external expenditure of R&D to ensure that pharmaceutical enterprises have sufficient funds when they carry out cooperation innovation activities.
4.3 Relevant departments should establish a platform for cooperation by creating a sound environment for scientific and technological innovation
Relevant government departments should provide a good development environment for scitech innovation.Meanwhile,they should give macro guidance to the transformation of sci-tech innovation to stimulate the enthusiasm of pharmaceutical enterprises for innovation.They also can set up a platform for sharing scientific and technological resources.For example,some exchange meetings and exhibitions on innovative achievements can be organized,which will encourage the exchange between pharmaceutical enterprises,institutions of higher learning and scientific research institutions for the cooperation of R&D.Pharmaceutical enterprises,universities and scientific research institutions with more scientific and technological resources and R&D resources make use of each other’s advantages to cooperate,which will break through the barriers of innovation.
4.4 Promoting collaborative innovation among enterprises through policy support
In view of the positive effect of cooperation innovation expenditure of pharmaceutical enterprises on their economic output,the awareness of enterprises should be enhanced to carry out cooperation innovation.In addition to the enterprises’ initiative,relevant departments should formulate a series of supporting policies to solve the difficulties of pharmaceutical enterprises in carrying out cooperation innovation.For example,the government should strengthen the protection of intellectual property rights to increase the enthusiasm of enterprises in innovation.Besides,the government should increase financial input,encourage banks’ financing support for R&D projects,which can provide certain financial guarantee for enterprises to cooperate in R&D.
- 亚洲社会药学杂志的其它文章
- Analysis of Factors Affecting Online Drug Purchase -Based on Factor Analysis
- Benefit-Risk Assessment for PD-1/PD-L1 lnhibitors in the Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Research on the Price Level of Drugs in Short Supply in China
- Research on Problems and Countermeasures of Patent Evaluation System in Pharmaceutical Enterprises
- Comparative Study and Enlightenment on lnnovation Achievements of Pharmaceutical lndustry in Liaoning Province
- Development Strategy of Green Marketing of Pharmaceutical Enterprises against the Background of Building a Beautiful China

