Clinical significance of DNAH14 gene in uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma based on bioinformatics
Nan Li ,Yu-Han Duan ,Lei Chen ,Kun Zhang
1Department of Clinical Laboratory,Jilin University Second Hospital,Changchun 130000,China.2Department of Research Center,Jilin University Second Hospital,Changchun 130000,China.
Abstract Background: To analyze the effect of DNAH14 gene on the development of endometrial carcinoma and its clinical significance by using tumor comprehensive database.Methods: First,the aberrant expression of the DNAH14 gene in multiple tumor tissues was obtained in the gene expression profiling interactive analysis.Then clinicopathological data were obtained at the cancer genome atlas.The expression and prognostic value of the DNAH14 gene in endometrial cancer were assessed.Subsequently,Kaplan-Meier mapping instrument analysis was used to assess the significance of DNAH14 mRNA expression and DNAH14 gene mutations in the prognosis of uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma patients.The relationship between immune infiltrating cells and uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma survival was analyzed using the Tumor Immune Estimation Resource database.Finally,the Mu Target database was used to analyze and identify genes that exhibit altered expression in samples containing mutated genes,then the Database for Annotation,Visualization and Integrated Discovery was used to explore the biological processes closely associated with DNAH14 mutations and enriched signaling pathways,and the Search Tool for Recurring Instances of Neighbouring Genes database to construct protein interaction networks that may interact with DNAH14 and explore their potential mechanisms of action.Results: The overall survival rate and relapse-free survival rate in patients with high expression of DNAH14 were significantly lower than those with low expression and there were significant differences in clinical stage,age,menopausal status and histological types (P <0.05).DNAH14 gene mutation exists in patients with endometrial carcinoma,indicating a good prognosis.Correlation analysis showed that DNAH14 gene mutation might play a role through proteoglycan and Wnt,T cell receptor,toll-like receptor signal pathway in cancer.In addition,DNAH14 mutation is related to the level of immune infiltration;protein interaction analysis showed that DCTN3,HAP1,ACTR1,DNAH12,ACTR1B and other proteins interact with DNAH14.Conclusion: DNAH14 is highly expressed in endometrial carcinoma and its high expression is related to the poor prognosis of the patients.DNAH14 gene mutation in patients with endometrial carcinoma may affect the level of immune infiltration and improve prognosis through proteoglycan,Wnt,T cell receptor and toll-like receptor signal pathway in cancer.DNAH14 may be an index to judge the prognosis of patients with endometrial carcinoma.
Keywords: endometrial carcinoma;DNAH14;gene mutation;prognosis
Background
Endometrial carcinoma (uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma,UCEC) is the sixth most common malignant tumor in women.Its occurrence and development mechanism is related to tumor mutation load and immune cell infiltration.It is estimated that there will be 65,620 new cases and 12,590 deaths in the United States in 2020,second only to ovarian cancer [1].At the same time,the mortality rate of UCEC has increased over the past decade.The 5-year survival rate of stage I UCEC is more than 90%,while that of stage IV is only 20%[2].The traditional treatment is surgery,radiotherapy and chemotherapy and hormone therapy.For patients with metastasis,surgery and radiotherapy can not reach a satisfactory level of treatment,which left only chemical or hormone therapy,which can cause more significant damage to normal human cells and lead to recurrence.
Therefore,it is urgent to explore the molecular mechanism of the progression of UCEC and the factors affecting the prognosis and to find tumor markers that can be used for molecular diagnosis and targeted therapy.In 2017,a study identified DNAH14 mutations in UCEC as potential passenger genes [3].In the tumor genome,frequent mutations are considered to be driving genes,while less frequent mutations are called passenger genes.Some biological functions of some passenger genes exist in the pathway of cancer development and have the potential to become driving genes,which may play a vital role in the development of cancer.
By searching the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database,some researchers found that DNAH14 germline polymorphism is related to the survival rate of ovarian cancer and can be used as a prognostic biomarker and a potential target for individualized therapy [4].In addition,its genetic variation can be used as a biomarker to predict the response of locally advanced rectal cancer to neoadjuvant radiotherapy and chemotherapy [5].These studies suggest that DNAH14 may be a potential tumor-driving gene.Still,few studies have been carried out at home and abroad on its regulation of the progression of endometrial carcinoma.The purpose of this study is to analyze the expression of DNAH14 gene and the effect of its mutation on UCEC in patients with UCEC through a variety of tumor comprehensive databases,to explore the role of DNAH14 in the occurrence and development of UCEC,and to provide a reference basis for accurate treatment of UCEC.
Material and methods
The Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis (GEPIA) database(http://gepia.cancerpku.cn/) integrates TCGA cancer big data and Genotype-Tissue Expression) normal tissue big data.Abnormal expression of the DNAH14 gene in a wide range of tumor tissues can be obtained.
UALCAN-TCGA database (http://ualcan.path.uab.edu/) was used to analyze the expression of DNAH14 in UCEC patients with different stages,ages,menopausal status and histological subtypes.
Kaplan-Meier Plotter database (http://kmplot.com/analysis/) was used to analyze the significance of DNAH14 mRNA expression and DNAH14 gene mutation in the prognosis of UCEC patients,including overall survival (OS) and relapse-free survival (RFS).
Tumor Immune Estimation Resource (TIMER) database(https://cistrome.shinyapps.io/timer/) was used to analyze the mutation frequency of DNAH14 in each TCGA cancer and to analyze the relationship between immune infiltrating cells and UCEC survival rate.
Mu Target database (https://www.mutarget.com/) analyzed and identified the altered expression genes in the samples containing mutant genes and searched the related genes of DNAH14 mutation.
Database for Annotation,Visualization and Integrated Discovery(DAVID) database (https://david.ncifcrf.gov/) was used to analyze the biological processes and enrichment signal pathways closely related to DNAH14 mutations.
The interaction between DNAH14 protein and other proteins was analyzed by the Search Tool for Recurring Instances of Neighbouring Genes (STRING) database (https://www.string-db.org/),and the protein interaction network that might interact with DNAH14 was obtained.
Results
The surveys of the GEPIA database on the mutation status and distribution of DNAH14 gene in endometrial carcinoma patients
It showed that DNAH14 was abnormally expressed in many kinds of tumor tissues and the expression was increased in UCEC (Figure 1).The results of the UALCAN database search showed that there were significant differences in the distribution of DNAH14 gene between normal tissues and UCEC in different stages,ages,menopausal status and histological types.Compared with the normal group,the level of DNAH14 in the tumor group increased significantly.The level of DNAH14 in different stages of the tumor increased and compared with the stage I tumor group,the level of DNAH14 in stage Ⅱ,Ⅲand Ⅳtumor tissues increased,and there was no significant difference in the grouping.The level of DNAH14 in UCEC increased in all age groups and there was no difference in age groups.For different menopausal states,the level of DNAH14 in UCEC increased and there was no difference in a menopausal state.According to different histological subtypes,the level of DNAH14 in each subtype of UCEC increased significantly and there was no difference in subtypes(Figure 2).
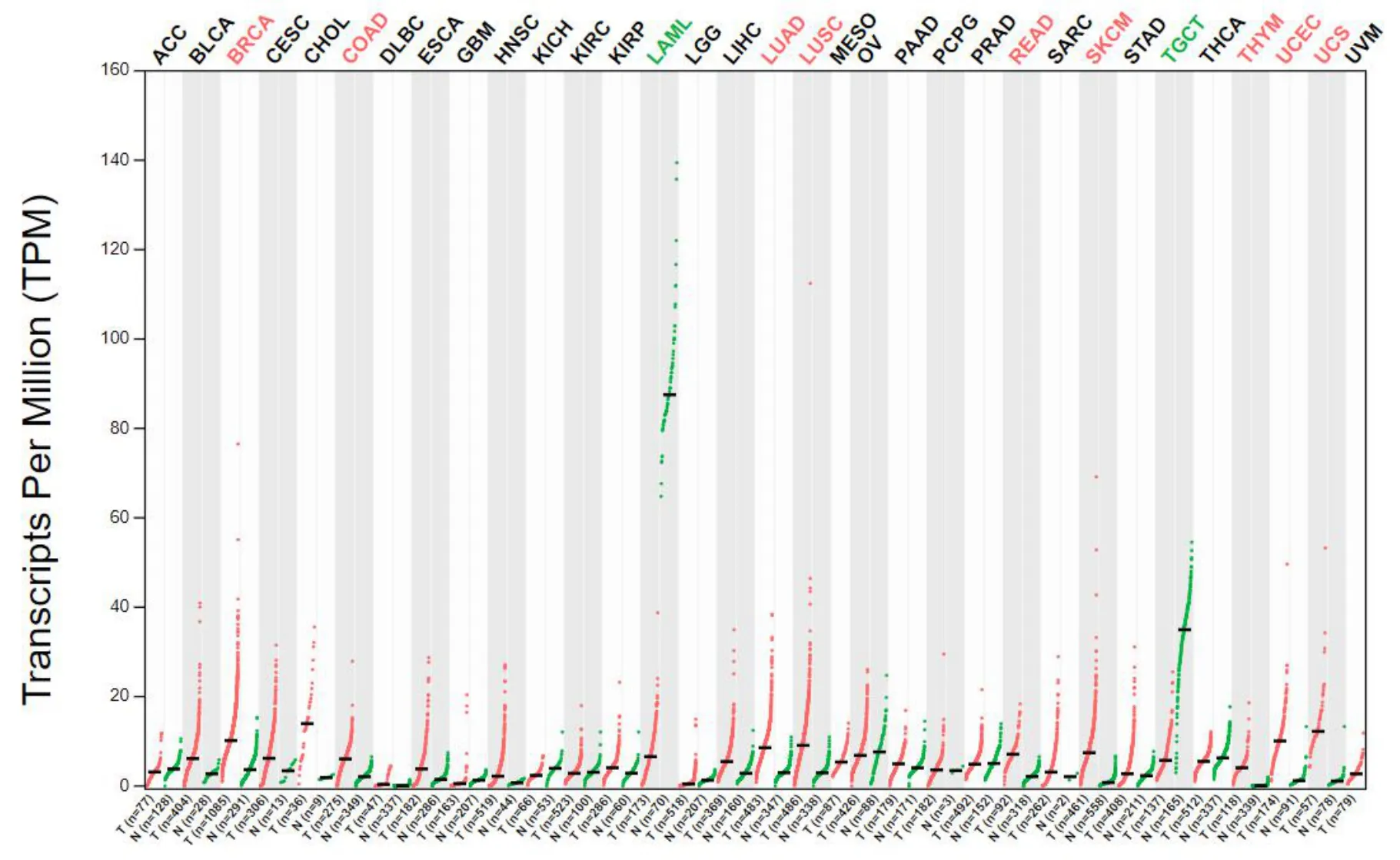
Figure 1 Expression of DNAH14 gene in different tumor types and normal control tissues
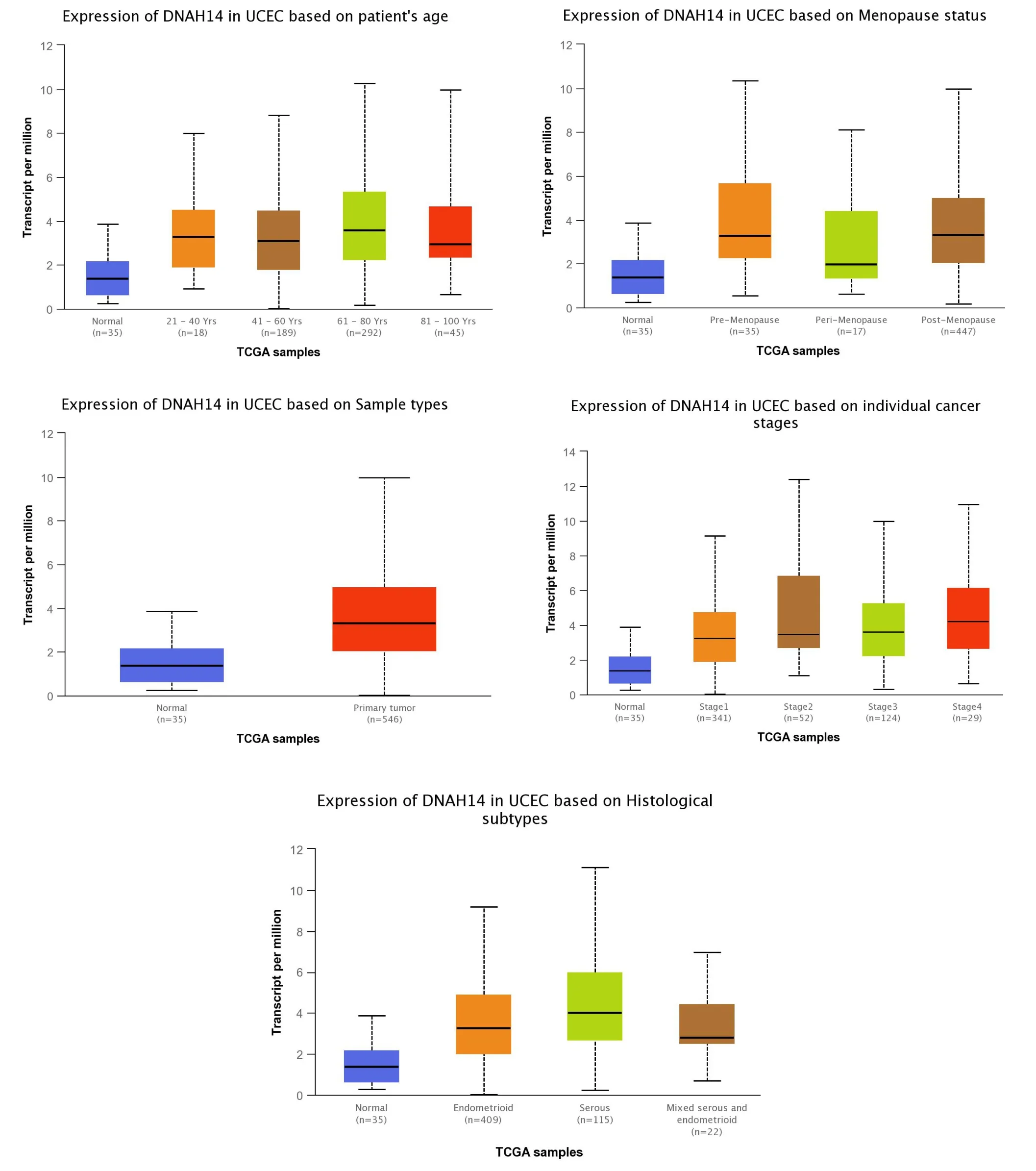
Figure 2 Differences in the distribution of DNAH14 in different samples,stages,ages and histological types.UCEC,uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma.
Significance of DNAH14 gene mutation in the prognosis of UCEC
Through the Kaplan-Meier Plotterg database,according to log-rank method and survival curve comparison,higher DNAH14 mRNA level was associated with shortened OS and disease RFS,and DNAH14 mutation prolonged OS and disease RFS in UCEC patients compared with natural genotypes (Figure 3).
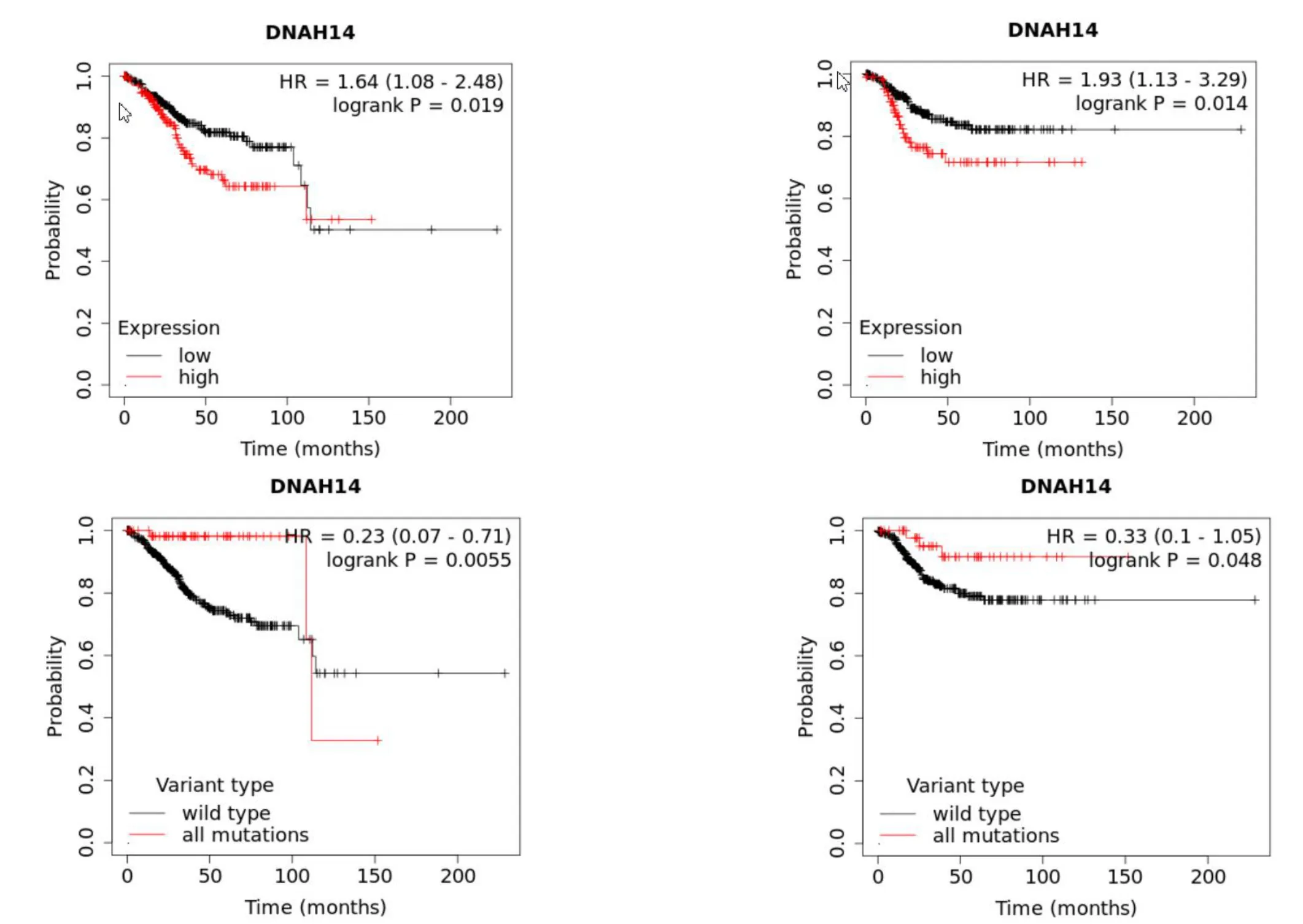
Figure 3 The relationship between the expression level and mutation state of DNAH14 and OS and RFS.OS,overall survival;RFS,relapse-free survival.
Mutation status and functional prediction of DNAH14 gene in patients with UCEC
The mutation frequency of DNAH14 in each TCGA cancer was obtained by searching the TIMER database and the results showed that the mutation frequency was the highest in UCEC (Figure 4).The genes related to DNAH14 mutation were searched by the Mu Target database.Then Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomeswere (KEGG) used for functional enrichment analysis and signal pathway prediction.Through the DAVID database,it is found that the biological processes closely related to DNAH14 mutation include Wnt signal pathway,chemokine-mediated signal pathway,negative regulation of endopeptidase activity,positive regulation of synaptic assembly,neuronal differentiation,sodium ion transport,cell fate locking,regulation of calcium-dependent exocytosis,calcium-regulated neurotransmitter exocytosis,response to unfolded proteins,etc.The changes of molecular functions such as chemokine activity,endopeptidase inhibitor,inhibition of cyclin-dependent serine/threonine kinase activity,crimp binding,potassium channel activity,grid protein binding and voltage-gated calcium channel activity are related to DNAH14 gene mutation,while the changes of cellular components such as T cell receptor complex are associated with the abnormal expression of DNAH14 (Figure 5).Through KEGG analysis,these related gene mutations are mainly related to the regulation of proteoglycan,Wnt signal pathway,T cell receptor signal pathway and toll-like receptor signal pathway in cancer.
Relationship between DNAH14 expression and UCEC immune cell infiltration
TIMER database analysis showed that the expression of DNAH14 was positively correlated with the level of immune infiltration of B cells,CD4+T cells and CD8+T cells (Figure 6),which may be involved in the process of immune infiltration of UCEC cells.
Analysis of DNAH14 protein interaction network
The STRING 11.0 database analyzed the interaction between DNAH14 protein and other proteins,and the protein interaction networks that may interact with DNAH14 were obtained: the proteins that interact with DNAH14 include DCTN3,HAP1,ACTR1,DNAH12,ACTR1B,DCTN5,DCTN6,DCTN1,DNAH1,ACTR1A (Figure 7).
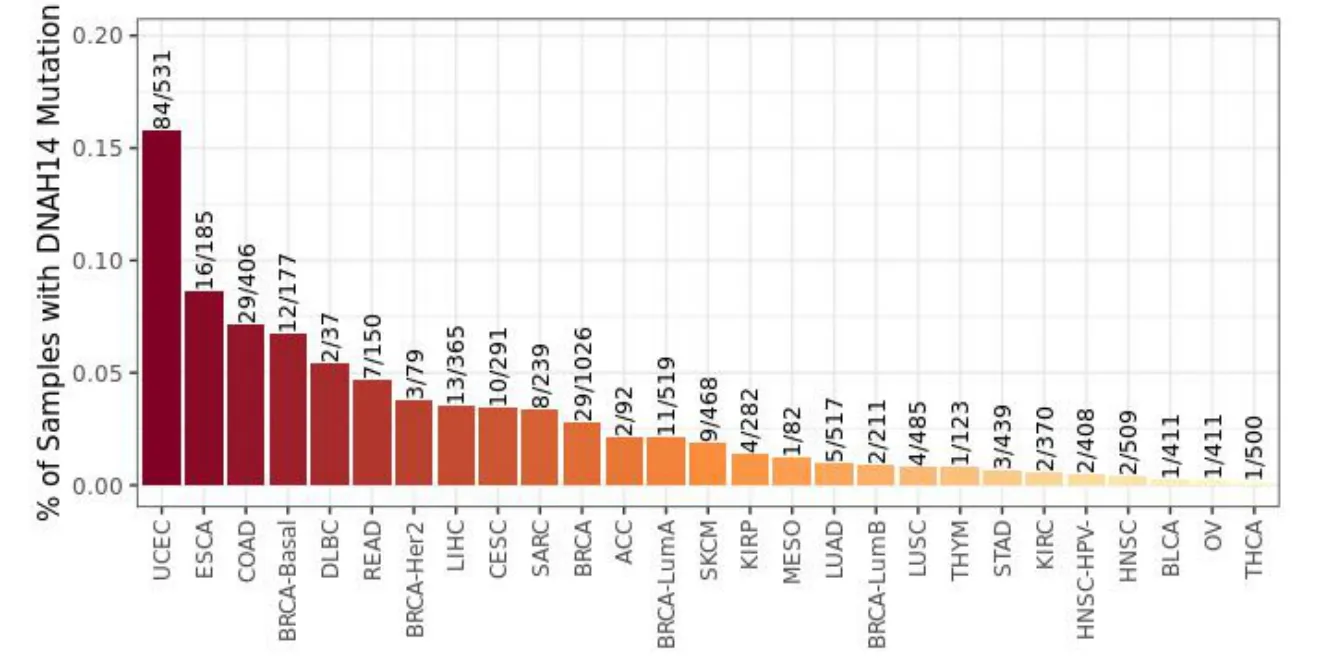
Figure 4 Mutation frequency of DNAH14 in TCGA cancer type.TCGA,the cancer genome atlas.
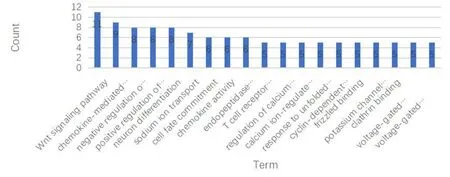
Figure 5 GO analysis of biological process of genes related to DNAH14 mutation.GO,Gene Ontology.

Figure 6 Relationship between DNAH14 gene mutation and UCEC immune cell infiltration.UCEC,uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma.
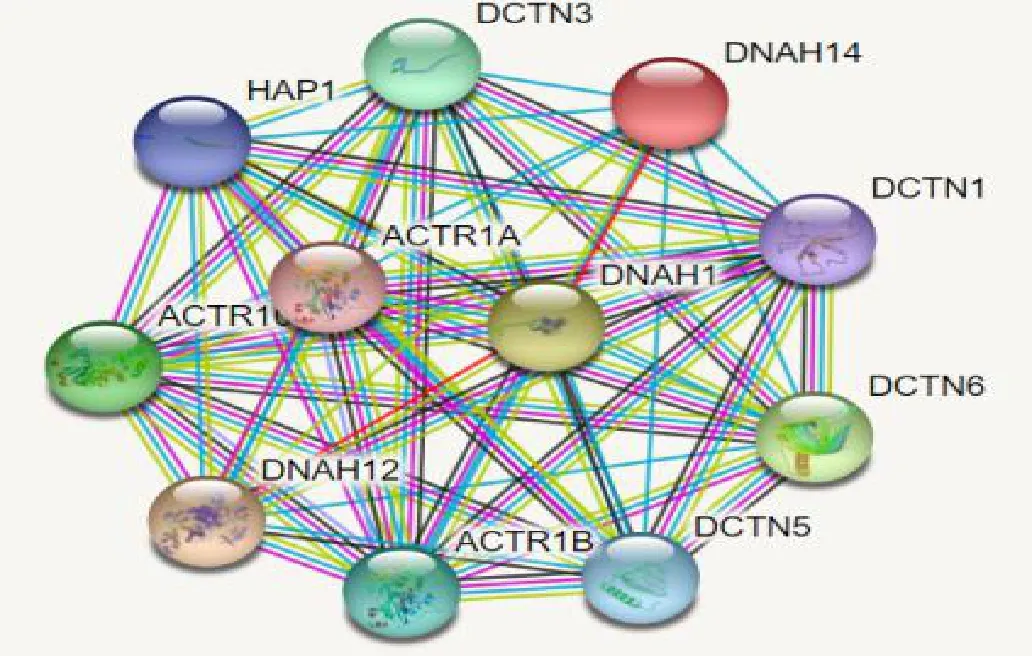
Figure 7 Protein network diagram of DNAH14
Discussion
This study shows that DNAH14 is highly expressed in UCEC and its high expression is associated with poor prognosis.In addition,DNAH14 has gene mutation in UCEC.Through the survival analysis of GEPIA and Kaplan-Meier Plotter database,it is found that DNAH14 gene mutation is a good prognostic factor for UCEC and is related to both OS and RFS.Although the prognostic value of DNAH14 mutation in UCEC has never been reported,a large sample analysis of the public database shows that the mutation status of the gene does increase survival.There is still a lack of reliable basic biological research on how DNAH14 gene mutation plays a role and affects the prognosis.Through GO and KEGG analysis,it is found that DNAH14 mutation-related genes are involved in biological processes,including regulation of signal transduction,ion channels,regulation of cell cycle and so on.Searching the TIMER database,it was found that there was a correlation between DNAH14 mutation and UCEC immune cell infiltration,which may improve the prognosis by slowing down the process of immune infiltration.
In our analysis,DNAH14 gene mutation related genes were enrichedin proteoglycan,Wnt signal pathway,T cell receptor signal pathway and toll-like receptor signal pathway in cancer.The invasion of cancer cells into the surrounding tissue is a key step in tumor metastasis.In the process of metastasis,tumor cells can interact with extracellular matrix components and secrete proteolytic enzymes to reshape the surrounding tumor microenvironment.Proteoglycan is one of the main components of extracellular matrix.They participate in many processes of cancer cell invasion and metastasis by interacting with soluble bioactive molecules,surrounding matrix,cell surface receptors and enzymes.Studies have confirmed that a variety of proteoglycan family members can promote the progress of UCEC by regulating the biological behavior of cancer cells [6-8].Wnt signaling pathways are involved in a variety of cellular processes of the female reproductive system,including development,cell proliferation,cell survival,adhesion and movement,and the regulation of menstrual cycle.Abnormal regulation of Wnt signaling pathway in endometrium leads to endometrial hyperplasia,which may promote the occurrence and progression of endometrial carcinoma [9].Studies have shown that steroid receptor activators,ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolases and miR-15a-5p can promote/inhibit UCEC progression through Wnt signaling pathway[10-12].Toll-like receptor signal pathway is one of the important pathways of immune response.Recent studies have shown that activated toll-like receptors on tumor cells can inhibit the anti-tumor effect and function of infiltrating immune cells,thus changing the inflammatory response and promoting tumor growth[13].The continuous stimulation of toll-like receptors by molecular products derived from pathogens can lead to the tumorous transformation of the epithelial cells of the female reproductive system.For example,the activation of toll-like receptor 4 promotes the survival of ovarian cancer cells by inducing the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins [14].Toll-like receptor 5 and toll-like receptor 9 may be involved in the occurrence and development of cervical cancer[15,16].A bioinformatics analysis shows that epidermal growth factor plays a vital role in the pathogenesis of UCEC through specific toll-like receptors [17].The T cell receptor’s main function is activating T cells after recognizing specific antigens.T cell receptors on the surface of T cells can specifically recognize the antigen peptides presented by major histocompatibility complex on the surface of antigen-presenting cells,activate extracellular regulated protein kinases,c-Jun N-terminal kinase,nuclear factor-κB and other signal pathways in T cells,and activate transcription factors of cell division and differentiation.Thus regulating the proliferation,differentiation and death of T cells.The activation of T cell receptor signal not only causes T cell proliferation and cytokine production,but also promotes its differentiation into effector T cells and functions.However,the relationship between this pathway and UCEC has not been revealed.
Conclusion
To sum up,DNAH14 is highly expressed in UCEC and its high expression is closely related to tumor progression and poor prognosis.At the same time,DNAH14 gene mutation may slow down the process of immune infiltration of UCEC cells;DNAH14 gene mutation participates in proteoglycan,Wnt signal pathway,T cell receptor signal pathway and toll-like receptor signal pathway in cancer through interaction with other genes,which is expected to become a diagnostic and prognostic marker of UCEC.Dynamic monitoring of gene expression also helps to assess disease progression.
- Medical Data Mining的其它文章
- Necroptosis signature predicts neuroblastoma outcome
- The role of CXCL chemokine family in the development and prognosis of colorectal cancer
- Integrated bioinformatics analysis of potential biomarkers and candidate drugs of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Construction of prognostic model of cervical cancer based on necroptosis-related lncRNAs
- Increased expression of TUBA1C predicts poor prognosis of breast cancer by regulating cell cycle
- Analysis of low expression of ferroptosis-related gene DECR1 on poor prognosis and immune cell defects of bladder urothelial carcinoma

