Jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.(Rhamnaceae)): a review on its pharmacological properties and phytochemistry
Ensiye Aafi,Mohammad Reza Shams Ardakani,Mehran Mirabzadeh Ardakani*
1Department of Traditional Pharmacy, School of Persian Medicine, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran 1416663361, Iran.2Department of Pharmacognosy,Faculty of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences Research Center,Tehran University of Medical Sciences,Tehran 1417614411,Iran.
Abstract Jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) belongs to the Rhamnaceae family.It is distributed in the tropical and subtropical regions of Europe and Asia, including India, China, Iran, Russia,and the Middle East.Jujube is a highly tolerant tree that is resistant to soil salinity and alkalinity.Jujube possesses many phytochemical components and pharmacological properties that make it a good choice for the human diet.Jujube fruit is nutritious and rich in proteins, minerals, vitamins, organic acids, and carbohydrates.It also contains phytochemical components such as polyphenols, flavonoids, terpenoids, anthocyanins,alkaloids, and carotenoids.Jujube has both nutraceutical and cosmeceutical properties.All parts of this plant possess medicinal properties.Jujube has a long history of use in traditional medicine, especially in traditional Persian medicine.It has many pharmacological properties according to traditional Persian medicine, which include anti-pruritic and tranquilizing effects for renal and bladder pain.In Chinese medicine,jujube is used to increase appetite and treat diarrhea and fatigue.This indicates that jujube has several chemical constituents and beneficially affects multiple organs and tissues.These properties include antioxidant, anti-cancer, antimicrobial, neuroprotective,cardioprotective, and hepatoprotective activities.It also has health-promoting effects,including anti-aging properties.
Keywords:Ziziphus jujuba; jujube; phytochemical; pharmacological effect
Background
Chinese jujube (Ziziphus jujubaMill.) belongs to the Rhamnaceae family [1, 2].The plant is native to China.However, it is also distributed in the tropical and subtropical regions of Europe and Asia,including India, China, Iran, Russia, and along the “Silk Road” in the Middle East.Jujube is tolerant to drought-stress [3–6] and resistant to soil salinity and alkalinity-growing in various soil conditions [7].The fruits, seeds, leaves, and bark of jujube all have medicinal effects(Figure 1) [5].Jujube trees are 20 to 30 feet tall, not branched, with shiny oval to ovate leaves measuring 2–4 cm wide and 2.5–5.5 cm long.The aromatic flowers are greenish-yellow in color.Its flowers include five petals, sepals, and anthers [6].Mature jujube fruits are round, red to purplish-black, and wrinkled with a delicious taste because of the high sugar content.It also contains olive-like seeds [8].Jujube fruits are consumed fresh or in the form of dried pickles and chutneys [9].China is the largest exporter of jujube (producing 7,345,300 tons in 2014) [3].In Iran, South-Khorasan Province is the leading producer of jujube producing [10] approximately 98% of jujubes in the said country.In 2012, approximately 3,000 tons of raw jujube fruit were harvested, with an economic value of approximately 20 million USD [11].
Figure 1 The medicinal part of Ziziphus jujuba plant
Several studies have been conducted on medicinal plants over the past few decades.Carrying out an ethnobotanical study means documenting indigenous knowledge to not only protect cultural biodiversity and traditions but also to enhance drug development and improve public health.It is estimated that 350,000 plant species are distributed worldwide, of which only a small proportion have been identified.The decoction of jujube fruits is used as depurative and febrifuge agents, and it is also used to treat jaundice in traditional Persian medicine [12, 13].The Iranian term for this plant is “Annab”or “Onnab”.Jujube has long been used as a nourishing fruit and medicinal plant in Persian medicine.In some traditional documents,including “Makhzan-al-adviya”, which was written by Mohammad Hossein Aghili Khorasani Shirazi in the 12thAH century, “Al-Qanun fit-Tibb”, which was written by Ibn Sina (Avicenna) in the 11thAH century, and “Al-Havi”, which was compiled by Abu Bakr Mohammad Ibn Zakariya Al-Razi (Rhazes) in the 10thAH century, jujube was mentioned [14].It has many pharmacological properties in traditional Persian medicine, including antipruritic-, renal and bladder pain tranquilizing-, digestive disorders resolving-, anti-asthmatic-,expectorant-, cough-suppressing-, blood purifying-, and hematopoietic activities.However, excessive consumption of jujube causes flatulence[15].
A fossil of a jujube seed was discovered by Chinese archeologists,which showed that jujube was grown in China at least 8,000 years ago.Jujube has been used for medicinal purposes for more than 3,000 years and is one of the main herbal medicines used in traditional Chinese medicine.According to the Chinese history of the Western Zhou Dynasty (11thcentury–771 B.C.E.), jujube was used as a decoction on special occasions by particular guests.Moreover, jujube has been described in classic poetry.Shennong’s Materia Medica(300 B.C.E.–200 C.E.) is an ancient book on herbal medicines, and jujube was mentioned as a vital herbal medicine that improved people’s life span by regulating their digestive system, nourishing their blood, and improving their quality of sleep.The second ancient Chinese book on herbal medicine,Inner Canon of Yellow Emperor(475–221 B.C.E.),mentions jujube as an excellent fruit [16, 17].In Chinese medicine,jujube is used to increase appetite, treat diarrhea and fatigue, purify the blood, and it is believed to have anti-aging effects [18].Jujube fruits are highly nutritious and possess many pharmacological properties, including neuroprotective, antioxidative, anti-cancer, antiinflammatory, hepatoprotective, antimicrobial, and immunomodulatory activities [19–25].It also has health- promoting effects like anti-aging properties [26, 27].The fruits are nutritious,rich in proteins, minerals, vitamins, organic acids, and carbohydrates,and contain phytochemical components such as polyphenols,flavonoids, terpenoids, anthocyanins, alkaloids, and carotenoids [28,29].
The aim of this study was to evaluate the traditional uses, assess the phytochemical and pharmacological properties of jujube fruits, and lay down a scientific foundation for further investigating the usage of jujube.Moreover, this review indicates that jujube possesses a nutricosmetic effect because of its high nutritional value and cosmetic properties, in addition to its pharmacological activities.Nutricosmetics is a new approach that has spread worldwide.
Phytochemistry
Many components of theZiziphus jujubafruits (ZJF) have been placed into several different classes of chemical compounds.Various studies have reported the phytochemical components of ZJF (Table 1).Its chemical components include polyphenols (flavonoids, anthocyanins,and tannins), alkaloids, terpenoids, polysaccharides, organic acids,carotenoids, fatty acids, sterols, proteins, vitamins, and minerals.Jujube is a good source of minerals and vitamins.
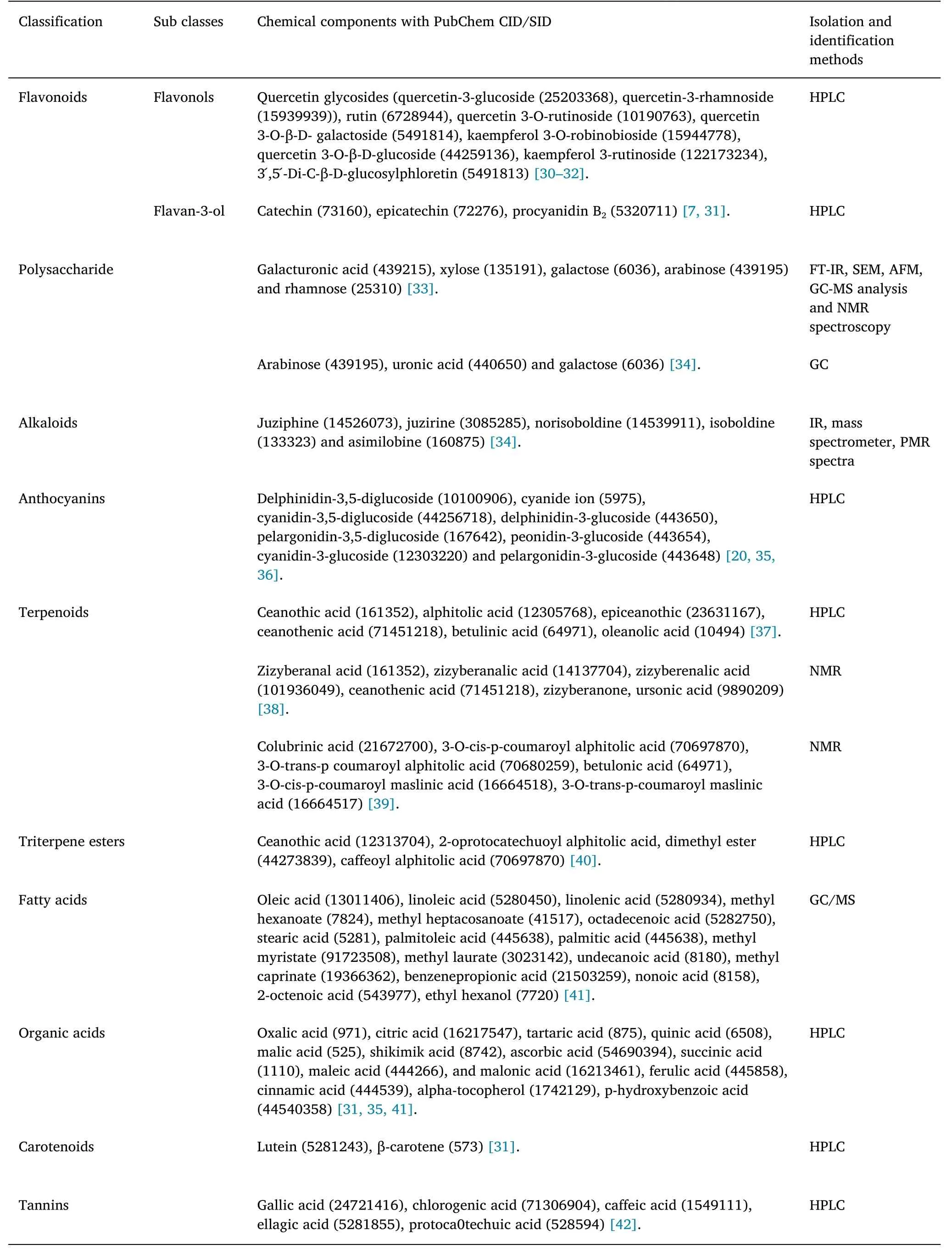
Table 1 Chemical components isolated from fruits of Ziziphus jujuba
Flavonoids.Studies have shown that the flavonoids extracted from fruits ofZiziphus jujubaare quercetin glycosides (quercetin-3-glucoside, quercetin-3-rhamnoside), rutin, quercetin 3-O-rutinoside,quercetin 3-O-β-D-galactoside, kaempferol 3-O-robinobioside,quercetin 3-O-β-D-glucoside, kaempferol 3-rutinoside,3՜,5՜-Di-C-β-D-glucosylphloretin, catechin, epicatechin, and procyanidin B2[7, 30–32].
Polysaccharide.Several polysaccharides have been identified in jujube fruits, such as galacturonic acid, xylose, galactose, arabinose,rhamnose, arabinose, uronic acid, and galactose[33, 34].
Alkaloids.Zhao et al.reported that the alkaloids they collected from jujube fruit were juziphine, juzirine, norisoboldine, isoboldine, and asimilobine[34].
Anthocyanins.Several anthocyanins have been reported to be present in jujube fruit, including delphinidin-3, 5-diglucoside,cyanide, cyanidin-3,5-diglucoside, delphinidin-3-glucoside,pelargonidin-3,5-diglucoside, peonidin-3-glucoside, cyanidin-3-glucoside, and pelargonidin-3-glucoside[20, 35, 36].
Terpenoids and triterpene esters.Several terpenoids and triterpene esters have been identified, including ceanothic acid, alphitolic acid,epiceanothic, ceanothenic acid, betulinic acid (BA), oleanolic acid,zizyberanal acid, zizyberanalic acid, zizyberenalic acid, ceanothenic acid, zizyberanone, ursonic acid, colubrinic acid, 3-O-cis-p-coumaroyl alphitolic acid, 3-O-trans-p coumaroyl alphitolic acid, betulonic acid,3-O-cis-p-coumaroyl maslinic acid, 3-O-trans-p-coumaroyl maslinic acid, ceanothic acid, 2- oprotocatechuoyl alphitolic acid, dimethyl ester, and caffeoyl alphitolic acid [37–40].
Fatty acids.Jujube fruit contains many fatty acids, including oleic acid, linoleic acid, linolenic acid, methyl hexanoate, methyl heptacosanoate, octadecenoic acid, stearic acid, palmitoleic acid,palmitic acid, methyl myristate, methyl laurate, undecanoic acid,methyl caprinate, benzenepropionic acid, nonoic acid, 2-octenoic acid, and ethyl hexanol [41].
Organic acids.Numerous organic acids have been reported in jujube fruit, including oxalic acid, citric acid, tartaric acid, quinic acid, malic acid, shikimik acid, ascorbic acid, succinic acid, maleic acid, malonic acid, ferulic acid, cinnamic acid, alpha-tocopherol, and p-hydroxybenzoic acid[31, 35, 41].
Carotenoids.Gao et al.reported two new carotenoids from jujube fruit: lutein and β-carotene [31].
Tannins.Studies have shown that tannins extracted from jujube fruit include gallic acid, chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, ellagic acid, and protocatechuic acid[42].
Pharmacological activity
The pharmacological properties ofZiziphus jujubaand its components have been evaluated both in vivo and in vitro, but only a few clinical trials have been carried out.Therefore, further studies are required.The pharmacological properties ofZiziphus jujubaand its components are summarized in Supplementary Table S1.
Anti-inflammatory activity
The hydroalcoholic extract of ZJF exhibited anti-inflammatory activity in acute and chronic models of inflammation in rats.One study found that acute anti-inflammatory effects were mediated through inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX), nitric oxide (NO), and histamine.Chronic inflammation decreases the level of activity of the NO isoforms and inhibits prostaglandin production through inhibition of COX-1 and COX-2 [22].Ziziphus jujubacontains active components that inhibit inflammatory cells.Jujube decreased NO release from macrophages and splenocyte proliferation.Among the 21 compounds isolated fromZiziphus jujuba, the terpenoid acid fraction had the highest anti-inflammatory effect in vitro [43].
Antioxidant activity
Jujube fruit exhibits high levels of antioxidant activity in various in vitro models.This activity has been shown in ferric reducing antioxidant power, 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl, reducing power,and lipid peroxidation assays.Plants grown in regions with environmental stresses exhibited high antioxidant activity, and jujube trees grown under a harsh climate and high altitude showed potential antioxidant activity [20].The antioxidant activity of various parts of jujube fruit (seed, pulp, and peel) was determined.The peel showed the highest antioxidant activity owing to its high content of anthocyanins, flavonoids, and phenolic compounds [44].Water-soluble polysaccharide fractions (ZSP1b, ZSP2, ZSP3c, and ZSP4b) from the jujube fruit were isolated, and their antioxidant activities were determined.The two fractions (ZSP3c and ZSP4b) that contained more uronic acid exhibited a higher antioxidant activity than ZSP1b, which contained no uronic acid.This observation indicates that the antioxidant activity may be related to the uronic acid content in each fraction [45].
Antimicrobial activity
Ziziphus jujubaextracts exhibited antibacterial activity againstEscherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus.The methanolic, chloroform,and hexane fractions exhibited antibacterial properties in vitro [46].Different jujube fractions have exhibited various antibacterial effects.The n-hexane and aqueous fractions were effective againstBacillus pumalisandPseudomonas aeruginosa.The ethyl acetate fraction was active againstB.pumalis,P.aeruginosa,Salmonella typhiandStaphylococcus epidermidis.However, these fractions were inactive againstStreptococcus pneumonia, but they showed activity againstEnterobacter aerogenes.The methanolic and n-hexane fractions had no activity againstK.pneumonia,S.pneumoniaandE.coli[24].Snakin-Z,a peptide isolated from jujube, was evaluated for antimicrobial activity.The results showed that it possessed antimicrobial and antifungal effects againstE.coli, K.pneumonia, B.subtilis, S.aureus,Aspergillus niger, Candida albicans, Phomopsis azadirachtae,andPythium ultimum.This peptide is more effective against Gram-negative bacteria than Gram-positive ones [47].
Antiviral activity
BA, isolated from jujubefruits, is a pentacyclic triterpene.It has many potential biological effects and a study was performed with an infected A549 human lung adenocarcinoma epithelial cell line (in vitro) and C57BL/6 mice (in vivo).BA downregulated interferons-λ,an important cytokine in innate and adaptive immunity.Moreover,BA improved pulmonary pathology, including pulmonary edema and inflammation induced by the influenza A/PR/8 virus.Therefore, BA possesses antiviral effects and is a potential therapeutic agent for the treatment of influenza infections owing to its anti-inflammatory properties [48].
Neuroprotective activity
ZJF have neuroprotective activity against glucose-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 (pheochromocytoma) cells (in vitro).ZJF antagonized glucose cytotoxicity, prevents the activation of caspase-3(an apoptosis biomarker), and decreases the levels of reactive oxygen species in PC12 cells.One study demonstrated that ZJF exhibited protective effects against PC1 cell glucose-induced toxicity by decreasing apoptosis and reactive oxygen species production [49].Another study evaluated the effect of jujube fruit extract on oxidative stress in the hippocampus and spatial memory of rats treated with ethanol.Treatment with jujube extract (JE) after ethanol exposure increased the level of glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and decreased the level of lipid peroxidation (malondialdehyde (MDA)); however, it had no significant effect on the level of superoxide dismutase.These results indicated thatZiziphus jujubaextract reduced spatial memory impairment induced by ethanol because of high levels of antioxidant compounds[50].
Anti-Alzheimer’s activity
Oleamide has been isolated from jujube fruit and it exhibits protective effects against scopolamine-induced cholinergic toxicity and activates choline acetyltransferase.Oleamide may be an effective component against Alzheimer’s disease [51].Snakin-Z was evaluated for its neurobiological activities, including cholinesterase inhibition and antioxidant activity.Snakin-Z exhibits potential antioxidant activity and anticholinesterase (acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase) inhibition.This peptide is a good natural source for treating Alzheimer’s disease [52].
Antiepileptic activity
The hydroalcoholic extract of jujube fruit (HEJF) exhibited anti-seizure activity in rats.HEJF exhibited anticonvulsant activity against generalized tonic-clonic seizures and tonic hindlimb extension in rats.This study revealed that HEJF attenuated epileptic-induced cognitive impairment through improving learning and memory,reversing oxidative stress, decreasing cholinesterase activity, and exhibiting anticonvulsant activity [53].Moreover, HEJF showed that co-administration with sub-therapeutic conventional antiepileptic drugs (phenytoin, phenobarbital, and carbamazepine) revealed no significant changes in the serum concentrations of antiepileptic drugs.It also decreased MDA levels, and increased glutathione levels.Co-administration of HEJF with phenobarbital and phenytoin improved their activities, whereas co-administration with carbamazepine resulted in no significant change[54].
Hepatoprotective activity
Jujube polysaccharides (JP) have hepatoprotective activity in mice and can suppress the injury caused by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) in the liver.JP significantly reduced the CCl4-elevated activities of lactate dehydrogenase, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and alanine aminotransferase(ALT) in the serum of mice(p<0.01).Moreover, JP decreased hepatic MDA levels.Mice treated with JP demonstrated normal GPx and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activities [23].Furthermore, the hepatoprotective activity was evaluated.The results revealed that hepatoprotective activity increased the levels of antioxidant enzymes(SOD and catalase(CAT)) and glutathione(GSH),and decreased the levels of aminotransferase enzymes (ALT and AST)and MDA.Furthermore, hepatoprotective activity improved the histological effects.The investigation showed that hepatoprotective activity possesses hepatoprotective activity because of its potential antioxidant capacity [55].Jujube fruit extract was evaluated for ischemia-reperfusion-induced liver injury by clamping the hepatic artery and portal vein in rats.The findings revealed that JE decreased ischemia-reperfusion-induced liver damage because of its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities [56].In addition, JE decreased the levels of aminotransferase (ALT and AST) and MDA and elevated the activity of antioxidant enzymes (glutathione peroxidase(GSH-Px), SOD, and CAT).Moreover, JE was beneficial against liver toxicity [57].Maslinic acid in the pulp of jujube fruit exhibits hepatoprotective activity against CCl4-induced liver toxicity [9].
Cardioprotective activity
The phenolic compounds of jujube peel showed preventive activity against myocardial injury induced by isoproterenol and aluminum chloride (AlCl3) biotoxicity in rat brains.A histological investigation showed that the co-administration of jujube phenolics showed protective activity against brain and cardiac injury.Jujube phenolic compounds decreased the activity of the antioxidant enzymes(Ca2+-ATPase, Mg2+-ATPase, Na+/K+-ATPase) and the level of lipid peroxidation, improved hematological parameters, and maintained the normal activity of acetylcholinesterase[58].
Nephroprotective activity
The activity of the aqueous extract ofZiziphus jujubafruit was evaluated on ibuprofen-induced nephrotoxicity in rats.The histological parameters and kidney biomarkers were investigated.Ibuprofen damaged the proximal convoluted tubules and glomeruli.The co-administration of JE with ibuprofen reduced the elevated levels of serum urea and creatinine, improved histological damage,and decreased the activity of CAT and GSH.This extract has nephroprotective activity against ibuprofen-induced toxicity[59].
Gastrointestinal protective activity
The effect of HEJF on ulcerative colitis in rats was evaluated in a study with two different forms (topical gel and oral consumption).The results indicated that topical gel (40%) was more potent than oral jujube (3,000 mg/kg), although both forms were effective (oral and trans-rectal).The extract improved colon tissue histopathology,reduced the levels of interleukin-1β (IL-1β), myeloperoxidase, and GPx, and increased the activity of GPx and SOD [60].Jujube fruit extract has been used to treat chronic constipation in a double-blind placebo-controlled trial in humans.The extract and placebo were administered to 50 patients over 12 weeks.The severity of constipation decreased in the group that received jujube compared with that of the control group.Furthermore, there was decreased bloating, abdominal pain, and difficulty evacuating.This treatment was effective and safe for chronic constipation [61].The chemopreventive activity of the jujube fruit on colon cancer was evaluated.The protective effect of jujube on colon carcinogenesis-related colitis was investigated in azoxymethane-dextran sodium sulfate-treated mice.The mice showed significantly decreased aberrant crypt foci (ACF) formation.AOM is a colon cancer agent that causes ACF formation in animal models for experimental study.Histopathological evaluation revealed that the consumption of jujube fruit decreased the formation of ACF and inflammation, which could postpone the progression of colon cancer.Jujube fruit decreases the number of white blood cells and platelets by decreasing inflammation and colon cancer progression [62].
Respiratory protective activity
The anti-allergic and anti-asthmatic activity of theZiziphus jujubafruit extract were evaluated in ex vivo and in vivo models.The results showed that treatment with jujube exerted anti-asthma and anti-allergic activity via the stabilization of mast cells due to the compounds found in jujube (flavonoids and steroidal saponins) [63].The anti-asthmatic activities of the extract of jujube fruit and one of its saponins, jujuboside B, were evaluated in a study.The extract of jujube fruit and jujuboside B suppressed asthmatic exacerbations via various mechanisms, including immunomodulatory,anti-anaphylactic, mast cell-stabilizing, anti-allergic,anti-inflammatory, and antihistamine activities [64].
Biochemical and hematological activity
The effects of jujube fruit on biochemical and hematological parameters were evaluated.Jujube fruit increased multiple hematological parameters (Red blood cell and white blood cells) and decreased platelet counts.Furthermore, jujube fruit decreases multiple biochemical parameters (blood glucose, triglyceride, and cholesterol levels) [65].
Anti-obesity and hypolipidemic activity
The extract of ZJF has anti-obesity activity through the differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes to adipocytes, suppression of the activity of glycerol-3 phosphate dehydrogenase, and accumulation of lipids.There is also no effect on cell death.Organic fractions, such as the chloroform fraction of jujube, have the highest inhibitory effect on transcription factor expression [66].The anti-obesity and hypolipemic activity ofZiziphus jujubafruit powder have been evaluated in a previous study.The results showed that this powder reduced the levels of total cholesterol, low-density lipoproteins, and body mass index in all groups, while the level of triglyceride decreased, and the level of high-density lipoprotein increased slightly at a high dose.The AST level decreased but the ALT level increased.The results showed that jujube fruit powder had hypolipidemic and anti-obesity activity [67].
Hypoglycemic activity
One study assessed the effect of jujube fruit extract for hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic activities in rats.Adiponectin, a protein hormone secreted from adipocytes, modulates the fatty acid and glucose metabolic pathways.In diabetic rats, jujube fruit decreased the levels of fasting blood sugar, very low-density lipoprotein, and TG and increased the levels of high-density lipoprotein and adiponectin, but had no effect on the levels of low-density lipoproteins and total cholesterol [68].
Immunomodulatory activity
One study investigated the immunological effects of two polysaccharides isolated fromZiziphus jujubafruit, Ju-B-2 and Ju-B-3.The study showed that Ju-B-2 had immunological effects on splenocyte proliferation at doses above 30 µg (dose-dependent),whereas Ju-B-3 did not show any proliferative effects when compared to the control group.Evaluation of splenocyte proliferation indicated that Ju-B-2 induced proliferation in a dose-dependent manner, but Ju-B-3 did not exhibit a stimulatory effect [69].The crude and purified polysaccharides of jujube fruit were evaluated immunological activity in mice.Four water-soluble fractions (ZSP1, ZSP2, ZSP3, and ZSP4) were obtained.The ZSP3 and ZSP4 fractions enhanced the proliferation of peritoneal macrophages and splenic cells and they also had anti-complementary activity.ZSP3 exhibited the highest effect out of all the fractions.The ZSP3a, ZSP3b, ZSP3c, ZSP4a, and ZSP4b fractions were evaluated for lymphocyte proliferation in spleens.The study showed that ZSP3c and ZSP4b were the most active compounds.The ZSP3c fraction (rich in pectin) showed a potential immunological response with 49% esterification, which may be related to its immunologic effects [70].Furthermore, JE was investigated for non-specific immune parameters and its effect on mRNA levels of immune-related genes in carp fingerling skin.The mucus immune parameters (total Ig, protease, and lysozyme activity) of the skin and the cytokine genes (TNF-α, IL-10, IL-8, and IL-1b) were examined at the end of the study.The results showed that jujube supplementation had an immunostimulatory effect on fish.JE administration increased mucosal immunity and this was proven through measuring cytokine gene expression and immune parameters [71].Moreover,ziziphus-arabinan is a water-soluble polysaccharide obtained from jujube fruit that exhibits anti-complementary effects through alternative and classical pathways[72].
Anti-cancer activity
One study found that JE inhibited the growth and induced apoptosis in breast cancer cell lines (estrogen receptor alpha (ERα)-positive MCF-7 (human breast cancer cell line) and ERα-negative SKBR3(human breast cancer cell line).ZE1, ZE2, and ZE4exhibited anti-proliferative effects in ERα-positive MCF-7 and ERα-negative SKBR3 cells.The extracts (ZE2and ZE4) exhibited the most significant effect on inducing apoptosis in malignant cells owing to the high content of triterpenic acids [18].The aqueous extract of jujube exhibited anti-tumor activity against nitrosourea-induced breast cancer in female rats.Jujube is a good natural source of chemotherapeutic agents [73].In another study, an aqueous extract induced apoptosis and inhibited proliferation of the HeLA (human cervical carcinoma cell line) tumor cell line, HEp-2 (human larynx carcinoma) cell line, and Jurkat cell line(T cell leukemia).Jurkat cells are the most sensitive cell line and jujube exhibits the highest anti-proliferative activity in this cell line [8].The jujube fruit extract exhibited anti-cancer activity against hepatoma cells (HepG2) by inducing arrest at different stages of the cell cycle and induced apoptosis.A low concentration arrested the G1phase, and a high concentration arrested the G2/M phase of the cell cycle.This study demonstrated that the anti-tumor activity of jujube fruit was dose-dependent on cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in HepG2 cells [21].The chloroform fraction (CHCl3-F)of jujube with green tea extract was evaluated on HepG2.The results showed that this combination increased the levels of p21Waf1/Cip1and p53 and arrested the G1phase.This combination enhances cell growth inhibition via a mechanism different from that of CHCl3-F alone [74].All stages of jujube ripeness were evaluated in different cell lines (Hel299 normal lung, HeLa cervical cancer, A549 lung cancer, and U937 lymphoma cells).All variations in jujube ripeness inhibited HeLa cervical cancer cells in a dose-dependent manner, while mature fruits decreased the inhibition of Hel299 normal lung and A549 lung cancer cells.This inhibition is due to the flavonoid content and antioxidant activity.However, JE did not have any effect on U937 lymphoma cells [75].However, JE exhibited anti-cancer effects on human thyroid carcinoma cells(C643).It plays anti-proliferative and apoptotic roles by inhibiting growth and inducing apoptosis in the C643 cell line [76].The deproteinized polysaccharide isolated fromZiziphus jujubahas anti-cancer effects on melanoma cells.Deproteinized polysaccharide(DPP) inhibited cell proliferation in a time- and dose-dependent manner.DPP induced cell cycle arrest in the G2/M phase and induced apoptosis.Furthermore, DPP increases the activity of caspase-3 and caspase-9 [77].JE also demonstrated apoptotic and anti-tumorigenic activities in MCF-7 (breast cancer cells) and OV2008 (cervical cancer cell line).JE selectively inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis[78].
Anti-genotoxic activity
The activity of jujube andOriganum majoranaextract on hydroquinone-induced genotoxicity in mice has been studied.Hydroquinone induces DNA damage, chromosomal aberrations, and oxidative stress in mice.The results showed that these two extracts possessed protective activity against hydroquinone-induced genotoxicity because of their high antioxidant content.Ziziphus jujubashowed more genotoxic effects thanO.majorana[79].The polyphenolic and hydroalcoholic extracts of jujube fruit were evaluated for their effects on genotoxicity induced by methyl methane sulfonate in HepG2 cells.The polyphenolic extract exhibited a better genoprotective effect at lower concentrations because of its high antioxidant activity [80].The ethanolic extract of jujube fruit and its component BA were evaluated for their effects on genotoxicity induced by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and methyl methane sulfonate in mice and in vitro models.The results showed that jujube fruit and BA possess antioxidant and anti-genotoxic activities owing to their potential antioxidant activity and high polyphenolic content [81].
Wound healing activity
One study found that jujube fruit extract had wound-healing properties in vivo in second-degree burn wounds.In this study,Vaseline and silver sulfadiazine were used as the negative and positive groups, respectively.There was a significant difference in burn healing between the control and jujube groups, and JE accelerated the wound-healing process [82].The effect of the jujube fruit lotion was evaluated in 100 lactating females with nipple fissure pain in a double-blind controlled clinical trial.The results showed that jujube lotion significantly attenuated the severity of nipple fissure pain by the 7th and 14th days after intervention [83].Water-soluble glucans isolated from jujube improve cell migration and cellular survival,which are important for wound healing.Soluble glucans are a suitable choice for wound healing and damaged skin regeneration [84].
Anti-melanogenic activity
One study showed the anti-melanogenic activity in vitro of jujube fruit extract using two different methods: Soxhlet extraction and percolation with 80% methanol.The results showed that the JE had anti-tyrosinase activity and anti-melanogenic activity.This study concluded that it may be effective in dermatological disorders,including age spots, melasma, and acne, and can be used as a dermatological whitening agent [85].
Anti-aging activity
Jujube fruit exhibited anti-aging effects in aDrosophilamodel (in vivo).The consumption of jujube fruits byDrosophilaextended their lifespan and promoted their health.In this investigation, flies were fed two doses of jujube fruit powder (30 mg/mL and 150 mg/mL) in contrast to the control group.The results showed that jujube fruit powder increased their lifespan and improved their health at a dose of 150 mg/mL [27].
Conclusion
It is possible that most of the studies discussed in this present review have not been performed in accordance with a standardized protocol employing the best practices in pharmacological research on bioactive preparations from plants.In this review, data from the phytochemical and pharmacological investigations showed that jujube fruit has medicinal and nutritional properties and it is also a good choice for the human diet.Jujube is an important and well-known herbal medicine.Jujube has been used in ethnomedicine for many diseases because of its numerous secondary metabolites.Furthermore, jujube is a valuable fruit in traditional Persian medicine.It has both nutraceutical and cosmeceutical effects.Because of these two valuable effects, jujube can be classified as a nutricosmetic fruit.There are no reports of toxicity or serious side effects of jujube; therefore, it seems to be a safe and valuable fruit.
 Traditional Medicine Research2022年4期
Traditional Medicine Research2022年4期
- Traditional Medicine Research的其它文章
- Integration of multi-omics in investigations on the mechanisms of action of Chinese herbal medicine interventions in metabolic diseases
- Active compounds in RenShenJian decoction ameliorate insulin resistance in vitro
- Quality evaluation of Pinelliae Rhizoma using network pharmacology and multicomponent quantitative analysis
- Inhibition of rat prostate smooth muscle contractility by extracts of Costus speciosus(crepe ginger)
- Biologically active components for cosmeceutical use extracted from Chaetomorpha aerea
- Advances in traditional Chinese medicine for respiratory disease therapy in 2021
