Study on the mechanism of “Salvia chinensis and Radix Ranunculi Ternati” drug pair in the treatment of lung cancer
Jia-Qi Hu, Bo-Wen Xu, Meng-Qi Cheng, Yu-Wei Zhao, Xing Zhang, Hong-Gang Zheng, Bao-Jin Hua✉
1. School of Graduates, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China
2. Department of Oncology, Guang’anmen Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing, China
Keywords:"Salvia chinensis and Radix Ranunculi Ternati" drug pair Lung cancer Network pharmacology
ABSTRACT Objective: To explore the molecular biological mechanism of the "salvia chinensis and radix ranunculi ternati" drug pair in the treatment of lung cancer based on network pharmacology.Methods: Searching the TCMSP database and previous literatures to screen the active compounds which resist lung cancer activity in salvia chinensis and radix ranunculi ternati.The candidate compounds were unified in the DrugBank to find the corresponding drug targets which were corrected to the standard gene names by the UniProt database. The SwissTargetPrediction platform was used to predict other targets. Searching GeneCards,OMIM and DrugBank to obtain genes related to lung cancer. After taking the intersection,the candidate gene target of drug pair in the treatment of lung cancer could be obtained. The"herbs-compounds-targets-disease" network was bulit with Cytoscape, and the PPI network was bulit on the STRING platform while the core network nodes were screened. GO and KEGG analysis on candidate genes was implemented through Metacape platform, and a"pathways-targets" network was bulit to further screen key genes. Results: A total of 16 active compounds in salvia chinensis, 18 active compounds in radix ranunculi ternati, 164 candidate targets, 2443 GO functions and 170 KEGG pathways was obtained. Conclusion: The effective compounds of " salvia chinensis and radix ranunculi ternati " drug pair in the treatment of lung cancer are quercetin, ursolic acid, β-sitosterol and caffeic acid. The key targets are MAPK1,AKT1, PIK3R1, RAF1 and EGFR. GO functions mainly include cytokines, oxidative stress,plasma membrane transmission, protein kinase binding and activity, apoptosis. KEGG could directly regulate pathways in cancer, non-small cells lung cancer pathway and small cell lung cancer pathway. KEGG also involves EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance, IL-17, TNF,PI3K-AKT signaling pathway and apoptosis. This study reveals the molecular biological mechanism of "salvia chinensis and radix ranunculi ternati" drug pair in the treatment of lung cancer. It is reasoned that its potential targets affect multiple signaling pathways and ultimately resist the proliferation, differentiation, invasion, metastasis and promote apoptosis of lung cancer cells. Evidence for further experimental study is provided by this study.
1. Introduction
Lung Cancer is a type of malignant tumor that poses a serious threat to human health. According to the Global cancer statistics,there are 19.3 million new cases and 10 million deaths in 2020,with lung cancer morbidity and mortality rates of 11.4% and 18%. Respectively, lung cancer ranks second and first among all malignant tumors[1]. The incidence of lung cancer is closely related to smoking, environmental contact, genetics and other factors.Surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy are the main treatments of it.It is reported that about 80% of patients with limited-stage small cell lung cancer and almost all of the extensive-stage small cell lung cancer relapse, progress or die within one year of treatment[2].From 1973 to 2010, the average five-year survival rate for lung adenocarcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma was no more than 20%, while for small cell lung cancer it was only 5.6%[3].
Lung cancer is also known as "Fei Ji" in Traditional Chinese medicine. Study has found that traditional Chinese medicine can not only enhance the effectiveness of conventional treatment, but also reverse drug resistance, reduce adverse reactions and toxicity and improve the quality of life[4], which has a big potential in medical development. Modern Chinese practitioners believe that lack of healthy qi, cancerous toxin, phlegm coagulation and blood stasis are the key pathological factors in the development of lung cancer[5],so "heat-clearing and detoxifying", "reducing phlegm and resolving masses" and "promoting blood circulation to remove blood stasis"are main treatment methods for Chinese practitioners to treat lung cancer[6]. Salvia Chinensis is the whole grass of the Purple Ginseng belonging to Salvia in the labiaceae. Chinese Herb records it can promote blood circulation to remove blood stasis, reduce swelling and resolve masses. The basic research shows that the extract of Salvia Chinensis can significantly inhibit the proliferation of human lung cancer cells A549[7][8]. Radix Ranunculi Ternati is the earthnut or whole grass of Ranunculus ternatus Thunb. Chinese Herb records it can detoxification, reduce phlegm and resolve masses. The basic research shows that the total glycoside of Radix Ranunculi Ternati can inhibit the growth of transplant tumor in naked mouse[9].Clinically, the two are often used together to treat lung cancer[10][11][12], but the effectiveness of specific mechanism of the drug pair on lung cancer has not been reported.
Network pharmacology can systematically expound the mechanism of action of single Chinese herb or compounds by constructing a "compounds-targets-disease" network to consider the diverse compounds of Chinese herbs and the rich targets[13][14]. Predicting the target might guide the direction of scientific research and the development of new drugs. Therefore, this study discusses the specific mechanism of “Salvia Chinensis and Radix Ranunculi Ternati” drug pair on the treatment of lung cancer through network pharmacology, which provides evidence for further basic research.
2. Materials and methods
2.1 The active ingredients and target screening of Salvia Chinensis and Radix Ranunculi Ternati
According to the ADME screening principle, the entire compounds of Salvia Chinensis and Radix Ranunculi Ternati were screened on the TCMSP platform by following the oral bioavailability(OB) ≥30% and Druglikeness (DL) ≥0.18. The rest of effective compounds that have been shown to resist lung cancer of Salvia Chinensis and Radix Ranunculi Ternati were also screened by screening literatures. Targets of all candidate compounds were searched on DrugBank and corrected by UniProt as standard gene names. Finally, the 2D structure of those compounds were searched by Pubchem Cid and the targets prediction were realized by SwissTargetPrediction. The targets data set of "Salvia Chinensis and Radix Ranunculi Ternati" drug pair was obtained by removing the duplicate targets of drug targets and predicted targets.
2.2 Screening of lung cancer related target
The potential targets for the treatment of lung cancer were searched in GeneCards and OMIM by using the keyword called "Lung Cancer". The complementary targets were obtained in Drug Bank by using the keyword called
"Lung Cancer", "SCLC", and "NSCLC". In the case of too many disease targets, screening disease targets under the condition of Relevance score 15 in GeneCards.
Removing the duplicate targets of disease targets and establishing the targets data set of Lung cancer.
2.3 Common targets acquisition for drugs and disease
The common targets acquisition for drugs and disease and Venn diagram were obtained by using Venny (Version 2.1.0). The common targets can be considered as the candidate targets of "Salvia Chinensis and Radix Ranunculi Ternati" drug pair on the treatment of lung cancer.
2.4 Construction of the "drugs-compounds-targets-disease"network
The construction of the "Chinese herbs-compounds-targets-disease"network was obtained by using Cytoscape3.7.2. In the network,nodes represent Chinese herbs, compounds, targets and diseases, the node degree value represent the size of nodes and the edge represent the relationship between nodes.
2.5 Construction of PPI network
The PPI network was obtained by the STORING (Version 11.0)platform, defining species as "Homo sapiens" and the confidence level of 0.900. BioGrid, InWeb_IM, OmniPath or other databases were used for further analysis and MCODE was used for core network nodes.
2.6 Enrichment analysis
GO analysis can predict the connection of target genes in biological processes (BP), molecular function (MF) and cellular components(CC), while KEGG analysis is used to study the main signaling pathways involved in the study. GO and KEGG analysis can be realize by using Metascape. Based on the relevant targets mapped by KEGG results, the "pathway-targets" network was constructed to obtain the key target genes of "Salvia Chinensis and Radix Ranunculi Ternati" drug pair for the treatment of lung cancer.
3. Results
3.1 Acquisition of active compounds and targets of Salvia Chinensis and Radix Ranunculi Ternati
A total of 2 active compounds of Salvia Chinensis and 12 active compounds of Radix Ranunculi Ternati are obtained. Although OB and DL values of some compounds did not meet the requirements,10 active compounds of Salvia Chinensis and 6 active compounds of Radix Ranunculi Ternati were included by viewing the “Lung Cancer” in "Related Disease”. By looking for literatures, the active compounds named “maslinic acid”[15][16], “emodin”[17][18], “salvianolic acid A”[19][20] and “kaempferol”[15][21] were complemented. Finally, 16 active compounds of Salvia Chinensis and 18 active compounds of Radix Ranunculi Ternati are included.
3.2 Targets acquisition
The targets of active compounds were screened in DrugBank. 321 targets of Salvia Chinensis and 117 targets of Radix Ranunculi Ternati are obtained. Besides, targets of all active compounds were predicted under the condition of Probability >0.8 in SwvisTargetPrediction.103 targets of Salvia Chinensis and 1 target of Radix Ranunculi Ternati are obtained. A total of 276 drug targets are obtained after duplicating. A total of 2121 disease targets consisting 1675 and 504 targets obtained in Genecards and OMIM and 293 targets obtained in DrugBank for the treatment of lung cancer are obtained. A total of 164 common targets of drugs and disease are obtained by using Venny2.1.0 and 30 effective compounds are obtained by targets mapping. The common compound of Salvia Chinensis and Radix Ranunculi Ternati is beta-sitosterol. (Figure 1 and Table 1)
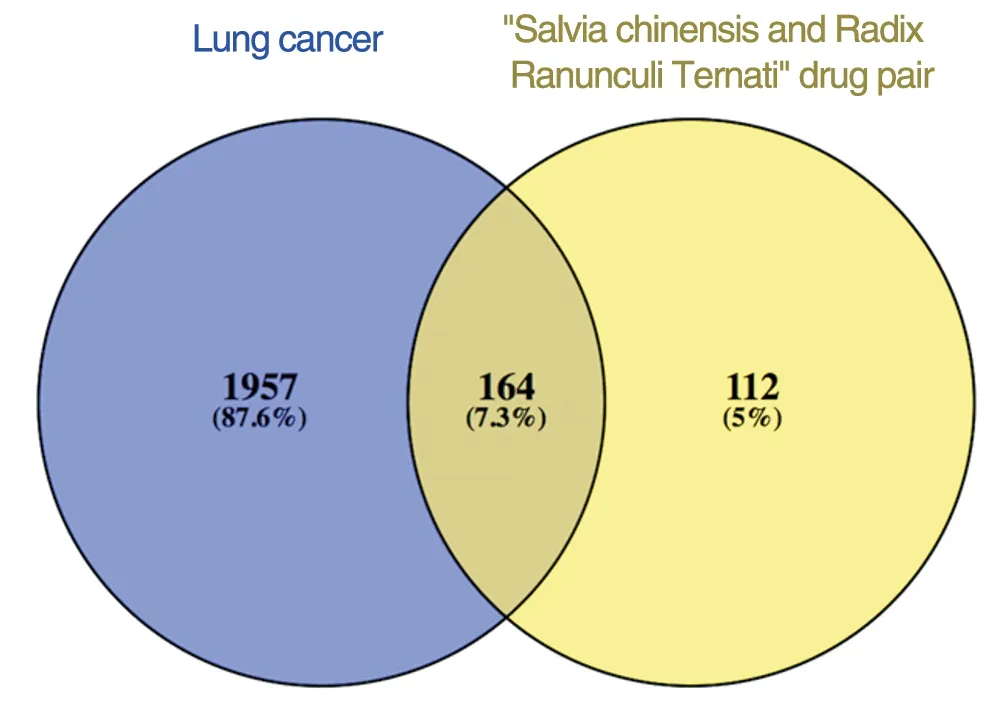
Figure1 Venn diagram of targets
3.3 Construction of the "drugs-compounds-targets-disease"network
The "drugs-compounds-targets-disease" network consists of 197 nodes and 521 edges, as shown in Figure 2. By analysing the node degree values, top 4 compounds named quercetin, ursolic acid, betasitosterol and caffeic acid, which correspond to 134, 43, 32, 20, were obtained which might be the active compounds of Salvia Chinensis and Radix Ranunculi Ternati for the treatment of lung cancer.
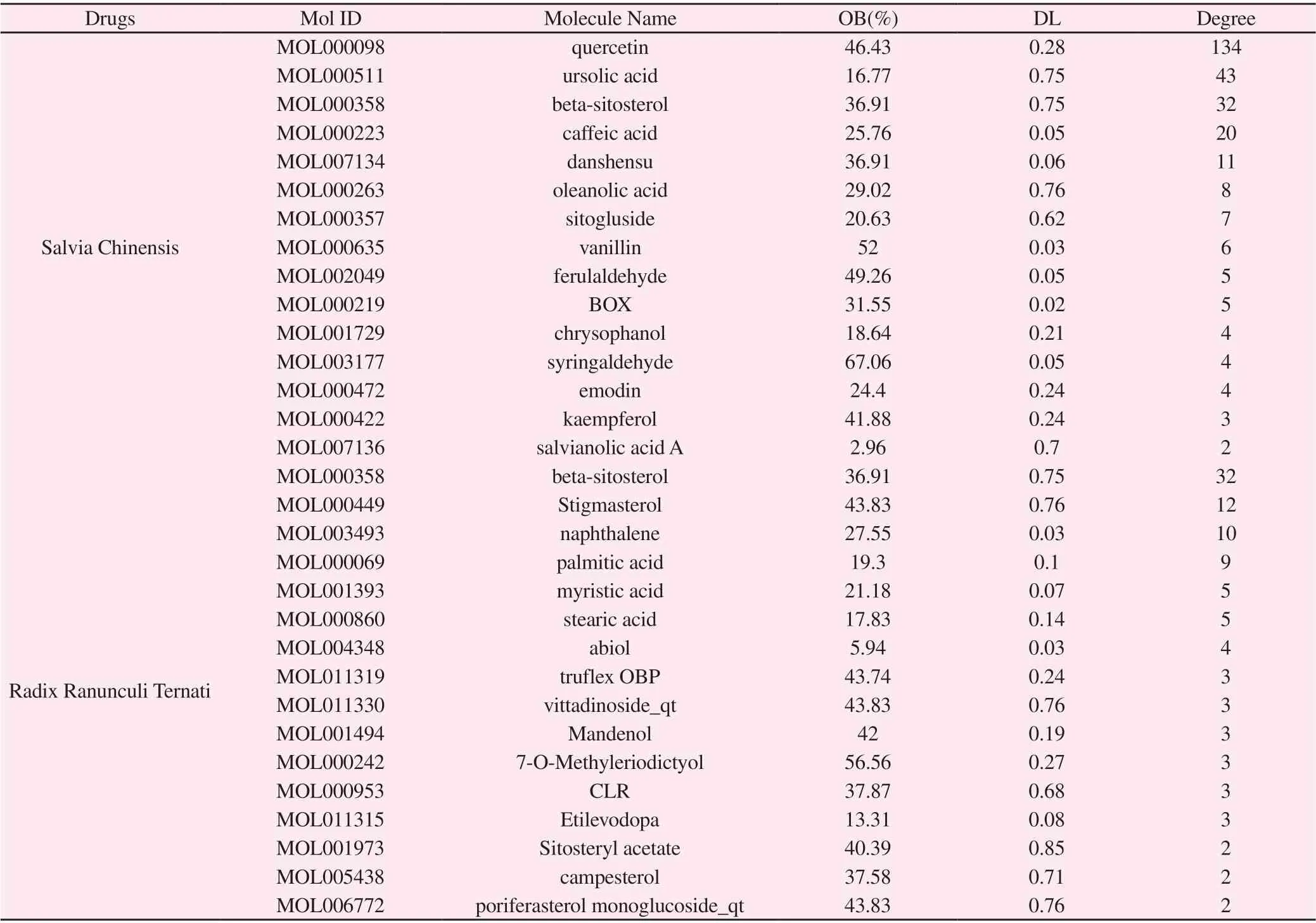
Table 1 Potential active compounds of drugs
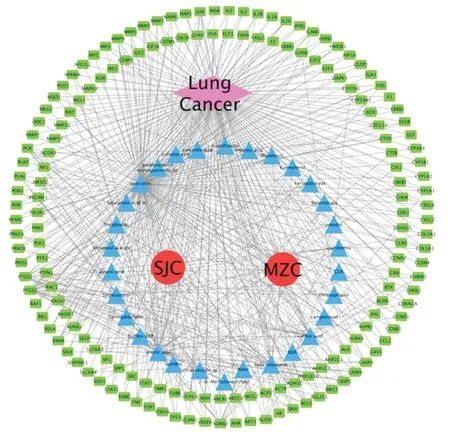
Figure2 "Drugs-compounds-targets-disease" network
3.4 Construction of PPI network
PPI network was obtained after uploading 164 common targets to STRING and removing 13 free targets, which contains 151 targets and 727 edges, as shown in Figure 3.
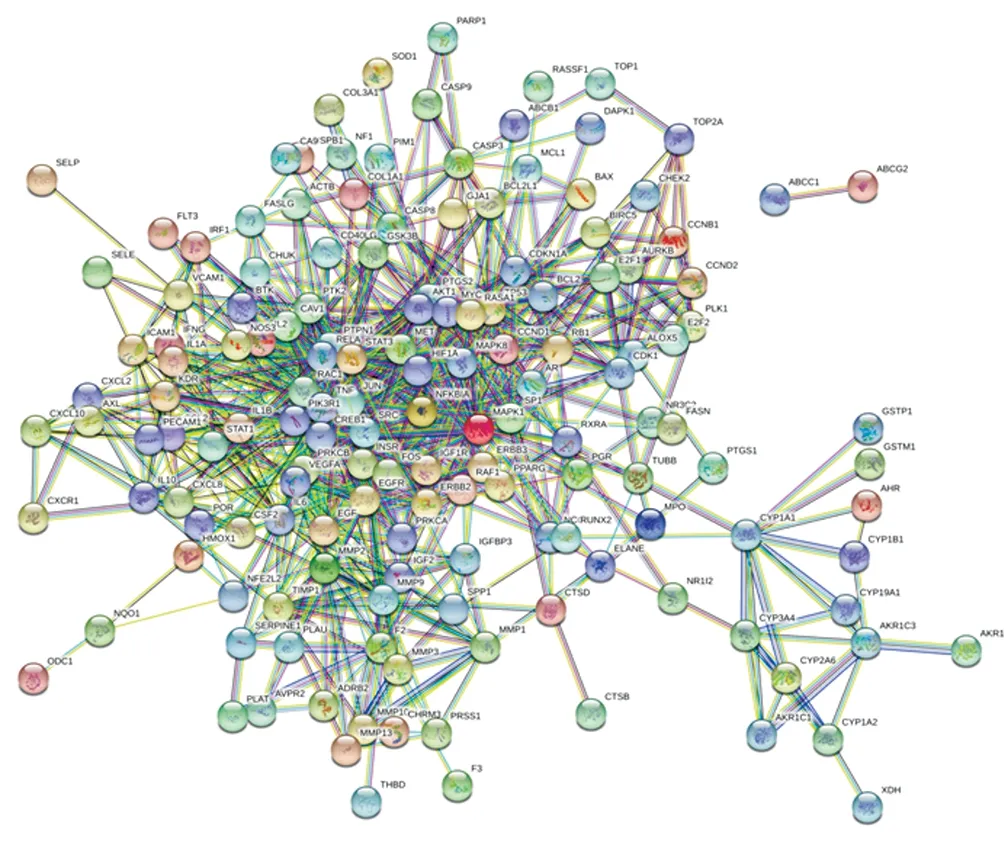
Figure3 PPI network
In order to analyze the mechanism of action of “Salvia Chinensis and Radix Ranunculi Ternati” drug pair for the treatment of lung cancer more accurately, the connections in this network were analyzed by MCODE, as shown in Figure 4. According to the Log10(P) value, three biological processes in the PPI network were retained, as shown in Table 2.
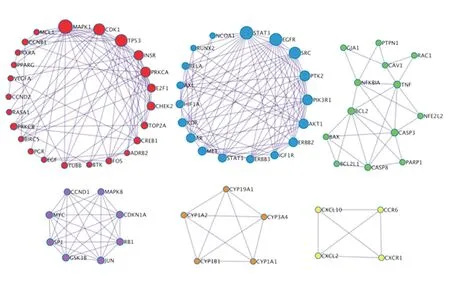
Figure4 Internal core network module in PPI
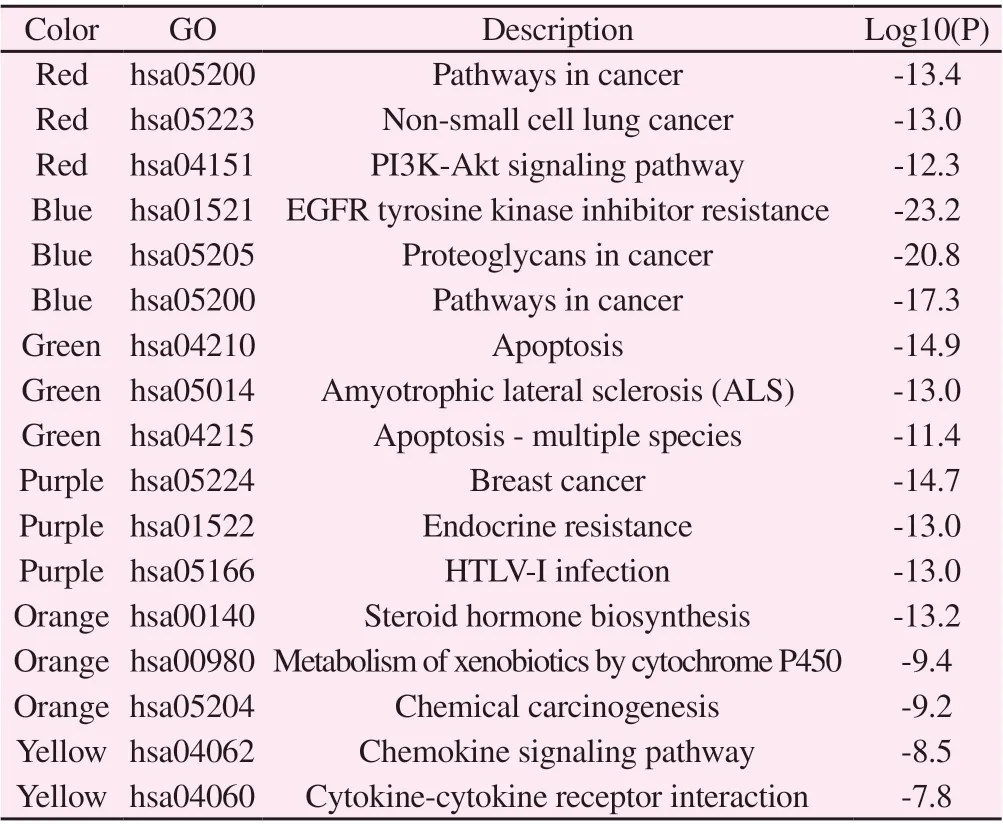
Table 2 Description of the function of the internal core network module in PPI (top 3)
3.5 Enrichment analysis
A total of 2443 GO terms show enrichment, consisting 2174 of BP,84 of CC, 185 of MF, while KEGG enrichment shows 170 signal pathways. According to the sort of negLogP value, GO bubble chart was drew according to the top 20 by using R language, while KEGG bubble chart was drew according to the top 20 lung cancer related pathways, as shown in Figure 5.
As can be seen from Figure 5, the main GO biological processes involved are Cytokines, Apoptosis, oxidative stress, hormone stimulus, Plasma membrane transmission, protein kinase binding and activity, etc. The main signal pathways involved are Pathways in cancer, Non-small cell lung cancer, Small cell lung cancer,Proteoglycans in cancer, EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance,IL-17 signaling pathway, TNF signaling pathway, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, Apoptosis, etc.For further analysis of the relationship between signal pathways,candidate targets and compounds, a "pathways-targets" network was constructed, as shown in Figure 6. As can be seen from Figure 6, MAPK1, AKT1, PIK3R1, RAF1 and EGFR are the key targets because of large Degree.
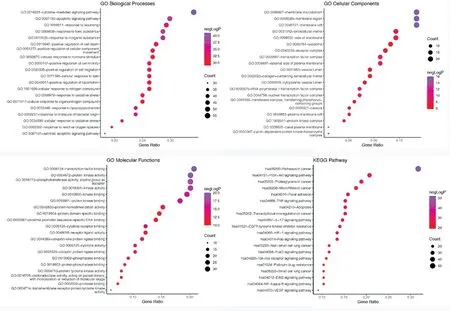
Figure5 Bubble chart of enrichment analysis
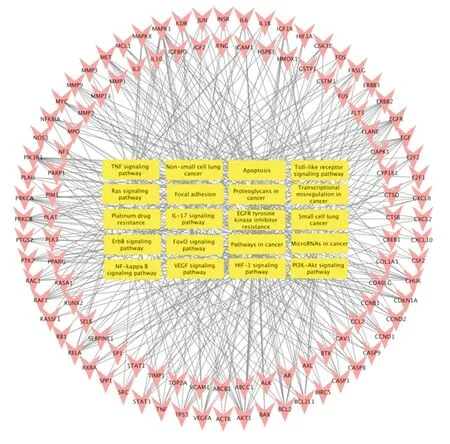
Figure6 "Pathways-targets" network
4. Discussion
The combination of different Chinese herbs has synergistic promotion, but more compounds and more targets result in difficulty of elucidating the specific mechanism of action. This study analyzes existing databases by using network pharmacology to explore molecular mechanism for the treatment of lung cancer of “Salvia Chinensis and Radix Ranunculi Ternati” drug pair on the active compounds, key targets and signaling pathways.
4.1 Potential active compounds
This study predicts that the main compounds of " Salvia Chinensis and Radix Ranunculi Ternati” drug pair for lung cancer include quercetin, ursolic acid, beta-sitosterol and caffeic acid.The existing experiments have shown that quercetin can promote the apoptosis, autophagy and inhibition of proliferation and invasion of lung cancer cells through STAT3, AMPK/mTOR pathways[22][23][24][25]. Wang Jing[26] has further found that the use of quercetin and gifitinib in combination might play a synergistic effect in inhibiting the proliferation of lung cancer cells by promoting apoptosis. Wang Yubo[27] have found that the mechanism which quercetin reverses resistance to Lung adenocarcinoma might be associated with the reduction of P-glycoprotein and survivin protein. The achievement of tumor suppression effect of ursolic acid mainly via inhibiting the proliferation, migration and invasion[28][29] and promoting apoptosis[30][31] of human A549 cells by regulating miRNA. Stage G2/M is the key period that determines the mitosis of cells. Zhou Lingyu[32] found that beta-sitosterol could cause apoptosis of lung cancer cells by blocking this period. Wang X[33] found that betasitosterol has the potential to treat NSCLC. There are no studies showing the effectiveness of killing tumor cells of caffeic acid,which is mainly used to prevent the reduction of white blood cells in lung cancer patients after radiation and chemotherapy[34][35].
4.2 Key gene targets
This study predicts that MAPK1, AKT1, PIK3R1, RAF1, and EGFR are potential genetic targets for the treatment of lung cancer of " Salvia Chinensis and Radix Ranunculi Ternati” drug pair.
MAPK1/ERK2 is an important protein kinase for MAPK/ERK signaling pathways. Several studies have shown that the overactivation of MAPK/ERK pathway in lung cancer cells will promote the proliferation, metastasis, and increased resistance of tumor cells[36][37][38]. Chen Ting[39] has found that the drugcontaining serum of water extract of tcaus mairei can reduce the MAPK1/ERK2 expression to enhance the inhibition of gifitinib on the proliferation of A549 cells in human lung cancer. Xu Haiping[40]found that the mechanism of improving the recent efficacy of patients with non-small cell lung cancer by nimotuzumab was related to the reduction of MAPK1/ERK2 expression. Chen Weizhuang[41]found that the plasma MAPK1/ERK2 content of lung cancer patients was significantly higher than that of the control group, which has useful guides for the diagnosis of lung cancer.
AKT1 is involved in tumor cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis[42], which is closely related to the incidence of lung cancer[43]. Pan ZH[44] found that increase of AKT1 expression promotes the proliferation, metastasis and inhibition of apoptosis in lung adenocarcinoma cells. Wang Jia[45] found that the expression of AKT1 in cancer tissue of 65 cases of NSCLC patients significantly increased. Yang Yanrong[46] further observed the long-term survival of 90 patients with NSCLC, and found that the positive expression of AKT1 in cancer tissue have lower 3-year survival rate than the negative, which indicates that AKT1 protein overexpression might be the risk factor of tumor progression and adverse prognosis. Some studies[47][48] have shown that AKT1 and AKT2 reverse regulation in the incidence and progression of lung cancer. Reducing AKT1 will inhibit lung cancer growth while reducing AKT2 will promote lung cancer growth, which indicates that the targeting inhibition of AKT1 might be more effective than simultaneous suppression of three subtypes of AKT for lung cancer treatment. The findings of Paige M Chorner support this view[49].
p85 protein is encoded by PIK3R1, which is a regulated subunit of PI3K. p85 promotes PI3K activation and then activates the PI3K/AKT pathway to promote tumor cell proliferation, inhibit tumor apoptosis, promote tumor angiogenesis, regulate tumor cell cycle and promote tumor cell invasion and metastasis[50]. Tian F[51] found that miR-486-5p directly regulates PIK3R1 to inhibit cell proliferation,invasion, and induce apoptosis. By analyzing the data of miRNA chip data of pulmonary fibrosis and mRNA chip data of lung cancer,Sun Zhanbing[52] believes that PIK3R1 is a potential therapeutic target for lung cancer.
RAF1 is an important up initiation factor for RAS-RAF-MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Qiu Z[53] found that the reduction of RAF1 could reduce proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer cell, promote apoptosis and block cell cycle. Tian Y[54] found that the reduction of RAF1 might be achieved by miR-135 acting on RAB1B. Tian H[55]and Cai Qin[56] found that the overexpression of RAF1 or reduction of RAF kinase inhibitor protein was an independent risk factor for progression time in NSCLC patients, and RAF1 might be a potential therapeutic target for improving prognosis in NSCLC patients[57].
EGFR mutation results in activation of some signaling pathways such as PI3K-AKT, RAS-RAF-MAPK/ERK, and promotes tumor cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis, and inhibits apoptosis[58].EGFR mainly has 3 mutation types. Comparing to exon 20 T790M mutation and exon 21 L858R mutation, Xu Guanghui[59] found that NSCLC patients who had EGFR exon 19 mutation had better tumorfree survival time, and the difference types of EGFR mutation might be related to postoperative recurrence and transfer site.
4.3 GO and KEGG analysis
GO analysis shows that the "Salvia Chinensis and Radix Ranunculi Ternati" drug pair regulates cytokines, oxidative stress, plasma membrane transmission, protein kinase binding and activity and apoptosis to treat lung cancer.
Cytokines is a kind of small molecule peptides or glycoproteins,which consists of a variety of cells with rich biological functions such as regulating cell growth, immune response, promoting apoptosis and participating in inflammatory responses, which are important parts of tumor microenvironment[60] and closely related to tumor incidence and development[61]. The steady state of redox in cells is essential to maintain the correct transmission of signals within cells[62]. Oxidative stress can lead to genome instability,which is related to the incidence, metastasis and progression of cancer[63]. Nrf2 is a key to oxidative stress. Cancer patients with significantly increased levels of Nrf2 expression in tumor tissue have lower survival rate[65], which is an important molecular marker for judge prognosis. Plasma membrane transmission, protein kinase binding and activity are the key to biological processes of intracellular signaling, which directly regulate the proliferation,differentiation, apoptosis, invasion and metastasis of tumor cells.
KEGG analysis shows that the "Salvia Chinensis and Radix Ranunculi Ternati" drug pair could directly regulate the pathways in cancer, non-small cell lung cancer pathways and small cell lung cancer pathways and also regulate EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance, IL-17, TNF, PI3K-Akt and apoptosis, which is basically consistent on the function of the targets predicted in this study and also confirmed the authenticity of this study and the high degree of correlation within the network.
In conclusion, this study predicts that the active compounds of "Salvia Chinensis and Radix Ranunculi Ternati” drug pair for lung cancer are quercetin, ursolic acid, beta-sitosterol and caffeic acid,which target on MAPK1, AKT1, PIK3R1, RAF1, EGFR or other targets to regulate cytokines, oxidative stress, plasma membrane transmission, protein kinase binding and activity and apoptosis and other biological processes. The signaling pathways are mainly related to pathways in cancer, non-small cell lung cancer pathways,small cell lung cancer pathways, IL-17, TNF, PI3K-AKT and apoptosis signaling pathways. This study provides scientific evidence for the rational application of the " Salvia Chinensis and Radix Ranunculi Ternati” drug pair for lung cancer and further basic research by using network pharmacology.
Author’s Contributions
Hu Jiaqi and Xu Bowen screened the drug and disease targets,constructed an interactive network, and finally wrote the whole article. Cheng Mengqi conducted an enrichment analysis. Zhao Yuwei and Zhang Xing discussed the results. Zheng Honggang and Hua Baojin provided guidance and financial support for this study.
 Journal of Hainan Medical College2022年11期
Journal of Hainan Medical College2022年11期
- Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Potential targets and mechanism of Xingxiao Pill for the treatment of lung cancer were analyzed based on network pharmacology and molecular docking
- Effect of total glucosides of paeony on serum cytokines in patients with psoriasis and its clinical efficacy: A meta-analysis
- Effects of post-dilation on coronary blood flow and MACE events following primary percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with STEMI
- Correlation study between dendritic cell and eosinophil in refractory rhinosinusitis
- An exploration on the protective mechanism of Xuduan Zhongzi prescription against epididymis oxidative damage in oligoasthenospermia model rats based on Nrf2-NQO1/γ-GCS signaling pathway
- Effects of compatibility of Scutellaria baicalensis stems and Polygonum cuspidatum on TRPV1 expression and inflammatory cytokines in rats with acute lung injury
