Effect of total glucosides of paeony on serum cytokines in patients with psoriasis and its clinical efficacy: A meta-analysis
Wen-Ting Chen, Yu-Hong Yan, Jing-Jie Yu, Xiao-Yu Chen ,Chuan-Jian Lu,3,4✉
1. Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, China
2. Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510120, China
3. State Key Laboratory of Dampness Syndrome of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510120, China
4. Key Laboratory of TCM Syndrome Clinical Research of Guangdong Province, Guangzhou 510120, China
Keywords:Psoriasis Total glucosides of Paeony Cytokines Randomized controlled Meta-analysis
ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate the relationship between the changes of inflammatory cytokines and clinical efficacy in patients with psoriasis treated with Total glucosides of paeony by Meta analyses, and to explore the microcosmic mechanism of effective treatment of psoriasis with Total glucosides of paeony from the point of view of evidence-based medicine. Methods: The databases of CNKI, Wanfang, VIP, SinoMed, PuMed, Embase and Cochrane Library were searched by computer, and the time range was from the establishment of the database to May 2020. After screening, data extraction and bias risk assessment, Revman5.3 software was used for statistical analysis. Results: A total of 998 patients were included in 11 clinical studies,including 502 patients in the trial group and 496 patients in the control group. The results of Meta analysis showed that there was significant difference in the expression of cytokines between the two groups (MD=-10.97, 95%Cl[-15.56,-6.37]). The effective rate of treatment(OR=3.57, 95%Cl[2.58, 4.94]) and the decrease of PASI score (MD=-4.55, 95%Cl[-5.91,-3.20]) in the combined use of Total glucosides of paeony group were superior to those in the control group. Conclusion: Total glucosides of paeony can regulate immune and inflammatory response and improve skin lesions by inhibiting the expression of cytokines such as IL-2, IL-8,IL-23 and TNF-α in serum of patients with psoriasis. In view of the low overall quality of the included studies, larger samples and higher quality clinical trials are still needed to obtain more sufficient evidence.✉Corresponding author: LU Chuan-jian, Professor, M.D., Doctoral Supervisor.
1. Introduction
Psoriasis as a chronic, inflammatory and recurrent skin disease caused by immunity or inflammation, psoriasis vulgaris is the most common, with red papules at the beginning, which can be expanded and fused into patches. White scales, shiny film and punctate bleeding are its typical characteristics, and finger (toe) nail spot depression can be seen, and most of the disease shows the seasonal change of severe winter and light summer. At present, it is believed that the pathogenesis of psoriasis is caused by the interaction of genetic, environmental and immune factors [1], in which cytokines play a key role in the pathophysiology of psoriasis [2]. Keratinocytes are easy to proliferate abnormally under the stimulation of inflammatory mediators [1]. Pharmacological studies show that total glucosides of paeony (TGP) can regulate immunity and inhibit inflammation, and can affect the expression of cytokines such as IL-8, IL-10, IL-17, IL-23, IFN-γ, TNF-α [3-4]. Therefore, it is rare to use total glucosides of paeony in the treatment of dermatosis,and it also has a certain curative effect on psoriasis. At present,the Meta analysis of the relationship between total glucosides of paeony and cytokines in patients with psoriasis has not been reported, so this study used Meta analysis to explore the effect of total glucosides of paeony on the expression of serum cytokines in patients with psoriasis.
2. Data and methods
2.1 Inclusion criteria
(1) study types: randomized controlled trials; (2)subjects: patients diagnosed as psoriasis according to clinical criteria; (3) intervention measures: the control group was treated with other drugs or physiotherapy without total glucosides of paeony preparation, and the experimental group was treated with total glucosides of paeony preparation combined with control group.(4) outcome index: the main index was the test value of cytokines (IL-2, IL-4, IL-8, IL-10, IL-17, IL-18,IL-23, IFN-γ, TNF-α), and the secondary index was treatment effective rate or PASI score. Due to the differences in the definition of the total effective rate in each study, in order to facilitate statistics, the curative effect criteria of each study are unified as follows: total effective rate = (number of cured cases +number of markedly effective cases) / total number of cases×100%.
2.2 Exclusion criteria
Observational studies, animal experiments, in vitro cell experiments, conferences, reviews, empirical literature;the data are incomplete.
2.3 Retrieval strategy
Four Chinese databases (CNKI, SinoMed, Wanfang,VIP) and three English databases (PubMed, Cochrane Library, Embase) are searched by computer. The search time range is from the establishment of the database to May 2020. By using the combination of subject words and free words, the Chinese search words include"psoriasis", "Baibi", "total glucosides of paeony","cytokines", "randomized control", "clinical study" and so on, while the English words include "psoriasis","cytokine", "Total glucosides of paeony" and so on.
2.4 Literature screening, data extraction and quality evaluation
The work of literature screening and data extraction was completed by two independent researchers according to the established criteria, and checked and
proofread each other. If there is any objection, it will be discussed and decided by two researchers, and the third party will be consulted when it is critical. After importing all the retrieved documents into Endnote X9 for preliminary checking, we read the title and abstract to delete the irrelevant literature. finally, we browsed the full text of the remaining literature and screened them to meet the requirements. The required data information was extracted and sorted into the Excel table, and the main information was the first author, the year of publication, the sample size of each group and intervention measures, course of treatment, outcome report.
The biased risk assessment tool recommended by Cochrane Handbook 5.1.0 was used to evaluate the quality of the literature. High risk, low risk and unclear were evaluated in six areas: random sequence generation, allocation hiding, blind implementation,data integrity, selective reporting bias and other biases.
2.5 Statistical methods
Use RevMan 5.3 the software carries on the Meta analysis, the effect value of the measurement data is described by the mean difference (MD), and the effect value of the counting data is described by the ratio ratio(OR), both of which take 95% confidence interval(Cl).X2 qualitative and I2quantitative analysis were used to test the heterogeneity between studies. When I2<50%,P> 0.1, the heterogeneity was considered to be low,and the fixed effect model could be directly applied to merge. If I2> 50% and P<0.1, the heterogeneity was considered to be obvious. It is necessary to explore the source of heterogeneity and analyze the possible causes of heterogeneity by subgroup analysis. If heterogeneity still exists, random effect model is used for Meta analysis, and sensitivity analysis is used to test the stability of the results.
3. Results
3.1 Search results
A total of 180 articles were retrieved from the above 7 databases, including 64 articles of Wanfang, 50 articles of CNKI, 34 articles of SinoMed, 27 articles of VIP, 3 articles of PuMed, 2 articles of Embase and 0 articles of Cochrane Library. After several times of screening,11 articles were included, with a total of 998 subjects,including 502 in the experimental group and 496 in the control group. The specific process is shown in figure 1.The baseline data of the subjects were included in each study, and the consistency between groups was good.The basic characteristics of the included literature are detailed in Table 1.
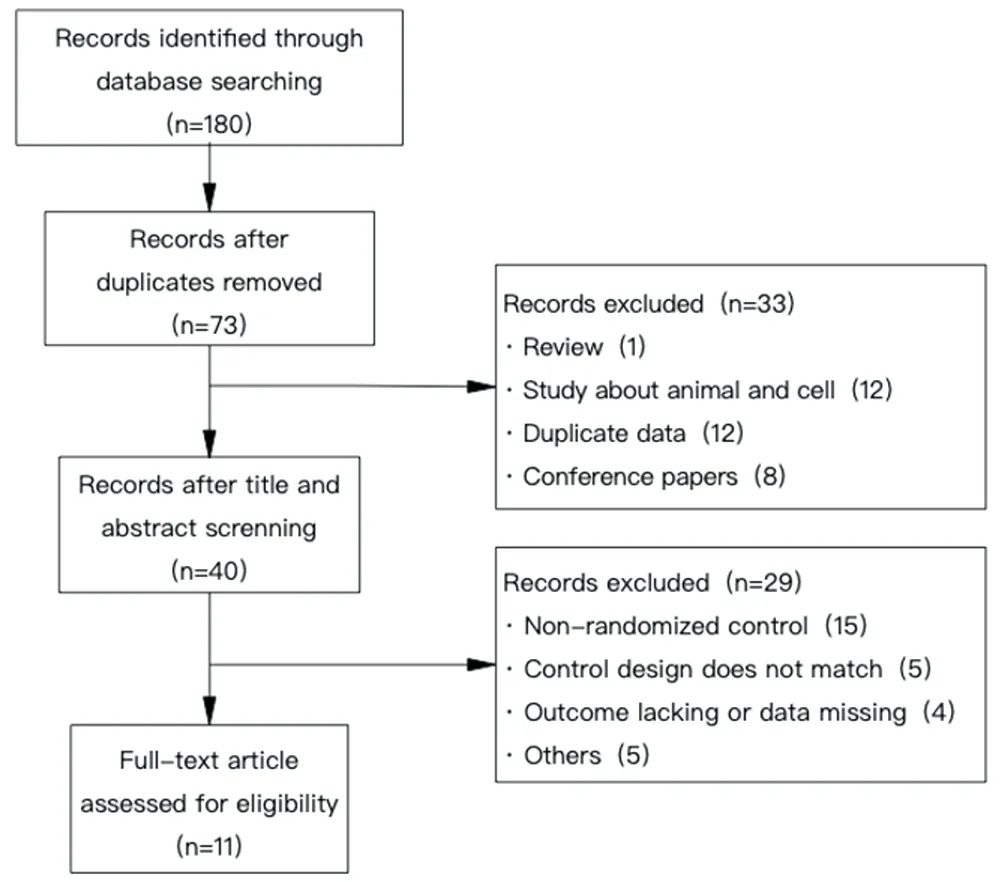
Figure1 Document screening process
3.2 Inclusion of research quality evaluation
Although all the studies reported the specified outcome indicators and the data integrity was good, only 5 studies were grouped with random number tables, and the random allocation methods used in 4 studies were unknown. Hu Yin E's two studies were randomly assigned according to the order of treatment, so they were rated as"high risk". In terms of distribution concealment, except for two articles by Hu Yine, none of the other studies were mentioned;because all studies could not blind subjects and researchers and rated them as "high risk"; all studies did not say whether they were blind to outcome evaluators, so they were rated as "unclear"; taken together, the quality of the included study was low, and the specific evaluation was shown in figure 2.
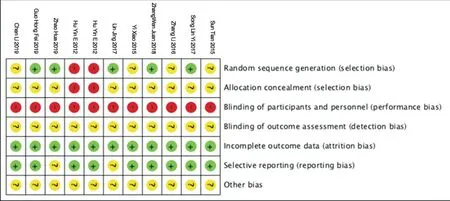
Figure2 summary map of bias risk assessment
3.3 Meta analysis results
3.3.1 CytokinesA total of 11 articles were included, and the results showed that the total effect of the two groups was MD=-10.97,95%Cl[-15.56,-6.37], P<0.00001, indicating that TGP could significantly affect the expression of cytokines in patients with psoriasis. The heterogeneity test was P<0.00001, which mainly came from the diversity and complexity of cytokines. The results of subgroup analysis showed that the values of the following four cytokines decreased significantly after taking TGP: IL-2 (MD=-11.42,95%Cl [-13.21,-9.63]), IL-8(MD=-15.67,95%Cl [-24.58,-6.76]), IL-23 (MD=-16.12,95%Cl[-25.04,-7.20]) and TNF-α (MD=-21.82). 95%Cl [-29.23,-14.41]).In the four subgroups of IL-4, IL-17, IL-18 and IFN-γ, the detectionvalue of the test group was lower than that of the control group, but the difference was not statistically significant (P>0.05). For the IL-10 subgroup, the value of the test group was higher than that of the control group, but the difference was not statistically significant. See figure 3 for details:
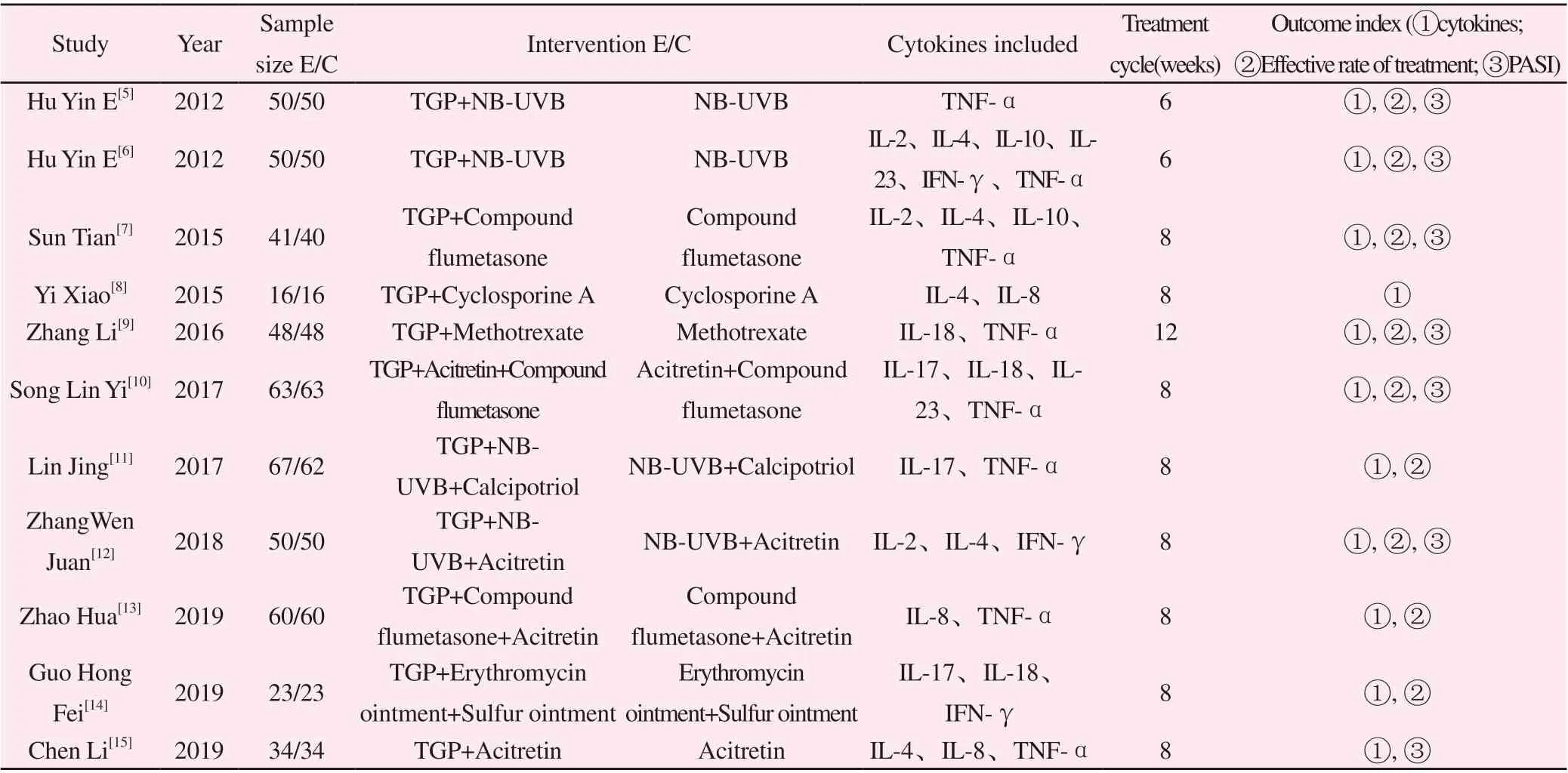
Table 1 Basic characteristics of literature included
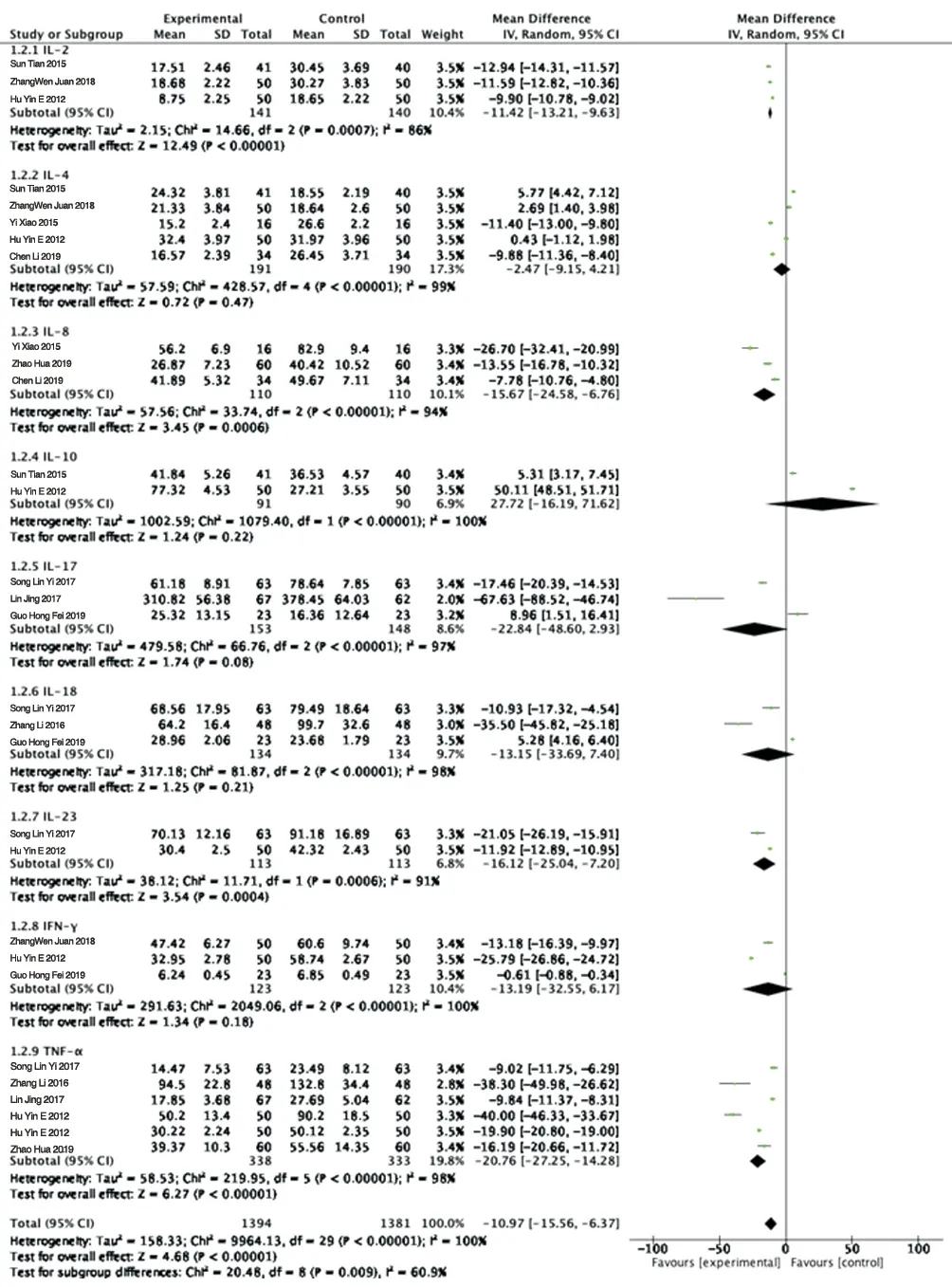
Figure3 Forest map of Meta analysis of cytokines
3.3.2 Effective rate of treatment
Nine studies reported therapeutic efficacy, which was combined with a fixed-effect model and showed no significant heterogeneity among the studies (P=0.36 I2=10%). There was a significant difference in the effective rate between the two groups, and the effect of combined use of TGP was better than that of unused TGP(OR=3.57,95Cl% [2.58,4.94]). See figure 4.
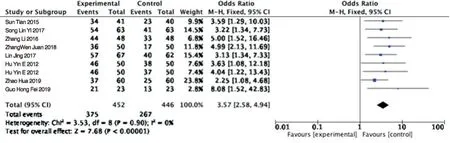
Figure4 Forest map of Meta analysis for effective treatment
3.3.3 PASI score
The outcome index of 7 articles reported the PASI score, and the results showed that there was significant difference between the two groups (P<0.00001), indicating that the effect of routine treatment alone (oral western medicine, topical ointment or NBUVB) on reducing PASI score was worse than that of combined use of TGP. The heterogeneity test was P<0.00001, and the source of heterogeneity was speculated to be related to different courses of treatment, so the random effect model was used for subgroup analysis, as shown in figure 5.
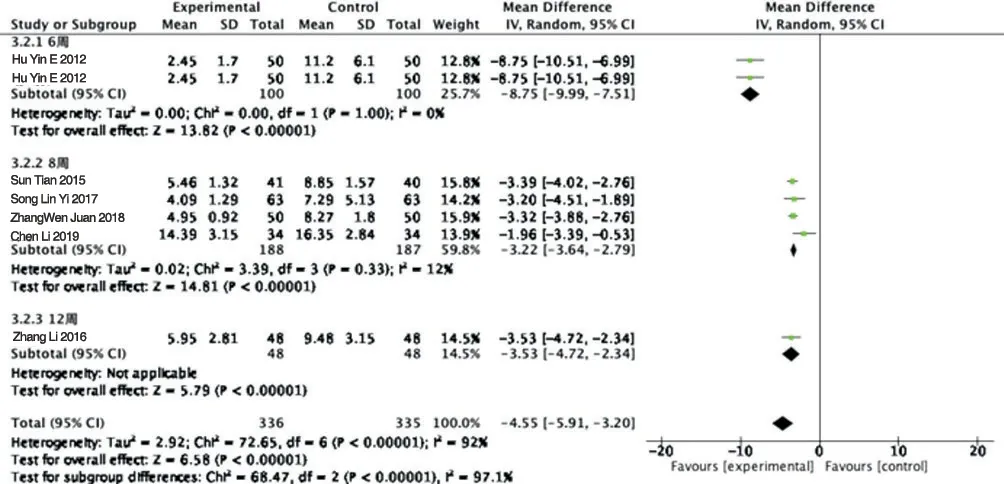
Figure5 Forest map of PASI subgroup analysisFig. 5 Forest map of PASI subgroup analysis
3.3.4 Sensitivity analysisMeta analysis of other studies after single study was excluded one by one. It can be seen from figure 6 that study 13 (Hu Yin E IL-10) has the greatest influence on the total combined effect. If it is removed, the combined effect will change from-1.60(-2.26, -0.94)to-1.99(-2.60, -1.37), while other studies have little effect on the total combined effect.
4. Discussion
At present, it is believed that the abnormal activation of T lymphocytes is the most important immune factor leading to psoriasis [16], and many kinds of interleukin, such as IL-2, IL-4, IL-17, IL-18, IL-22, IL-23 and so on, can stimulate the proliferation of activated T lymphocytes, thus induce the synthesis and release of inflammatory mediators and produce inflammatory response. IL-8 has a chemotactic effect on T lymphocytes and neutrophils, which can promote the proliferation of epidermal keratinocytes and new angiogenesis [17]. Moreover, there is also a cascade reaction between inflammatory mediators. IL-23 can promote Th17 cells to synthesize IL-17, IL-22 and act on keratinocytes, making them produce a large number of other inflammatory factors, chemokines and antimicrobial peptides to enhance immune response [18-19]. TNF-αcan induce and enhance the pathological state of inflammatory infiltration in psoriasis by activating neutrophils and vascular endothelial cells [20-21].
The application of total glucosides of paeony to the treatment of psoriasis mainly shows the biological characteristics of negative immune regulation. It can not only inhibit the activation and proliferation of T lymphocytes, reduce the release of inflammatory factors, but also directly inhibit the cytokine secretion of HaCat cells[22], so as to reduce the level of inflammatory mediators in the serum of patients with psoriasis and stabilize the autoimmune system.Huang Aiping's study found that IL-8 and TNF-αare important pathological factors in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. TGP can treat psoriasis by inhibiting the abnormal expression of both. Zhang Yuhong's research conclusion shows that total glucosides of paeony can significantly control the abnormally high expression of IL-17 and IL-23 and maintain the balance of the immune system [24]. Wang Hongquan's research points out that TGP has a two-way regulating effect on IL-2 [25].
A total of 11 clinical studies were included in this study. for the main outcome indicators, cytokines, TGP could alleviate the inflammatory response in patients with psoriasis (MD=-10.79,95Cl%[-15.47,-6.11]), and significantly inhibited the expression of IL-2, IL-8, IL-23 and TNF-α (P<0.05). It also affected the expression of IL-4, IL-17, IL-18, IFN-γ and IL-10,but there was no significant difference between the two groups. The effective rate of treatment and the decrease of PASI score in the experimental group treated with TGP were better than those without TGP (P<0.05). Therefore, from the perspective of evidence-based medicine, this study verified that TGP can improve the clinical effect of psoriatic lesions by reducing the pharmacological effects of IL-2,IL-8, IL-23 and TNF-α.
This study also has some limitations: (1) the number of literatures is small, the sample size is insufficient, and the overall quality is not high; (2) there are clinical heterogeneity among different studies,such as the course of treatment and the severity of baseline skin lesions of the subjects. (3) the detection methods used in each study are different, and the sensitivity of the detection reagent is not clear,the above factors will affect the stability of the research conclusion.therefore, we look forward to more multi-center, large samples, highquality research to provide high-level evidence-based basis.
 Journal of Hainan Medical College2022年11期
Journal of Hainan Medical College2022年11期
- Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Study on the mechanism of “Salvia chinensis and Radix Ranunculi Ternati” drug pair in the treatment of lung cancer
- Potential targets and mechanism of Xingxiao Pill for the treatment of lung cancer were analyzed based on network pharmacology and molecular docking
- Effects of post-dilation on coronary blood flow and MACE events following primary percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with STEMI
- Correlation study between dendritic cell and eosinophil in refractory rhinosinusitis
- An exploration on the protective mechanism of Xuduan Zhongzi prescription against epididymis oxidative damage in oligoasthenospermia model rats based on Nrf2-NQO1/γ-GCS signaling pathway
- Effects of compatibility of Scutellaria baicalensis stems and Polygonum cuspidatum on TRPV1 expression and inflammatory cytokines in rats with acute lung injury
