Study on Extraction Techniques of Celastrol from Celastrus orbiculatus Thunb.
Wenhua ZHANG Congkui TIAN Tiancai ZHONG Zengbao WU
Abstract[Objectives] This study was conducted to investigate the extraction technology of celastrol from Celastrus orbiculatus Thunb. [Methods]Solvent ultrasonic extraction was selected, and with the content of celastrol as the evaluation index, the effects of different solvents, extraction time, temperatures and material-to-liquid ratios on the extraction rate of celastrol were investigated by single factor and orthogonal experiments. [Results] The optimal extraction conditions were as follows: a solvent ratio of petroleum ether to ethyl acetate at 1∶1, a ratio of solvent to material at 10∶1 (v/w), extraction time of 30 min, and an extraction temperature at 30 ℃. [Conclusions]This method has high extraction rate, and is simple and feasible.
Key wordsCelastrol; Celastrus orbiculatus Thunb.; Extraction technique
Celastrus orbiculatus Thunb., also known as Nanshefeng, Dananshe, Xianglongcao, Guoshanteng, etc., is a plant of the genus Celastrus[1]. It is widely distributed in China, and is mostly used for expelling wind and eliminating dampness, promoting blood circulation and relieving internal heat or fever, activating blood circulation and detoxicating and resisting inflammation. Modern pharmacological studies have shown that it has anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, insect antifeedant, antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anti-fibrosis and anti-fertility pharmacological effects[2]. Celastrol, as the main triterpenoid constituents of C. orbiculatus, has been reported to have anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive, anti-obesity, and anti-tumor effects, and is widely used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, obesity, and tumors[3-5]. Existing extraction processes mainly focuses on the use of solvents such as different concentrations of ethanol and single petroleum ether or ethyl acetate[6-7]. Previous experiments found that the extraction effect of the mixed solvent of petroleum ether∶ethyl acetate is better than that of single solvent and ethanol. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out further research on the extraction process of celastrol from C. orbiculatus.
Materials and Methods
Experimental materials
InstrumentsLC-20 semi-preparative high performance liquid chromatograph (Shimadzu Corporation, Japan); KQ-500DE desktop ultrasonic cleaner (Zhejiang Saide Instrument Co., Ltd.); RE-1002 rotary evaporator (Henan Airuide Instrument Equipment Co., Ltd.); UPW-20NE ultrapure water device (Votel Co., Ltd.); CPA225D one ten-thousandth analytical balance (Sartorius, Germany).
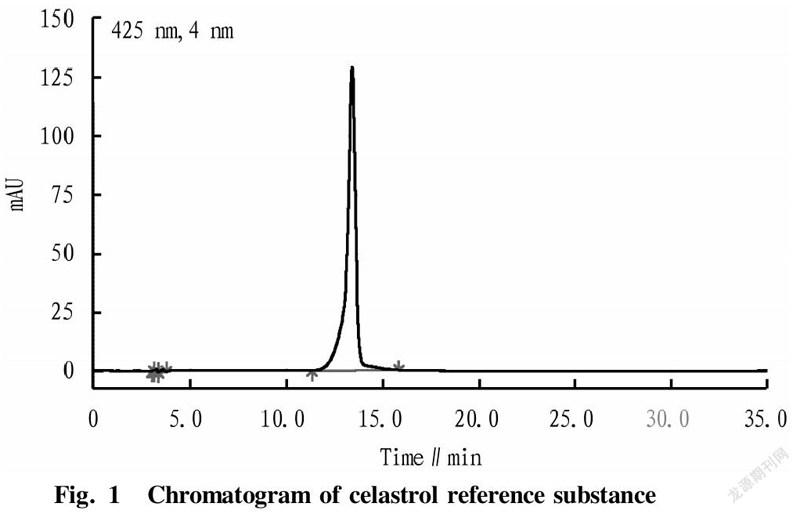
ReagentsC. orbiculatus plants were collected from Enshi, Hubei. Other reagents were domestic analytical or chemically pure. Celastrol reference substance was self-made (≥98%, the chromatogram is shown in Fig. 1).
Experimental methods
Preparation of celastrol extractFirst, 10.527 0 g of C. orbiculatus medicinal powder was weighed and extracted ultrasonically with petroleum ether∶ethyl acetate (1∶1) at the material-to-liquid ratio of 1∶10 for 30 min. The extraction was repeated twice, and filtrates were merged and evaporated to dryness. The residues were diluted with methanol to constant volume, obtaining a solution, which was filtered with 0.22 μm filter heads for testing.
Preparation of reference substanceFirst, 0.003 0 g of celastrol reference substance was precisely weighed, dissolved in methanol, and diluted to 10 ml to obtain a 0.3 mg/ml celastrol standard solution, which was respectively prepared to 0.300, 0.100, 0.030, 0.010 and 0.003 mg/ml reference solutions.
Chromatographic conditionsColumn: Extend-C18 column (5 μm, 4.6 mm×250 mm); mobile phase: acetonitrile (90)-0.1% phosphoric acid aqueous solution (10); flow rate: 0.8 ml/min; column temperature: room temperature; injection volume: 10 μl.
Results and Analysis
System suitability test
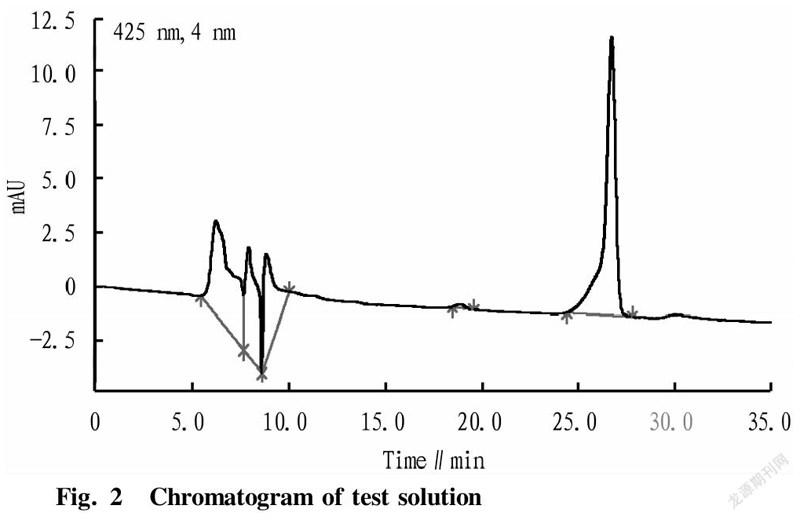
Under the above-mentioned chromatographic conditions, the same amount of reference substance solution and test solution were measured for the contents of celastrol. By comparison, it was found that a celastrol peak were detected under the chromatographic conditions in the test solution of C. orbiculatus (Fig. 2), and the separation of celastrol was relatively complete, indicating that the method had good specificity.
Examination of linear relationship
Five equal volumes of the reference solutions of different concentrations were taken and measured in turn. With the concentration of reference solution (mg/ml) as the abscissa (x) and the peak area of celastrol as the ordinate (y), a standard curve was drawn obtaining a linear regression equation of celastrol: y=13 852 215.751x-24 918.316, R=0.999 9, indicating that the concentration of celastrol had a good linear relationship with the peak area in the concentration range of 0.003-0.300 mg/ml.
Precision test
The reference substance of the same concentration (0.300 mg/ml) was injected 6 times continuously according to the chromatographic conditions, and the peak areas of celastrol were recorded. The results showed that the peak areas of different samples were similar, with RSD=2.34% (n=6), and the precision was good.
Stability test
The same test solution was injected once every 4 h for a total of 6 times, under the same chromatographic conditions, and the peak areas were recorded. The experimental results showed that the peak areas of celastrol measured at different time periods were similar, with RSD=2.31% (n=6), so the test solution had good stability within 24 h after preparation.
Repeatability test
Six test solutions were prepared with the same batch of samples, and injection was performed 6 times in parallel to record the peak areas. The experimental results showed that the peak areas of celastrol obtained in the 6 times were similar, with RSD=2.91% (n=6), which indicated that the experiment had good repeatability.
Single factors
Extraction solventsThe extraction solvents for ultrasonic extraction were petroleum ether, petroleum ether∶ethyl acetate (1∶1) and ethyl acetate. The results showed that the contents of celastrol were 31.562, 51.560 and 40.186 μg/ml, respectively. In this study, the ratios of petroleum ether to ethyl acetate at 2∶1, 1∶1 and 1∶2 were determined as the investigation levels for subsequent orthogonal experiment.
Ratio of material to liquidThe material-to-liquid ratios of 1∶6, 1∶9 and 1∶12 (w/v) were selected for the ultrasonic extraction with the mixed solvent of petroleum ether and ethyl acetate. The results showed that the contents of celastrol were 45.824, 55.266 and 54.824 μg/ml, respectively. With the increase of the material-to-liquid ratio, the content of celastrol increased and then decreased. Finally, the investigation level of material-to-liquid ratio was determined as 1∶8-1∶12 for subsequent orthogonal experiment.
Extraction timeThe extraction time was 15, 30, 45 and 60 min for ultrasonic extraction. The results showed that the contents of celastrol were 46.534, 53.299, 53.941 and 54.162 μg/ml, respectively. The extraction rate of celastrol was higher within 30-45 min, and the increase was not significant after 45 min. Therefore, the investigation level of extraction time was determined as 30-50 min for subsequent orthogonal experiment.
Extraction timesThe extraction times were 2, 3 and 4 times, respectively, for ultrasonic extraction. The results showed that the contents of celastrol were 51.269, 52.941 and 53.162 μg/ml, respectively, but the increase was not significant. Considering the actual cost, the extraction times were fixed at 2.
Extraction temperatureThe extraction temperatures were 20, 30 and 40 ℃ for ultrasonic extraction. The results showed that the contents of celastrol were 50.682, 54.801 and 53.207 μg/ml, respectively. With the increase of temperature, the content of celastrol increased and then decreased. The investigation level of extraction temperature was determined as 25-35 ℃ for subsequent orthogonal experiment.
Orthogonal experiment
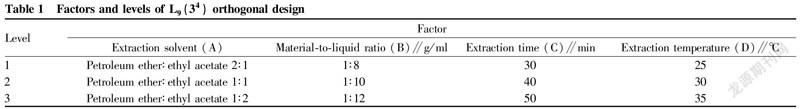
The factors to be investigated were extraction solvent (A), material-to-liquid ratio (B), extraction time (C) and extraction temperature (D), and the investigation index was the content of celastrol. An orthogonal experiment with 4 factors and 3 levels was designed.
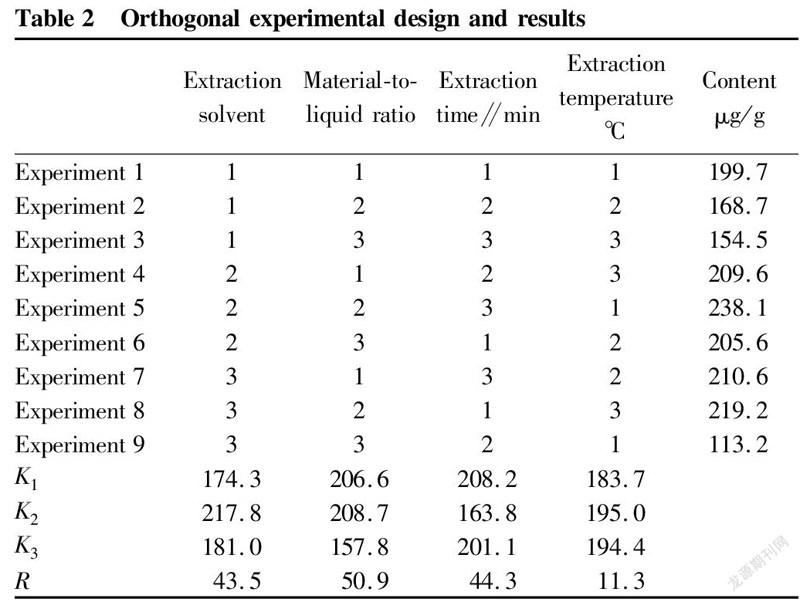
The medicinal material of C. orbiculatus was dried and crushed, and 10 g was weighed, added with quantitative solvent, and extracted twice ultrasonically. The extraction system was filtered, and the filtrates were merged and concentrated, and diluted to constant volume with methanol. The obtained extract was filtered with a 0.22 μm filter, and the content of celastrol was determined by HPLC. The results are shown in Table 2.
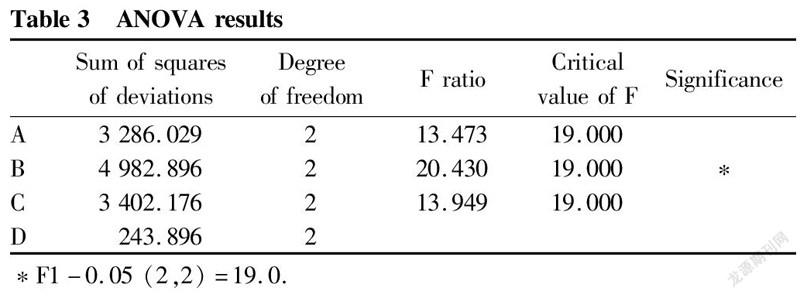
It can be seen from Table 2 that the variances of various factors ranked as B>C>A>D, that is, the order of the effects of various factors on the extraction rate was material-to-liquid ratio>extraction time>extraction solvent>extraction temperature. The variance analysis results are shown in Table 3.
It could be obtained from Table 3 that the most significant factor affecting the content of celastrol was the solvent ratio. The optimal conditions for theoretical analysis were ABCD, that is, the extraction solvent petroleum ether∶ethyl acetate 1∶1, the ratio of solvent to material 10∶1 (v/w), the extraction time 30 min, and the extraction temperature 30 ℃.
Verification test
According to the optimal extraction process, three parts of the medicinal powder of C. orbiculatus were weighed, and after treatment, the test solutions were injected to determine the contents of celastrol according to the proposed chromatographic conditions. The results showed that the average content was 253.833 μg/g (RSD=2.85%, n=3), which indicated that with these conditions, the process had good repeatability and stability, and could be used for the extraction of celastrol.
Conclusions and Discussion
In this study, the ultrasonic extraction method was selected, and with the content of celastrol as the index, the optimal extraction process of celastrol from C. orbiculatus was screened by single factor and orthogonal design experiments. The optimal extraction conditions were as follows: a solvent ratio of petroleum ether to ethyl acetate at 1∶1, a ratio of solvent to material at 10∶1 (v/w), extraction time of 30 min, and an extraction temperature at 30 ℃. The method is simple, efficient, and has a high extraction rate, so it can be used for the extraction of celastrol from C. orbiculatus.
References
[1] YANG N. Study on chemical constituents and anti-chronic obstructive pulmonary disease activity of Celastrus orbiculatus Thunb.[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2021. (in Chinese).
[2] ZHOU YL, ZHAO JS, YANG JH, et al. Experimental study on inhibitory effect of Nansheteng (Celastrus orbiculatus) extract on HepG2 hepatoma cell proliferation and adhesion[J]. Chinese Archives of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 39(8): 234-237, 282-284. (in Chinese).
[3] WONG VKW, QIU C, XU SW, et al. Ca signalling plays a role in celastrol-mediated suppression of synovial fibroblasts of rheumatoid arthritis patients and experimental arthritis in rats[J]. Br. J. Pharmacol., 2019(176): 2922-2944.
[4] CHELLAPPA K, PERRON IJ, NAIDOO N, et al. The leptin sensitizer celastrol reduces age-associated obesity and modulates behavioral rhythms[J]. Aging Cell, 2019(18): e12874.
[5] YANG Y, CHENG SY, LIANG GK, et al. Celastrol inhibits cancer metastasis by suppressing M2-like polarization of macrophages[J]. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2018(503): 414-419.
[6] WANG LH, ZHANG W, ZHANG ZY, et al. Study on extraction and purification of celastrol from Celastrus orbiculatus Thunb.[J]. Journal of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2013,15(6): 48-50. (in Chinese).
[7] LYU Y, XU SW, CHEN L. Study on the extraction technology of celastrol from the root bark of Celastrus orbiculatus Thunb.[J]. Anhui Science & Technology, 2011(9): 38-39. (in Chinese).
Editor: Yingzhi GUANGProofreader: Xinxiu ZHU
- 农业生物技术(英文版)的其它文章
- Report on the Breeding of Dahen 799 Broilers
- Evaluation and Analysis for Survey of Tea Production Quality Safety Management and Control
- Study on the Preparation of "Oil-tea" Instant Tea from the Compound Extract of Green Tea and Ginger
- Research Progress on Chemical Constituents and Pharmacological Effects of Zhuang Medicine Cocculus laurifolius DC.
- Study on Quality Standard of Lujing Yiqi Shengxue Pills
- Research on the Development of Guangxi Zhuang and Yao Ethnic Medicine Industry

