Efficacy of Qihuang decoction (芪黄煎剂) on enteric nervous system in rats after gastrectomy
ZHANG Qi,ZHENG Zhou,HUANG Long,PENG Hui,YU Qingsheng,WANG Laiyong
ZHANG Qi,ZHENG Zhou,HUANG Long,PENG Hui,YU Qingsheng,WANG Laiyong,Department of General Surgery,First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Chinese Medicine,Hefei 230031,China
ZHANG Qi,ZHENG Zhou,HUANG Long,PENG Hui,YU Qingsheng,WANG Laiyong,Institute of Chinese Medicine Surgery,Anhui Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Hefei 230031,China
Abstract OBJECTIVE:To investigate the influence of Qihuang decoction (芪黄煎剂) on enteric nervous system after gastrectomy in rats.METHODS:The morphology,distribution and number of intestinal neurons in enteric nervous system (ENS) were observed by immunofluorescence labeling and confocal laser scanning microscopy.Reverse transcriptionpolymerase chain reaction and Western blot were used to detect the mRNA and protein expression of intestinal neurotransmitters and corresponding receptors in ENS. RESULTS:The morphology and distribution of enteric neurons in ENS were changed after gastrectomy,and these neurons in Qihuang decoction group were similar with that of sham operation group.The number of ACh and SP positive neurons,mRNA and protein expression of excitatory neurotransmitters (AChE,SP) and receptors(M3R,NK1R) were decreased after gastrectomy.And the intervention of Qihuang decoction could increase the number of ACh and SP positive neurons and promote the expression of their mRNA and protein.For vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) and nitric oxide synthase (NOS),the number of neurons and mRNA and protein expression of inhibitory neurotransmitters (VIP and NOS) and receptors (VIP2R) were increased after gastrectomy.And these rising indexes fall back after the intervention of Qihuang decoction.Besides,the intestinal propulsion rate in QH group was significantly increased than that in SEN and IEN group.CONCLUSIONS:These experimental results showed that after gastrectomy,early intervention with Qihuang decoction in small intestine will contribute to the postoperative recovery of enteric nervous system and intestinal propulsion rate,and consequently enhance gastrointestinal motility.
Keywords:Gastrectomy;gastrointestinal motility;enteric nervous system; neurotransmitter agents; receptors,neurotransmitter;Qihuang decoction
1.INTRODUCTION
Enteric nervous system (ENS) is a network structure system consisting of neurons in the gastrointestinal tract and intermediate nerve fibers.1-5It contains about 100 million neurons,nearly the same number of neurons found in the spinal cord.1This system plays a vital role in most physiological processes in gastrointestinal tract,such as regulating endocrine secretion,blood flow,immune system,and gastrointestinal motility.2-4In general,the ENS functions as the “brain of the gut” and is able to work independently from the central nervous system.2It has been reported that in ENS neurons,there are over 20 different kinds of neurotransmitters,and even one neuron can coexist with several kinds of neurotransmitters to play different coordination roles.3,4Among them,noradrenaline (NE),vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP),pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide,nitric oxide (NO),and opioids are representative inhibitory transmitters.Meanwhile,excitatory stimuli are characterized by tachykinins such as substance P (SP),acetylcholine (ACh),and serotonin(5-hydroxytryptamine,5-HT).4The wide range of enteric neurotransmitters and corresponding receptors provide a foundation of normal ENS function and intestinal homeostasis,which closely rely on neural integrity.However,disorders of the enteric nervous system can result from different reasons,for instance achalasia,gastric stasis and outlet obstruction,leading to motility,secretory,and immune dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract.3In particular,dysfunction of gastrointestinal motility could be induced by developmental abnormalities in enteric nervous system,or by external surgery stress such as gastrectomy.6-8
China is a country with high incidence of gastric cancer,accounting for the first place of digestive tract tumors,and the third place of mortality.9Due to the high incidence and mortality,gastric cancer is a serious threat to human health and could be life-threatening.10-11Until now,surgical resection has been developed as an effective treatment for gastric cancer,with about 400 000 patients undergoing gastrectomy each year.12However,the operation itself brings a series of problems,especially the postoperative gastrointestinal motility dysfunction caused by traumatic stress and gastrointestinal reconstruction.13Gastrointestinal motility dysfunction can lead to nutritional malabsorption and impaired immune function,normally associated with increased postoperative complications and early tumor recurrence.Presently,different treatments have been applied in the intervention of gastrointestinal motility dysfunction,14,15including Chinese medicine treatment.16-19According to our long-term clinical practice,patients often have symptoms ofQiand blood weakness as well asQistagnation and intestinal blood stasis in the early stage after gastrectomy.Based on the enlightenment of Buzhong Yiqi Tang recorded inPi Wei Lunand Dachengqi Tang recorded inShang Han Lun,Huangqi(Radix Astragali Mongolici),Baizhu (Rhizoma Atractylodis Macrocephalae) and Dangshen (Radix Codonopsis) in Buzhong Yiqi Tang were used to enhance theQiand blood weakness,20and Dahuang(Radix Et Rhizoma Rhei Palmati),Zhishi (Fructus Aurantii Immaturus) and Houpu (Cortex Magnoliae Officinalis) in Dachengqi Tang were used to relieve the Qi stagnation and intestinal blood stasis.Compatible with Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) and Huangqin (Radix Scutellariae Baicalensis),the Chinese herbal formula was named Qihuang decoction.Qihuang decoction is a traditional Chinese medicine which can invigorate the spleen and activate the interior,and may contribute to the regulation of the gastrointestinal movement after gastrectomy.21,22According to our previous works that investigating the effects of Qihuang decoction on intestinal mucosal barrier and lymphocyte homing in rats after gastrectomy,we found that Qihuang decoction can enhance the gastrointestinal function and nutrition absorption remarkably.23,24However,the underlying mechanism of enhanced gastrointestinal motility after gastrectomy intervened by Qihuang decoction is still not clear.In the present work,we studied the changes of enteric nervous system as well as its neurotransmitters and receptors secretion after Qihuang decoction intervention.Meanwhile,we also investigate the intestinal propulsion rate between different groups,aiming to provide an in-depth understanding of enhanced gastrointestinal motility intervened by Qihuang decoction.
2.MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1.Experimental Materials
The Qihuang decoction is formulated by the mixture of Huangqi (Radix Astragali Mongolici),Dahuang (Radix Et Rhizoma Rhei Palmati),Baizhu (Rhizoma AtractylodisMacrocephalae),Dangshen (Radix Codonopsis),Zhishi (Fructus Aurantii Immaturus),Houpu (Cortex Magnoliae Officinalis),Danshen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae) and Huangqin (Radix Scutellariae Baicalensis),with a mass ratio of 20∶10 ∶20 ∶20 ∶10 ∶10 ∶15 ∶12.Totally 234 g mixed medicine was dissolved in 500 mL water and boiled for 30 min,and then underwent filtration and concentration into 1.0 g/mL.The prepared Qihuang decoction was stored in refrigerator and warmed up before administration.All the Chinese herb and medicine were supplied by Traditional Chinese Medicine pharmacy of the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine.The standard enteral nutrition was Fresubin (H20040722),and the immune enteral nutrition was Supportan (H20040722).Both of them were brought from Huarui Pharmaceutical Co.Ltd.(Jiangsu,China).The protein nutrients (H20130888) were brought from Milupa Gmbh (Fulda,Germany).Healthy male Wistar rats of clean grade,weighing (200 ± 10) g,were purchased from experiment animal center in Anhui University of traditional Chinese Medicine (Hefei,China)[Certificate of quality No.SCXK (Wan) 2019-0003].
2.2.Laboratory reagents
Anti-AChE (ab2803),anti-SP (ab14184),anti-VIP(ab22736),anti-nNOS (ab15203),anti-M3R (ab126168),IgG-HRP sary antibody (ab205718) and GaMIgG-HRP sary antibody (ab205719) were supplied by abcam company (Cambridge,MA,USA).Anti-VIP2R (VPAC2)(sc-52759),anti-NK1R (sc-365091) were brought from Santa Cruz company (Dallas,TX,USA);Trizol (1596-026) from Invitrogen (Carlsbad,CA,USA).SYBR green polymerase chain reaction (PCR) kit (BL705A) from Biosharp (Beijing,China).Reverse transcription kit(#K1622) from Fermentas (Shenzhen,China).
2.3.Rat model establishment of gastrectomy
The rats were randomly and equally divided into sham operation group (SO),standard enteral nutrition group(SEN),immune enteral nutrition group (IEN) and Qihuang decoction group (QH) with 20 rats in each group.The rat model of gastrectomy was established by referring to our previous work.25In sham operation group,only surgical incision and closing were conducted at the central abdomen without undergoing gastrectomy.One day after surgery,the rats were free to drink and eat,but neither enteral nutrition nor medicine intervention was supplied in this group.The standard enteral nutrition group was given standard enteral nutrition (Fresubin)from the first day after gastrectomy operation as referred to our previous work.23,246 mL of saline solution was instilled before the Fresubin instillation.The intervention procedure lasted for 7 d.And in immune enteral nutrition group,except that Fresubin was substituted by immune enteral nutrition (Supportan),other treatments were similar with standard enteral nutrition group.In Qihuang decoction group,6 mL Qihuang decoction was also instilled with a dose of 10 g·kg-1·d-1.After that,Fresubin was supplied through intestinal instillation with the same dose and method as standard enteral nutrition group.The Qihuang decoction intervention also lasted for 7 d.
2.4.Sample collection
The rats were sacrificed by chloral hydrate through intraperitoneal injection after all intervention measures were finished.The full length of small intestine,from the ligament of Treitz to ileocecal region,was obtained by laparotomy.The mesentery was cut lengthwise along the edge and then cleaned by normal saline rinsing.Only the ileum was used for further study.
This study was audited and approved by Animal Ethics Committee of Anhui University of Chinese Medicine.All experimental procedure and animal care were carried out under the guidance of the Ethics Committee in order to minimize the suffering of animals.
2.5.HPLC and fingerprinting analysis
Ten batches of Qihuang decoction compound were prepared according to our previous method for HPLC analysis.Methanol was added into Qihuang decoction filtrate with a volume ratio 4∶1 for precipitation.The mixed solution was filtered with 0.22 μm microporous membrane before test and analyzed by Agilent 1260 liquid chromatography (Agilent,Santa Clara,CA,USA).
2.6.Detection of intestinal propulsion rate
The small intestinal propulsion rate was measured by phenol red evacuation method.0.04% phenol red solution was orally administrated to each group at a dose of 0.0125 mL/g before the samples were collected.After 30 min,the whole intestine was taken out immediately by opening the abdomen.The whole length of the small intestine (from pylorus to ileocellum) and the length of phenol red in the small intestine were measured to calculate the small intestine propulsion rate.Calculation formula:small intestine propulsion rate=propulsion length/ total length of small intestine × 100%.
2.7.Morphology and distribution of enteric nervous system
The morphology,structure,distribution,density and integrity of enteric nervous system were observed and detected using confocal laser scanning microscope(LEICA TCS-SPS II,Buffalo Grove,IL,USA).The sample was labeled by anti-VAChT,anti-SP,anti-VIP and anti-NOS antibody immunofluorescence labeling.Then the sample was characterized by confocal laser scanning microscope (LEICA TCS-SPS II,Buffalo Grove,IL,USA) to collect image.484 nm laser was used for excitation and the image was analyzed by Leica image analysis software (LEICA,Buffalo Grove,IL,USA).
2.8.Detection of the number of enteric neurons
Fluorescence microscopy was applied to detect the location and number of enteric neurons.The sample section was rinsed by 0.05 mol/L phosphate buffer saline(pH=7.3) for 3 times and then glutamic acid decarboxylase immunohistochemical staining was performed.Later the sample was processed by 3,3’-diaminobenzidine and H2O2to present color,then dehydrated and sealed by distyrene,plasticizer and xylene.Anti-VAChT,anti-SP,anti-VIP and anti-NOS antibody were added for double dyeing.Finally,the sample was observed under fluorescence microscopy to count the number of enteric neurons.
2.9.Real-time PCR
The mRNA expression of ENS neurotransmitters and receptors were determined by real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR.Trizol one-step kit was used to extract the total RNA of colonic tissue cells and identified their purity and integrity.After measuring optical density value by ultraviolet spectrophotometer,the total RNA was reverse transcribed into cDNA and then reverse transcription reaction of mRNA was performed by cDNA kit.The polymerase chain reaction reactions system was as follows:SYBR Green Mix 12.5 µL,Primer F 0.5 µL,Primer R 0.5 µL,ddH2O 9.5 μL,cDNA 2 µL,and the total volume was 25 µL.
The cycling conditions were 95 ℃ for 10 min followed by 40 cycles of 95 ℃ for 15 s and 60 ℃ for 45 s.The copy number and relative mRNA expression of the target genes was normalized to an endogenous reference(glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase,GAPDH).The fluorescence curve and CT value were obtained automatically by the analyzing software of the instrument.The data was processed by 2-ΔΔCtmethod to calculate the relative expression of target gene and then the mRNA expression levels were acquired.Primer design and synthesis:the AChE,SP,VIP,NOS,M3R,VIP2R and NK1R mRNA gene sequences were retrieved from NCBI,and the specific primers of rats were designed and synthesized using primer design software Premier 5.0 by Shanghai bioengineering Co.,Ltd.(Shanghai,China).
The reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction primer are as follows:GAPDH for forward (F):5'-GGAGTCTACTGGCGTCTTCAC-3'and reverse (R):5'-ATGAGCCCTTCCACGATGC-3';AChE-F:5'-CTCCCACACCTGTCCTCATCTG-3' and AChE-R:5'-GGGCTTCTCTGCTTCCTGGTAG-3';SP-F:5'-GCCCTTTGAGCATCTTCTTC-3' and SP-R:5'-TCTGCATTGCGCTTCTTTC-3';VIP-F:5'-TCTTCAGTGTGCTGTTCTC-3' and VIP-R:5'-TTCTCCGCTAAGGCATTC-3';NOS-F:5' GGGGCTCAAATGGTATGG 3' and NOS-R:5'-TGGTCACCTTGTCACTCTGG-3';M3R-F:5'-TACTGTTTCGTGCTGTTC-3' and M3RR:5'-TCAAACTGGGCTTAGTTC-3';VIP2R-F:5'-AAGAGGCTCGCCAAGTCC-3' and VIP2R-R:5'-CCCTGGAAGGAACCAACAC-3';NK1R-F:5'-CTACCTGGCAAATCGTTC-3' and NK1R-R:5'-TGGTCACTGTCCTCATTC-3'.
2.10.Western blot analysis
Western-blot method was used to detect the protein expression of ENS neurotransmitters (AChE,SP,VIP,NOS) and receptors (M3R,VIP2R,NK1R).Because of its fat solubility,NO can exert its biological effect directly without binding to specific receptor.Therefore,the effect of Qihuang decoction on NO receptor was not observed.100 mg colonic tissue was homogenized in 1 mL radioimmunoprecipitation assay buffer containing 1%Phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride,then the samples were centrifuged at 12 000 rpm for 15 min under 4 ℃.The concentration of protein was detected by Bradford assay.
After that,50 μg protein in each group was electrophoresed on 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gel at 120 V for 1 h,and then transferred onto nitrocellulose filter (NC) membranes at 25 V for 30 min.After blocking by Tris Buffered Saline Tween (TBST) containing 5% fat-free milk for 2 h at room temperature,the membranes were incubated with primary antibody for AChE (ab2803,1 ∶1000),SP(ab14184,1∶1000),VIP (ab227736,1∶1000),nNOS(ab15203,1∶500),M3R (ab126168,1∶2000),VIP2R(sc-52795,1∶500),NK1R (sc-365091,1∶500) and at room temperature for 2 h.Later on,the membranes were washed three times by TBST and incubated with the HRP-conjugated goat anti-rat IgG (1∶10 000) at 37 ℃for 2 h and developed with ECL regent (Thermo Fisher,Waltham,MA,USA).Meanwhile,the expression of GAPDH was used as the reference bands.
2.11.Statistical analysis
The data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation().The data were analyzed by SPSS 23.0(International Business Machines Corporation,Armonk,NY,USA).Statistical significance was performed by using Student’st-test or one-way analysis of variance.P<0.05 was considered significant.
3.RESULTS
3.1.Fingerprint of Qihuang decoction
The reference fingerprint of Qihuang decoction was processed by the similarity evaluation software of chromatographic fingerprint.The fingerprint of Qihuang decoction was shown in Figure 1.The similarity evaluation data indicated that the similarity between the fingerprints of different batches and the control spectrum was above 0.96,which meet fingerprint requirements and indicate the main components of 10 batches of Qihuang decoction were basically the same.

Figure 1 Fingerprint of Qihuang decoction
3.2.Intestinal propulsion rate
The intestinal propulsion rate in SEN,IEN and QH group were significantly declined (37% ± 5% in SEN group,37% ± 4% in IEN group and 46% ± 4% in QH group,P<0.001,<0.001,<0.01) compared with sham operation group (64% ± 4% in sham operation group),which indicated that the intestinal propulsion rate declined after gastrectomy.And the intestinal propulsion rate in QH group were significantly increased than that in SEN and IEN group (bothP<0.01).
3.3.Structure and distribution of enteric neurons ACh,SP,VIP and NO
The morphology and distribution of enteric neuronal cells were observed under confocal laser scanning microscopy using immunofluorescent staining.As shown in Figure 2,positive neurons in ENS were mainly located at intestinal muscle layer and submucosal plexus,which was clearly visible and dyed green.The ganglia presented as circles,ovals,stripe or other irregular shape with different size.The ACh and SP neuron in Qihuang decoction group showed larger cell body,deeper staining and stronger intersegmental nerve fiber,which was comparable to sham-operated group.While in standard enteral nutrition group and immune enteral nutrition group,the ACh and SP neuronal cell body was relatively smaller,and the staining of intersegmental nerve fibers was lighter.In addition,the structure and distribution of VIP and NOS neuron in Qihuang decoction groups was also comparable to sham operation group,which showed smaller cell body and lighter intersegmental nerve fiber staining as compared with standard enteral nutrition group and immune enteral nutrition group.
3.4.Influence of Qihuang decoction on the munber of intestinal neurons after gastrectomy
Compared with sham operation group,the number of positive ACh and SP neurons in standard enteral nutrition group and immune enteral nutrition group were significantly decreased (P <0.001,<0.01,<0.001,<0.001).However,the number of positive ACh and SP neurons in Qihuang decoction group showed no statistical difference than sham operation group (P >0.05),and they were significantly increased than standard enteral nutrition group and immune enteral nutrition group (P <0.001,<0.01,<0.001,<0.001).The number of positive VIP and NO neurons in standard enteral nutrition group and immune enteral nutrition group were significantly increased than sham operation group (P <0.001,<0.01,<0.001,<0.01).In Qihuang decoction group,the number of positive VIP and NO neurons showed no statistical difference than sham operation group,but remarkably decreased as compared with standard enteral nutrition group and immune enteral nutrition group (P <0.001,<0.001,<0.01,<0.01)(Figure 3).

Figure 2 Morphology and distribution of enteric neuronal cells under confocal laser scanning microscopy (× 200)
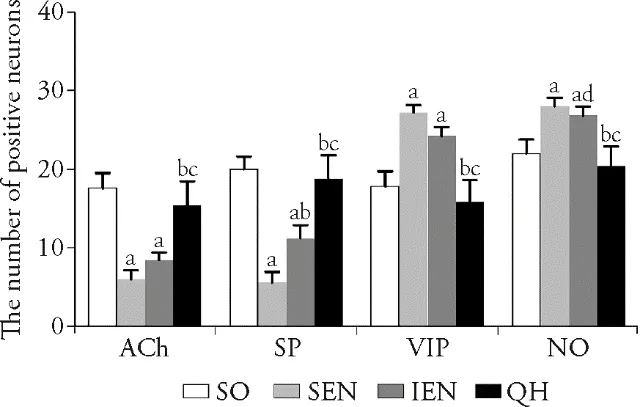
Figure 3 Number of positive neurons
3.5.mRNA transcription of ENS neurotransmitters and receptors
Figure 4 showed the mRNA transcription of ENS neurotransmitters and receptors.Compared with sham operation group,the mRNA transcription of AChE,SP,M3R,and NK1R in Qihuang decoction group were significantly decreased (P <0.001,<0.01,<0.001,<0.001),and the mRNA transcription of VIP,NOS,and VIP2R were significantly increased (P <0.05,<0.05,<0.01).Compared with standard enteral nutrition group and immune enteral nutrition group,the mRNA transcription of AChE,SP,M3R,NK1R in Qihuang decoction group were significantly increased (P <0.001,<0.001,<0.001,andP <0.05,<0.05,<0.01).Compared with sham operation group,the mRNA transcription of AChE,SP,M3R,and NK1R in standard enteral nutrition group and immune enteral nutrition group were significantly decreased (allP <0.001),and the mRNA transcription of VIP,NOS,and VIP2R were significantly increased (allP <0.001).
3.6.Protein expression of ENS neurotransmitters and receptors
The protein expression of ENS neurotransmitters and receptors were shown in Figure 5.Compared with sham operation group,the protein expression of SP and M3R in Qihuang decoction group were significantly decreased(P <0.05,<0.001),while the protein expression of VIP,NOS and VIP2R significantly increased (allP <0.001)and the protein expression of AChE and NK1R showed no statistical difference (bothP >0.05).Compared with standard enteral nutrition group and immune enteral nutrition group,the protein expression of AChE,SP,M3R,and NK1R in Qihuang decoction group were significantly increased (allP <0.001),while the protein expression of VIP,NOS,and VIP2R significantly decreased (P <0.001,P <0.001,P <0.001 andP <0.05,P <0.01,P <0.01).Compared with sham operation group,the protein expression of AChE,SP,M3R,and NK1R in standard enteral nutrition group and immune enteral nutrition group were significantly decreased (allP <0.001),and the protein expression of VIP,NOS,and VIP2R significantly increased (allP <0.001).

Figure 4 mRNA transcription of ENS neurotransmitters and receptors

Figure 5 Protein expression of ENS neurotransmitters and receptors
4.DISCUSSION
ENS is a large network of ganglion plexus composed of nerve cells and glial cells.26This network structure is usually composed of two parts,namely,myenteric plexus(MP) or Auerbach's plexus and submucousal plexus(SMP) or Meissner's plexus.The major structural elements constituting MP and SMP are numerous neurons,and the material basis for neurons to promote and coordinate intestinal movement is the neurotransmitter secreted by them (produced after binding with corresponding receptors).ENS plays a major role in the movement and secretion of gastrointestinal tract.27-30The normal structure and function of ENS network(morphological integrity,quantity,distribution) and its secreted transmitters are the key factors to maintain normal gastrointestinal motility.Among them,ACh and SP are the main and most representative excitatory transmitters in the intestinal tract.VIP and NO are the main and most representative inhibitory transmitters.4They coexist in distribution,promote each other functionally and coordinate with each other.After gastrectomy,the morphology,distribution and number of neurons in ENS network can be affected,thus damaging the gastrointestinal motility function.31
The results of this study showed that the structure,location and number of positive nerve cells in the intermuscular nervous layer of the intestine were observed by fluorescence microscopy.The positive nerve cells were mainly located in the intermuscular layer.The body of each neuron in the ganglion was clearly visualized and most of the nerve ganglia were star-shaped,long-zonal or irregular,with different sizes.
Compared with the standard enteral nutrition group and the immune enteral nutrition group,ACh and SP intestinal neurons in the Qihuang decoction group were larger and darker,and the nerve fibers in the intersegment were larger,while those in VIP and NOS intestinal neurons were smaller.The results showed that Qihuang decoction could promote the activity of ACh and SP intestinal neurons,and meanwhile inhibit the activity and the synthesis of VIP and NOS neurons,indicating that Qihuang decoction could enhance the gastrointestinal motility.As for the intervention effect on the number of intestinal nerves,the results showed that compared with the sham operation group,the number of ACh and SP intestinal nerves in the standard enteral nutrition group and the immune enteral nutrition group decreased significantly (bothP <0.05),and the number of VIP and NOS neurons increased significantly (bothP<0.05),while the neurons number in Qihuang decoction group did not show significant decrease as compared with sham operation group (P >0.05).The number of ACh and SP intestinal nerve cells in Qihuang decoction group increased significantly than that in standard enteral nutrition group and immune enteral nutrition group,with the number of VIP and NOS neurons decreased significantly.This study indicated that Qihuang decoction could regulate the number of neurons in the enteric nervous system after the gastrectomy,that is,increase the number of inhibited or damaged cholinergic neurons,inhibit the number of nitrogen neurons excited by abnormal activation,and thus improve the gastrointestinal movement and function.
ENS network neurotransmitters are often mediated by receptors to play its role in regulating gastrointestinal function,that is to say,the binding between neurotransmitter and corresponding receptor is a necessary prerequisite to perform their function effectively.The main receptors for ENS transmitters are M3R,VIP2R and NK1R.32-35In addition,it should be pointed out that NO is different from normal biological effector molecules,which directly functions without combining with receptor due to its fat-solubility.36-38The present study found that compared with sham operation group,the mRNA and protein expression of AChE,SP,M3R,NK1R in standard enteral nutrition group and Qihuang decoction group were significantly decreased(bothP <0.05),and the expression of VIP,NOS and VIP2R increased significantly (bothP <0.05).These results suggested that surgical trauma,anesthesia or other stress can lead to the inhibition or damage of excitatory and functional cholinergic nerve cells in ENS,while the nitrergic nerves which on behalf of inhibitory motor neurons can be abnormally activated,resulting in gastrointestinal motility disorders.In general,the change of ENS neurons may be related to the changes of neural and gastrointestinal hormones caused by the operation process,trauma and stress response.39During operation,the pulling of intestinal tissue and surgical exposure can stimulate the intestinal tract and lead to circulatory disturbance,causing abnormal neurotransmitter and gastrointestinal hormone secretions released by the central and visceral nerves that innervate the intestinal tract.The cut and suture of the intestinal tube itself destroys the integrity of the intestinal tract and remove the control of intestinal pacemaker cells to the detached intestinal tissue,which will inevitably lead to obvious changes in the intestinal neurotransmitter and receptor of ENS.Besides,the surgical trauma and the stress of anesthesia can also result in systemic inflammatory response syndrome,multiple organ dysfunction syndrome,abnormal intestinal feedback,and sympathetic nerve excitation.37In our work,it was found that the mRNA and protein expression of AChE,SP,M3R,NK1R were significantly increased in Qihuang decoction group as compared with the immune enteral nutrition group and the standard enteral nutrition group(bothP <0.05),while the mRNA and protein expressions of VIP,NOS and VIP2R in Qihuang decoction group were significantly decreased (bothP <0.05).The results indicated that Qihuang decoction could promote the mRNA and protein expression of excitatory neurotransmitters,and restrict the mRNA and protein expression of inhibitory transmitters.Meanwhile,the intestinal propulsion rate was significantly increased in QH group than that in SEN and IEN group (bothP <0.01).All these results suggested that Qihuang decoction intervention may induce resultant enhanced gastrointestinal motility,which is beneficial for gastrointestinal absorption of nutrients and improving immune function.
Particularly,we’d like to note that compared with Chengqi formula or other basic tonifying prescriptions,Qihuang decoction has the effect of invigorating spleen,nourishingQi,activating the interior and removing stasis simultaneously.On the other hand,although some Chinese herbal compound such as Sijunzi Tang40and Buzhong Yiqi Tang41have been reported to enhance gastrointestinal function,there is still a lack of systematic studies about those Chinese herbal formula on gastrointestinal motility especially after gastrectomy.In our study,we showed that early intervention with Qihuang decoction in small intestine will contribute to the postoperative recovery of gastrointestinal motility after gastrectomy in rats.
In conclusion,External stimulus such as surgical trauma and the stress of anesthesia can lead to the impairment of cholinergic nerve function,affecting the number of corresponding positive neurons in ENS and causing gastrointestinal motility dysfunction.After gastrectomy in rats,early intervention with Qihuang decoction in small intestine will contribute to the postoperative recovery of enteric nervous system and intestinal propulsion rate,and may consequently enhance gastrointestinal motility.The underlying mechanism may be related to the regulation effect of Qihuang decoction on the number and structure of positive enteric neurons,combining with regulated mRNA and protein expression of ENS neurotransmitters and receptors including AChE,SP,VIP,NOS,M3R,VIP2R and NK1R.
5.REFERENCES
1.Furness JB,Costa M.The enteric nervous system.New York:Churchill Livingstone 1988;94:549-50.
2.Gershon MD,Kirchgessner AL,Wade PR.Functional anatomy of the enteric nervous system.In:Johnson LR,ed.Physiology of the gastrointestinaltract.3rd ed.New York:Raven Press,1994:381-422.
3.Goyal RK,Hirano I.The enteric nervous system.N Engl J Med 1996;334:1106-15.
4.Hansen MB.The enteric nervous system II:gastrointestinal functions.Pharmacol Toxicol 2003;92:249-57.
5.Reddy PM.Effects of the autonomic nervous system,central nervous system and enteric nervous system on gastrointestinal motility.East Cent Afr J Pharm Sci 2010;13:50-7.
6.Kalff C,Schraut WH,Billiar TR,et al.Role of inducible nitric oxide synthase in postoperative intestinal smooth muscle dysfunction in rodents.Gastroenterology 2000;118:316-27.
7.Mans E,Serra-Prat M,Palomera E,et al.Sleeve gastrectomy effects on hunger,satiation,and gastrointestinal hormone and motility responses after a liquid meal test.Am J Clin Nutr 2015;102:540-47.
8.Endo M,Hori M,Ozaki H,et al.Daikenchuto,a traditional Japanese herbal medicine,ameliorates postoperative ileus by antiinflammatory action through nicotinic acetylcholine receptors.J Gastroenterol 2014;49:1026-39.
9.Bray F,Ferlay J,Soerjomataram I,et al.Global cancer statistics 2018:GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries.CA Cancer J Clin 2018;68:394-24.
10.Gu QH,Hu B,Zhang XD,et al.Clinical observation on Xiaotan Sanjie formula combined with chemotherapy for 32 cases of advanced gastric cancer.J Tradit Chin Med 2013;54:2008-2011.
11.Ruan YP,Liu YX,Yao L.Influence of Yiqi Bushen Formula on the ability of invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer cells.J Tradit Chin Med 2012;53:148-50
12.Hu Y,Huang C,Sun Y,et al.Morbidity and mortality of laparoscopic versus open D2 distal gastrectomy for advanced gastric cancer:a randomized controlled trial.J Clin Oncol 2016;34:1350-57.
13.Javed I,Jhuma S.Systemic inflammatory response syndrome(SIRS) and sepsis -an ever-evolving paradigm.Indian J Pediatr 2015;82:675-76.
14.Long L,Wang J,Deng Y,et al.Curcumin ameliorates reserpineinduced gastrointestinal mucosal lesions through inhibiting IκBα/NF-κB pathway and regulating expression of vasoactive intestinal peptide and gastrin in rats.J Med Food 2016;19:528-34.
15.Cong W,Pan Z,Yanan Z,et al.Chinese rice wine inhibits contraction activity of the isolated rat small intestine through intestinal myenteric plexus.Food Sci 2019;40:173-8.
16.Shaorong Z,Lannong J,Jiangen Y,et al.The effect of Shunqi Tongfu mixture on plasma levels of gastrointestinal hormones in rats with gastrointestinal motility disorder.Yunnan Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2015;38:10-2.
17.Yuxiang Z.The effect of modified Wumo decoction on slow transit constipation and the level of substanceP,vasoactive intestinal peptide,nitric oxide and neuropeptide Y in serum.Zhong Guo Lao Nian Xue Za Zhi 2016;8:4008-9.
18.Yu C,Hangjun G,Gan H,et al.Clinical study on Amomum villosum’s promotion of gastrointestinal function recovery after gastric operation.Xian Dai Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2019;28:19-22.
19.Chen ZQ,Cao LX,Shang WF,et al.The effect of Xiangbin Fang(香槟方) on gastrointestinal motility of dogs after abdominal operation.J Tradit Chin Med 2015;2:1953-57.
20.Xiong LH,Su PP,Wang Z.Research on prescription ofQideficiency and blood stasis syndrome based on the ancient books.J Tradit Chin Med 2015;56:1645-47.
21.Liu YC,Yu QS.Effect of early use of medicinal herbs through intestinal canal on gastrointestinal peristalsis after gastric cancer operation.Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Wai Ke Za Zhi 2008;14:538-41.
22.Yu QS,Zheng Z,Peng H,et al.Effect of Qihuang decoction combined with enteral nutrition on postoperative gastric cancer of nutrition and immune function.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2020;2020:1795107.
23.Peng H,Shen Y,Zhang Q,et al.Qihuang decoction promotes the recovery of intestinal immune barrier dysfunction after gastrectomy in rats.Am J Transl Res 2018;10:827-36.
24.Zhang Q,Cheng L,Huang L,et al.Enhanced intestinal lymphocyte homing intervention using Qihuang decoction intestinal instillation in rats after gastrectomy.Int J Clin Exp Med 2020;13:5790-8.
25.Yu QS,Zhang Q,Pan JF,et al.Effects of Qihuang decoction on immunity function and bowel mucosal barrier on early days after gastric cancer operation in rats.Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Wai Ke Za Zhi 2009;15:135-8.
26.Walsh KT,Zemper AE.The enteric nervous system for epithelial researchers:basic anatomy,techniques,and interactions with the epithelium.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepato 2019;8:369-78.
27.Kirchgessner AL,Gershon MD.Innervation of the pancreas by neurons in the gut.J Neurosci 1990;10:1626-42.
28.Szurszewski JH,Miller SM.Physiology of prevertebral ganglia.In:Johnson LR,editor.Physiology of the gastrointestinal tract.3rd ed.New York:Raven Press,1994:795-878.
29.Worl J,Mayer B,Neuhuber WL.Nitrergic innervation of the rat esophagus:focus on motor endplates.J Auton Nerv Syst 1994;49:227-33.
30.Gabella G.Structure of muscles and nerves in the gastrointestinal tract.In:Johnson LR,editor.Physiology of the gastrointestinal tract.3rd ed.New York:Raven Press,1994:751-94.
31.Gershon Michael D.Nerves,reflexes,and the enteric nervous system:pathogenesis of the irritable bowel syndrome.J Clin Gastroenterol 2005;39:S184-93.
32.Russell John P,Mohammadi E,Ligon C,et al.Enteric RET inhibition attenuates gastrointestinal secretion and motilityviacholinergic signaling in rat colonic mucosal preparations.Neurogastroenterol Motil 2019;31:e13479.
33.Turner DJ,Martin PC,Rao JN,et al.Substance P regulates migration in rat intestinal epithelial cells.Ann Surg 2007;245:408-14.
34.Majkowska-Pilip A,Halik PK.The Significance of NK1 receptor ligands and their application in targeted radionuclide tumour therapy.Pharmaceutics 2019;11:1-28.
35.Lissak K,Eedroczi E.Effect of cortical denervation upon acetylcholin-cholinesterase system and excitability of the central nervous system.Acta Physiol Hung 1952;3:39-48.
36.Fu XY,Li Z,Zhang N,et al.Effects of gastrointestinal motility on obesity.Nutr Metab (Lond) 2014;11:3.
37.Schwerdtfeger LA.Vasoactive intestinal peptide regulates ileal goblet cell production in mice.Physiol Rep 2020;8:e14363.
38.Guerra DD,Bok R,Lorca RA.Protein kinase A facilitates relaxation of mouse ileum via phosphorylation of neuronal nitric oxide synthase.Br J Pharmacol 2020;177:2765-78.
39.Hogan S,Steffens D,Rangan A,et al.The effect of diets delivered into the gastrointestinal tract on gut motility after colorectal surgery-a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.Eur J Clin Nutr 2019;73:1331-42.
40.Xiu ZC,Chen Q,Shang WF.Discussion on VIP/NO signal transduction mechanisms of abnormal small intestine function of spleen-deficiency syndrome.Shanghai Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2006;40:55-6.
41.Pan HS,Zhong GL,Qiu WM,et al.Effect of Buzhong Yiqi decoction on gastrointestinal function of exercise-induced fatigue rats.Guangzhou Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2013;30:864-7.
 Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine2022年4期
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine2022年4期
- Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine的其它文章
- Editorial Board Listing
- Mixed methods research in complementary and alternative medicine:a scoping review
- Herbal anthelmintic agents:a narrative review
- Factors influencing physician's behavioral intention to use Traditional Chinese Medicine to treat coronavirus disease 2019 based on the theory of planned behavior
- Identification of novel biomarkers and therapeutic target candidates for stasis-heat symptom pattern of acute intracerebral hemorrhage by quantitative plasma proteomics
- Effect of three tongue needles acupoints Lianquan (CV23) and Hegu(LI4) combined with swallowing training on the quality of life of laryngeal cancer patients with dysphagia after surgery
