Countermeasures for Scientific Utilization of Forest Resources in China
Mei DONG Qingning WANG
AbstractEcological environment in China refers to the state of people's living environment, which is mainly represented in soil erosion, garbage pollution, air pollution, noise pollution and so on. The basic situation of ecological environment in China is that the governance capacity is far behind the speed of destruction, and the ecological deficit is gradually expanding. Excessive deforestation, indiscriminate reclamation, exceeding hunting, and random wild plants picking have been failed to be prohibited. Forest fires and pests and diseases are still very serious threats to forestry. In this paper, based on the generality of sustainable development, a systematic discussion was made to the framework theory of sustainable forestry development and sustainable forest management, followed by further exploration of forest resources and sustainable development. Moreover, based on the investigation on related concepts of forest resources, review of historic process of forest resources, and analysis on the grim situation of forest resources, some countermeasures were proposed to carry out the sustainable utilization of forest resources in China.
Key wordsNatural resources; Ecosystem; Lucid waters and lush mountains, invaluable assets; Ecological environment construction
Forest Resources and Sustainable Development
Economic development is closely related to population, resources and the environment, which is directly related to the survival and development of a country. The ecological environment is the basic condition for human survival and development, and the foundation of economic and social development. It is one of the basic policies that must be adhered to in the modernization of China to protect and build good ecological environment, and to realize sustainable development. It is also a major strategic step for China to fully drive modernization into the 21 century so as to build the beautiful mountains and rivers through efforts that are made to give full play to the advantages of socialism, carry forward the spirit of hard work and entrepreneurship, vigorously carry out tree planting and grass cultivation, implement the return of farmland to forest and grassland, control soil erosion and desertification, and build ecological agriculture. The full implementation of such mega-project is not only a pioneering work in the development of the Chinese nation, but also a practical action to implement relevant international conventions and an important contribution to world civilization. After the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development in 1992, the Chinese government first formulated and promulgated the 21 Century Agenda in China, clearly declaring that taking the road of sustainable development is the own needs and inevitable choice for China in the future and the next century . The 21 Century Agenda in China is a framework document to guide China's sustainable development. According to the National Forest City Development Plan[1] and the 14 Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development of the People's Republic of China and Vision Outline for 2035, during the 14 five-year period of China, China's economic growth mode will be transformed from extensive to intensive, so that resources can be allocated rationally, and lower energy is to be consumed to generate higher benefits. Moreover, ecological problems is listed as one of the major problems which must be attached great importance to and make great efforts to solve in the next 15 years, and sustainable development must be implemented into specific action plans for economic construction, institutional reform and environmental protection[2]. Therefore, the focus at home and abroad is the population, land, forest resources, environment, agriculture and other issues faced by the economic development in the 21 century. Sustainable development of forests and returning farmland to forests are effective measures to reduce soil erosion, relieve disasters, and improve the ecological environment, and also important ways to increase farmers' income, adjust agricultural production structure and promote the local economic development.
The 14 Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development of the People's Republic of China and Vision Outline for 2035 specifies the environmental protection goals during the 14 five-year plan period and in 2035 in China. According to the goal of struggle and the efforts of the people of the whole country, China will walk in the forefront of the world with a new attitude that is more harmonious between the environment and the economy. According to the goal of China's Sustainable Forestry Development Strategy Research Report, by 2050, China's forest coverage rate will reach 28%, with a net increase of 110 million hm2. Forestry is the main body of ecological construction and a basic industry and public welfare undertaking for sustainable economic and social development. The development of high-efficiency forestry is to produce more wood through intensive management instead of cutting down natural forests, which can achieve the marketization of forestry as well as bringing social and economic benefits. In China, the forestry industry is a resource-limited industry based on forest resources (region-tree species-yield-processed products-resource balance). The forestry industry spans the primary, secondary and tertiary industries of the national economy. It covers a wide range and has a long industrial chain, and it is a relatively complete industrial system. With the progress of reform and opening up, the forest industry has been developed, with the structure continuously optimized and economy growing. It was reported that in 2019, the total output value of the national forestry industry reached 7.56 trillion yuan, and the import and export trade volume reached $160 billion , suggesting remarkable industrial development and ecological poverty alleviation results. "The economic value of forests in China is 1 741.451 billion yuan, and the value of environmental resources is 7 521.8 billion yuan", said Hou Yuanzhao, a researcher of the Chinese Academy of Forestry in the mid-1990s when chairing the Report on the Value Accounting of Forest Resources in China. The forestry industry has developed into one of the most promising sunrise industries in the 21 century, and is playing an increasingly important role in promoting the development of the national economy. Accelerating the development of the forestry industry is an objective requirement for comprehensively advancing the socialist modernization and building a prosperous, strong, democratic, culturally advanced, harmonious and beautiful socialist modernized country. It is also a historical responsibility entrusted to forestry by the sustainable development of the national economy and society.
Concepts Related to Forest Resources
Trees are the general term for woody plants, including arbors, shrubs and woody vines. Trees are mainly seed plants. Among ferns, only tree ferns are trees. There are about 8 000 species of trees in China. In the long history of human development, in addition to being used to build houses, make furniture, labor tools, vehicles, weapons, measurement tools, paper making, decoration and handicrafts, trees have also been used to burn fire for cooking and heating. Trees also provide humans with fruits, food, dishes, tea, beverages, medicinal materials, seasonings, detergents, rosin, turpentine, lacquer, resin, rubber, tannin extract, shellac, white wax, and the wood from trees is also used to process particleboard, fiberboard, man-made fibers, extraction of sugar products and methanol, ethanol, furfural, activated carbon, acetic acid. The branches, shoots and leaves of trees can be used as feed and fertilizer. Modern scientific research proves that forests composed of trees are the largest ecosystems on earth.
Forests are the most complex, functional and stable terrestrial ecosystems on earth. Forest is a precious natural resource, an important pillar and natural foundation for human survival and development, and is known as the "lung" of the earth. Forest coverage is often an important indicator to measure the level of economic development and environmental quality of a country or region. This is not only because forests have important economic value and are renewable resources, but also play an important role in maintaining ecological balance and the normal function of the biosphere. Forests are divided into the following five categories: (1) protection forests; (2) commercial forests; (3) economic forests; (4) fuelwood forests; (5) special-purpose forests.
Forest resources refer to the general term of woodland and the forest organisms that grow on the land[3], mainly the trees, but also include undergrowth plants, wild animals, soil microorganisms. Forest land includes arbor woodland, sparse woodland, shrub woodland, glade, cutover land, fire site, nursery land and nationally planned land suitable for forestry. Forests can be renewed and are regenerative natural resources. The main indicators reflecting the quantity of forest resources are forest area and forest growing stock. Forest resources are one of the most important resources on earth and the basis of biodiversity, which not only provide a variety of valuable wood and raw materials for production and life, but also provide a variety of food for human economic life. More importantly, forests can adjust the climate, preserve water and soil, prevent and mitigate natural disasters such as droughts, floods, sandstorms, and hail; forests can also purify the air and eliminate noise. In addition, forests are also a natural park for plants and animals, nurturing various birds and beasts and growing a variety of precious trees and medicinal herbs.
Forest coverage rate, also known as forest vegetation rate, refers to the percentage of the forest area in a country or region to the land area. It is one of the important basis for the development and utilization policy.
The concept of "Forestry Development" is interpreted from the two common concepts of economic growth and economic development. The economic growth of forestry refers to the increase of the economic production capacity of forestry, which is generally measured by the proportion in gross national product (GNP). The major indicators are the volume of forest tree growth and the output value, wood cut volume and the output value, the production of wood products and the output value, the production of various non-wood forest products and the output value. Like traditional economics, it is believed that the sources and driving forces for forestry economic growth are capital, division of labor, investment, labor productivity, technological progress, innovation, and institutions. In China, the traditional forestry economic growth refers to that since the forestry sector came into being. At this stage, forests are primarily viewed as an economic resource. Forestry economic development should be a concept reflecting the overall economic and social development level of the forestry sector. There is still no clear statement on the concept of "forestry economic growth". However, this concept actually exists in the knowledge of forestry sector and the practice of national statistical system in China.
The sustainable development of forestry is a forestry practice activity on the premise of ensuring the productivity and renewability of the forest ecosystem, as well as protecting the species and ecological diversity of the forest ecosystem. It is to perform the various functions of forests through overall development and utilization. At the same time, it can protect the quality of soil, air and water, as well as the living environment of forest animals and plants, which not only meets the needs of current social and economic development, but also does not damage the ability of forestry to meet the future needs. Sustainable forestry not only reflects the multiple values of modern forests in terms of health, complete ecosystems, but also contributes to regional, national and global socio-economic development and improvement of living environment, making it irreplaceable. Such irreplaceable effect penetrates into almost every field of human existence.
"Clear waters and lush mountains are invaluable assets". This is a scientific conclusion made by Xi Jinping, then secretary of the Zhejiang Provincial Party Committee, during his inspection tour in Anji, Huzhou, Zhejiang in August 2005. Planning first is the premise of both invaluable assets and green environment, and it is also the top-level design to make lucid waters and lush mountains into invaluable assets. Special attention was paid to regional planning throughout the whole Zhejiang Province, which strengthened the subject function positioning, optimized the development pattern of land and space, and regarded it as a strategic plan and precondition to achieve "clear waters and lush mountains are invaluable assets". From 2005 to 2015, the 10 years after the scientific thesis put forward, the cadres and the masses in Zhejiang regarded "beautiful Zhejiang" as the biggest capital of sustainable development, protected the beautiful, clear waters and lush mountains, made the assets bigger, and constantly enriched the dialectical between economic development and ecological protection. Thus, in practice, the scientific conclusion of "clear waters and lush mountains are invaluable assets" has become a vivid reality and a conscious action of millions of people.
Review of forest resources
Due to the excessive utilization of forest resources by human beings, such as over-cutting, over-excavating, over-cultivation, over-hunting, the total amount of resources has dropped significantly. The size of the forest area has a significant impact on the stock of forest resources. The higher the level of forest management, the wider the scope of forest resources, and the greater the economic effect and the role it plays in supporting human development[3]. The amount of forest resources is usually expressed in terms of the number of plant species, the number of animal species and the total stock of each species in a certain area. The more species and the greater the number of each species, the richer the forest. The protection of forest resources is the premise of the sustainable use of forests, which must be developed in an orderly manner, and used in an appropriate manner. Experience at home and abroad has proved that if a large country or region has a forest coverage rate of more than 30% and the distribution is relatively uniform, then the ecological environment of this country or region is relatively superior, and the agricultural and animal husbandry production is relatively stable[4]. Forest is the largest plant group on the earth, which is one of the largest ecosystems on the earth, and an ecological barrier for the sustainable development of the national economy and society[5].
The forest is one of the most complex autofocus ecosystems in the world. It has a huge impact on the cycle of matters and energy flow in the earth's biosphere. It is predicted that the forest area on the earth is about 7.2 billion hm at its maximum, accounting for 2/3 of the land area with the coverage rate of 60%. In 1962, the earth's forest area decreased to 55 million km. In the 20th century, with the surge of population, it had been reduced to 26 million km by 1975, and the forest coverage rate was about 20%. At present, it was reported that in the past 20 years, the global forest coverage area had decreased by nearly 100 million hm, and despite at a lower rate than before, it was stable. According to the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization, the proportion of global forest area to total land area in 2020 dropped from 31.9% in 2000 to 31.2%, and the global forest area was about 4.1 billion hm. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, this indicated "a net loss of almost 100 million hm in global forest area"[6].
In China, the climatic conditions in the distribution areas of natural forests are that the total solar radiation is 3 500-6 200 MJ/m2, with the average temperature of -2-26 ℃ and annual precipitation of 350-2 400 mm. Subjected to the effect of temperature and water conditions, the forest vegetation in China is distributed in the order of tropical rain forest and monsoon forest belt, subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest belt, warm temperate deciduous broad-leaved forest belt, temperate coniferous deciduous broad-leaved forest belt and cold temperate coniferous forest belt from south to north. There is also a non-zonal distribution of vegetation in the northwest and southwest regions. Among these forest vegetation, the arbor-dominated community has 14 vegetation types, 25 vegetation subtypes, and 48 phylogenetic groups; the climate resources, especially the water and heat resources, within each vegetation type have their own characteristics. Diversified climatic resources and various forest vegetation types have created favorable conditions for the formation and development of forest ecosystem biodiversity in China.
The forest resources are concentrated in the northeast and southwest regions of China (Fig. 1). The forest resources in Northeast China are mainly centred in the Daxing'anling, the Xiaoxing'anling and the Changbai Mountains. The northeast forest area is characterized by concentrated forestry and timber production, large-scale state-owned forestry enterprises, high level of mechanization, high cutting rate, high forest road density, and high forest management level[7]. The Daxing'anling forest is the largest and most important coniferous forest area in China. Its mountain is 1 400 km long and 300 km wide from east to west. With a forest coverage of 62%, and the forest area reaches 15 million hm. The Xiaoxing'anling forest, second only to the Daxing'anling forest, covers an area of 11 million hm. In China, it is the wood production base, and it is responsible for 1/5 of the wood production tasks. Located in the east of Jilin Province, Changbai Mountain forest has a forest area of more than 10 million hm. With a great variety of plant species, it is a rare and colorful forest museum and has been approved by UNESCO as an international biosphere reserve. The main forest areas in the southwest region are located in the Hengduan Mountains, which are influenced by both the Pacific Ocean and the Indian Ocean. Most of the mountains and water systems go from south to north, and the oceanic humid air mass can penetrate from the south to the north to the far place. There are dense forests on the west slopes, which constitute the main part of the forestry in the southwest. Xishuangbanna Tropical Forest, located in the southern border of Yunnan, is the largest treasure house of natural plants in China. There are more than 4 000 species of higher plants in the forest alone, and more than 100 species of precious trees. The tallest broad-leaved tree in China, Parashorea chinensis, grows here. In addition, there are many economic trees such as rubber tree, cinchona tree, oil palm, coconut and so on. Located in the northwest of Hubei Province, Shennongjia Primitive Forest, with a forest area of about 500 000 hm, was once famous at home and abroad for the "Mystery of the Savage". Wuyishan Forest, located in the northwest of Fujian Province, is the best protected primitive forest in the southeast, with an area of about 57 000 hm. The forests of Taiwan Province, located in the eastern part of Taiwan Province, have a large number of camphor trees growing, and the natural camphor produced there accounts for 2/3 of the world's total. In addition, Benihi in Alishan is 60 m high with a tree age of more than 3 000 years, and it is often referred to as the "Sacred Tree".
China used to be a big eastern country rich in forest resources in history. During the Western Zhou Dynasty, the forest coverage rate of the Loess Plateau alone was as high as 50%[8]. Due to the long-term destruction of the past dynasties, the forest area in 1949 was 187 million hm, with a coverage rate of 13.0%. In the late 1970s, it was reduced to 180 million hm, with a coverage rate of 12.7%. After years of persistent afforestation, the long-term decline of forest resources has been reversed. By the end of the 1980s, the coverage rate had risen to 12.98%, equivalent to the level in 1949. In 1991, the forest area reached 128.63 million hm, and the forest coverage rate was 13.4%. The annual "deficit" of forest stocks increased from 30 million m in the early 1980s to the current surplus of 38 million m, indicating that there is a good momentum for the sustainable development of China's forests. However, the consumption of timber forests is still higher than the growth, together with poor forest quality, low canopy closure (the national average of 0.52%), and large tracts of forest subjected to uncontrollable degradation, arbitrary conversion to other uses, rural energy shortage as well as forest pests and diseases, making it urgent to make great efforts to cultivate forest resources, make the public aware of the significant impacts of forests and participate in various activities of forest resources protection so as to eradicate the "deficit" between timber forests and the destruction or degradation of forest.
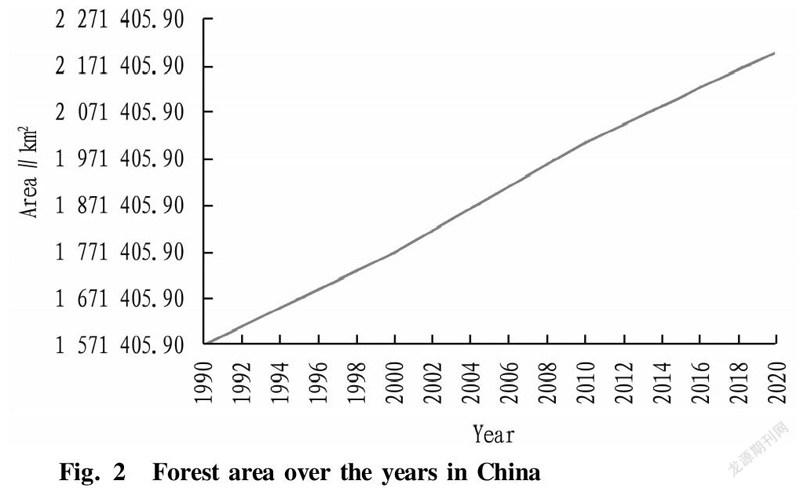
The forest coverage rate of is about 20% in China, which is lower than that of most countries in the world, ranking 139th. The per capita value is less than 1/4 of the world's average. Due to the excessive cutting for a long time, most of the famous forest resources in China are on the verge of exhaustion[9]. In 1990, China's forest area was 157 million hm2, or about 0.107 hm2 per capita, while the world's forest area was about 4.049 billion hm2, or about 0.8 hm2 per capita; China's forest coverage rate was 12.98%, while the world's forest coverage rate was 31%; China's forest stock was 9.14 billion m, about 8 m per capita, while the world's forest stock was about 310 billion m, about 72 m per capita. On the other hand, people in mountainous areas have accumulated rich experience in afforestation and forest management for a long time, and they cultivated large-scale artificial forests, especially fir and bamboo forests in southern mountainous areas. In 2000, China's forest area was 177 million hm, and in 2005, the forest coverage rate reached 18.21%, while in 2000, the forest coverage rate reached 16.55%. From 2000 to 2018, the national forest increased by 26.90%. By the end of 2020, China's forest coverage rate reached 23.04%, and the forest area reached 220 million hm (Fig. 2). Pan Jiahua, a member of the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences and director of the Sustainable Development Research Center, said that from 1949 to the early stage of reform and opening up, the average annual increase in forest area was about 1 000 km in China; over the past 40 years of reform and opening up, the average annual increase in forest area exceeded 2 500 km. Therefore, since the founding, China has been making continuous efforts to protect the forests. According to the statistics from the Ninth National Forest Resources Inventory, the area of natural forests in China is 140 million hm and the area of artificial forests is 80 million hm. In the world's newly added green area from 2000 to 2017, China's contribution rate ranks first in the world, and 1/4 of the newly added area comes from China. Afforestation and forest protection is a long-term and arduous task that requires the unremitting efforts of generations of people.
In 2008, the forest coverage rate in the western region of China was 17.05%, 6.9% in some places, only 37.89% of the average, while the forest coverage rate in the vast western arid and semi-arid regions was less than 1%, only 5.49% of the average of China. For example, the forest coverage rates of Qinghai, Xinjiang, the forest coverage rate are 4.33%, 0.35%, 0.99% and 1.54%. However, even in the southwest region with abundant rainfall, the forest coverage rate is not high, such as Sichuan Province, which only has a coverage rate of 13%. Among the 50 counties in the hilly area of Sichuan Province, the forest coverage rate is only 3%, of which 19 counties are less than 1%. Among them, the forest area of the state-owned forest areas in Sichuan, Yunnan and eastern Chongqing is 59.483 7 million hm2, and the private forest area is 24.899 7 million hm, accounting for 23.17% and 19.37% of the national total[10]. There are very few forests in the northwest region where the ecological environment is very fragile[11]. In the past 10 years, the forest area and forest coverage rate in the western region have increased significantly, but the forest ecosystem has increased in quantity and decreased in quality. There are many young and middle-aged forests, accounting for 33.5% and 32.2% of the total forest area, respectively. The forest age structure is unreasonable and the ecological function is poor[12]. The western region has 121 million hm of forest land, accounting for 52.45% of the national total, and the forest coverage rate in the western region with fragile ecology is less than 10%, with low forest quality and poor production functions.
Grim Situation of Forest Resources
Global forests are disappearing at a rate of 16-20 million hm per year, and 80% of the original forests have disappeared on the earth. The current situation of global forests is worrying. It has been reported that the World Resources Institute had released a report saying that the disappearance of forests on the earth is accelerating. While efforts to curb deforestation have increased over the decades, satellite imagery analysis shows that nearly 10% of the world's primary forests have still been deforested since 2000. From 2000 to 2017, humans lost an average of more than 200 km2 of forest area every day. In addition, between 2014 and 2016, the world's lost area of intact forests was larger than the size of Austria, which has a land area of about 84 000 km, and forests were shrinking 20% faster than in the past 10 years[13].
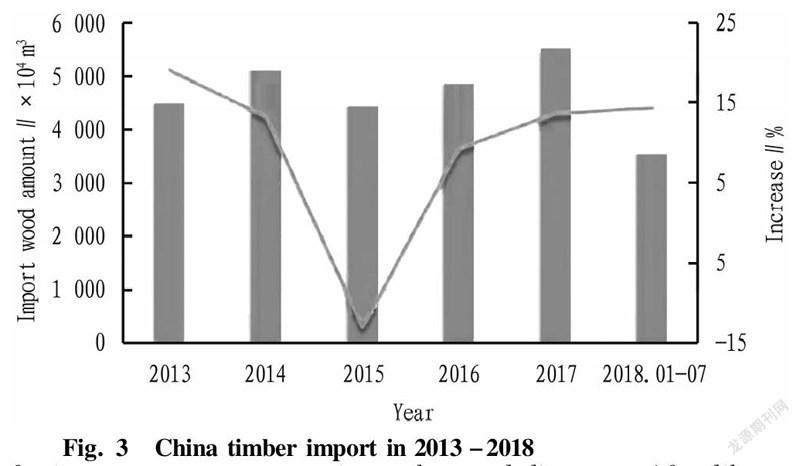
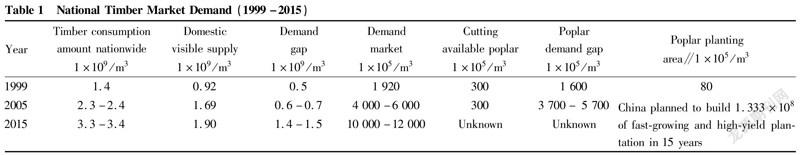
Since the reform and opening up, with the pace of urban modernization speeding up and rapid development of urban infrastructure, China has seen booming progress in the decoration industry, tourism, transportation, communications, furniture, exhibition, catering, sports and so on, all of which have demands for wood and its products. China's forest stock ranks sixth after Russia, Brazil, the United States, Canada and Congo in the world. However, on a per capita basis, it is in great shortage of wood, with the per capita forest area of 22% of the world average, ranking 134th in the world, and the per capita forest stock volume is 14.6% of the world average, ranking 122nd in the world. Since 1981, the amount of imported wood and products have increased year by year. In 1999, the imported wood in China was 2.178 million m and plywood was 1.04 million m. Moreover, the 2016-2021 China wood industry market demand and investment consulting report showed that the import demand of China was equal to 10% of the global total, and the relatively slow growth rate of timber harvesting meant a substantial increase in demand. In 2016, China imported 21.07 million m of pine wood, an increase of 3.6 million m3 from last year's 17.46 million m with an increase of over or 20.6%. In terms of import sources, the pine wood imported from Russia in 2016 rose by 38%, accounting for half of the total import with an annual reaching 11.6 million m; the import from Canada slightly declined to 5.22 million m3 in 2016, a decrease of 350 000 m compared with last year; the import from Finland increased by more than 50% for the second consecutive year, reaching 950 000 m, firmly becoming the third largest source country of converted timer for China. China is a country with limited resources, especially in terms of per capita possession, which is rather poor. Among all kinds of resources, forests are the most scarce in China. China has an area of 9.6 million km, accounting for 7% of the world's total, but it has a population of 1.4 billion, accounting for 22% of the world's. The forest area only accounts for 2.9% of the world's forest area. There are no forests available for cutting in China, and it will take at least 30-50 years for China to completely change the status quo, so it must rely on imports (Fig. 3). According to the survey (Table 1): there is a considerable gap compared with the consumption level of 1.16 m per capita in developed countries. China is the second largest timber consumer in the world, and the largest timber processing and trading country in the world, but China's timber mainly relies on imports. As the world's second largest wood consumer and largest wood importer, China's total wood consumption has increased by 173% in the past 10 years. At present, China has an annual wood consumption of more than 600 million m, and its dependence degree on imports exceeds 55%. In 2020, China had a wood demand of over 800 million m. In 2021, the value of import and export of wood and wood products was $69.588 billion, a year-on-year increase of 27.18%; among which, the import value was $25.277 billion, a year-on-year increase of 19.60%; the export value was $44.311 billion, a year-on-year increase of 31.95%.
The 20th century was the most developed period of human material civilization, and it was also the period when the ecological environment and nature suffered the most serious damage. Traditional industry is a double-edged sword of good news and disaster. Due to the inadequate natural endowment, China's industry is not big enough, together with the reasons like extensive development, it has entered the embarrassing situation of destroying the natural ecology and the environment prematurely, and the development is unimaginable. Before the founding of the People's Republic of China, the forests suffered unprecedented catastrophe due to war,famine, government corruption and natural disasters. After liberation, the population expanded rapidly, the contradiction between food supply and demand was very prominent, and due to backward technology, food production had been hovering at a low level for a long time. The forestry was severely damaged for deforestation to make more land for grain production. From the 1950s to the 1970s, there were three large-scale upsurges in land reclamation characterized by deforestation[14]. Excessive logging, indiscriminate deforestation, and deforestation to open up wasteland have caused the few forests in China to suffer unprecedented disasters[14]. It has found that since the 1950s, forest areas in northeast China have experienced severe over-cutting. Take Heilongjiang, which had the most prominent forest coverage rate in the Northeast, as an example. The area of natural forests in the Sanjiang Plain decreased by 25% in the 14 years from 1962 to 1976[14]. The Beishi River and Xifeng Mountain in Aihui County, Xiaoxing'an in Dedu County and other communes built their reclamation points on the ridge in the south of the Xiaoxing'anling. Due to deforestation, the main vein of the Xing'anling in the southern part of the Xiaoxing'anling was close to being reclaimed, and it became a breakthrough in the natural protection forest system of the Xiaoxing'anling. Due to the gradual decline of forest resources and the intensive over-logging in the past 20 years, the recoverable resources have been decreasing day by day. Among the 48 forestry (enterprise) bureaus in the province, 35 bureaus have found it difficult to maintain the current production level, and 12 forestry bureaus, including Bamantong and Bamantong, have been forced to stop production and turn into management bureaus because their exploitable resources have been exhausted. Half of the bureaus cannot be used sustainably, and they are hard to return. Jilin is in the similar situation. Changbai Mountains was threatened by excessive deforestation from 1958 to 1966, and the excessive deforestation was particularly serious during the 10-year Cultural Revolution. Just take Songjianghe Forestry Bureau as an example[15]. The felling area in 1971-1975 was double that of the previous five years and five times that of 1958-1962. From 1958 to 1978, the total felling area was 40 000 hm, of which the clear-cutting area was 20 000 hm2. Although most of the logging bases have been reforestation, the area has changed from tall virgin forests to low young jungles. In particular, the amount of logging in the Changbai Mountain forest area reached its peak in the 1960s, and compared with the pre-mining in 1930, great changes took place in terms of precipitation and other aspects. In 1985, the 9 southern provinces suffered serious unlawful felling, and within one year, the forest resources lost 160 million m, reducing the number of counties that could provide commercial timber from nearly 300 to 172. During more than two years from 1986 to the beginning of 1988, 29 000 trees were felled illegally in the Wugong Mountain Forest Area of Jiangxi Province, and the destroyed forest area reached 160 hm2. In Hainan Province, the 3 major forest areas of Diaoluo Mountain, Jianfengling and Bawangling also suffered great damage. An illegal felling organization with nearly 200 people was discovered in Qingshuijiang Township, Liling City, Hunan Province, which later developed into armed violence and illegal felling. In 1986, the national forestry public security organs accepted more than 67 000 forest cases, including more than 50 000 cases of illegal felling. In 1987, 74 600 forest cases were accepted, including more than 50 000 cases of illegal felling. In 1988, according to the statistics of 7 provinces including Liaoning, Zhejiang and Hunan, forest cases increased by over 20% over the previous year, and economic losses also increased over 30% over the previous year. In the first half of the year, there were more than 20 000 cases of deforestation in China, among which cases of extreme deforestation showed a sharp increase in Guangxi, Jiangxi, Yunnan and Hunan. At the beginning of the year, more than 800 people from the Yunnan Riverside Forestry Bureau publicly looted state-owned forests. Within a month, more than 1 000 vehicles were dispatched, destroying more than 520 hm of forests. Soon after, dozens of state-owned forest farms in Jiangxi, Hunan, Guangxi and Hainan were also looted by open illegal activities. In a forest farm in Guangxi, more than 90 000 trees were illegally felled in the first quarter of 1988, more than the total illegal felling of the previous year. Beginning on January 9, 1990, an incident of looting state-owned forests occurred in the riverside area of Mile County, Yunnan Province. The number of vehicles involved in the looting exceeded 100 per day. Within a few days, more than 360 hm of forest were destroyed, 8 000 m of trees were taken away, many forestry and public security personnel were injured, and official vehicles and cameras were taken away. According to the analysis of the forestry department, the reason for the increasing trend of deforestation cases in recent years is that with the continuous strengthening of China's efforts to protect forest resources and improve the ecological environment, the price of timber has risen, and some illegal persons have made huge profits. Under the temptation, some people took the risk and wanted to cut down the forest. On January 12 and February 4, 2021, the Economic Information Daily reported twice on the issue of illegal coal mining and deforestation by Heshun Hongrun Coal Industry Company of Shanxi Coal Transportation and Marketing Group. On February 8, the State Forestry Administration of the People's Republic of China arranged a working group to supervise the handling on the spot, and on March 30, the case was listed for supervision. After investigation, it found that Heshun Hongrun Coal Industry Company had illegally occupied 121.25 hm of forest land since 2014, with an illegal timber felling stock of 1 617 m. Heshun County Forestry Bureau successively issued 11 notices of suspension of work, 7 notices of rectification and 2 documents, but the illegal activities still continued without stopping for a long time, which was of vile nature. After supervision, the Heshun County Public Security Bureau, the Procuratorate, and the court set up a special class to investigate the case and took compulsory measures against 16 criminal suspects. The case was then transferred to the Procuratorate for review and prosecution. The forestland involved has been fully recovered and regreened, and Heshun Hongrun Coal Industry Company was imposed a comprehensive administrative penalty of 106 million yuan, and paid 315 million yuan for mine environment restoration and land reclamation. The Heshun County Commission for Discipline Inspection filed a case for review on 19 relevant personnel.
Problems for Sustainable Forest Development
It is necessary to re-recognize the concept of China's vast territory and abundant resources, and to have a sense of crisis for some problems that cannot meet the needs of development. The problem of ecological deterioration has made people aware of the severe situation facing China's economic development, natural resource protection and ecological restoration and reconstruction. Especially the series of environmental disasters in the past ten years, the people of China pay more attention to the relationship between population, resources and environment. The sharp loss of forests and the reclamation of wasteland for farming result in bare land, serious drought and water shortage. As we all know, if soil and water loss continue to be intensified, oases become deserts, humans will lose their living conditions. The 1998 flood was the biggest revenge for soil and water loss caused by the destruction of forests and grasses, which lost their functions of wind prevention, sand fixing, water conservation, climate adjustment and dust retention. At the same time, the destruction also led to decreased numbers of wildlife species, making hundred of animals that depended on forests for survival became homeless[16]. Although China's forestry has made remarkable achievements, there are still serious problems faced with the implementation of sustainable development. One is the sharp decline of forest resources. At present, the quality of forest resources in China is not high, and with the emergence of individuals who cut down forest resources arbitrarily and irrationally use forest resources, the forest resources are decreasing year by year, and the forest resources management also faces serious situation. Even in recent years, although the government has stepped up efforts to restore vegetation and protect forests, forest resources continue to be destroyed. This is mainly because people's ecological awareness is too shallow, who believe that forest resources are renewable resources that can be cut arbitrarily, making the ability of forest restoration unable to keep up with the speed of destruction. The second is the imbalance between supply and demand of forest resources. With the continuous development of industries and the gradual shortage of forest resources, the annual output of forest resources in China is far from meeting the actual needs of social and economic development, and there are contradictions between forest resources in promoting economic production and responding to ecological protection[17]. The third is the lack of scientific forest cultivation. As far as the current situation is concerned, the ratio of species in the major cultivated forests is not scientific enough, and there is generally a large-scale distribution of a single species, which leads to the inability to meet the biodiversity in the forest[18]. The fourth is the lack of concern. Relevant personnel do not pay enough attention to breeding work, which leads to the low survival rate of forest trees in the subsequent growth and development process due to insufficient management and the influence of external factors[19]. Fifth, forest protection has not been fully implemented. Forest protection is a kind of long-term development work, which cannot bring short-term benefits. However, many forestry producers pay more attention to the immediate production benefits. Therefore, in the forest management process, they pay more attention to the work in the development and production process, but fail to well accomplish the the follow-up tree planting and protection work. Thus, there are still problems of deforestation. In response to this problem, the government should investigate and punish the lawbreakers through tough institutional norms. At the same time, producers should also actively cooperate and actively participate in the work of forest protection to prevent forest diseases and insect pests, and do a good job in forest fire protection[20].
Countermeasures for Scientific Utilization of Forest Resources in China
The survival and development of forests are closely related to human beings. Humans can not only develop forests, but also destroy them. However, forests can be threatened and damaged by the results of policy mistakes such as non-compliance with laws and lax law enforcement; indiscriminate deforestation and blind development of industrialization; poor management and short-term behavior; population expansion and poverty; irrational farmland cultivation like the "slash-and-burn" farming method, all of which can lead to the deterioration of the environment and the depletion of resources. Therefore, we must control and stop these behaviors, and protect forest resources.
Strengthen protection and management of forest land
At present, environmental and ecological issues have become a hot spot of global concern. We should spare no efforts to promote the sustainable, rapid and healthy development of forestry. The development of forestry is the primary task of environmental construction, and afforestation is an important measure to protect the environment and improve the ecological environment. Developed forestry is not only of great importance in improving the ecological environment, ensuring the stable and high yield of agriculture and animal husbandry, and ensuring that water conservancy facilities give full play to the benefits, but also of high significance in accelerating the development of the national economy, promoting the reform and opening up and social progress, and promoting farmers to get rid of poverty and become rich. Forest resources are the basis for forest cultivation and development, a good forest ecosystem is an important part of ecological civilization, and the construction of ecological civilization should take the protection of forest land as an important measure. At present, faced with the severe situation of forest land resource protection and management, it is essential to take the strictest measures to strengthen the protection and management of forest land, and form a forest land management mechanism of "total control, quota management, reasonable land supply, optimal land utilization, and balanced requisition-compensation". First of all, it is necessary to effectively strengthen the management of forest rights, to further clarify the property rights of forest resources, to protect the legitimate rights and interests of forest land owners in accordance with the law, and to ensure the continuity and stability of policies. The second is to strengthen forest management. It is vital to conscientiously adhere to the examination and approval system for forest land acquisition and occupation, strictly implement forest land use control, and ensure that the forest land area can only be increased but not reduced. It is necessary to strengthen the supervision of the whole process of forest land occupation by key projects, so as to occupy as little or no forest land as possible. The strictest measures should be taken to resolutely crack down on the deforestation and reclamation and the illegal occupation and abuse of forest land, so as to prevent the illegal loss of forest land. All localities should prepare overall plans for forest land use as soon as possible, take measures to control the total amount, and implement forest land use control. In some places, the previously matured forest land has been illegally turned into cultivated land, and even the land certificate has been issued, it must be cleaned up and corrected immediately. In the future, those who do not have a forest right certificate will not be allowed to go through the examination and approval procedures for forest felling licenses and forest land acquisition and occupation. The third is to continue to do a good job in forest logging management. The best must be done to control natural forests, regulate plantations, and manage commercial forests. The fourth is to strengthen the management of circulation links. It is necessary to adhere to the timber certificate transportation system, strengthen the supervision and inspection of timber transportation in accordance with the law, and resolutely prevent illegal timber from entering the market. It is necessary to strengthen the supervision and management of timber operation, processing and marketing in accordance with the law, strengthen service guidance, standardize the market order, resolutely crack down on the illegal operation and processing of timber, and strive to improve the management of forest resources to a new level. Fifth, strengthen the protection and management of wild animals and rare plants. People's governments at all levels should take the protection of wild animals and rare plants as an important responsibility, establish a post responsibility system, and implement various protection measures. We must resolutely crack down on the current illegal activities of indiscriminate hunting and reselling, smuggling of rare and endangered wild animals and rare plants and their products.
Realize the responsibility of forest resource protection work
Forestry authorities at all levels should earnestly perform the duties of those directly responsible based on the requirements of the National Forest Management Plan (2016-2050) that "the local governments at all levels should fully responsible for the forestry work in the region, the comrades in charge of the government should the first responsible persons for forestry construction, and the comrades in charge should be the main persons in charge of forestry construction". At present, forestry authorities at all levels and relevant departments should promptly improve forest resource management measures and implement management and protection responsibilities for the weak links identified in special governance activities. Key areas and key roads must be strictly guarded against. All timber checkpoints must earnestly perform their duties, strengthen day and night duty, and never let off criminals who steal and transport timber. State civil servants who leave their posts without permission, gang up with outsiders, or commit crimes in partnership must be seriously investigated. Forest guards who are unable to perform their duties must be resolutely cleaned up. In order to strengthen the responsibility of the work, the government should sign the prevention and control target responsibility letter with the relevant towns and farms every year, implement the prevention and control tasks at each level, and clearly define their respective responsibilities, rights and interests, so as to implement all preventive measures. It should also carry out scientific planning and layout, conduct rational management and make good use of forest resources. Moreover, the government should strengthen the comprehensive utilization of wood and forest land, and prolong the service life of wood, as well as promote saving consumption, strengthen recycling, and develop circular economy.
Comprehensively start disease, insect pest and forest fire management
Pests and diseases are important factors that threaten the development of forestry. When developing forestry, relevant departments should do a good job in protecting forest resources, strengthen the prevention of pests and forest fires, and formulate emergency plans according to the specific local conditions. To control pests and forest fires in the bud, we should learn from the experience of grain production, apply it to forestry construction, and do regular inspections carefully to ensure the safety of forest resources. For forestry to have a great development, the key lies in leaders at all levels raising their awareness of the significance of protecting forest resources, strengthening forestry production and construction and giving full play to the advantages of forests, effectively strengthening the leadership of forestry production, and formulating practical plans and measures based on local actual conditions. The pest disease and forest fire control projects should be listed on the agenda, and forestry production should be inspected seriously on a regular basis like food production. According to the unified arrangement of the competent forestry department, the "Plan for the Control of Diseases and Pests and Fire Projects" should be prepared, the forest plant quarantine and forest disease and insect forecasting and prevention should be carefully handled, introduction of harmful organisms should be strictly prevented, and the forest should be well protected from pest disasters, so as to ensure the safety of forest resource. Management and implementation plans should be formulated according to the plan for pest diseases and fire engineering, and specific studies and arrangement should be made on the project content, project investment estimate, project construction progress, project management measures, so as to accurately grasp the epidemic situation. Fires should be strictly controlled and prevented in the forest areas for production and living. When a fire breaks out, it is necessary to carry out emergent actions in time, which should be as early and small but effective as possible, and great efforts should be made to reduce losses as much as possible.
Raise funds through multiple channels
It is necessary to establish a supporting policy for forest tending and management, and set up a special fund for forest tending. The capital investment of forest tending should be solved through multiple channels: the forest tending funds of ecological public-welfare forests should be collected by the state opening up special funds for forest management of public welfare forests; the forest tending funds of commercial timber forests should be paid in advance through special financial treatment or special working capital, or by soft loans. It is also necessary to encourage forestry enterprises to vigorously develop the forestry industry, especially high value-added industries, invest more funds to improve the cultivation of forest resources, enhance the management of afforestation funds, and reform the management system of forest tending and logging quotas. The government at all levels should ensure the direction of fund use, improve the effect of fund use, establish a rigid and transparent afforestation fund management system, clarify the scope of use, conduct strict audits and rigorous evaluation, and clear rewards and punishments. The forest tending and logging quota management should be gradually improved based on the principles of being beneficial to forest cultivation, management entities, and forest resource protection. In order to intensify the prevention and control efforts, multichannel and multiform fund-raising practice is adopted to ensure that the prevention and control work is completed with high quality and quantity. The first is to raise some by local governments, through which the towns and villages can pay part of the labor wages in the form of labor. The second is to squeeze out from the finance as a prevention and control subsidy. The third is to strive for some funds for prevention and control from the provincial governments in accordance with the project management requirements, so as to ensure the smooth completion of various tasks.
Severely crack down on criminal activities of deforestation
Special governance should be carried out to resolutely stop illegal and criminal acts that destroy forest resources. Based on the local reality, all localities shall, in accordance with the requirements of the filing standards for the crime of deforestation in 2020, carry out a full clearing to the forest resources protection and management situations together with the forestry, land, public security, industry and commerce, taxation and other departments in view of the current prominent problems and serious areas of destruction of forest resources. Governments at all levels should attach great importance to the construction of forest public security teams, adjust the layout of police forces, provide reliable service support, increase efforts to fight against illegal actions and do everything possible to improve forest public security's ability to prevent and control illegal and criminal activities that destroy forest resources, based on the principles of enriching strength and improving functions. Local and forest public security organs at all levels should give full play to their functional roles, continue to follow the principle of "integrating inside and outside the forest area, integrating actions in and out of the forests, and integrating local public security and forestry public security" to combine daily work with centralized and unified actions starting from armed clearing mountains, road inspections, investigating cases, and cracking down on gangs. Emphasis should be laid on cracking down on illegal and criminal activities that seriously damage forest resources, such as illegal logging and transportation, forged tickets, rushing through customs and checkpoints, and violent resistance to the law.
Establish compensation mechanism for the use of forest resources
According to the relevant provisions of the Forest Law of the People's Republic of China and the Regulations on the Implementation of the Forest Law of the People's Republic of China, the central finance and local finance have established forest ecological benefits compensation, which is used to construct, tend, protect and manage the shelter forests of ecological benefits and special-purpose forests. According to the Notice on the State Forestry Administration and the Ministry of Finance on Printing and Distributing the "Measures for the Delimitation of National Public Welfare Forests" and the "Measures for the Management of National Public Welfare Forests" (Linzifa [2017] No.34), the national-level public welfare forests included in the forest ecological benefit compensation scope of the central government refer to the shelter forests and special purpose forests that have extremely important ecological locations or extremely fragile ecological conditions, play an important role in national ecological security, biodiversity protection and sustainable economic and social development, and mainly managed to give full play to the forest ecological and social service functions. It is necessary to strengthen the construction of ecological forests with the ecological environment as the main body, implement the project of nourishing mountains and enriching the people with ecological environment protection as the main content, and establish a compensation mechanism for the utilization of forest resources in mountain areas as soon as possible. In the process of maintaining and constructing ecological forests in mountainous areas, a compensation mechanism for ecological forests in mountainous areas should be established to properly handle the relationship between the ecological functions of forest resources in mountainous areasand the interests of farmers. The establishment of a water resource tax, on the one hand, can relieve the pressure of water supply in cities, and on the other hand, increase farmers' income by returning the collected taxes to farmers in mountain areas to compensate their interests, which enable them to actively participate in the maintenance and construction of forest ecology in the mountain areas.
References
[1] LI Y. National Forest City Development Plan (2018-2025) released[N]. People's Daily, 2018-07-06.
[2] ZHANG L, ZHAO LH. Effects of different revegetation patterns on soil and water conservation in sandy-hilly region of northern Shanxi Province[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 32(6): 107-111.
[3] WANG Y. Total output value of national forestry industry in 2019 was 7.56 trillion yuan[N]. China Green Times, 2020-01-03.
[4] LIU D. Soil and water conservation monitoring in dot engineering of development and construction projects[J]. Technology of Soil and Water Conservation, 2012(1): 21-23.
[5] WANG H, LI Q, MIAO ZM. Report on the development of ecological civilization with Chinese characteristics and forestry(2020-2021)[M]. Beijing: Social Sciences Academic Press, 2020.
[6] Red Net. World's forest area decreased 100 million hm2 in the past 20 years, and what is the current situation[N]. Straits Times, 2020-09-15.
[7] State Forestry Administration. China forestry ecological construction and governance model[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 2003.
[8] GAO ZL. Ecological restoration and returning farmland to forests and grasslands in west China[M]. Beijing: China Literature and History Press, 2005.
[9] CAI HW. Forest area increased 26.5 million hm2 in China[N]. People's Daily, 2021-11-18.
[10] ZHAO SK. Causes and transformation technologies of degraded forest stands: an case study of Shanxi Province[J]. Shanxi Forestry Science and Technology, 2016, 45(4): 39-41.
[11] SHEN GF, LI WH, ZHANG XSH. Encyclopedia of Chinese forestry[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 2019.
[12] QU LJ. Transformation of degraded poplar stands in the Beijing-Tianjin sandstorm source control project area in Shanxi[J]. Forestry Science and Technology, 2014, 231(4): 23-24.
[13] World Resources Institute. "One Austria" a year disappears, satellite image shows terrible data[N]. Global Times, 2018-06-22.
[14] PENG KS. Main disaster problems and countermeasure analysis of forest resources over to the next century in China[J]. Forestry Economics, 2006(5): 17-23.
[15] TAO Y. Historical changes of Chinese forests[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 1994.
[16] LI HZH. Evaluation on ecological service of ecological public welfare forest in Liaoning Province[J]. Shaanxi Forestry Science and Technology, 2022(1): 31-35.
[17] LIU NY, TIAN YX, LIU B, et al. Evaluation on ecosystem service of ecological public welfare forest in Xiangxi Tujia and Miao Autonomous Prefecture[J]. Hunan Forestry Science and Technology, 2021(4): 68-78.
[18] FU ZJ, PENG KSH. Introduction to natural disasters[M]. Xi'an: Shaanxi Education Press, 2006.
[19] WANG X, ZHU XJ. Problems and solutions in the construction of forestry ecological engineering[J]. Modern Agricultural Research, 2017(7): 33-33.
[20] QI FX. Forest management and forestry sustainable development[J]. Frontiers of Engineering Management, 2019(2): 5-6.
Editor: Yingzhi GUANG Proofreader: Xinxiu ZHU
- 农业生物技术(英文版)的其它文章
- Report on the Breeding of Dahen 799 Broilers
- Evaluation and Analysis for Survey of Tea Production Quality Safety Management and Control
- Study on the Preparation of "Oil-tea" Instant Tea from the Compound Extract of Green Tea and Ginger
- Research Progress on Chemical Constituents and Pharmacological Effects of Zhuang Medicine Cocculus laurifolius DC.
- Study on Quality Standard of Lujing Yiqi Shengxue Pills
- Research on the Development of Guangxi Zhuang and Yao Ethnic Medicine Industry

