Two-Dimensional Copper-Based Coordination Polymer:Synthesis,Structure and Ion Effect on Adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ)
LI Shi⁃XiongFENG An⁃QiHU YuanLIANG Gui⁃ChunLU Li⁃FeiLU Hui⁃Ping
(1School of Mechanical and Resource Engineering,Wuzhou University,Wuzhou,Guangxi 543002,China)
(2Wuzhou Resource Recycling Engineering Technology Research Center,Wuzhou University,Wuzhou,Guangxi 543002,China)
Abstract:Coordination polymers usually have the characteristics of large specific surface area and easy control of structure,which can effectively adsorb and remove Cr(Ⅵ) in water.A copper⁃based coordination polymer:{[Cu(bipy)4(1,3 ⁃dab)][Cu(bipy)2(ClO4)2](ClO4)2· (1,3 ⁃dab)}n(1),was successfully synthesized by the hydrothermal synthesis method using 4,4′⁃bipyridine(bipy),1,3⁃isophthalonitrile(1,3⁃dab),Cu(ClO4)2·6H2O as raw materials.The structure of 1 was characterized by IR,X⁃ray single⁃crystal diffraction,elemental analysis,and X⁃ray photoelectron spectros⁃copy.The results show that 1 belongs to the orthorhombic crystal system,P2221space group,a=1.115 52(5)nm,b=1.116 66(4)nm,c=3.116 84(15)nm,V=3.882 5(3)nm3.The performance study of adsorbing Cr(Ⅵ)showed that the optimal dosage of adsorbent 1 was 0.04 g·L-1.It had good adsorption performance and pH adaptability in a pH range of 1⁃9.The adsorption performance was the best when pH=5,and the adsorption capacity could achieve 250 mg·g-1.The ion coexistence experiments showed that the greater the ion concentration and the higher the valence,the more obvious their effect on the adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ)by 1,and the inhibition of anion was higher than that of metal cations,followed the order of
Keywords:coordination polymers;synthesis;structure;Cr(Ⅵ);adsorption
0 Introduction
With the continuous development of industry,the unreasonable exploitation of natural resources,and the random discharge of wastewater,the problem of water pollution has become particularly prominent[1⁃5].The current water pollution problems mainly include organ⁃ic pollution,heavy metal ion pollution,and biological pollution[6].The metallic chromium(Cr)is a common non⁃ferrous metal in life,and it has been widely used in material processing,paint making,and electroplat⁃ing[7].Although Cr is an essential trace element for the human body,the heavy metal Cr(Ⅵ)ion is difficult to degrade,difficult to digest,easy to accumulate in the body,and has high biological toxicity.It is already an indicator of water quality testing[8].The removal meth⁃ods of Cr(Ⅵ)ions include photocatalytic reduction,ion exchange,membrane separation,chemical precipita⁃tion,and adsorption separation[9⁃12].Among them,the adsorption removal method is to use the adsorbent to adsorb Cr(Ⅵ) ions through coordination bonds,electro⁃static attraction,hydrogen bonds,and other forces to achieve the effect of removal.The adsorption method has the advantages of simple operation,low cost,fast and efficient,reproducible recycling,and has been widely studied and applied[13⁃15].The current adsorbents used for the removal of heavy metal ions such as Cr(Ⅵ)mainly include activated carbon,biomass activated car⁃bon,zeolites,molecular sieves,gels,and carbon nano⁃tubes[16].And research shows that adsorbents with high specific surface area,abundant adsorption sites,and well⁃developed pore size distribution often have good adsorption performance.However,the adsorption and removal of heavy metal ions by most adsorbents have the disadvantages of low adsorption capacity,poor selectivity,and difficulty in regeneration and reuse.Coordination polymers usually have a large specific surface area and the structure is easy to modify,and there are extensive studies in the fields of fluorescence,magnetic,adsorption separation,and photocatalytic degradation[17⁃29].They are showing the potential for application.
In this paper,a copper⁃based coordination poly⁃mer:{[Cu(bipy)4(1,3⁃dab)][Cu(bipy)2(ClO4)2](ClO4)2·(1,3⁃dab)}n(1)was successfully synthesized by using 4,4′⁃bipyridine (bipy),1,3⁃isophthalonitrile (1,3⁃dab),Cu(ClO4)2·6H2O as raw materials.The structure of 1 was characterized by IR,X⁃ray single⁃crystal diffrac⁃tion,elemental analysis,and X⁃ray photoelectron spec⁃troscopy(XPS).The influence of the dosage,tempera⁃ture,pH,and coexisting ions on the adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ)by adsorbent 1 was explored.
1 Experimental
1.1 Instruments and reagents
The Nicolet 5DX FT⁃IR spectrometer was used to characterize and test the presence of hydroxyl functional groups in 1.The structure of 1 was tested and analyzed by using Rigaku′s D/max 2500 X⁃ray powder diffrac⁃tometer(XRD).The test conditions were as follows:Cu Kα (λ=0.156 04 nm),40 kV(tube voltage),150 mA(tube current),graphite monochromator,5°⁃65°(2θ).The morphology of 1 was observed by the Hitachi SU8010 scanning electron microscope(SEM),the acceleration voltage during the test was 1.0 kV.The structure of 1 was tested using APEX⁃Ⅱ CCD X⁃ray single crystal diffractometer produced by Bruker,Ger⁃many.The N2adsorption⁃desorption curve of 1 was gained at 77 K by AUTO CHEM II 2920 from Ameri⁃can Micro Instrument Company,and the specific sur⁃face area was calculated by the Brunauer⁃Emmett⁃Teller method.The concentration of Cr(Ⅵ)was analyzed using UV⁃2601 UV⁃Vis spectrophotometer produced by Beijing Ruili Analytical Instrument Co.,Ltd.
The chemical reagents used in the experiment,such as bipy,Cu(ClO4)2·6H2O,1,3 ⁃dab,NaCl,KCl,MgCl2,CaCl2,CuCl2,FeCl3,NaNO3,Na2SO4,NaHCO3,Na2CO3,Na3PO4,and methanol were analytically pure reagents,produced by Energy Chemical Co.,Ltd.(Shanghai,China).The pure water used in the experi⁃ment was prepared by reverse osmosis in the laboratory.
1.2 Synthesis of complex 1
A mixture of Cu(ClO4)2·6H2O(0.074 0 g,0.2 mmol),and bipy(0.061 0 g,0.2 mmol)in 10 mL of water and 10 mL of anhydrous methanol was added 5 mg of 1,3⁃dab,and a blue solution was obtained.After the reaction was over,the mixture was filtered and the filtrate was collected in a 50 mL beaker.The filtrate was naturally volatilized for 5 d to obtain blue⁃purple massive crystals.The yield was about 78%(based on Cu2+).Elemental Anal.Calcd.for C80H64Cl4Cu2N16O16(%):C 54.10,N 12.62,H 3.61;Found(%):C 54.10,N 12.61,H 3.61.IR(KBr,cm-1):3 443(s),2 978(m),2 911(w),2 263(w),1 626(s),1 384(w),1 095(w),1 036(m),878(m),630(w).
1.3 X-ray single crystal diffraction
A single crystal with a size of approximately 0.13 mm×0.12 mm×0.11 mm for 1 was used for structural test analysis on a Bruker′s APEX⁃Ⅱ CCD single crys⁃tal diffractometer.The test conditions were as follows:MoKα(λ=0.071 073 nm),T=150(2)K.A total of 9 218 reflections were collected during the test,of which 7 120 reflections were used.Olex2 software was used to analyze the structure of 1,add hydrogen atoms and refine the structure.The parameters of 1 are listed in Table 1,and selected bond lengths and bond angles are listed in Table 2.
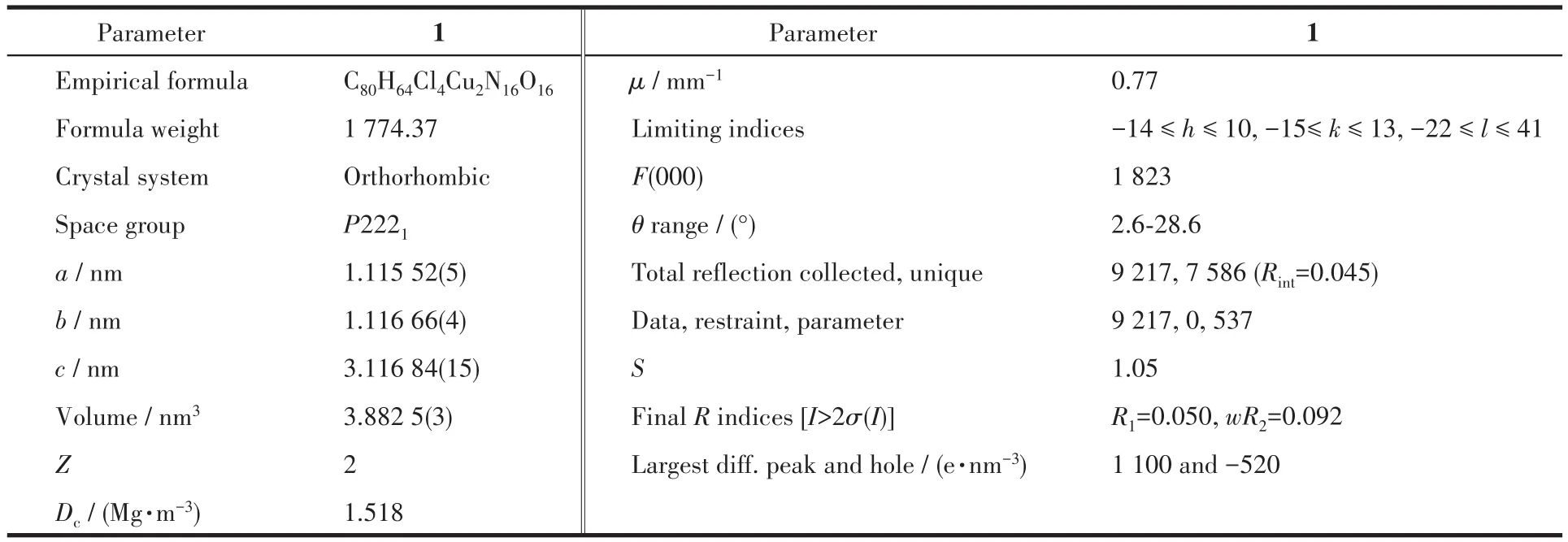
Table 1 Crystal data and refinement parameters of 1
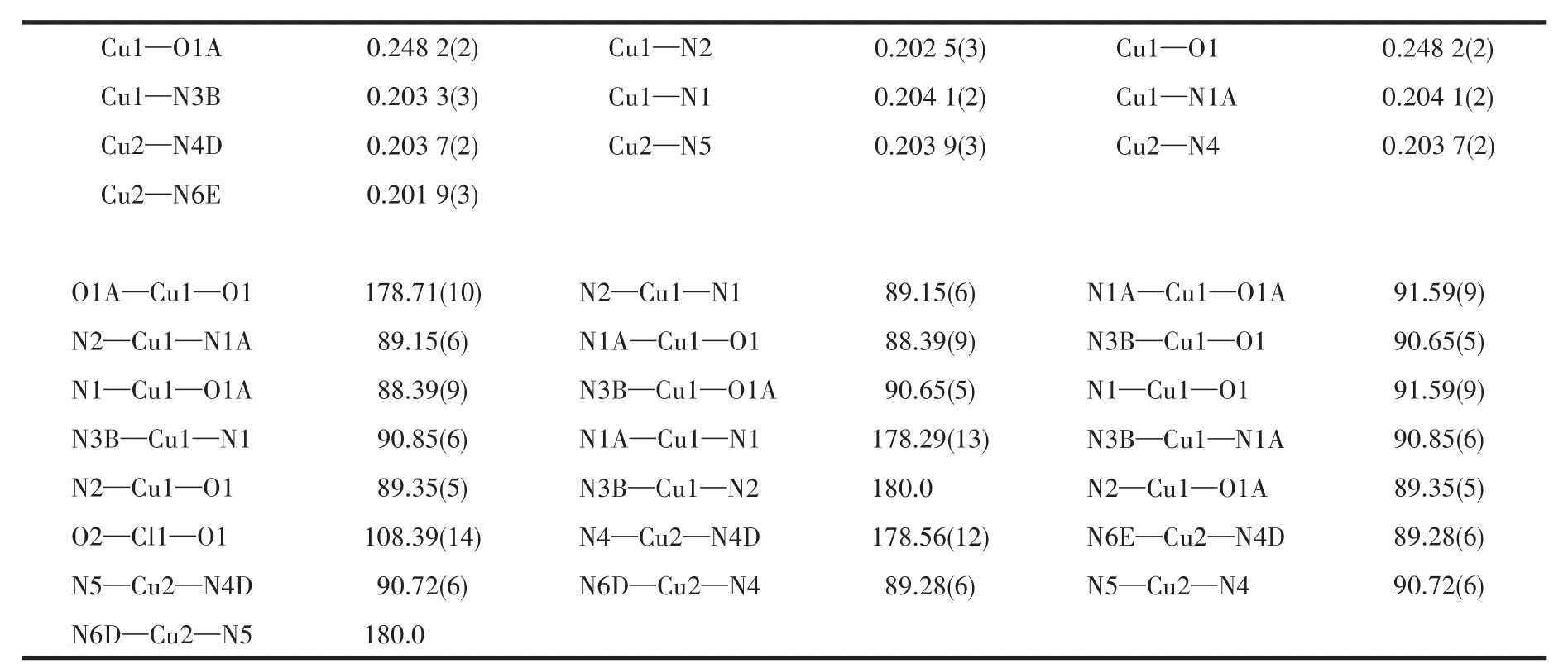
Table 2 Selected bond length(nm)and bond angle(°)of 1
CCDC:2114736.
1.4 Adsorption experiment
During the experiment,a certain amount(0.001 0⁃0.005 0 g)of 1 was put into a 250 mL beaker with a circulating water system,and then 50 mL of Cr2O72-(5 mg·L-1,pH=3⁃7)was added into the beaker.After stirring and adsorbing for 30,60,90,and 120 min at a certain temperature(25,30,35,40,45℃),5 mL of the mixed solution was drawn with a 10 mL syringe equipped with a 0.45µm filter,and the collected filtrate was put into a cuvette.The absorbance was mea⁃sured with an UV ⁃Vis spectrophotometer at a wave⁃length of 420 nm.The corresponding concentration ofwas calculated by the standard curve:A=0.005 4c-0.001 6(R2=0.994 5),where A is the absor⁃bance of the solution and c is the concentration of Cr2O72-.The adsorption performance was evaluated by the change of Cr2O72-concentration before and after the adsorption.The adsorption rate(R)was calculated as follows:
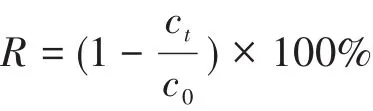
For the adsorption experiment,the c0and ctare the initial concentration and the concentration at t,respec⁃tively(mg·L-1).
The regeneration of the adsorbent will affect its application.Therefore,a high⁃speed centrifuge was used to collect 1 after the adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ) by centrif⁃ugal separation.The HCl solution with pH=1 was add⁃ed to the adsorbent,then the mixture was sonicated for 20 min,and centrifuged to collect the solid powder.The solid powder was washed with deionized water and dried in a blast drying oven at 100℃for 12 h.Then,the desorbed 1 was used for the cycling experiment insolution with T=30℃and pH=5.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Structure of 1
Herein,a copper⁃based coordination polymer:{[Cu(bipy)4(1,3 ⁃dab)][Cu(bipy)2(ClO4)2](ClO4)2· (1,3 ⁃dab)}n(1)was successfully synthesized by the bipy,Cu(ClO4)2·6H2O,and 1,3 ⁃dab as raw materials.The XPS test result(Fig.1a)showed that 1 was composed of Cu,C,N,and O elements.The XPS spectra of 1 showed that it had characteristic diffraction peaks relat⁃ed to copper ions at 933,934,943,952,954,and 963 eV(Fig.1b).Among them,the diffraction peaks at 933 and 934 eV are the characteristic diffraction peaks of the Cu2p3/2orbital in Cu2+.The diffraction peaks at 943 eV are the shock peaks of the Cu2p3/2orbital in Cu2+.The two diffraction peaks at 952 and 954 eV belong to the Cu2+spin⁃orbit splitting peak.The diffraction peak at 963 eV is the excitatory peak of the Cu2p1/2orbital in Cu2+.Therefore,the metal ions in 1 are all Cu2+,and its outermost nuclear electron arrangement should be 3d9.
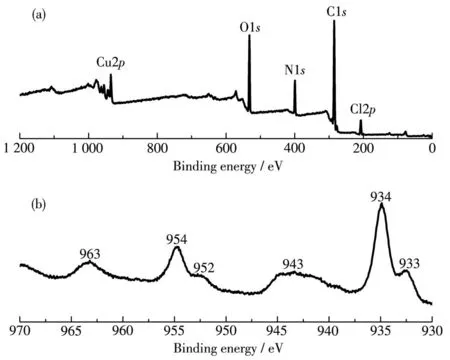
Fig.1 XPS spectra of 1:(a)survey;(b)Cu2p
The X⁃ray single⁃crystal diffraction analysis results show that 1 belongs to the orthorhombic crystal system P2221space group.The asymmetric structural unit of 1(Fig.2a)shows that it is composed of two Cu2+ions,six bipy molecules,four ClO4-anions,and two 1,3⁃dab molecules.In 1,the Cu2+has two different coor⁃dination modes:[Cu(bipy)4(1,3⁃dab)]2+and[Cu(bipy)2(ClO4)2].In the structural unit of[Cu(bipy)4(1,3⁃dab)]2+,the central Cu2+is coordinated with six N atoms,among which four N atoms are from four bipy molecules,and two N atoms are from 1,3⁃dab molecules(Fig.2b).While in the structural unit of[Cu(bipy)2(ClO4)2],the central Cu2+is coordinated with four N atoms from two bipy molecules and two O atoms from ClO4-anions(Fig.2c).
Due to the influence of the Ginger⁃Taylor effect,in the structural unit of[Cu(bipy)2(ClO4)2],the four N atoms in the ab plane approach the Cu2+ion.The bond length of the Cu—N bond ranges from 0.202 5(3)to 0.204 1(2)nm.The O atom in the z⁃axis direction departs from Cu2+,causing the bond length to be elon⁃gated(Cu—O 0.248 2(2)nm).In complex 1,since there are two N atoms in the bipy molecule,it can coor⁃dinate with two Cu2+.Therefore,the bipy molecule in 1 bridges two similar Cu2+ions by the form of μ2.Thus,a 2D material is formed(Fig.2d).Usually,during the syn⁃thesis of the complex,the organic molecule bipy is introduced into the material in the form of a second ligand.Its coordination with metal ions can often form 1D[30],2D[31],and 3D complexes[32].These complexes are constructed from more than two kinds of ligands.Com⁃plex 1 is similar to their coordination mode.The N2adsorption⁃desorption curve of 1(Fig.3)showed that it belongs to a typical s⁃type adsorption isotherm,and its specific surface area was 145 cm2·g-1.
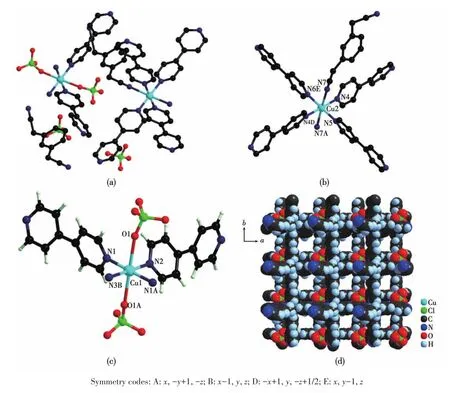
Fig.2 (a)Asymmetric structural unit of 1;(b)Structural unit of[Cu(bipy)4(1,3⁃dab)]2+;(c)Structural unit of[Cu(bipy)2(ClO4)2];(d)2D structure of 1
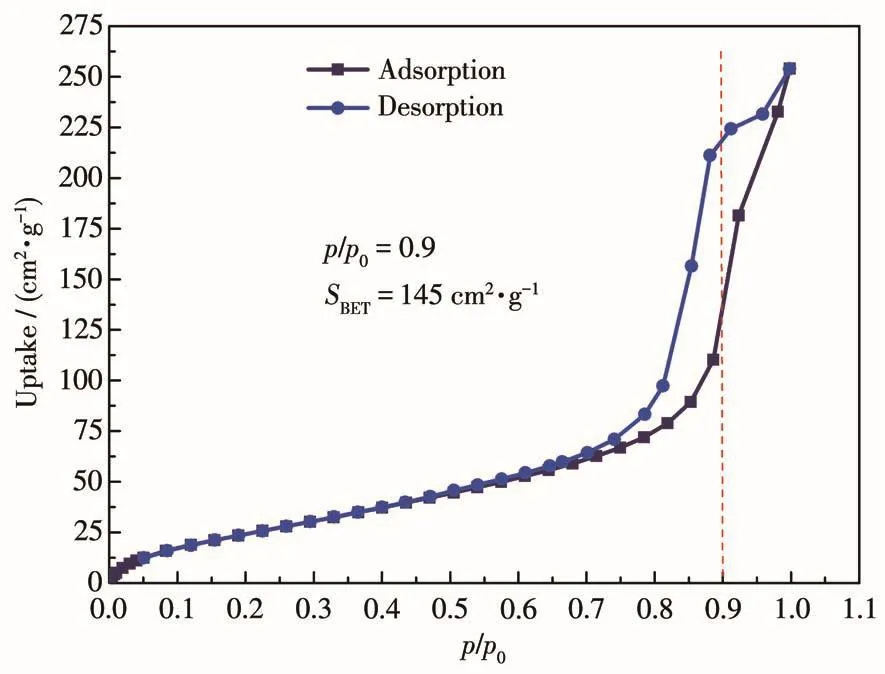
Fig.3 N2adsorption⁃desorption curve of 1
2.2 Adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ)
2.2.1 Effect of adsorbent dosage on the adsorption
At 30 ℃,a certain amount(0.001 0⁃0.005 0 g)of 1 adsorbent was added to the Cr2O72-solution with pH=7 to study the effect of adsorbent dosage on the adsorp⁃tion of Cr(Ⅵ).The experimental results(Fig.4a)showed that adsorption of Cr2O72-by 1 reached equilibrium after 120 min of adsorption.At this time,the adsorp⁃tion capacities(qe)were 230,250,220,211,and 198 mg·g-1,respectively.It can be seen that the qeof the adsorbent does not increase with the increase of the adsorbent dosage,but there is an optimal qe.The opti⁃mal dosage of 1 adsorbent was 0.002 0 g(Fig.4b).That is when the adsorbent mass concentration(ρ1)was 0.04 g·L-1,the adsorption performance of 1 was the best.Therefore,the subsequent experiments of pH and tem⁃perature effects on 1 adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ)were carried out when the adsorbent dosage was 0.002 0 g.Although the maximum qeof 1 can be as high as 250 mg·g-1,which is better than most adsorbents[33],which may be due to the structure of 1.Because 1 has a cationic structural framework,in addition to being able to adsorb Cr(Ⅵ)through hydrogen bonding,it can also adsorb Cr(Ⅵ)through strong electrostatic attraction.However,it is inferior to the maximum qeof 372.6 mg·g-1reported in the literature[34].
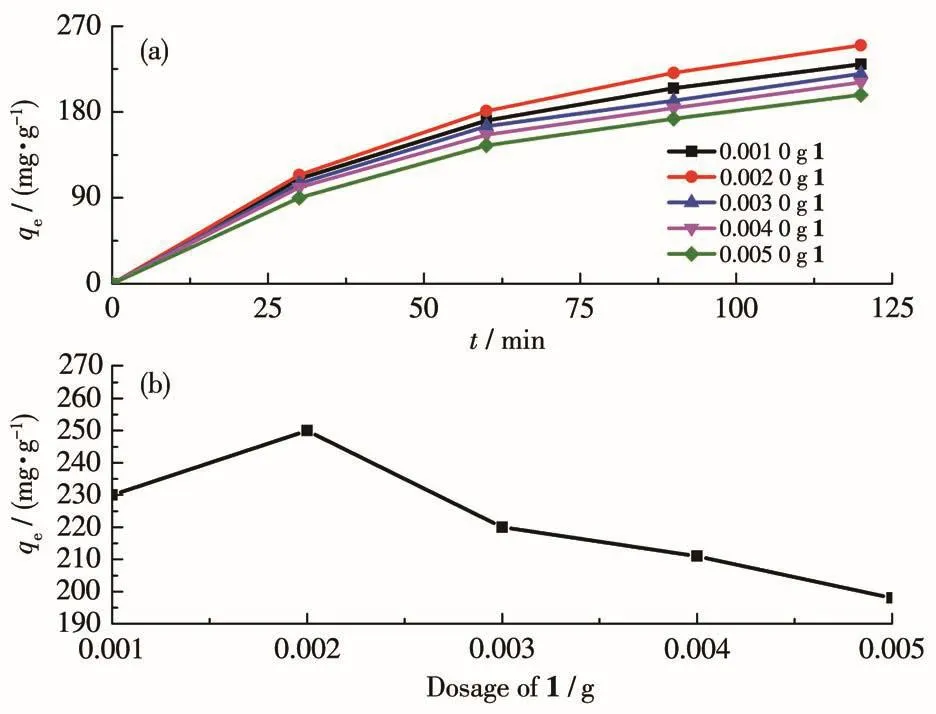
Fig.4 Effect of dosage of 1 on(a)the adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ),and(b)the maximum qe
2.2.2 Effect of pH on the adsorption
At 30℃,0.002 0 g of adsorbent was added to the solutions with different pH values to study the effect of pH on the adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ).The experimental results(Fig.5)showed that when pH=1 the adsorption rate(R)could reach 91.7% after 120 min;when pH=3 and 7,R=100% after 120 min;when pH=5,R=100% after 90 min;pH=9,R=81.8% after 120 min.It can be seen that the performance of 1 adsorbing Cr(Ⅵ)under acidic conditions is better than that under alkaline conditions.When pH=5,1 has the best adsorption performance,and the average removal rate could reach 0.002 8 mg·min-1.
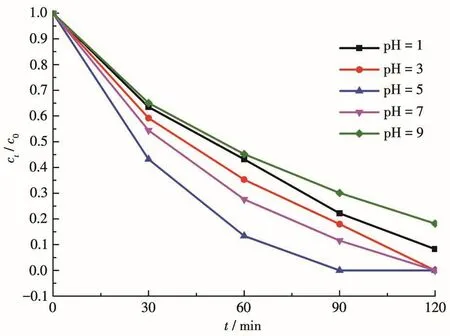
Fig.5 Effect of pH on the adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ)by 1
2.2.3 Effect of temperature on the adsorption
To explore the effect of temperature(25⁃45 ℃)on the adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ),0.002 0 g of 1 was added to the Cr2O72-solution with pH=5.The experimental results(Fig.6)showed that when T=25℃,R=94.9% after 90 min;when T=30℃,R=100.0% after 90 min;when T=35℃,R=85.4% after 90 min;when T=40℃,R=73.5% after 90 min;when T=45℃,R=63.5% after 90 min.Therefore,when the pH of the Cr(Ⅵ)solution was 5,the optimal adsorption temperature of 1 was 30℃.
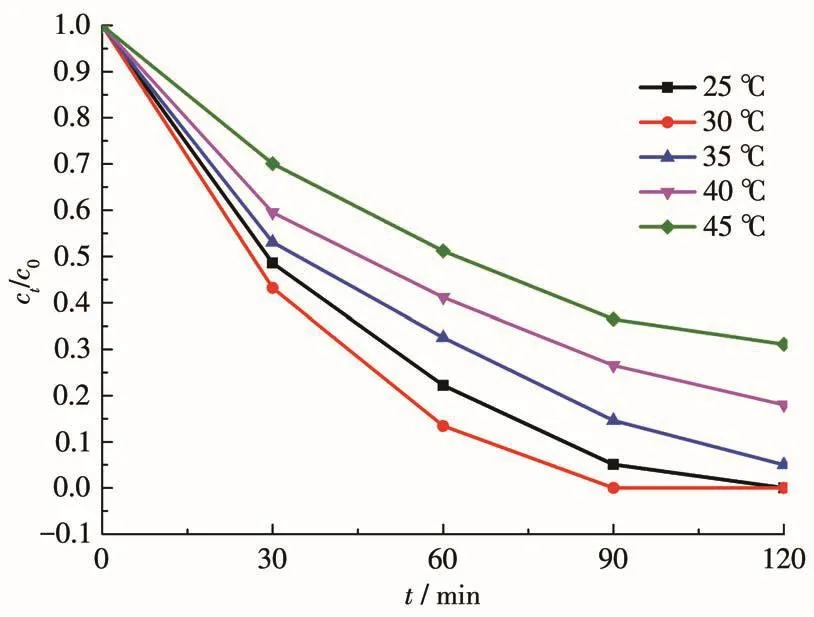
Fig.6 Effect of temperature on the adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ)by 1
2.3 Effect of ions on the adsorption
Whether it is rivers,seas,domestic wastewater,or industrial wastewater,there are various ions in the water.These ions sometimes have a significant effect on adsorption.Therefore,the influence of ions on adsorption cannot be ignored.1 L of inorganic salt solu⁃tion with pH=5 was prepared(NaCl,KCl,MgCl2,CaCl2,CuCl2,FeCl3,NaNO3,Na2SO4,NaHCO3,Na2CO3,Na3PO4;c=0.1,0.01,0.001,and 0.000 1 mol·L-1).At 30℃,0.002 0 g of 1 was added to explore the influ⁃ence of ions on the adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ).
In the influence experiment for Na+(Fig.7a)and K+(Fig.7b),the study found that when the ion concen⁃tration was 0.000 1 mol·L-1,the amount of Cr (Ⅵ)adsorbed by 1 was similar to that of the blank;but when the ion concentration was greater than 0.01 mol·L-1,the Na+,and K+had a certain effect on the removal of Cr(Ⅵ)by 1,and the adsorption rate remained above 80% after 120 min.In the experiment of the influence for Mg2+(Fig.7c),Ca2+(Fig.7d),and Cu2+(Fig.7e),the study found that the adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ) by 1 was simi⁃lar to that of Na+and K+.However,the inhibitory effect of Mg2+,Ca2+,and Cu2+was higher than that of Na+and K+;when the ion concentration was 0.000 1 mol·L-1,1 could adsorb about 98.3% of Cr(Ⅵ)after 120 min.The Fe3+(Fig.7f)inhibited 1 adsorbing Cr(Ⅵ)more obviously.When the ion concentration was 0.000 1 mol·L-1,1 could adsorb about 79.8% of Cr(Ⅵ)after 120 min.The effect of metal ions on the adsorption shows that the higher the ion concentration and valence,the greater the impact on the adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ)by 1.
In the study of the effect of inorganic anions on the adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ) by 1,it is found(Fig.8)that inor⁃ganic anions can significantly inhibit the adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ),and the higher the ion concentration and the valence,the more obvious the inhibitory effect.Since sodium salt was used in the experiment,the effect of Cl-(Fig.8a)on the adsorption was the same as that of Na+(Fig.7a).The inorganic anions NO3-and HCO3-are both negative monovalent anions,and their influence(Fig.8b and 8c)on the adsorption was similar to that of Cl-.The SO42-,CO32-,and Cr2O72-are all negative diva⁃lent anions,and the ionic radius of SO42-or CO32-is smaller than that of Cr2O72-,which significantly inhibit⁃ed the adsorption.When the concentration of CO32-and SO42-was 0.000 1 mol·L-1(Fig.8d and 8e),1 could adsorb about 78.1% and 79.9% of Cr(Ⅵ)after 120 min,respectively.The PO43-is a negative trivalent anion,which has a higher valence state than Cr2O72-,and had a greater inhibitory effect on the adsorption.When the concentration of PO43-was 0.000 1 mol·L-1(Fig.8f),1 could only adsorb about 68.3% of Cr(Ⅵ)after 120 min.The inhibitory effect of anions on 1 adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ)is more obvious than that of metal cations,mainly because anions are more likely to be adsorbed on the surface of 1.They thus compete with Cr(Ⅵ) for adsorp⁃tion.Although these ions can inhibit the adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ)by 1,they will not seriously affect the perfor⁃mance of 1 for adsorption and removal of Cr(Ⅵ).
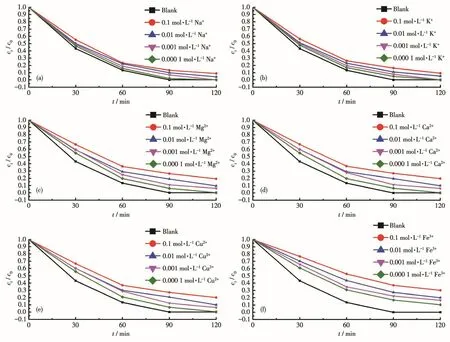
Fig.7 Effect of metal ions on the adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ)by 1
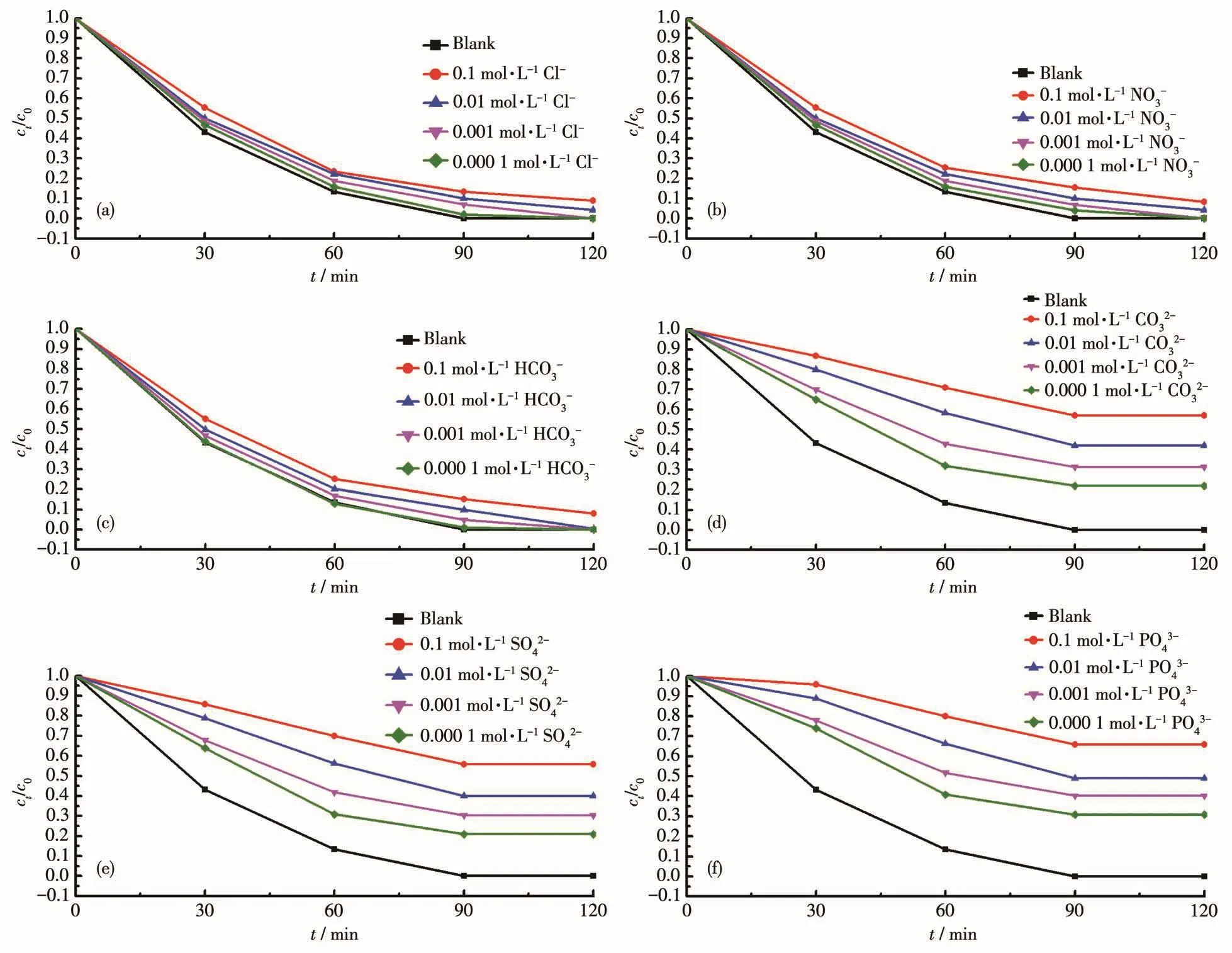
Fig.8 Effect of anions on the adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ)by 1
2.4 Regeneration and cycling experiment of the adsorbent
For the regeneration of 1,the XRD results of 1 after desorption showed that its diffraction peaks were consistent with the theoretical simulation peaks(Fig.9).This indicates that the structure of1 remains unchanged after adsorption⁃desorption.The results of the cycle experiment(Fig.10)showed that when the desorbed 1 was subjected to an adsorption cycle experi⁃ment,the qewas still 250 mg·g-1;when 1 was subjected to five adsorption cycles,the qewas 248 mg·g-1.The above results show that 1 has the advantages of easy regeneration and good Cr(Ⅵ)adsorption cycle perfor⁃mance.
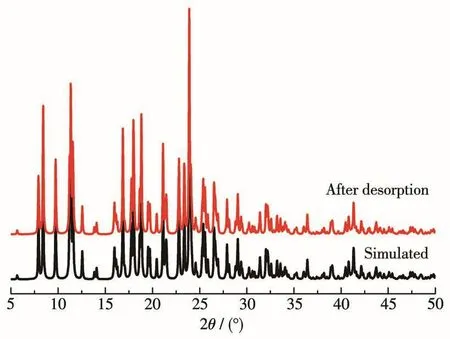
Fig.9 XRD patterns of 1 after desorption
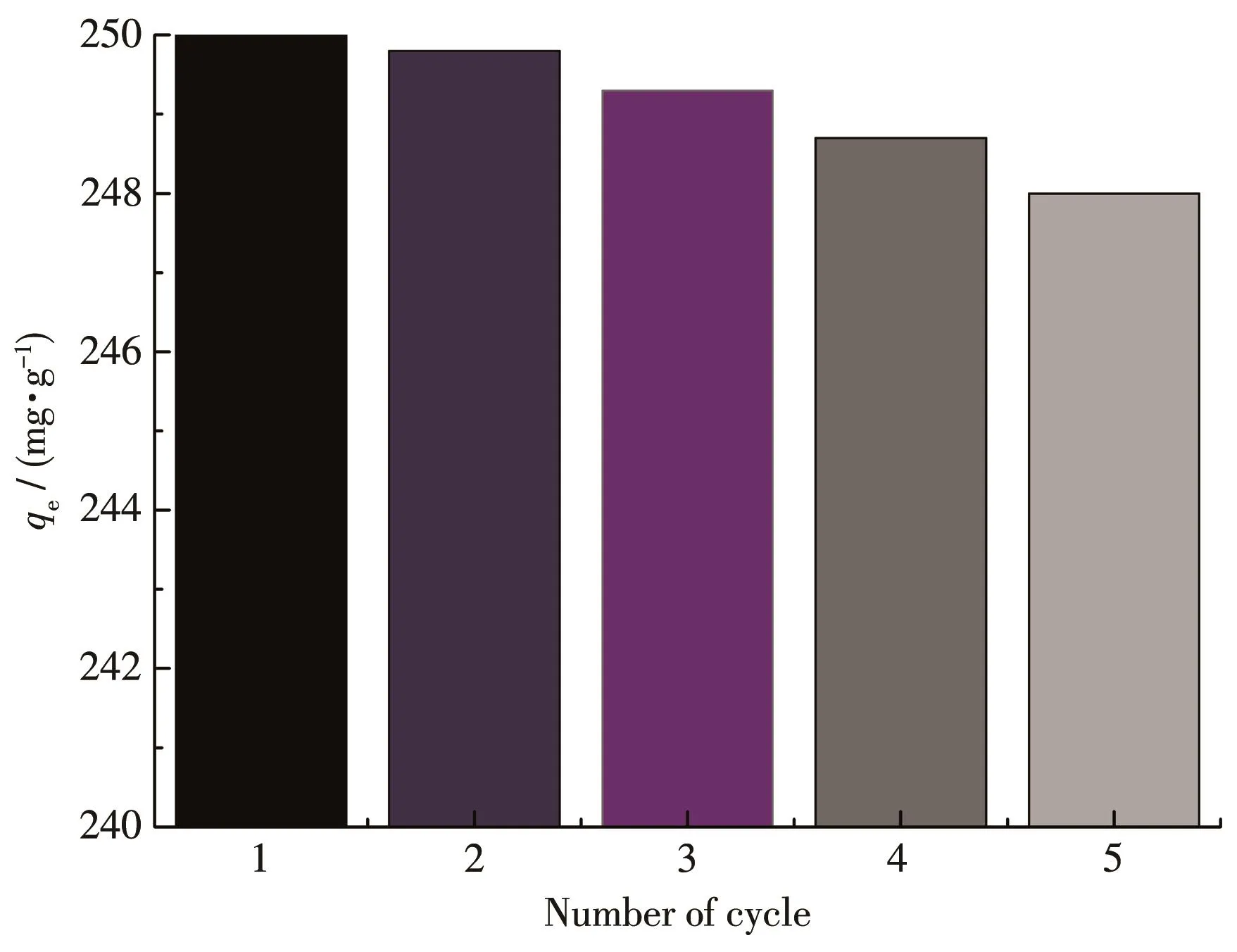
Fig.10 Cycle experiment of the Cr(Ⅵ)adsorption by 1
3 Conclusions
In summary,a 2D copper⁃based coordination poly⁃mer:{[Cu(bipy)4(1,3⁃dab)][Cu(bipy)2(ClO4)2](ClO4)2·(1,3⁃dab)}n(1),was successfully synthesized by hydrother⁃mal synthesis.The effects of adsorbent dosage,temper⁃ature,and pH on the adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ) by 1 were stud⁃ied.The results show that the optimal adsorption condi⁃tions are:ρ1=0.04 g·L-1,pH=5,T=30 ℃.The ion coex⁃istence experiments show that the greater the ion con⁃centration and the higher the valence state,the more obvious their influence on the adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ)by 1,and the inhibition of anion follows the order:PO43->SO42->CO32->Cl->HCO3->NO3-.The regeneration and cycling experiments of 1 show that it has the advantages of easy regeneration and good Cr(Ⅵ) adsorp⁃tion cycle performance.Therefore,it has the potential for application.
- 无机化学学报的其它文章
- 无机材料在骨质文物加固保护中的应用
- 百香果皮基原位氮掺杂多孔碳/硫复合正极的制备及储锂性能
- 氯钯共掺对Cs2TiBr6光电性能影响的第一性原理计算
- Performance of Different Metal-Modified HZSM-5 Catalysts for Methanol Carbonylation
- Interactions of a Water-Soluble Diiron Hexacarbonyl Complex with Biologically Relevant Molecules and Their Promotion in CO-Release
- Crystal Structures and Magnetic Refrigeration Properties of Two Gd2Complexes

