The role of CXCL chemokine family in the development and prognosis of colorectal cancer
Jun Zhang ,Xue-Tao Wang ,Jing Xia
1Department of Gastroenterology,Tongling People’s Hospital,Tongling 244000,China.2Department of Gastroenterology,Jining No.1 People's Hospital,Jining 272000,China.3College of Agriculture,Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University,Fuzhou 350000,China.
Abstract Objective: Colorectal cancer (CRC)is a major cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide.The class of chemokines known as cysteine-x-cysteine (CXC) motif ligands (CXCL) is thought to have a significant role in inflammation.A previous study implicated that CXCL family may play a role in angiogenesis and tumor development.In this comprehensive study,16 CXCLs in CRC will be analyzed for their prognostic values and expression patterns.Methods: To investigate CXCLs expression,immune cell infiltration,prognostic value significance,and genetic alteration among CRC patients,Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis 2(GEPIA2),Kaplan-Meier plotter(K-M plotter),Gene Set Cancer Analysis (GSCA),STRING,GeneMANIA,and Sangerbox3.0 were employed.Results: As a result of our study,there was a significant increase in the levels of CXCL1/2/3/4/5/8/9/10/11/13/14/16 in CRC tissues,whereas CXCL12 was reduced.The expression of CXCL1/2/3/9/10/11 in CRC was linked to tumor stage.High expression of CXCL2/3/14 was associated with longer overall survival (OS) in colon adenocarcinoma (COAD) patients,and the overexpression of CXCL2/6/9/11/13 was related to long OS in rectum adenocarcinoma (READ) patients.Additionally,patients with CRC who expressed high levels of CXCL9/10/11 tended to have a longer disease-free survival (DFS).Furthermore,the functions of differentially expressed CXCLs were mainly involved in cytokine activity and chemokine effects.A significant correlation has been found between CXCLs expression and the infiltration of diverse immune cells in COAD and READ,including six types of CD4+ T cells,macrophages,neutrophils,B cells,CD8+ T cells,and dendritic cells.Conclusions: According to our study,CXCLs may not only serve as prognostic markers for CRC patients but also affect the immune status of CRC tissues,thereby providing new ideas for immunotherapy.
Keywords: bioinformatics analysis;CXCL chemokine family;CRC;biomarker;prognosis
Introduction
Cancer of the colon and the rectal are referred to collectively as colorectal cancer,which is one of the most common types of cancer and one of the major causes of cancer-related mortality globally [1].In recent years,the incidence of early-onset CRC (usually defined as CRC diagnosed prior to 50 years of age) has been increasing worldwide [2].The detailed pathogenesis of CRC is not well understood,and the survival of CRC patients is unsatisfactory.Therefore,in order to effectively improve prognosis and individualized treatments,it is necessary to find molecular markers that can predict the recurrence and prognosis of CRC,and to explore the specific mechanisms for recurrence and metastasis of CRC.
Chemokines are low-molecular-weight cytokines divided into four general categories-C,CC,CXC,and CX3C-identified by the proximity of the first two cysteines position to the amino terminus.Among them,the CXCL family is defined as a class of chemokines with CXC motif at the end of its amino acids.The CXCLs that have been discovered and named so far are CXCL1/2/3/5/6/8/9/10/11/ 12/13/14/16/17,PF4(CXCL4) and PPBP (CXCL7).It was known that the infiltration of immune cells,tumor cell growth,survival,migration,and angiogenesis are all regulated by the intricate chemokine network that was present in many types of cancer [3-6].CXCLs and their specific receptors play a role in every stage of carcinogenesis,including progression,proliferation,cancer cell adhesion,angiogenesis,and metastasis.For instance,CXCL8 promotes CRC metastatic progression by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT),as well as tumor proliferation,migration,and invasion have been attributed to it[7,8].It was shown that CXCL10/CXCR3 signaling plays a crucial role in tumor cell proliferation,motility,and metastasis,was also related with early progression of metastatic illness and poor OS [9].In contrast,studies had shown that CXCL10 enhances the anti-tumor effect by acting on CD8+T cells,improving the prognosis of CRC [10,11].
Thus,CXCLs play an extremely complex role in CRC tumor development and progression.However,the complex CXC chemokine network’s significance in tumor development requires further investigation,providing new avenues for therapeutic application in CRC patients.The present study aimed to analyze in-depth the expression and mutation of CXCLs,their association with CRC patients’ prognosis and immunological infiltrates.
Materials and methods
GEPIA2
The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and Genotype-Tissue Expression(GTEx) databases have been upgraded and expanded using GEPIA2(http://gepia2.cancer-pku.cn/#index) to assess gene expression data based on tumor and normal samples.GEPIA2 is able to expand gene expression measurement from the gene level to the transcript level,and it features 198,619 isoforms and 84 different cancer subtypes.Additionally,it is able to provide analysis of a particular cancer subtype as well as comparison between cancer subtypes [12].In this study,differential gene expression analysis was used to compare tumor and normal tissues,analysed the pathological stage,and predicted prognostic information by GEPIA2.
K-M plotter
Gene chips and RNA-seq data were obtained from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO),the European Genome-phenome Archive (EGA),and TCGA and were used to develop the K-M plotter(http://kmplot.com/analysis/).The K-M plotter is capable to assess the correlation between the expression of all genes (mRNA,miRNA,protein) and survival in 30k+samples from 21 tumor types,such as breast,ovarian,pulmonary,and stomach cancer,are evaluated.Using K-M plotter,the expression of different CXCLs was analyzed for its prognostic value in READ patients.P-values lower than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
GSCA
An integrated platform for genomic,pharmacogenomic,and immunogenomic gene set cancer analysis,GSCA (http:// bioinfo.life.hust.edu.cn/GSCA/) allows us to analyse and visualise the expression/variation/correlation of a gene set in cancers in a flexible manner.Gene differential expression,OS,single nucleotide variation(SNV),copy number variation (CNV),methylation,path-way activity,miRNA regulation,normal tissue expression and drug sensitivity are among its analyses [13].Genetic alterations,and the differential methylation of CXCLs were obtained from GSCA.
STRING
STRING (https://string-db.org/) is a used to predict protein-protein interactions (PPI),with a goal to construct data networks that are comprehensive and objective,and complement data with distinctive predictions [14].In order to analyze the various CXCLs expressions and probable interactions,a PPI network analysis via STRING was performed.
GeneMANIA
GeneMANIA (http://www.genemania.org) provides a variety of resources that can be used to generate hypotheses about the function of genes,analyse gene lists,and prioritise genes for functional assays based on an algorithm that has a high level of predictability [15,16].From the GeneMANIA database,we investigated the relation between CXCLs and related genes and constructed an interaction network to clarify this relation.
Sangerbox3.0
SangerBox3.0 (http://vip.sangerbox.com/home.html)is a comprehensive,user-friendly bioinformatics analysis tool that is capable of conducting a wide range of bioinformatics analyses and visual mappings.Using the SangerBox3.0 website,we explored the correlation between CXCLs expression and levels of immune infiltration in COAD and READ.
Results
Differential expression of CXCLs in CRC patients
Based on GEPIA2 dataset,expression levels of CXCLs were compared between CRC and normal tissues.As shown in Figure 1,we found that CXCL1/2/3/5/8/9/10/11/13/14/16 and PF4 were markedly upregulated in tumor tissue,whereas CXCL12 was significantly downregulated.
Then we assessed the association of CXCLs expression with pathological stage in CRC patients.The results indicated that CXCL1/2/3/9/10/11 were markedly different.Among them,CXCL1/2/3 were significant negative association with tumor stage,that is,CXCL levels were generally lower in patients with more advanced tumor stages (Figure 2).According to these results,CXCL1/2/3 may have a significant part in the inhibition of CRC metastasis and tumorigenesis.
Prognostic value of the expression of CXCLs in CRC patients
By using GEPIA2,we got the survival significance map of all CXCLs in pan-cancer.In pan-cancer,the prognostic value of CXCLs played a different role,according to the results,however,higher levels of expression of most members of the CXCL family leaded to a better prognosis in the CRC (Figure 3).
To further explore the prognostic value in CRC patients,we used the survival analysis module in GEPIA2 to determine the survival rate of distinct CXCLs expression levels in CRC patients.Figure 4 shows the disease-free survival (DFS) and OS curves.The groups with high CXCL2/3/14 expression had a better overall survival rate,while the rest had no effect on OS.There was a statistically significant association between increased CXCL9/10/11 levels and a longer DFS(P<0.05).
Moreover,a subgroup analysis was conducted on the publicly available website K-M plotter for determination the predictive significance of CXCLs in READ patients,demonstrated that a higher level of CXCL2/6/9/11/13 expression was tied to a longer OS in READ patients(Figure 5).
These data indicated the upregulation of CXCLs expression in CRC is more likely to delay tumor progression to advanced stages.
Analyses of genetic alteration,expression,and interaction CXCLs in CRC
We used GSCA as a tool to analyze CXCLs genetic modifications in patients with CRC.Overall,the mutation rate of all CXCLs in COAD was higher than that in READ (Figure 6A).Then,the top 10 altered genes among CXCLs in CRC were shown in Figure 6B.With CXCL5 having the highest mutation rates (24%),followed by CXCL16 and CXCL9.For CNV,in addition to CXCL17,which was mainly deletion,the others showed a relatively high frequency of amplification (Figure 6C).Furthermore,CXCLs methylation level was significantly decreased in CRC tissue,particularly for CXCL2/3/10/12/14/16/17 and PF4 as shown in Figure 6D.Overall,our results provided a complete understanding of the methylation,SNV and CNV of CXCLs.Despite our finding that the variation in methylation level and gene mutation may be responsible for the changes in CXCL expression in CRC,we need further studies to explore the specific mechanisms.
Meanwhile,STRING was used to perform a PPI network analysis of CXCLs at different transcription levels to determine the function of CXCLs and their interacting genes.There were sixteen CXCL proteins and ten related proteins in the PPI network diagram.The latter included IL1B,IL6,CXCR1,CXCR2,CXCR3,CXCR4,CXCR5,CXCR6,ACKR1 and ACKR3(Figure 6E).GeneMANIA was used to illustrate the relationships between shared protein domains,physical interactions,predicted pathways and co-localizations.The CXCLs network revealed that the functions of the 20 most closely related genes were mainly associated with cytokine activity,chemokine receptor binding,cellular response to chemokine,migration of lymphocyte,regulation of leukocyte adhesion to vascular endothelial cell,regulation of leukocyte apoptotic process,and vasculature development regulation(Figure 6F).
Correlation of CXCLs with immune cell infiltration in COAD and READ
As immune cells are linked with tumor proliferation and progression,this research uses the Sangerbox3.0 to examine the relationship between CXCL members and immune cell infiltration in CRC (Figure 7).In patients with CRC,the expression of CXCL1 was found to have a positive correlation with the infiltration of CD8+T cells,neutrophils,and dendritic cells (DC).CXCL2 and CXCL3 were only positively associated with the infiltration of neutrophils in the two cancer types.They were correlated negatively with macrophage infiltration in COAD patients but not in READ patients.The expression of CXCL5 was positively associated with the infiltration of CD4+T cells,neutrophils,macrophages,and DC in COAD.Moreover,to macrophages,CXCL5 expression was positively correlated with immune cell infiltration in READ.All six host immune cells had a positive correlation with CXCL9/10/11/12/13/16 in patients with COAD,whereas,the infiltration of B cells,CD4+T cells,neutrophils,macrophages,and DC correlate positively in patients with READ.In addition,the expression of CXCL6 and CXCL8 was found to have a close relationship with the infiltration of CD8+T cells,neutrophils,macrophages,and DC in COAD patients.On the other hand,it appeared that the expression of CXCL14 was only associated with the infiltration of B cells in READ.
Discussion
The prevalence and mortality of colorectal cancer are growing annually.Nowadays,there are nearly 2 million cases,and 900,000 deaths occur annually,making it the third leading cancer-related death worldwide [17,18].The data shows that CRC in young people is on the rise [19].CXCL family plays an important role in inflammation.However,research suggested that inflammation also be considered another new feature of tumors [20].Researchers have shown that chemokines and their corresponding ligands play an important role in chronic inflammation and CRC [21].The CXCL family is involved in immunocyte recruitment and influences tumor progression,as migration and angiogenesis[22,23].Cervical cancer is associated with CXCL1/2/8 which contribute to the formation of the endothelial tube [24].CXCL1/5/16 assist in the metastasis of carcinomas like lung cancer and stomach cancer [25,26].Despite CXCLs play a significant part in the majority of cancers,the roles that they play in CRC are still not completely understood.By using an integrative bioinformatics approach,comprehensive research was conducted on the expression,mutation,prognostic value,and immune cell infiltration of CXCLs in CRC.
In terms of expression level,CXCLs revealed a significant differential expression in CRC.Furthermore,CXCL1/2/3 expression was higher in CRC tissues than in normal tissues,in addition to its expression exhibited a negative correlation with clinical tumor stage among patients with CRC.In contrast to our findings,another study has linked elevated CXCL1 expression to cancer progression and metastasis in patients with CRC[27].In consideration of differences in sample sizes,methods,cell lines,and sources of clinical samples used for exploration,there are differences in results that we believe are acceptable.
We used OS and DFS to assess the prognosis of patients with CRC,we found that the role that CXCLs play in the development of tumors is extremely complex,with different CXCLs in the same tumor act differently.For instance,we identified the expression level of CXCL1/2/3/5/8 and PF4 in cervical squamous cell carcinoma and endocervical adenocarcinoma (CESC) was positively correlated with risk,whereas CXCL9 was associated with lower risk.Studies with similar results,such as Wang Z et al.found that the CXCL12 expression in gliomas correlated negatively with risk,while CXCL9/10/11/14 was associated with high risk [28].Besides,in Figure 3,patients with kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma (KIRP)when CXCL10 is higher expressed have poorer OS and shorter DFS,whereas in Skin Cutaneous Melanoma (SKCM),overexpression of CXCL10 is that patients have better OS and longer DFS.Many studies have discovered that CXCL10 can both inhibit tumors and promote the growth of tumor cells in related in vivo and in vitro experiments[29-32].Overall,some chemokines can promote the development of tumors,and some play an inhibitory role in the oncogenesis and recurrence of tumors,which is consistent with many studies reporting the interaction between different tumors and CXCLs[22,33].
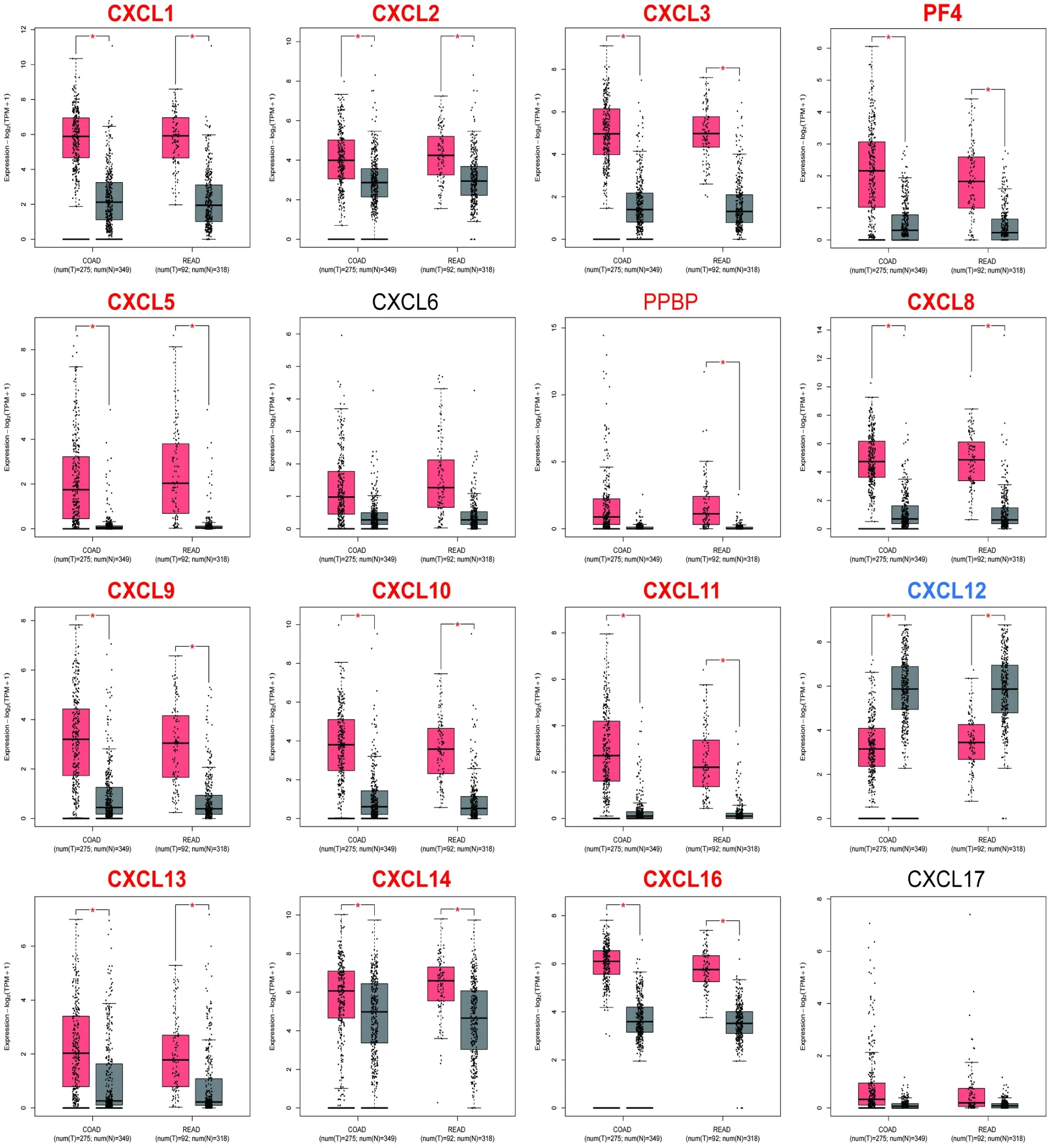
Figure 1 CXCLs expression levels in CRC tissue and normal tissue (GEPIA2).The red asterisk is located at the top of the boxplot to indicate significant records.Upregulated records’ titles are highlighted in red,while downregulated records’ titles are highlighted in blue.CXCL,CXC chemokine ligand;CRC,colorectal cancer;GEPIA2,Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis 2.
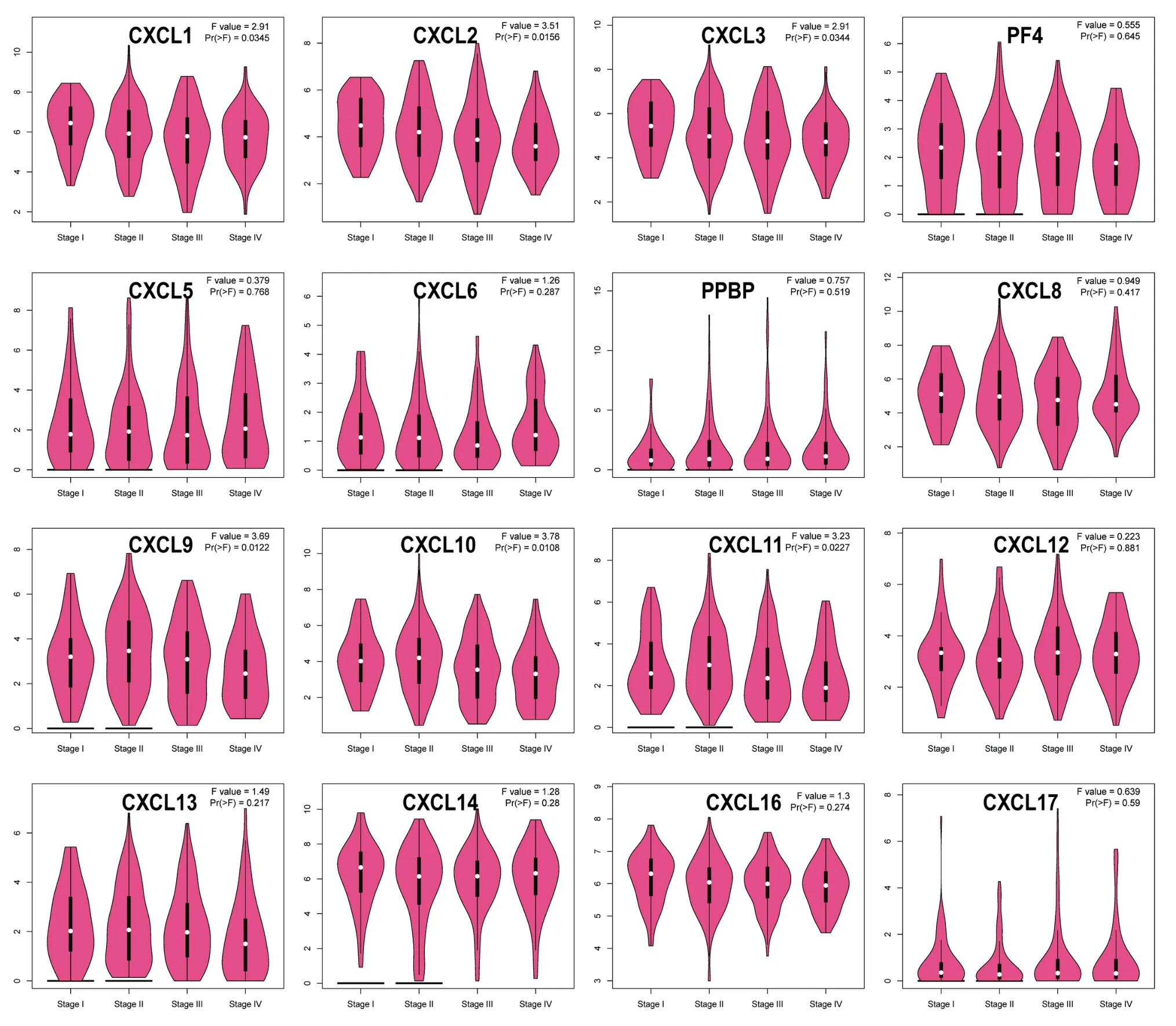
Figure 2 Correlations between the expression of CXCLs and the stage of the tumor in CRC patients(GEPIA2).CXCL,CXC chemokine ligand;CRC,colorectal cancer;GEPIA2,Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis 2.
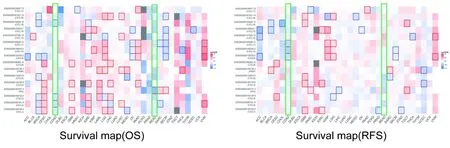
Figure 3 Prognostic value of CXCLs in various types of cancer (GEPIA2).Red and blue blocks represent higher and lower risks,respectively.Significant unfavourable and favourable results in prognostic analyses are represented by framed rectangles.CXCL,CXC chemokine ligand;GEPIA2,Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis 2.

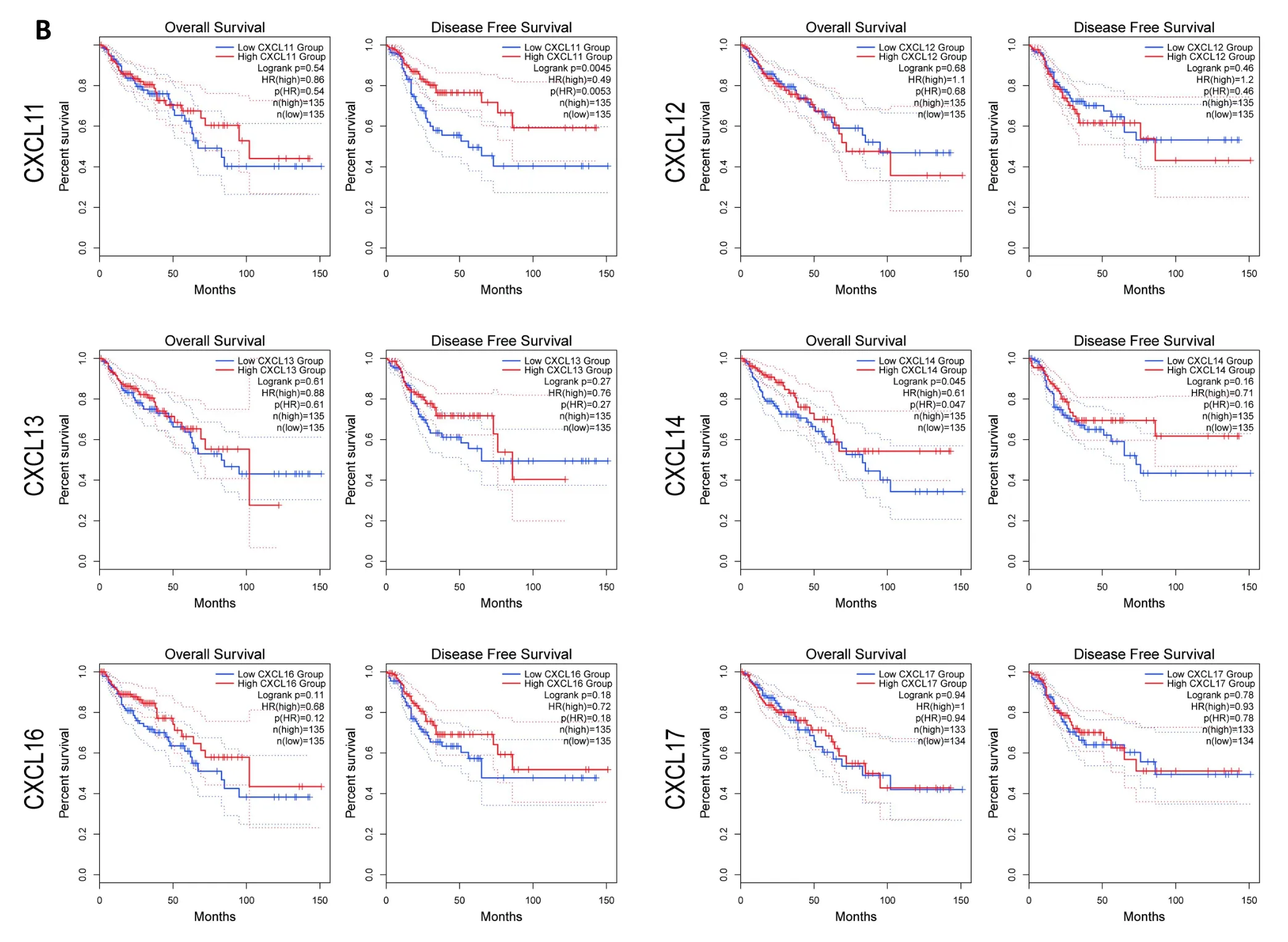
Figure 4 The prognostic value of CXCL family members expressed in CRC (GEPIA2).CXCL,CXC chemokine ligand;CRC,colorectal cancer;GEPIA2,Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis 2.
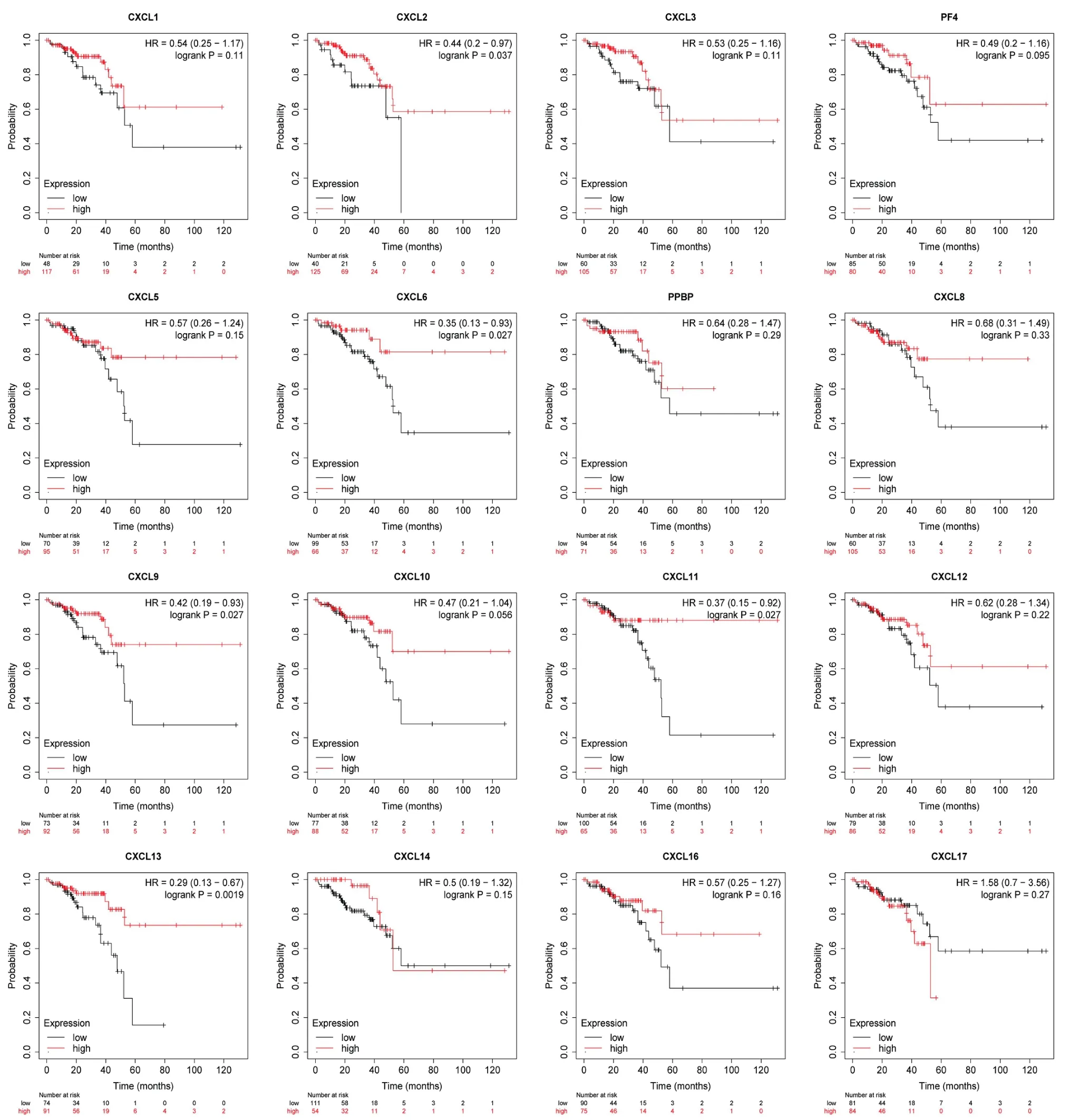
Figure 5 Prognostic value of CXCLs in READ (K-M plotter).CXCL,CXC chemokine ligand;READ,Rectum adenocarcinoma;K-M plotter,Kaplan-Meier plotter.

Figure 6 CXCLs genomic alterations and frequently altered neighbor genes analyses in CRC patients.(A) The mutation frequency of 16 CXCLs in CRC.(B)The situation of SNV of top ten mutated genes among CXCLs in CRC patients.Each column of the figure represents an individual patient.The tumor mutations burden (TMB) is represented by the upper bar plot.The frequency of mutations that occur in each gene is indicated by the number on the right.(C)The CNV percentage of CXCLs in CRC.(D)The relationship between methylation and mRNA expression of CXCLs in CRC is summarized.(E) PPI network based on information from the STRING database.(F) The network of CXCLs and the 20 neighbouring genes that are altered the most frequently according to GeneMANIA.CXCL,CXC chemokine ligand;CRC,colorectal cancer;SNV,single nucleotide variation;TMB,The tumor mutations burden;CNV,copy number variation;PPI,protein-protein interaction.

Figure 7 CXCLs expression and immune cell infiltration correlation in CRC (SangerBox3.0).Orange represents a positive correlation while blue represents a negative correlation.*P <0.05;**P <0.01;***P <0.001;****P <0.0001.
In our study,patients in the high-expression CXCL2/3/14 groups had a longer overall survival time than those in the lower-expressing group.The results of the study of Lin K et al.showed that the downregulation of CXCL14 expression in CRC is related to lymphatic metastasis,tumor site and clinicopathological staging,and CXCL14 may be thought to be a potential tumor suppressor gene for CRC,and its mechanism may be that overexpression of CXCL14 inhibits cell proliferation by blocking the cell cycle at G1 stage [34].The over expression of CXCL9/10/11 were markedly connected with long DFS.Combined with pathological staging,the results showed that CXCL2/3/9/10/11 may play an anti-cancer role in the tumorigenesis and COAD progression.We used K-M plotter for prognosis analysis of READ and showed that patients with READ had a better OS when CXCL2/6/9/11/13 were highly expressed.Similar findings included that CXCL14 inhibits tumor growth in liver cancer and squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (HNSC) [35,36].
The occurrence of tumors is often accompanied by genetic changes such as genetic mutations.Over the past few decades,relevant data have clearly demonstrated that epigenetic modifications are a major molecular hallmark that frequently appear in early stages.Epigenetic modifications,such as aberrant DNA methylation,altered histones,and altered production of non-coding RNA,have been found to regularly occur in tumors.In normal cells,the tumor suppressor gene’s promoter region is not methylated,and its expression is not hindered,while in the tumor cell,the promoter region of the tumor suppressor gene is methylated,so that it cannot be transcribed and translated normally,resulting in the occurrence and development of tumors [37,38].Early studies have found that methylation alterations in helicase-like transcription factor(HLTF)in serum of patients with CRC can distinguish between cancerous and non-cancerous patients [39,40].Subsequent studies have found that HLTF methylation status is closely related to tumor size,metastasis and tumor stage,and can serve as a predictor of disease recurrence in CRC [41].In this study,deeply genetic analysis of the CXCLs,which are differentially expressed in CRC,revealed frequent genetic alterations.The expression of multiple CXCL family member was found to be primarily negatively related to the methylation.The results suggest that reduced methylation levels may be responsible for the cancer-suppressing effect of CXCLs in CRC,CXCL2/3/4/5/10/12/14/16/17 methylation may predict CRC patient’s prognosis.
CXCLs have been shown to have an effect on immune cell infiltration levels and immune responses in a variety of tumors,thereby modulating tumorigenesis and progression [25,42].Therefore,we used Sangerbox3.0 to determine a strong statistical correlation regarding CXCLs expression and immune infiltrates among CRC.CXCL5/6/8/9/10/11/12/13/16 was significantly positively correlated with multiple immune cell infiltration levels.On the one hand,CXCL5 was found to inhibit tumor growth in CRC [43].On the other hand,CXCL5/CXCR2 axis might be responsible for CRC progression.Through activation of pathways such as ERK/Elk-1/Snail and AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin by CXCL5 tumor-derived mechanism,CRC metastasis can be induced [44].
As main inhibitors of anti-tumor immune response and variables that decrease the efficiency of cancer immunotherapy,myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) have attracted a significant interest in recent years.CXCL8 was found to attract immune cells such as neutrophils through CXCR1/CXCR2 receptors,and CXCR1 and CXCR2 are required for tumor-derived CXCL8 to entice MDSCs to the site of the tumor,and also playing a crucial role in inflammation and tumorigenesis [45].Based on Li et al.’s report,targeting CXCL8/CXCR2 might interfere with DC activation or recruitment,thus this axis might be a favorable role for CRC [46].
Similar to some previous studies,our findings indicated that the expression of CXCL8 was significantly higher in CRC.Additionally,positive correlations were observed between the expression of CXCL8 level and CD8+T cells infiltration,neutrophils,macrophages and DC in COAD,as well as CD8+T cells,neutrophils and DC in READ.CXCL9/10/11 and CXCR3 influenced the tumor microenvironment(TME) through their effects on angiogenesis,the recruitment of immune cells,and their effects on tumor cells in divergent ways,either by assisting or inhibiting tumor development [47].The results of our study also indicated that overexpression of CXCL9/10/11 is linked with DFS and clinical stage in CRC patients.Interestingly,we also found that infiltration by immune cells such as neutrophils,macrophages,B cells,CD4+T cells,CD8+T cells and DC was linked to CXCL9/10/11 expression.Two opposite effects of CXCL13/CXCR5 signaling on cancer development are observed.Immune cells can be recruited and strengthened to attack cancer via the CXCL13/CXCR5 signaling axis,on the contrary,this axis may induce tumor development by acting on relevant immunosuppressive cells infiltrating the tumor microenvironment,such as promoting downregulation of T cell immunity [48].In our study,patients with high expression of CXCL13 in READ had a higher OS and were significantly positively correlated in all six immune cells,except for CD8+T cells.
Taken together,these results show that CXCLs were significantly correlated with immune infiltration of CRC,with two different effects of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes.Due to CXCLs multiple biological functions,it probably accounts for this discrepancy.CXCLs can not only regulate the growth and invasion of tumor cells by chemotaxis various immune cells into the tumor site,and synthesize and release a large number of cytokines,but also activate downstream signaling pathways through the combination of chemokines and their corresponding receptors promote tumor growth.While,CXCLs may directly kill tumor cells by recruiting relevant immune cells into the TME and inhibit tumor angiogenesis,thereby exerting tumor suppressor effects.
Conclusion
Given all that,we examined systematically CXCL family members in CRC tissues for both their prognostic value and differential expression.The expression level of CXCL12 was diminished,despite the fact that the levels of CXCL1/2/3/4/5/8/9/10/11/13/14/16 were significantly increased in CRC tissues.The clinical cancer stage of CRC was related with the level of CXCL1/2/3/9/10/11.High expression of CXCL2/3/14 were associated with long OS in COAD patients,and the overexpression of CXCL2/6/9/11/13 were related to long OS in READ patients.Furthermore,overexpression of CXCL9/10/11 was found to be associated with long DFS in patients with CRC.Our findings suggest that the features of the differentially expressed CXCLs were principally related to cytokine activity and the effect of chemokines.High expression of CXCL related to the potential regulatory mechanism is specified with gene mutation,DNA methylation,and copy number alterations.Interestingly,CXCLs expression and tumor invasion by immune cell types were found to have a strong association.As a result,CXCLs may not only serve as predictive biomarkers for CRC patients,but they may also alter the immunological status of CRC tissues,thereby providing new ideas for immunotherapy.However,even though we performed a comprehensive and systematic analysis on CXCLs,there are some limitations to this research.Multiple online databases were utilized to retrieve data and analyze them,and their expression and biological functions were not detected by cell or animal experiments.In future studies,our findings need to be validated through further clinical studies.At the same time,it is necessary to further exploring molecular interactions,the possible mechanisms,as well as the clinical uses of the various CXCLs involved in CRC.
- Medical Data Mining的其它文章
- Necroptosis signature predicts neuroblastoma outcome
- Clinical significance of DNAH14 gene in uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma based on bioinformatics
- Integrated bioinformatics analysis of potential biomarkers and candidate drugs of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Construction of prognostic model of cervical cancer based on necroptosis-related lncRNAs
- Increased expression of TUBA1C predicts poor prognosis of breast cancer by regulating cell cycle
- Analysis of low expression of ferroptosis-related gene DECR1 on poor prognosis and immune cell defects of bladder urothelial carcinoma

