Advances in traditional Chinese medicine for respiratory disease therapy in 2021
Yuan-Chong Wang,Yu-Lin Wu,Jun-Yu Luo,Kun Wang,Xue-Chao Lu,Hai-Bo Hu,Hong-Wu Wang,Jun Kang
1Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Tianjin 301617,China.2Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital,Tianjin 300060,China.3The First Clinical Medical College of Yunnan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Kunming 650500,China.4Qingdao Municipal Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine(Qingdao Hiser Hospital),Qingdao 266033,China.5School of Life Sciences,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China.
Abstract Respiratory diseases are common conditions that endanger human health.Their etiology,pathogenesis, and prognosis are complex, and clinical research has been extensive.This paper reviews studies from the PubMed database to assess the progress of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of respiratory diseases in 2021, focusing on related animal and cell models of coronavirus disease 2019.Traditional Chinese medicine extracts, such as polysaccharides and emodin, and classic prescriptions, such as Mahuang decoction, respond to the treatment of influenza by reducing viral infections and regulating the body’s immune response.Chinese herbal extracts, such as schizandra B and andrographolide, treat asthma by inhibiting inflammatory response pathway formation, NLRP3 inflammasome formation, oxidative stress,and autophagy.Traditional Chinese medicine extracts such as fucoxanthin, and proprietary Chinese medicines such as the Xihuang pill is used in the treatment of lung cancer, as it regulates the cell cycle, inhibit tumor cell proliferation, and enhance the body’s immune function.Classic formulas such as the kidney tonic lung formula and proprietary Chinese medicine, such as compound grass stone silkworm granules, relieve airway inflammation and improve lung function in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Chinese herbal extracts, such as jostilbene and sage phenol, inhibit epithelial cell–mesenchymal transformation and regulate the levels of inflammatory factors to treat idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis to provide a reliable basis for the treatment of respiratory diseases.
Keywords: traditional Chinese medicine; respiratory diseases; research progress; mechanism of action
Background
Respiratory diseases including coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19),influenza,asthma,lung cancer,chronic obstructive pulmonary disease(COPD), and interstitial lung disease (IPF) are serious threats to human health.The incidence and mortality of respiratory diseases have increased annually, especially viral pneumonia caused by COVID-19, which poses a serious threat to human health.This study used the PubMed database to search for the keywords: “respiratory diseases” and “traditional Chinese medicine”.Representative literature on traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of respiratory diseases in 2021 was obtained and reviewed.This review provides a comprehensive review of the latest research on the prevention and treatment of respiratory disease with traditional Chinese medicine in 2021 and summarizes the important compound information (Table 1) [1–11].
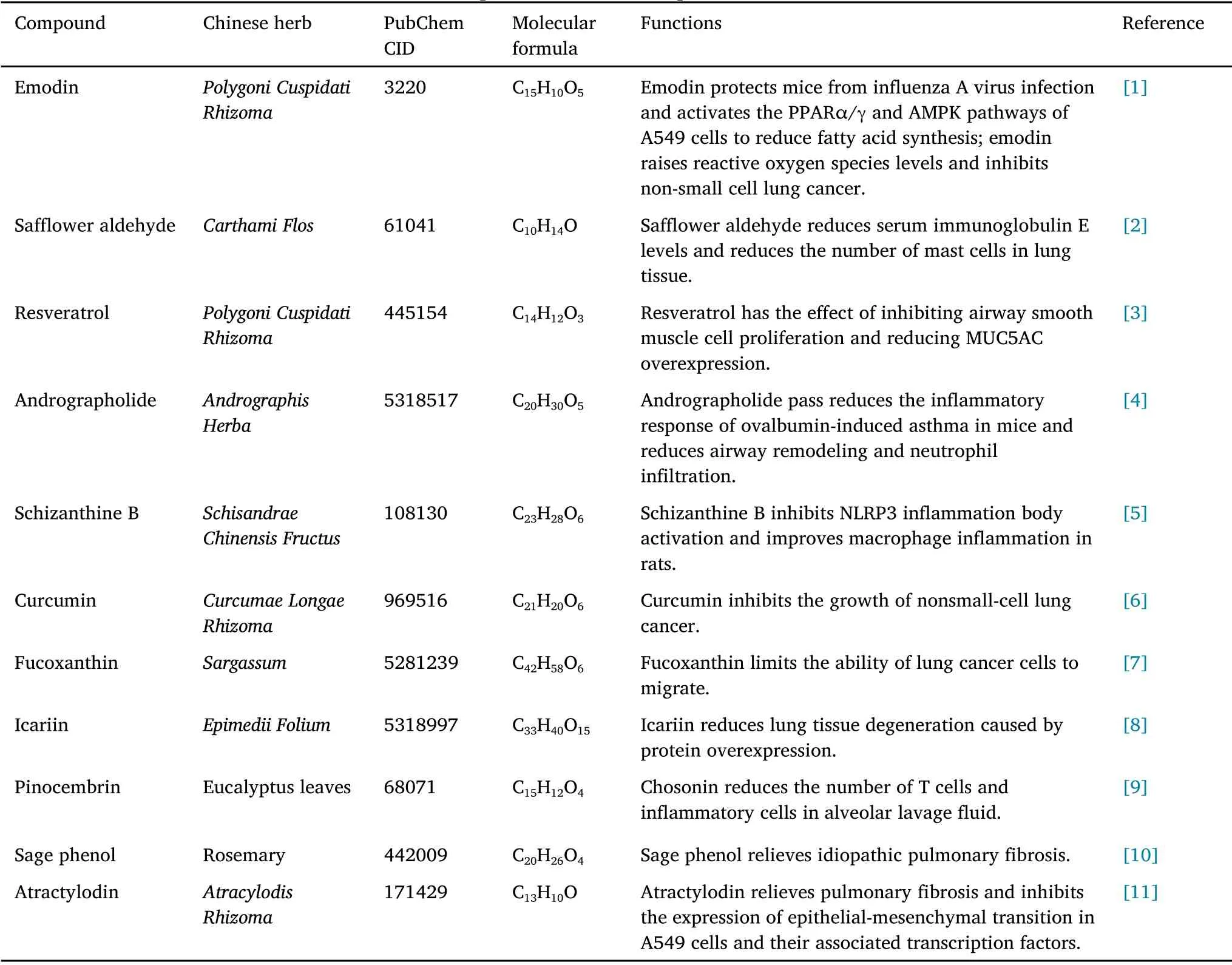
Table 1 Characteristics and functions of important chemical components isolated from traditional Chinese medicine
Compared with 2020, 2021 is marked by a deepening study of respiratory diseases, and new models, such as the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) pseudoviral infection model, are widely used in anti-COVID-19 drug experiments.In 2021, new host non-coding RNAs, such as microRNAs (miRNAs)and circular RNAs (circRNAs), which affect viruses, have provided new directions for the design of viral inhibitors.The latest research on COPD has further clarified the important role of interleukin (IL)-17A in promoting neutrophil inflammation in COPD.In addition, research on inhibitors of complement molecules is providing new bases for the treatment of lung cancer.The exacerbation of reactive oxygen species has become a new research direction for cancer treatment, and some studies have explored killing lung cancer cells by iron overload.Interestingly,RNA from any virus can induce mitochondrial extension.However, owing to the high degree of variability and complex pathogenic mechanisms of viruses, the research and development of vaccines and antiviral drugs are seriously restricted.Simultaneously,drugs used in the clinical treatment of respiratory diseases need to be further improved.Long-term medication may cause serious side effects, including liver and kidney damage.Therefore, exploring more effective and safe treatment methods for respiratory diseases and developing new therapeutic drugs have gained considerable interest in medical research.
The pathogenesis of respiratory diseases is complex, and conventional Western medicine tends to target the local disease,which can be considered one-sided to a certain extent.Traditional Chinese medicine has thousands of years of history in the treatment ofrespiratory diseases, and its therapeutic effects may work on multiple targets and mechanisms, acting on respiratory diseases from multiple perspectives.However, the specific mechanism remains to be elucidated.The mechanism of the effective components of traditional Chinese medicine is helpful in promoting the research process of respiratory disease treatment.In 2021,some progress was made in the research of Chinese medicine extracts and compound prescriptions for the treatment of respiratory diseases, focusing on inhibiting disease progression, alleviating inflammatory response, and improving respiratory function decline.In vitro models are often used to explore the cellular mechanisms of Chinese medicine in the treatment of respiratory diseases.
COVID-19
Lyu et al.reviewed the understanding of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of COVID-19 [12], including clinical analysis and potential mechanisms of action.This study comprehensively illustrated that traditional Chinese medicine played an irreplaceable role in the treatment of COVID-19.
It is worth mentioning that SARS-CoV-2, like many respiratory viruses, can cause lymphopenia.Severely ill patients may experience symptoms such as arteriologic and venous thromboembolism, or even“cytokine storms” from cytokines secreted by megakaryocytes and monocytes from lung tissue and peripheral blood, leading to multi-organ failure and dyspnea[13–15].In 2021,with the deepening of research on the combination of key proteins in viral infection, such as S protein and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), it was found that they can promote viral entry, cause an imbalance in the angiotensin system, and damage cardiomyocytes [16, 17].Researchers have carried out corresponding inhibition experiments,which have become the main direction of anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug research.At present, more and more models have been widely used in the basic experimental study of classical drug treatment of COVID-19(Table 2) [18–24], which is helpful to further explain the mechanism of TCM treatment of COVID-19 and accelerate the development of traditional Chinese medicine treatment of COVID-19.
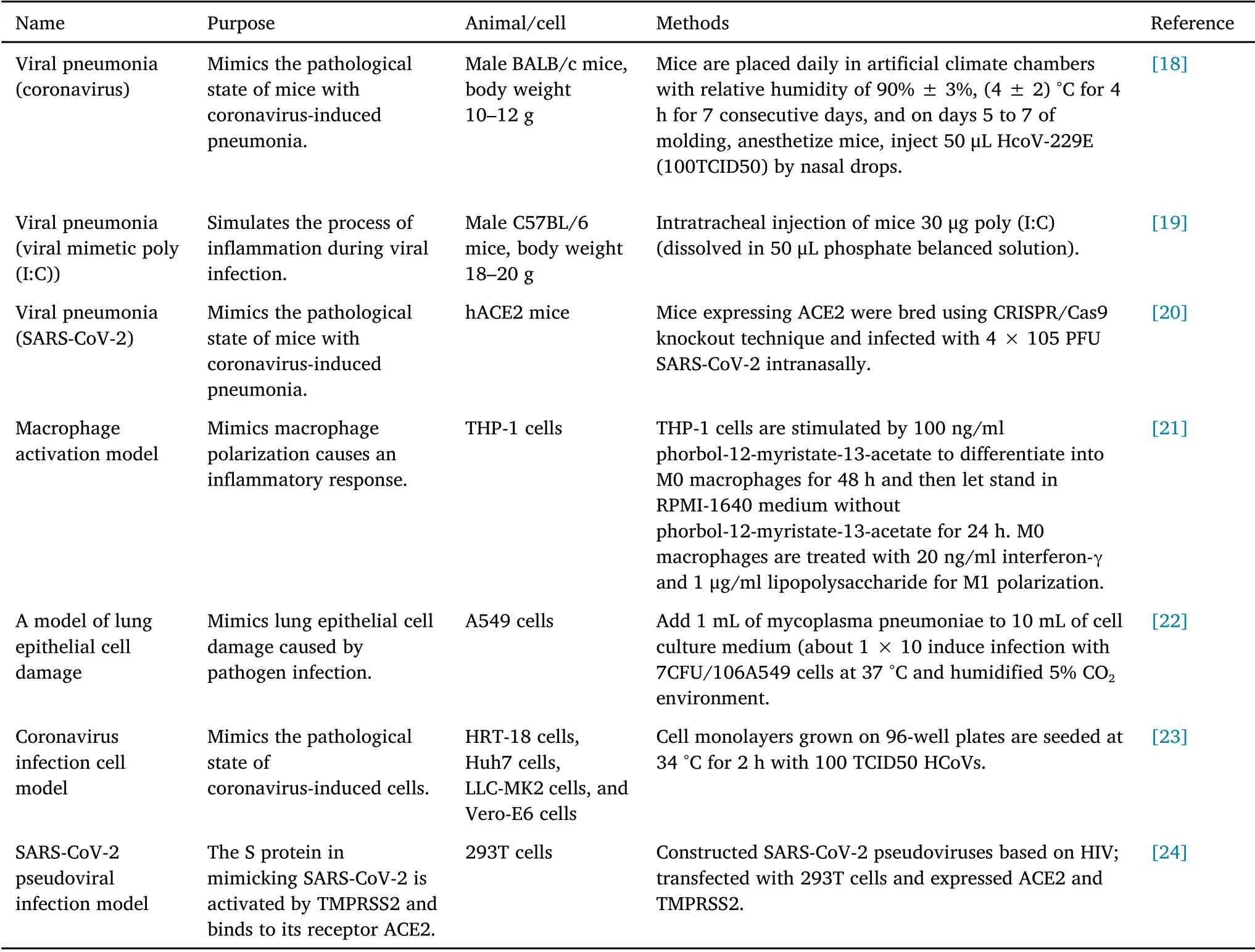
Table 2 Experimental model used for coronavirus disease 2019 studies
Influenza
There are hundreds of millions of patients with influenza worldwide each year.Most influenza infections present with a cough, fatigue,headache, high fever, and other manifestations [25], and a few even result in severe symptoms, such as multiple organ failure and acute respiratory failure.An increasing number of studies have shown that various new influenza strains have gained some resistance to traditional anti-influenza drugs such as oseltamivir [26, 27].Traditional Chinese medicine has certain advantages in reducing viral infection and regulating the immune response(Figure 1).
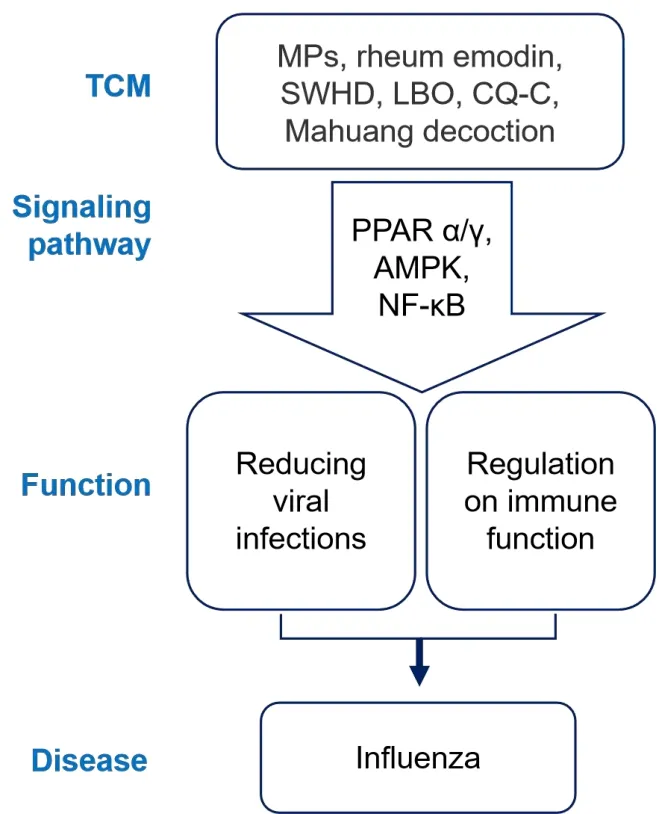
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of traditional Chinese medicine treatment of influenza.TCM, traditional Chinese medicine; MPs,mixed polysaccharides; SWHD, Sanwu Huangqin decoction; LBO,Luofu Mountain hundred grass oil; CQ-C, Chaiqian Qingning capsule;PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; AMPK, adenosine 5’-monophosphate-activated protein kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-B.
Reducing viral infections
Reducing viral infections is the main method used to eliminate the spread of viruses.Bei et al.found that emodin (C15H10O5, PubChem CID:3220) and its analogs fromPolygoni Cuspidati Rhizomaconferred resistance to influenza A virus (IAV) [1].In vivo experiments showed that emodin protected mice from IAV infection, and furtherpharmacological studies found that emodin activated the PPARα/γ and AMPK pathways in A549 cells, reduced fatty acid synthesis, and increased intracellular adenosine triphosphate levels, thereby inhibiting IAV-induced cell damage.In IAV-infected mouse models,inhalation of nebulized Luofu Mountain hundred grass oil (State Food and Drug Administration (SFDA) approval number: Z44022355)reduced pathological damage to lung tissue and serum IL-1β and IL-6 levels; further, Luofu Mountain hundred grass oil significantly downregulated the viral protein expression and phosphorylation levels of nuclear factor kappa-B(NF-κB)P65 and interferon regulating factor 3 in mouse lung tissue [28].The Chaiqian Qingning capsule (SFDA approval number: Z20090896) can effectively protect mice from influenza infections and alleviate lung lesions, and Chaiqian Qingning capsule in A549 cells downregulates IAV-induced IL-6, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 8, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and other genes in a dose-dependent manner.In addition, Chaiqian Qingning capsule induces the expression of phosphonated p-NF-κB protein and regulates NF-κB phosphorylation [29].Nishi et al.found that the Mahuang decoction(composed ofEphedrae Herba,Cinnamomi Ramulus,Armeniacae Semen Amarum, andGlycyrrhizae Radix) can improve the survival rate of mice and reduce the virus titer in a mouse model of influenza infection.The mechanism is related to changes in the lipid medium reaction of omega-3 and omega-6, affecting the expression of genes related to macrophages and T cells and regulation of inflammation [30].
Regulation of immune function
A robust immune response is vital for combatting viral infections.Mixed polysaccharides extracted from shiitake mushrooms,Smilacis Glabrae Rhizoma,Zingiberis Rhizoma, and driedTangerine Peelreduced H1N1 virus infection in mice, and further experiments showed that MP pretreatment enhanced humoral and cellular immune responses in mice[31].Sanwu Huangqin decoction(composed ofScutellariae Radix,Sophorae Flavescentis Radix,and driedRehmanniae Radix)can alleviate pathological damage to the lungs of IAV infection-infected mice, and further experiments have found that Sanwu Huangqin decoction reduces the levels of IL-6,TNF-α,IL-1β,and interferon-gamma(IFN-γ)in mouse serum,bronchoalveolar lung fluid(BALF),and lung tissue by modulating the NF-κB pathway, and elevates IL-4 levels to inhibit virus-induced inflammation.In addition, SWFD promoted the proliferation of T and B lymphocytes, enhanced natural killer cell activity, and promoted macrophage phagocytosis[32].
Influenza viruses can constantly mutate to escape immune memory responses and infect individuals previously exposed to similar strains[33].Therefore, the relatively conserved gene sequences in viruses and some non-coding host RNAs, such as miRNAs and circRNAs,have attracted considerable attention for the design of corresponding antiviral drugs.Liao et al.reviewed in detail some host non-coding RNAs that can directly or indirectly regulate the replication of influenza viruses, such as miRNAs that target key genes in the response to influenza viruses [34].IL-13 can affect airway inflammation and mucus hypersecretion, which are key targets in influenza-induced chronic lung disease [35].Influenza viruses can infect and induce mitochondrial extension and change the mitochondrial-endoplasmic reticulum contact sites.Interestingly,further studies have shown that viral RNA can induce mitochondrial extension[36].These studies can provide new ideas to further explain the mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine against influenza viruses in the future.
Asthma
Asthma is a disease characterized by inflammation, hyper-reaction,and remodeling of the airways.It manifests as wheezing, chest tightness, and other respiratory symptoms.The onset of asthma is related to diet, environment, genetics, and other factors.Western medicine mostly uses drugs such as glucocorticoids, leukotriene receptor antagonists, and β receptor inhibitors to alleviate asthma symptoms, which have good short-term effects; however, long-term medication may cause adverse reactions such as hormone resistance or even decreased immunity in some patients [37].Traditional Chinese medicine has certain advantages in the treatment of asthma, which can significantly improve patient symptoms, reduce recurrence, and have few toxic side effects by inhibiting the formation of inflammatory response pathways, inhibiting the formation of NLRP3(nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain, leucine-rich repeat and pyrin domain-containing 3) inflammasomes, oxidative stress, and autophagy (Figure 2).In particular, some traditional Chinese medicinal compounds show excellent biological activity and have broad prospects for the treatment of asthma.
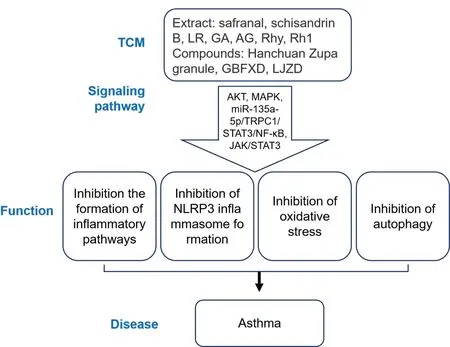
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of traditional Chinese medicine treatment of asthma.TCM, traditional Chinese medicine; LR,liquiritigenin; GA, glycyrrhizic acid; AG, andrographolide; Rhy,rhynchophylline; Rh1, ginsenoside Rh1; GBFXD, Gu-Ben-Fang-Xiao decoction; LJZD, Liujunzi decoction; AKT, protein kinase B; MAPK,mitogen-activated protein kinase; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-B; JAK, Janus kinase; NLRP3, nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain,leucine-rich repeat and pyrin domain-containing 3.
Inhibiting the formation of inflammatory pathways and NLRP3 inflammasome formation
Inflammation is one of the core factors in the development of asthma.Saffron aldehyde (C10H14O, PubChem CID:61041) fromCarthami Flosimproves the ovalbumin-induced mouse asthma model by lowering serum immunoglobulin E levels and reducing the number of mast cells in lung tissue, thereby normalizing Th1/Th2 cytokine levels [2].Bi et al.predicted that knotweed can regulate protein kinase B (AKT),mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and apoptotic signaling pathways using methods such as network pharmacology, and further in vitro experimental validation showed that resveratrol (C14H12O3,PubChem CID: 445154) inhibited airway smooth muscle cell proliferation and reduced recombinant mucin 5 subtype AC overexpression [3].Leaf of narrow-leaved oleaster reduces the production of eosinophils, white blood cells, and pro-inflammatory cytokines by inhibiting the MAPK pathway, thereby relieving inflammatory symptoms [38].Glycyrrhizin (C15H12O4, PubChem CID:114829) extracted fromGlycyrrhizae Radixis a potential anti-asthma drug that increases cAMP levels in a lipopolysaccharide-dependent manner, while also negatively modulating the downstream immune response.Further experiments have shown that glycyrrhizin can effectively inhibit the expression of multiple cytokines,alter the NF-κB pathway and T cell polarization, thus inhibiting inflammation caused by Treg polarization[39].Glycyrrhizic acid(C42H62O16,PubChem CID:14982) inLicoriceeffectively promoted small mothers against decapentaplegic (Smad) 7 mRNA and protein expression and downregulated the levels of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β)1 and Smad2 in the lung tissues of asthmatic mice, thereby improving airway inflammation and airway remodeling in mice [40].Andrographolide (C20H30O5, PubChem CID: 5318517) is a diterpenoid extracted fromAndrographis Herba, which reduces ovalbumin-induced inflammatory responses to asthma in mice by blocking Th17-regulated cytokines such as IL-6, IL-17A, and IL-17F and inhibiting the activation of the JAK1/STAT3 signaling pathway, thereby reducing ovalbumin-induced inflammatory responses to asthma in mice by reducing airway remodeling and neutrophil infiltration [4].In vivo experiments have shown that schizantoside B(C23H28O6,PubChem CID:108130) extracted fromSchisandrae Chinensis Fructuscan alleviate airway inflammation and airway remodeling in a rat model of asthma.Further in vitro experiments showed that schizantoside B inhibits NLRP3 inflammation, reduces apoptosis, and improves rat macrophage inflammation through the miR-135a-5p/TRPC1/STAT3/NF-κB axis [5].Ginsenoside Rh1 (C36H62O9, PubChem CID:12855920) can reduce the levels of eotaxin, IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, and IL-33 in BALF and serum by regulating the balance of Th1/Th2 cytokines,and simultaneous increasing the levels of IL-12 and IFN-γ.It can significantly reduce lung and airway resistance in the BALF of asthmatic mice, reduce the number of total inflammatory cells and lymphocytes in BALF,thereby playing an anti-inflammatory role[41].In a mouse model of cough-variant asthma, oral administration of Hanchuan Zupa granule (batch number: 180630) reduced the number of coughs and relieved airway inflammation by modulating Th1/Th2 imbalance and inhibiting the Toll-like receptor 4 inflammatory signaling pathway, thereby increasing t-bet mRNA and protein levels in lung tissue while reducing Toll-like receptor 4 and Th2-specific transcription factor GATA3 mRNA and protein levels[42].In a mouse model of asthma, Guben Fangxiao decoction (consisting ofAstragali Radix,Codonopsis Radix,Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma,Smilacis Glabrae Rhizoma,Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium,Saposhnikoviae Radixand other drugs) significantly reduced the level of lung inflammation and effectively alleviated airway inflammation.Further studies have found that Guben Fangxiao decoction can enhance adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase phosphorylation to regulate downstream fatty acid metabolism signals, thereby maintaining lipid homeostasis on the lung surface and alleviating asthma [43].In vivo studies have shown that Liujunzi decoction (composed ofCodonopsis Radix,Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma,Glycyrrhizae Radix,Smilacis Glabrae Rhizoma,Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium,and other drugs)can significantly reduce lung tissue edema and inflammatory cell infiltration, thus ameliorating symptoms in mouse models of asthma,in vitro studies have shown that Liujunzi decoction can reduce protein levels of IL-17a and thymic stromal lymphopoietin in lung tissue, and Liujunzi decoction may inhibit the expression of miR-21, miR-146a,and other proteins in the lung tissue through the NF-κB signaling pathway[44].
Inhibition of oxidative stress and inhibition of autophagy
Oxidative stress and autophagy are important factors in asthma development.Wang et al.summarized many active ingredients of traditional Chinese medicines [45], such as astragaloside (C41H68O14,PubChem CID: 13943297), paeoniflorin (C23H28O11, PubChem CID:442534),and ligustrazine(C8H12N2,PubChem CID:14296),which can be used to adjust signaling pathways such as JAK/STAT/MAPK,PI3K/AKT, and GATA3/T-bet.They can inhibit airway remodeling,relieve oxidative stress,lower pro-inflammatory and chemokine levels,regulates immune balance, and treats asthma.
Rhynchophylline(C22H28N2O4,PubChem CID:5281408) is an indole alkaloid isolated fromUncariae Ramulus cum Uncis.Rhynchophylline can reduce inflammation in asthmatic mice and improve airway remodeling and oxidative stress.In vitro studies have shown that rhynchophylline inhibits the activation of JAK2/STAT3 signaling,which reduces the levels of autophagy-related proteins such as beclin-1 in lung tissue,thereby inhibiting autophagy in airway smooth muscle cells [46].
Lung cancer
Lung cancer is the second most common type of cancer worldwide after breast cancer.Approximately 1.76 million patients die from lung cancer every year[47,48].In recent years, targeted therapeutic drugs and immune checkpoint inhibitors have alleviated the conditions of patients with lung cancer to some extent.Chinese medicine also plays an important role in the treatment of lung cancer.Many studies have shown that Chinese medicine can alleviate lung cancer by inhibiting tumor cell proliferation and enhancing immune function (Figure 3).
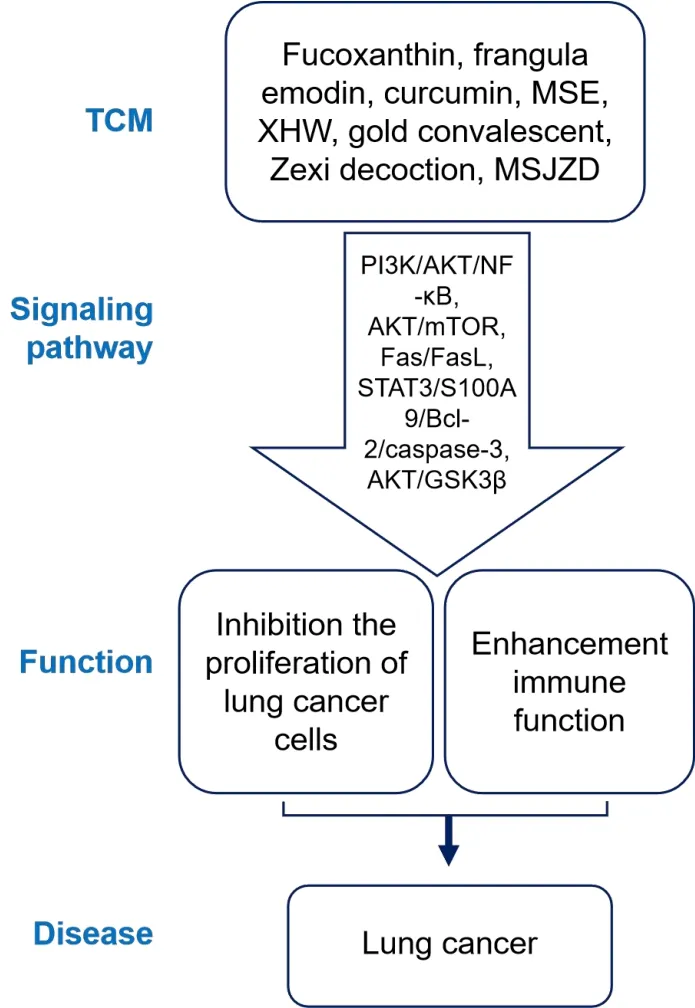
Figure 3 Schematic diagram of traditional Chinese medicine treatment of lung cancer.TCM, traditional Chinese medicine; MSE,Muyin extract; XHW, Xihuang Wan; MSJZD, modified Sijunzi decoction; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase; AKT, protein kinase B;mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; Fas, Fas cell surface death receptor; FasL, Fas ligand; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; GSK3β,glycogen synthase kinase 3β.
Inhibition of the proliferation of lung cancer cells
The cell cycle is an important factor affecting lung cancer cell proliferation, and interference of apoptosis causes lung cancer.Overexpression of secretory phospholipase A2-IIa can affect the development of lung cancer cells, and emodin can downregulate secretory phospholipase A2-IIa expression levels by influencing the relevant NF-κB metabolic pathways, thereby inhibiting the proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Related experiments have found that emodin can promote apoptosis of A459 and H460 cells with the oncogene KRAS and increase reactive oxygen species levels [49].Curcumin fromCurcumae Longae Rhizoma(C21H20O6, PubChem CID: 969516) downregulates circRNA hsa_circ_0007580 levels and regulates the expression of miR-384 and integrin beta 1, thereby inhibiting the growth of NSCLC [50].Muyin extract mixed withMomordica CochinchinensisandEpimedii Foliumimproved IFN-γ/IL-4 ratios, thereby inhibiting the proliferation of lung cancer cells in a mouse model transplanted with Lewis lung cancer cells.Further experiments have found that Muyin extract may inhibit the proliferation of NSCLC cells in NCI-H460 and NCI-H157 by blocking autophagy and apoptotic-triggered AKT/mTOR pathways[6].In a mouse model of Lewis lung cancer, oral administration of the Xihuang Wan inhibited the proliferation of Lewis lung cancer cells(lot number: 18041283), and RNA sequencing showed that the suppression mechanism of Lewis lung carcinoma mediated by Xihuang Wan is related to pathways involving tumor necrosis factor and estrogen[51].In the A459 lung cancer mouse model,Modified Sijunzi decoction (composed ofGinseng Radix,Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma,Smilacis Glabrae Rhizoma,Glycyrrhizae Radixand other drugs)can inhibit the growth of NSCLC.Further studies have found that Modified Sijunzi decoction can inhibit the expression of the AKT/GSK3β pathway and TGF-β1, thereby reducing the cell viability of NSCLC and promoting its apoptosis[52].
Enhancement of immune function
The appearance of lung cancer is related to decreased immune function and the inability to detect and eliminate cancer cells at an early stage.The immune function of lung cancer patients can also affect the speed of deterioration and the effectiveness of treatment.Fucoxanthin (C42H58O6, PubChem CID: 5281239), the main active component ofSargassum, can reduce epithelial cell–mesenchymal transformation (EMT)-related factor expression levels and limit the migration ability of lung cancer cells by influencing the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB pathway.Further studies have shown that fucoxanthin can enhance the sensitivity of lung cancer cells to the small-molecule drug gefitinib, thereby enhancing the effect of inhibiting lung cancer cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis [7].Matrine fromSophorae Flavescentis Radix(C15H22N2O2, PubChem CID:24721085) may enhance T cell-mediated antitumor immunity by inhibiting the mTOR/PI3K/AKT pathway to inhibit M2 macrophage polarization, thereby inhibiting the growth and metastasis of lung cancer cells[53].In vitro experiments showed that Jin Fu Kang(SFDA approval number: Z19991043) inhibits the proliferation and migration of the lung cancer cell line CTC-TJH-01 by regulating the integrin/Src pathway.At the same time, it was shown that Jin Fukang can promote the natural killer cell-mediated Fas/FasL signaling pathway and enhance its cytotoxic effect on circulating tumor cells,thereby promoting circulating tumor cell apoptosis [54, 55].Zexi decoction (composed ofPinelliae Rhizoma,Herba Salviae Chinesnsis,Euphorbia HelioscopiaL.,Zingiberis Rhizoma,Cynanchi Stauntonii Rhizoma et Radixand other drugs) can improve the survival rate of lung cancer mouse models.Through the STAT3/S100A9/Bcl-2/caspase-3 signaling pathway, Zexi decoction can induce the apoptosis of granulocyte-like myeloid derived suppressor cells and reduce the immunosuppressive effect on T cells, thereby inhibiting the development of tumors [56].
In recent years, with an increase in research, exosomes have been found to play an important role in the development of diseases,especially cancer.Exosomes are vesicles secreted by cells that play an important role in mediating cell communication, promoting the metastasis and proliferation of lung cancer cells, and regulating drug resistance in lung cancer cells [57].Further experiments have found that exosomes are stable in the body and can be used as markers and drug carriers [58, 59].Related studies currently are in progress.Studies have shown that the complement pathway also plays a role in promoting cancer, and complement molecules C3a and C5a can promote tumor growth and metastasis.Therefore, studying immune checkpoint inhibitors based on these molecules is crucial [60].In addition, the development of iron death inducers, which induce iron overload in lung cancer cells to trigger iron death, has introduced a new cancer treatment strategy [61].Of note, telomerase plays a key role in maintaining telomere length and tumor growth, but further research on the related mechanism is needed.Small molecule drugs targeting telomerase inhibitors are expected to be applied in the clinical treatment of lung cancer [62].These studies have broad prospects to improve anticancer drugs.
COPD
COPD is characterized by chronic cough and dyspnea,which seriously affects the quality of life of patients.Bronchial expanders and anti-inflammatory drugs are commonly used in the treatment of COPD in Western medicine.An increasing number of studies have focused on new inhaled drugs, and further screening for useful oral drugs is needed [63].Traditional Chinese medicine has made progress in relieving airway inflammation and improving lung function, which has played an important role in the treatment of COPD (Figure 4).
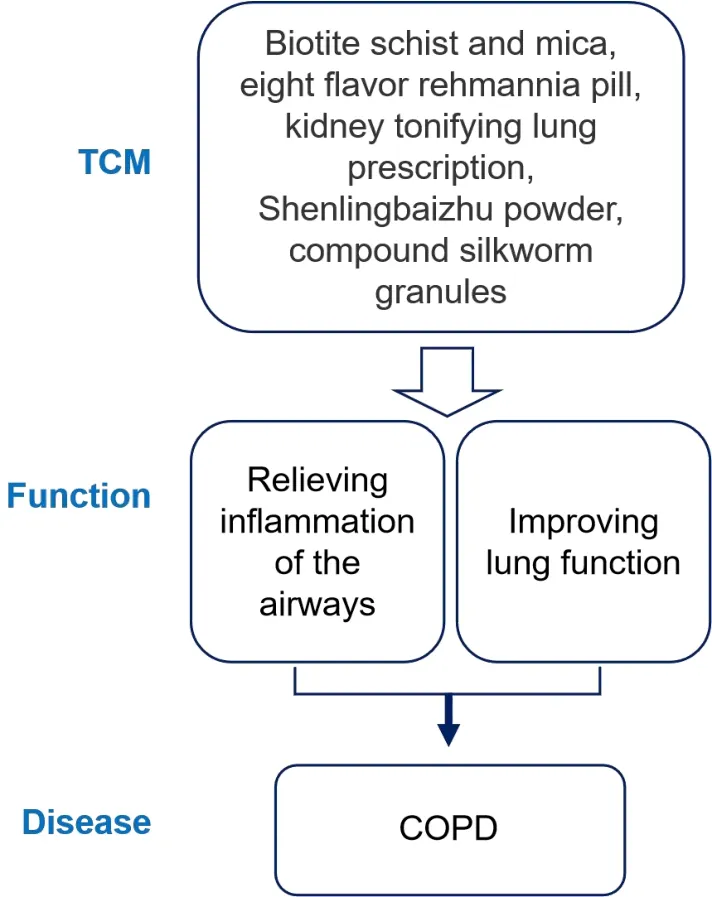
Figure 4 Schematic diagram of traditional Chinese medicine treatment of COPD.TCM, traditional Chinese medicine; COPD,chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Relieving inflammation of the airways
Inflammation of the airway is one of the main pathological features of COPD.In vivo experiments found that in acute exacerbations of COPD rat model, intragastric administration ofLapis Chloritireduced the levels of inflammatory factors in the serum and alleviated airway inflammation.The mechanism is related to increasing the levels of essential trace metal elements (such as iron and vanadium) in the plasma of model rats and reducing the levels of excess elements (such as magnesium) in the lung tissue [64].The Bawei Dihuang pill(composed ofCorni Fructus,Dioscoreae Rhizoma,Moutan Cortex,Smilacis Glabrae Rhizoma,Alismatis Rhizomaand other drugs) can inhibit COPD-related inflammatory responses by reducing the infiltration of inflammatory cells in the lung tissue of a mouse COPD model induced by cigarette smoke and lipopolysaccharide and reducing the levels of pro-inflammatory factors TNF-α and IL-6 in BALF [65].Compound grass silkworm granules (registration number:ChiCTR1800020441) can significantly reduce levels of the pro-inflammatory factors T helper cell 17 and IL-17A in the plasma of patients with stable COPD and significantly increase the anti-inflammatory factors IFN-γ and IL-10, reducing the probability of acute attack [66].
Improving lung function
Changes in lung function are important manifestations of COPD.Key active molecules such as icariin (C33H40O15, PubChem CID: 5318997)in the Bufei Yishen formula(composed ofRehmanniae Radix,Alismatis Rhizoma,Smilacis Glabrae Rhizoma,Corni Fructus,Cinnamomi Cortexand other drugs) can reduce the activity of NF-κB, p38, or p65 to inhibit the inflammatory response, and further related studies have confirmed that it reduces the levels of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and matrix metalloproteinase-12 in BALF, thereby reducing lung tissue degeneration caused by protein overexpression and improving lung function in patients [8].Clinical studies have shown that Shenling Baizhu San (composed ofLablab Album Semen,Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma,Smilacis Glabrae Rhizoma,Glycyrrhizae Radix,Platycodonis Radixand other drugs) has obvious advantages in improving lung function and exercise endurance in patients with stable COPD [67].
In recent years,many studies have shown that IL-17 plays a key role in the occurrence and development of COPD.Liu et al.reviewed the processes related to IL-17A and its downstream involvement in COPD.IL-17A is a proinflammatory cytokine produced by T cells.It can increase the levels of C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 1, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 2, and C-X-C motif receptor 2 by promoting the expression of the tumor suppressor gene p53 and its induced lung inflammation downstream factor plasminogen activator inhibitor-1,causing neutrophils to migrate to the damaged alveolar epithelial cells,thus leading to neutrophil inflammation in COPD (Figure 5) [68–70].These targets provide a reference for the future clinical treatment of COPD.
IPF
Interstitial lung diseases include IPF, sarcoidosis, and connective tissue disease-related interstitial lung disease.In 2021, most studies related to qualitative lung disease were IPF, which is characterized by progressive dyspnea and hypoxemia.Traditional Chinese medicine can be used to treat IPF by inhibiting EMT and regulating the levels of inflammatory factors (Figure 6).
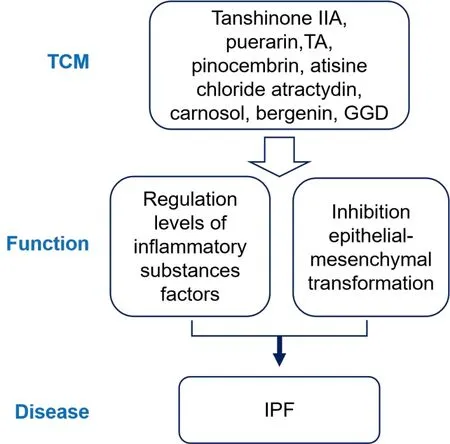
Figure 5 IL-17A and its downstream are involved in COPD related processes.TA, total alkaloids; GGD, Gancao Ganjiang decoction; IPF,idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; IL-17A, interleukin-17A.
Regulation of inflammatory substance factors levels
Inflammatory factors are vital to IPF pathology.Tanshinone IIA(C19H18O3, PubChem CID: 164676) and puerarin (C21H20O9, PubChem CID: 5281807) have anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effects, and combining these two treatments improved the survival rate of bleomycin-induced IPF model mice and reduce the degree of pulmonary fibrosis in mice, etc.Further studies have found that the combination of tanzanone IIA and pueraria can reduce the level of IL-6 in lung tissue, weaken the expression of Janus kinase, and inhibit the phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription-1 and signal transducer and activator of transcription-3,thereby reducing the activation and migration of fibroblasts and alleviating IPF [71].The total alkaloids extracted from theAlstonia scholariscan effectively inhibit bleomycin-induced mouse lung fibrosis,and further studies have found that indole alkaloids in total alkaloids can improve the infiltration of inflammatory cells in lung tissue,increase antioxidant enzyme levels, downregulate the expression of TGF-β and matrix metalloproteinase-1 genes to reduce collagen deposition, and maintain the dynamic balance of matrix metalloproteinase-1/anti-tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 [72].pinocembrin (C15H12O4, PubChem CID: 68071), extracted from eucalyptus leaves, improved lung function in sheep with bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis and reduced the number of CD8,CD4 T cells,and inflammatory cells in BALF[9].The extract sage phenol (C20H26O4, PubChem CID: 442009) from rosemary reduces IL-6 and TNF-α levels in rat lung tissue,inhibited myelin peroxide activity,and relieves IPF[10].
Inhibition epithelial-mesenchymal transformation
EMT plays an important role in IPF.Atractylodin (C13H10O, PubChem CID: 171429) extracted fromAtracylodis Rhizomacan downregulate EMT levels in the lung tissue of mice and alleviate pulmonary fibrosis.Further experiments showed that atractylodin inhibited TGF-β1-induced EMT and the expression of related transcription factors in A549 cells through Smad and non-Smad pathways [11].In vitro experiments showed that bergenin (C14H16O9, PubChem CID:66065) fromBergenia Purpurascensinhibited the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway, inhibited fibroblast activation and extracellular matrix accumulation, promoted autophagy and apoptosis of myofibroblasts, and alleviated bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice [73].Gancao Ganjiang decoction (composed ofGlycyrrhizae RadixandZingiberis Rhizoma)improves inflammation and relieves IPF in mouse lung tissue, and further studies have shown that Gancao Ganjiang decoction reduces the levels of programmed death 1,IL-17A,and TGF-β1 in lung tissue,inhibits EMT,and reduces the deposition of the extracellular matrix [74].
To date, the pathogenesis of IPF is not fully understood.Many studies have shown that cell senescence is closely related to IPF and that the aging acceleration mechanism plays an important role in the pathogenesis of IPF[75,76].Mitochondrial autophagy can induce the release of profibrotic factors, promote the differentiation and proliferation of fibroblasts, and play an important role in IPF [77].Studies have found that IPF is related to redox imbalance (oxidative stress) caused by reactive oxygen species accumulation [78].Looking for a new anti-IPF targets should provide new experimental and theoretical basis for the treatment or delay of the occurrence and development of IPF.
Future perspectives
In 2021, research on the mechanism of Chinese medicine extracts and compounds in the treatment of respiratory diseases mainly focused on reducing viral infections, inhibiting lung cancer cell proliferation, and reducing the inflammatory response.To date, many clinical trials and basic experimental studies have confirmed that traditional Chinese medicine has positive effects on many respiratory diseases.It is worth mentioning that the active ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine are natural products with structural diversity and low toxicity, which can play the role of multi-target synergistic treatment of diseases,with unique advantages and broad prospects.
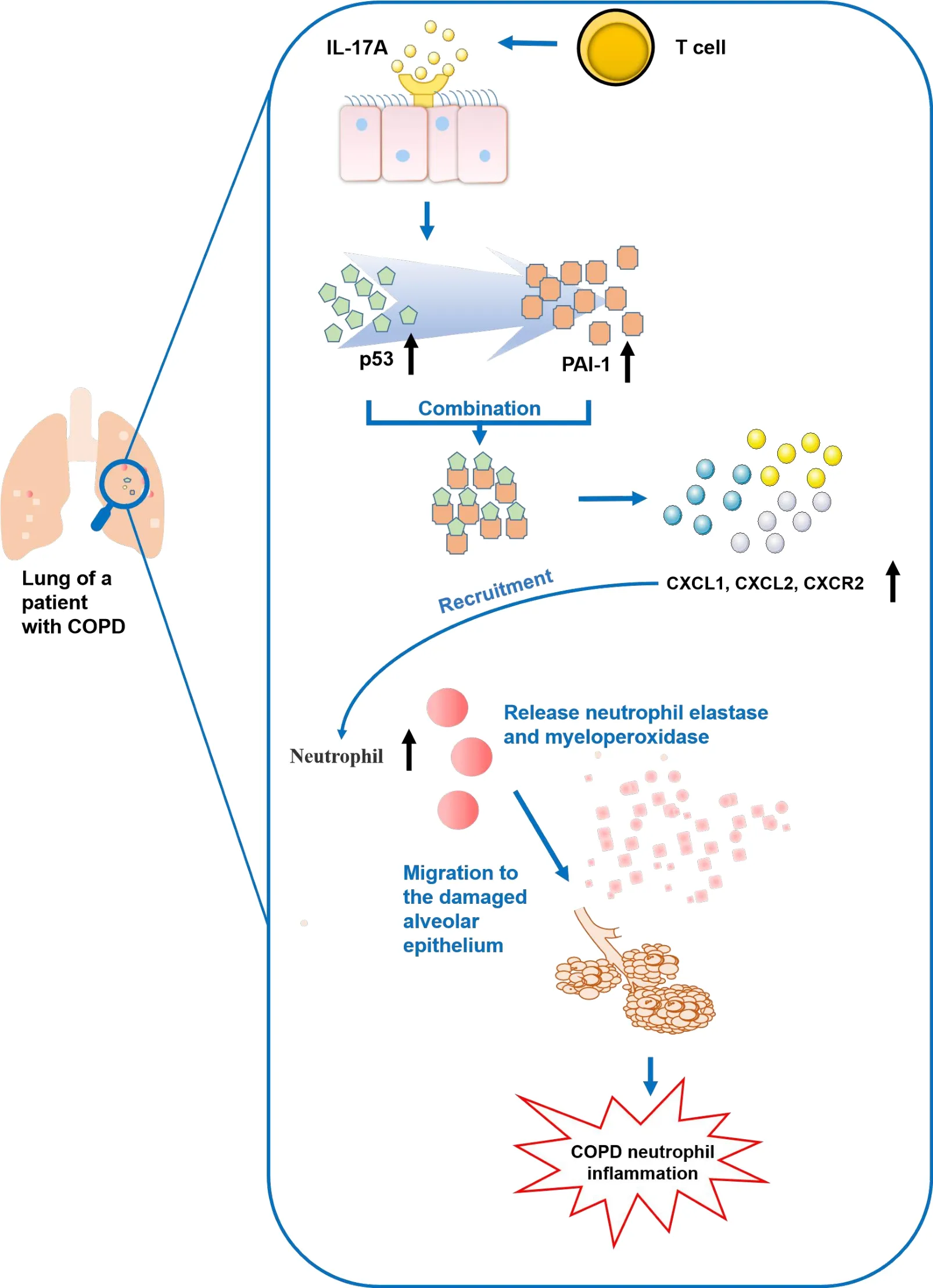
Figure 6 Schematic diagram of traditional Chinese medicine treatment of IPF.COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; IL-17A,interleukin-17A; PAI-1, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1; CXCL1, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 1; CXCL2, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 2;CXCR2, C-X-C motif receptor 2.
In recent years, an increasing number of studies have shown that miRNAs, circRNAs, and autophagy play important roles in the occurrence and development of respiratory diseases, meaning they have attracted wide attention.Research on the mechanism of action of traditional Chinese medicine has garnered great interest, and the emergence of some resistant viruses has also greatly promoted the development of traditional Chinese medicine against respiratory viruses.However,some problems with the study of traditional Chinese medicine against respiratory diseases remain.For example, most studies on anti-respiratory viruses have focused on the changes in T cell subsets, rather than dendritic, type 2 innate lymphoid, and structural cells.Most studies on anti-influenza traditional Chinese medicine focus on influenza A and less on influenza B; there are still many Chinese medicine treatments for disease mechanisms and related metabolic pathways that remain unclear.We should organically combine modern medical and biological technology with the action law of traditional Chinese medicine, make full use of modern evidence-based medicine methods, and carry out corresponding multidisciplinary and multi-level clinical research and basic experiments to provide new ideas for clinical treatment of diseases using traditional Chinese medicine.
 Traditional Medicine Research2022年4期
Traditional Medicine Research2022年4期
- Traditional Medicine Research的其它文章
- Integration of multi-omics in investigations on the mechanisms of action of Chinese herbal medicine interventions in metabolic diseases
- Active compounds in RenShenJian decoction ameliorate insulin resistance in vitro
- Quality evaluation of Pinelliae Rhizoma using network pharmacology and multicomponent quantitative analysis
- Inhibition of rat prostate smooth muscle contractility by extracts of Costus speciosus(crepe ginger)
- Biologically active components for cosmeceutical use extracted from Chaetomorpha aerea
- Toxicological advances of traditional medicine in 2021
