Study on Leaching Conditions of Miao Medicine Xiange Zuyu Powder
Yuanfeng YANG Yuchuan LI Renhui YANG Lida CHEN Qiqian CHEN

Abstract[Objectives] This study was conducted to optimize the soaking conditions of Miao medicine Xiange Zuyu Powder. [Methods]With the water-soluble extract as an investigation index, an L9(34) orthogonal test was carried out to investigate the amount of water added, soaking temperature, soaking times and soaking time, and the best soaking conditions for Xiange Zuyu Powder were screened. [Results] The optimal soaking conditions were as follows: adding 1 000 ml of boiling water at 100 ℃, soaking for 20 min each time, 3 times in total. [Conclusions]The soaking scheme is reasonable and can provide a reasonable basis for clinical medication.
Key wordsXiange Zuyu Powder; Soaking conditions; Orthogonal test; Water soluble extract
Arthralgia syndrome is caused by wind, cold, dampness, heat and other external exogenous pathogenic factors which invade the human body and block the meridians and the circulation of qi and blood, resulting in a clinical syndrome characterized by soreness, numbness, pain and burning in muscles, bones and joints and even swelling and deformation of joints[1]. There are many causes of this disease. Arthralgia syndrome has complex pathogenesis and lingering course and is easy to relapse, causing pain and suffering and economic burden to patients with arthralgia syndrome. Guizhou is located in the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau in the southwest, and the climate is cold and humid all year round, and the incidence of arthralgia syndrome is high. Traditional Chinese medicine has good curative effect in the treatment of arthralgia, and the curative effect is more accurate when being combined with adjuvant external therapy[2]. Foot bath is the main external treatment method of traditional Chinese medicine. Miao medicine Xiange Zuyu Powder is a clinical experience formula used by The Second Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine for the treatment of wind-cold-damp-heat arthralgia. It is composed of 19 traditional Chinese medicines such as Miao medicine Agrimonia pilosaLedeb, Pueraria lobata and Gentiana macrophμlla, and has the effects of nourishing yin and activating blood, dispelling wind and removing obstruction in the meridians and eliminating cold to stop pain. In order to provide a theoretical basis for rational drug use in patients, in this study, an L(3) orthogonal test was designed with the water-soluble extract of Xiange Zuyu Powder as the index to investigate the amount of water added, soaking temperature, soaking times and soaking time, so as to optimize the soaking conditions.
Materials and Methods
Experimental materials
InstrumentsElectronic medicine balance (Model JY 3001, Shanghai Minqiao Precision Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd.); electronic constant temperature water bath (Model DZKW-4, Shanghai Jinqiao Kexi Instrument Factory); electric blast drying oven (Model 101-1AB, Tianjin Taizhou Taisite Instruments Co., Ltd.).
ReagentsThe medicinal materials used for the test were all purchased from Guizhou Tongjitang Zhongyao Yinpian Co., Ltd. After passing the inspection, the decoction pieces were taken according to the formulation prescription, mixed, crushed and sieved, and then put into filter bags, 20 g per bag.
Experimental methods
With water-soluble extract as the investigation index, an L(3) orthogonal test was carried out to investigate the amount of water added, soaking temperature, soaking times and soaking time, and the best soaking conditions for Xiange Zuyu Powder were screened.
Results and Analysis
Soaking conditions for orthogonal test
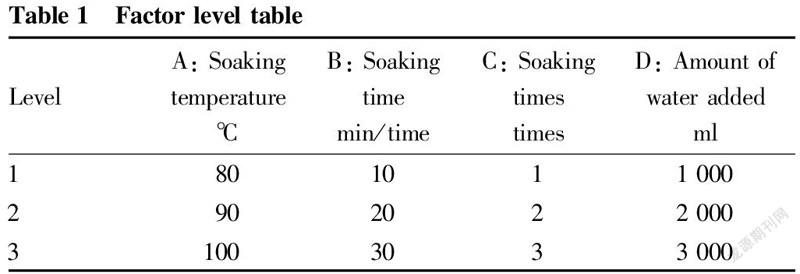
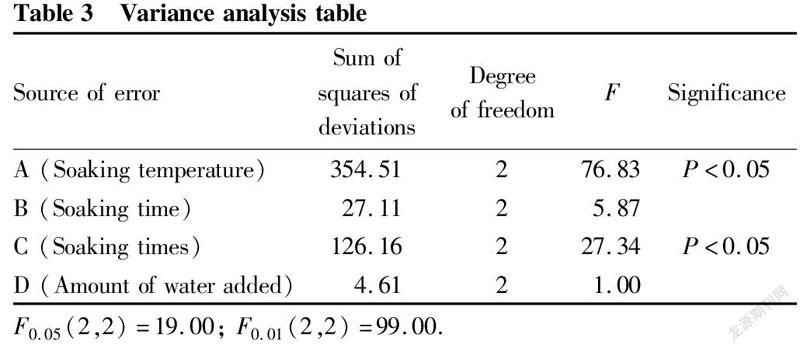
The main factors that affect the extraction effect are: soaking temperature, soaking time, soaking times, and the amount of water added. In order to optimize the best technological level of each factor, this study took the water-soluble extract as the investigation index, and screened the best soaking technological conditions through the L9(34) orthogonal test. The analysis of variance of the soaking orthogonal test is shown in Table 1-Table 3.
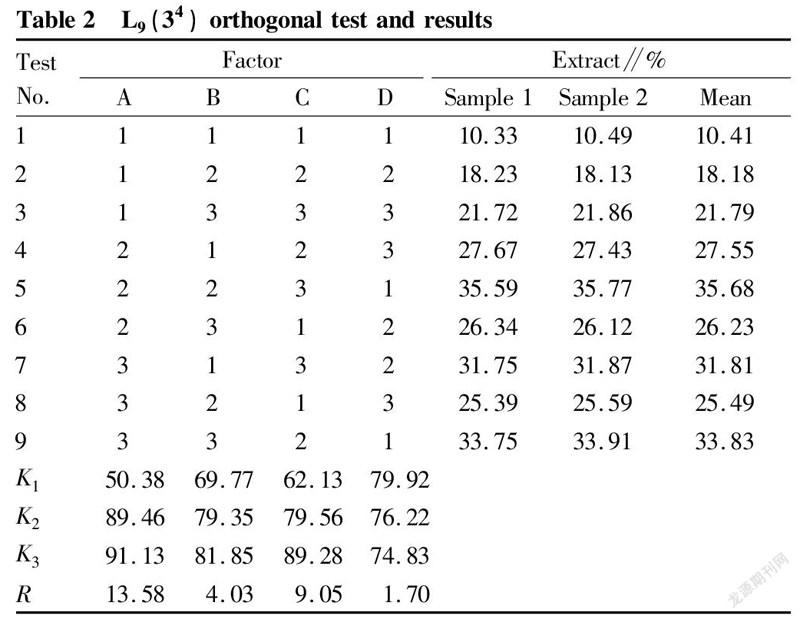
With the water-soluble extract as the evaluation index, it could be seen from the intuitive analysis of the orthogonal test results in Table 2 and the variance analysis in Table 3 that the primary and secondary effects of various factors were A>C>B>D. There were significant differences in factors A and C, of which factor A showed an order of A>A>A and factor C exhibited an order of C>C>C, so A and C were selected as soaking process parameters. There were no significant differences in factors B and D, of which factor B showed an order of B>B>B and factor D exhibited an order of D>D>D. According to the actual situation such as economy, B and D were selected as soaking conditions. As a result, the soaking process ABCD was selected, that is, the best soaking plan was to add 1 000 ml of boiling water at 100 ℃ and soak for 20 min each time, 3 times in total.
Validation of optimal soaking process conditions
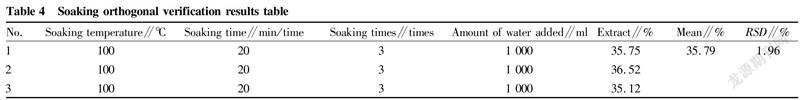
According to the optimal soaking conditions, three batches were verified, and the verification test results are shown in Table 4.
It can be seen from Table 4 that the RSD value of the water-soluble extracts of the three batches of samples was verified to be 1.96%, indicating that the optimal soaking process conditions are feasible and can be used as soaking process conditions.
Experimental study on water-soluble extracts of powder and decoction
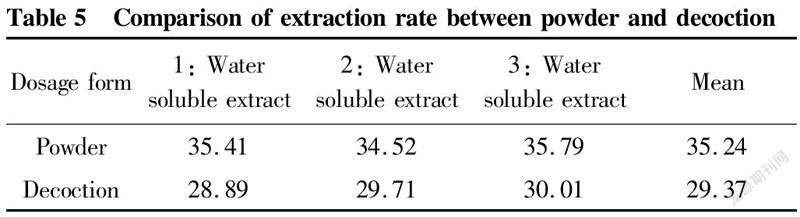
The powder was prepared according to the above optimal soaking conditions, and the soaking liquid was prepared for later use.The decoction was prepared according to the decoction method of Chinese herbal pieces in Regulations for the Management of Traditional Chinese Medicine Decoction Rooms in Medical Institutions. About 20 g of decoction pieces was weighed according to the prescribed proportion, and decocted 3 times for 20 min each time, and the decoction volume was made to be equal to the soaking liquid. From each of the soaking liquid and the decoction liquid, 50 ml was precisely measured and added in an evaporating dish that had been dried to constant weight, and evaporated to dryness in a water bath. The residues were dried in a 105 ℃ oven for 3 h, cooled in a desiccator for 30 min, and weighed. The extract content was calculated[3], and the results are shown in Table 5.
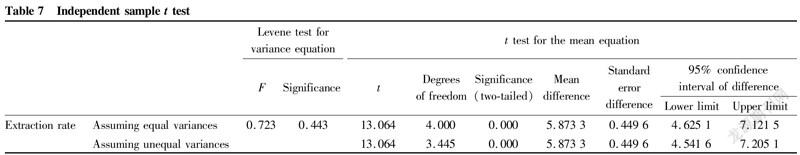
As can be seen from Table 5, the average content of water-soluble extract from the powder was higher than that from the decoction. The normality test of water-soluble extracts was carried out using SPSS 23.0 software, and the results are shown in Table 6. Due to the small number of samples, according to the Shapiro-Wilk results, the P values of the water-soluble extracts of powder and decoction were all greater than 0.05, so the water-soluble extracts obeyed a normal distribution. An independent sample t test was performed, and the results are shown in Table 7. It can be seen from Table 7 that P=0.443>0.05, indicating no difference and homoscedasticity. Therefore, looking at the line of "assuming equal variances", the output result of the independent sample t test was t=13.064, and the two-sided P=0.000<0.05, so there was a significant difference between the water-soluble extract of Xiange Zuyu Powder and the water-soluble extract of the decoction, and the extraction effect of powder was better than that of decoction.
Discussion and Conclusions
Traditional Chinese medicines and Chinese patent medicines are relatively common for the treatment of wind-cold-dampness arthralgia[4-7], but there are not many traditional Chinese medicines for the treatment of wind-cold-damp-heat arthralgia. Miao medicine compound Xiange Zuyu Powder is a foot bath medicine used in our hospital for the treatment of wind-cold-damp-heat arthralgia. In the prescription, the monarch medicines A. pilosaLedeb and P. lobata nourishes yin and activates blood circulation; and the ministerial medicines are Taraxacum mongolicum, Angelica sinensis, Ligusticum chuanxiong, Carthamus tinctorius, Lonicera japonica, Trachelospermum jasminoides, G. macrophylla, Morus alba and Clematis chinensis have the effects of dispelling wind and removing obstructon in the meridians, clearing heat and removing dampness. The auxiliary medicines including Caesalpinia sappan, Rehmannia glutinosa, Cinnamomum cassia, cinnamon sticks, Boswellia carterii prepared with vinegar, Commiphora myrrha prepared with vinegar and Angelica dahurica help the monarch and ministerial medicines to promote blood circulation to remove meridian obstruction and to benefit the bones and muscles. The whole prescription takes wind, cold, damp, heat and blood stasis into consideration, and has the functions of nourishing yin and promoting blood circulation, dispelling wind and dredging collaterals, clearing away heat and removing dampness, dispelling cold and relieving pain. Foot bath can make the qi and blood in the limbs of patients with arthralgia sufficient, improve the peripheral blood circulation, and strengthen the local nutrition supply of the limbs. Therefore, the clinical discomfort symptoms such as local soreness and numbness, cold pain, tingling and paresthesia in the limbs of patients with paralysis can be improved, and the prescription has been widely affirmed by the patients.
The efficacy of foot bath medicine mainly depends on the extraction degree of active ingredients in medicinal materials, and the main factors affecting the extraction rate of the medicinal materials are soaking temperature, soaking time, soaking times and amount of water added. Therefore, this paper investigated the extraction conditions of Xiange Zuyu Powder through an orthogonal test, and found that the soaking temperature and soaking times have a great influence on the extraction rate. According to the experimental results, the optimal soaking conditions were as follows: adding 1 000 ml of boiling water at 100 ℃, soaking for 20 min each time, 3 times in total. In addition, the comparison of the extraction rates of water-soluble extract from Xiange Zuyu Powder and its decoction showed that the extraction effect of Xiange Zuyu Powder was better than that of the decoction.
References
[1] HE HJ. Analysis of treating arthralgia syndrome[J]. Guiding Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacology, 2010, 16(9): 84-85. (in Chinese).
[2] ZHANG ZB. A little bit of experience in the treatment of arthralgia with traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Journal of Clinical Medical Literature: ElectronicEdition, 2020, 7(38): 66. (in Chinese).
[3] WANG T, SUN WN, CUI Y, et al. Comparative study on water soluble extract and total flavonoid content between Jinzhen Suanzao Teabag and Decoction[J]. China Pharmacy, 2016, 27(25): 3542-3544. (in Chinese).
[4] ZHU XC, JIAO J. Study on the effects of fangfeng decoction on rheumatoid arthritis of knee joint in the stage of attack[J]. Clinical Journal of Medical Officers, 2021, 49(2): 205-207. (in Chinese).
[5] SU JY, HE WQ, LU HR. Duhuo Jisheng Decoction combined with sodium hyaluronate acupuncture in the treatment of 40 cases of frozen shoulder caused by wind-cold-dampness arthralgia[J]. Zhejiang Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 55(8): 591. (in Chinese).
[6] WU HB, YU ZJ, BAI MM, et al. Clinical effect of Yangyuan Jiangu Decoction combined with acupuncture on patients with wind-cold-dampness knee osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine, 2021, 43(12): 3565-3567. (in Chinese).
[7] SU S, WANG R, ZHAO M, et al. Effect of different combinations of Gentianae Macrophyllae Radix on MMP-3 and TIMP-1 in rheumatoid arthritis rats with wind-cold-dampness arthralgia[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2019, 25(3): 8-14. (in Chinese).
Editor: Yingzhi GUANG Proofreader: Xinxiu ZHU
- 农业生物技术(英文版)的其它文章
- Report on the Breeding of Dahen 799 Broilers
- Evaluation and Analysis for Survey of Tea Production Quality Safety Management and Control
- Study on the Preparation of "Oil-tea" Instant Tea from the Compound Extract of Green Tea and Ginger
- Research Progress on Chemical Constituents and Pharmacological Effects of Zhuang Medicine Cocculus laurifolius DC.
- Study on Quality Standard of Lujing Yiqi Shengxue Pills
- Research on the Development of Guangxi Zhuang and Yao Ethnic Medicine Industry

