Biologic therapy for Crohn’s disease over the last 3 decades
INTRODUCTION
Crohn’s disease (CD),the main type of inflammatory bowel disease,is characterized as chronic,refractory,and relapsing transmural inflammation of the digestive tract[1].Due to the continuous activation of the intestinal immune system,CD patients would suffer chronic abdominal pain,diarrhea,weight loss,malnutrition,and other obstructive symptoms[2].Previously,the therapeutic strategy for CD was limited to corticosteroids[3],immunomodulators [methotrexate and thiopurines (azathioprine and mercaptopurine)][4-6],and surgery[7,8].In the past 3 decades,multiple biologics emerged for CD management,including anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF) agents(infliximab,adalimumab,and certolizumab),anti-integrin agents (vedolizumab and natalizumab),and anti-(IL)-12/23 agent (ustekinumab)[9].However,it is difficult for researchers to gain critical articles to guide their studies owing to the publication overload of varied scientific quality.
Bibliometrics is an increasingly conducted method for analyzing and summarizing the main characteristics of publications,including the citation count,the cooperative relationships among countries,institutions,and authors,the distribution of journals,and the hotspots in a certain field.By performing bibliometric analysis and creating infographics,researchers can identify and capture the research hotspots and rising patterns.Bibliometric analysis has been broadly performed in various diseases of gastroenterology,such asinfection[10],irritable bowel syndrome[11],acute pancreatitis[12],inflammatory bowel disease[13],and so on.Although Connelly[14] conducted a bibliometric analysis of the 100 classic articles in ulcerative colitis and offered a reference of highly-citable manuscripts,no bibliometric analysis of biologic therapy for CD has been reported.
In this study,we aimed to analyze the top 100 highest-cited original articles in the field of biologic therapy for CD over the last 3 decadesbibliometric citation analysis based on the total citations (TC),which reflect the direct academic significance of a study.In turn,the analysis would provide clinicians and researchers the meaningful insights into the future directions related to biologic therapy for CD.
At the end of the party, he invited her to have coffee with him, she was surprised but due2 to being polite, she promised. They sat in a nice coffee shop, he was too nervous to say anything, she felt uncomfortable, and she thought to herself, Please, let me go home...
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Literature search and screening
A systematic search of literature from January 1991 to December 2020 was performed in the Clarivate Analytics Web of Science Core Collection (WOSCC) database.We used search terms including “biologic therapy,” “Crohn disease,” “anti-tumor necrosis factor,” “infliximab,” “adalimumab,” “certolizumab,” “anti-integrin,” “vedolizumab,”“natalizumab,” “anti-IL-12/23,” “ustekinumab,” and their synonyms.The search strategy was shown in Supplementary Table 1.Original articles whose main topic was biologic therapy for CD were included.Literature that was not related to biologic therapy for CD was excluded,and reviews,commentary,case reports,editorials,consensus statements,and guidelines were also excluded.Two reviewers (J.L.S.and Z.Z.) independently identified the top 100 highest-cited original articles based on TC,and a third reviewer (J.S.C.) was recruited for discussion until any disagreement was settled.
Statistical analysis
After identifying the top 100 highest-cited original articles,the records with all available information were downloaded from the WOSCC database.Then,the bibliographic information of the top 100 highest-cited studies was converted and analyzed automatically by R version 4.0.4 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing,Vienna,Austria) with the “bibliometric” package[15].We further extracted and analyzed the information,including title,author,institution,country,TC,publication year,journal,2020 Journal Citation Reports impact factor (IF),and keywords,using the “bibliometric” package.
All collected data were entered in a spreadsheet and manipulated using Microsoft Excel 2019 (Microsoft Corp.,Redmond,WA,United States).Graphs and figures were created by using R version 4.0.4 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing,Vienna,Austria).Microsoft Excel 2019 Power Map (Microsoft Corp.,Redmond,WA,United States) was utilized for a global map of countries’ publications of the top 100 highestcited original articles.We used the VOS viewer (Version 1.6.10) to produce author cooperation network map,institution cooperation network map,keyword clustering map,and so on.The cooperation network map among all countries and the tree map of keywords were created on an online platform of bibliometric analysis (https://bibliometric.com/).Finally,2 researchers (Z.Z.and J.S.C) verified the collected data and further analysis independently.
RESULTS
Publication and citation count
A total of 5489 original articles focusing on biologic therapy for CD were identified from the WOSCC database from January 1991 to December 2020.The top 100 highestcited original articles were listed in Supplementary Table 2 according to the descending order of TC,and the TC ranged from 2978[16] to 307[17].The earliest influential original article,which focused on treating CD with anti-TNF and gained TC of 926,was published in 1995[18].The latest original articles were 4 studies published in 2017 that focused on biologic therapy for CD,including infliximab,adalimumab,and vedolizumab.Both the annual and the cumulative number of publications over the last 3 decades were presented in Figure 1.Interestingly,the 2000s (Period II,=66)yielded the most influential original articles and saw the most dramatic growth of them,followed by the 2010s (Period III,=28) and the 1990s (Period I,=6).Notably,the annual number of publications reached a peak of 11 in the year 2007 in Period II.

Countries
In analyzing the countries to identify the high-impact countries in this field,the top 100 highest-cited original articles originated from 15 countries (Figure 2).The top 10 countries with the most publications were listed in Table 1,including 8 European countries and 2 North American countries.Among the top 100 highest-cited original articles,the United States published the most articles (=37),followed by Belgium (=20),France (=9),Germany (=9),Spain (=6),United Kingdom (=5),Netherlands (=4),Norway (=2),Canada (=2),and Switzerland (=1).Notably,the United States has contributed the most studies and TC in the field of biologic therapy for CD,publishing 37 influential articles and 26179 citations.Meanwhile,as the top high-yield country in Europe,Belgium has published 20 articles with a TC of 13325.The ratio of TC to publication represented the average number of citations of each article,namely the average influence of each study.Although Switzerland ranked tenth in the number of original articles,contributing merely 1 article,it had the highest TC/Publication of 872.To be specific,Hueber W[19] from Switzerland conducted a randomized,double-blind placebo-controlled trial to explore the effect of a human anti-IL-17A monoclonal antibody,namely secukinumab,for moderate to severe CD,and they failed that blockade of IL-17A was ineffective and caused higher rates of adverse events.Thus,the scientific quality of the research in Switzerland may be generally high.Figure 3 showed the cooperation relationships among countries that contributed to the top 100 highest-cited original articles.The United States,Belgium,France,and Germany were intuitively observed to be involved in the close partnership.
No comprehensive analysis of biologic therapy for CD has been reported.



Institutions
The top 10 institutions with the most publications were listed in Table 2,including the University Hospital Gasthuisberg in Belgium,the University of Chicago in the United States,and the Mayo Clinic in the United States with 23,20,and 17 papers,respectively,and with 17529 citations,19342 citations,and 14879 citations,respectively.Although the University of Chicago ranked second in the publications,it had the highest TC/Publication of 967,followed by the University of Western Ontario(TC/Publication=952),the University of Pennsylvania (TC/Publication=909),and the University Hospital Kiel (TC/Publication=907).The average citations per article exceeded 900 for these 4 institutions above.The cooperation between institutions was a critical factor in promoting technological development,and Figure 4 showed the cooperation relationships of institutions that have co-published more than three topcited articles.

Authors
The top 10 most influential authors with the most publications were listed in Table 3,including Rutgeerts P in Belgium,Sandborn WJ in the United States,and Feagan BG in Canada with 32,23,and 18 papers,respectively,and with 26039 citations,18034 citations,and 16127 citations,respectively.Notably,Hanauer SB in the United States had the highest TC/Publication with merely 14 publications,which meant that his studies were of high scientific quality.The partnership among authors that have copublished more than 3 top-cited articles was shown in Figure 5.
The contributions of countries,institutions,and authors to biologic therapy for CD were identified in the study.The top 10 countries with the most publications were 2 North American countries and 8 European countries because the highest incidence rates have been shown in the United States and Europe[28].This phenomenon may be attributed to the confounding factors of genetics and the environment[29],and the latter,including diet,pollution,microbial exposure,and sanitation,were implicated in the development of CD[30].Notably,the United States,Belgium,France,and Germany occupied the leading positions and had the most cooperation among them in biologic therapy for CD,thus generating the most high-cited original articles with the highest TC in this field.Rutgeerts P from Belgium and Sandborn WJ from the United States have published the most influential studies and made excellent contributions to biologic therapy for CD,which was worth remembering.More attention should be paid to international cooperation,but it is not limited to the United States and Europe.Further multicenter clinical trials among different countries should be performed to offer evidence for biologic therapy for CD in the future.


Journals
The analysis of annual and cumulative publications in different publication periods(Period I,Period II,and Period III) enabled clinicians and researchers to understand the development of biologic therapy for CD intuitively.In the 1990s (Period I),the number of most influential articles grew slowly.Notably,there was an explosive growth of the number of studies in the 2000s (Period II) because the first biologic agent,infliximab,was approved for CD treatment by the Food and Drug Administration[20].Meanwhile,an increasing number of clinical trials were designed and conducted during Period II,including the ACCENT I trial (maintenance infliximab for CD)[16],the CLASSIC I and II trials (maintenance adalimumab for CD)[21,22],the CHARM trial (maintenance adalimumab for clinical response and remission of CD)[23],and other trials (ustekinumab,natalizumab,and certolizumab treatment for CD)[24-26].Especially in the year of 2007,with the appearance and clinical use of adalimumab,certolizumab,and natalizumab,the annual publications peaked.However,less high-cited articles were published since the 2010s (Period III).A possible explanation was that the emerging biologics were relatively novel drugs,and the TC of related articles could not be accumulated within the limited time.A study conducted by Azer[27] further confirmed that the year of publication would be relative to TC,and therefore the TC of recently published articles was low.


Analysis of keywords
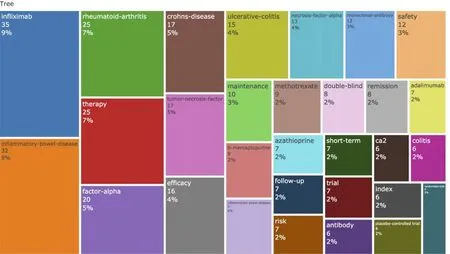
The research hotspots in the field of biologic therapy for CD were explored and demonstrated in the treemap (Figure 6).Infliximab,tumor necrosis factor,monoclonal antibody,and adalimumab accounted for 9%,5%,3%,and 2% of keywords,respectively.The cluster analysis of keywords that appeared more than seven times was also conducted to validate the results (Figure 7).

DISCUSSION
Due to the lack of a systematic approach to identifying the important information,it is challenging for clinicians and researchers to review the development of biological therapy for CD over the past 3 decades.In the study,we identified and ranked the top 100 highest-cited original articles by TC according to the WOSCC database.Through the bibliometric analysis,we summarized the basic characteristics of these original articles,such as publication,citation,countries,institutions,authors,journals,and keywords.In addition,we could identify research hotspots of biologic therapy for CD.
My mind went blank and I stood motionles overcome with gloom, when suddenly, I felt that familiar electrifying31 touch, the same shiver and the familiar thrill
Based on the descending order of the number of the top 100 most influential original articles,the top 10 journals were listed in Table 4.Over the last 3 decades,(IF=22.682) has published the extremely most articles on biologic therapy for CD,including 32 publications and 17654 TC.Among the top 10 most influential journals,5 journals had TC/Publication exceeding 500,in whichhad the highest IF of 91.245,the highest TC of 18379,and the highest TC/Publication of 1225,exceeding 90,18000,and 1225,respectively.The rest were(IF=79.321,TC/Publication=855),(IF=9.071,TC/Publication=799),(IF=25.391,TC/Publication=668),and(IF=22.682,TC/Publication=552.
“Here are your fur boots for you,” said she; “for it will be very cold; but I must keep the muff; it is so pretty. However, you shall not be frozen for the want of it; here are my mother’s large warm mittens22; they will reach up to your elbows. Let me put them on. There, now your hands look just like my mother’s.”
I will indeed do thee this service, Gray Wolf, wolf s son, said the crow, only harm not my child, and immediately flew away as swiftly as an arrow.
Perhaps, he said, I may bring the Princess back with me, so see that everything is in order; let the gold ornaments10 be arranged and the whole ship decorated
The research hotspots in the top 100 highest-cited original articles over the past 3 decades were infliximab,tumor necrosis factor,monoclonal antibody,and adalimumab treatment for CD,which belonged to the anti-TNF research.The anti-TNF biologics were approved by Food and Drug Administration in an early stage and have achieved excellent curative effects in clinical use.However,other biologics such as anti-integrin agents (vedolizumab and natalizumab) and anti-IL-12/23 agents(ustekinumab) emerged later,and most of them were still in the clinical trial stage.Thus the related original articles have not gained high TC.However,more influential articles would be published as the studies of novel biologics continue.
The study had several limitations that needed to be discussed.First,the current study may not include all influential articles in the field of biologic therapy for CD merely based on the WOSCC database.Although we did utilize broad search terms to search all related articles,it is possible that the search strategy may have missed some crucial literature.Further bibliometric analysis would be conducted with a precise search strategy from WOSCC,PubMed,and PMC databases.Second,the potential citation biases may affect the list of the top 100 highest-cited original articles and subsequently generate inaccurate results.In particular,the latest articles may have insufficient time to accumulate TC.Inappropriate citations,including self-citations,institutional biases,powerful author biases,and language biases,may also be inevitable and further affect the results of the analysis potentially.
CONCLUSION
In summary,the top 100 highest-cited original articles of biologic therapy for CD over the last 3 decades were identified and entered a bibliometric analysis to provide useful insights for clinicians and researchers.Moreover,the study offered an overview of countries,institutions,authors,and journals that had contributed significantly to the development of the specialized field.We focused on study keywords to explore the current and future research hotspots of biologic therapy for CD.Undoubtedly,studies and innovation of the field will continue to evolve and become an area of interest in the future.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
To determine knowledge gaps and identify areas of interest of biologic therapy for CD.
Research motivation
Indeed the Queen, whose name was Santorina, was so pretty and so kind-hearted that it would have been a wonder if her husband had not been fond of her, while King Gridelin himself was a perfect bundle of good qualities, for the Fairy who presided at his christening had summoned the shades of all his ancestors, and taken something good from each of them to form his character
Various medical journals were engaged in promoting the development of biologic therapy for CD.In terms of influence,the top 10 journals with the most publications were,,and,with a total of 57 articles.The others were,,,,,,and,making a total of 27 publications.The top 10 journals were mostly in the field of digestive diseases,while some of them were comprehensive journals,namelyand.Both journals have relatively high IF of 91.245 and 79.321,respectively,with high TC/Publication of 1225 and 855,respectively.The high scientific level of clinical trials in the top-cited original articles could contribute a lot to the higher citations per paper.One of the significant clinical trials,which was called the ACCENT I randomized trial,was focused on maintenance infliximab for CD and published inwith the highest TC of 2978[16].
Research objectives
There is an overloading amount of publications on biologic therapy for Crohn’s disease (CD).
Eventually we got better at asking. We d knock on the window, they d roll it down and we d say, Today is Thanksgiving. We d like to help some underprivileged people, and we re curious if you d be willing to drive us to an underprivileged area that we have in mind here in New York City. That seemed slightly more effective but still didn t work. Then we started offering people $100 to drive us. That got us even closer, but when we told them to take us to Harlem, they said no and drove off.
Research methods
We conducted a bibliometric analysis of biologic therapy for CD based on the top 100 highest-cited original articles,summarized the bibliographic information,and explored the research hotspots.
Research results
The 2000s yielded the most influential original articles and saw the most dramatic growth.The United States and Europe contributed the most publications,and the cooperation relationships between them were most frequent.Gastroenterology published the most articles on biologic therapy for CD.Anti-tumor necrosis factor biologics and monoclonal antibodies were the most studied topics.
Research conclusions
The bibliometric analysis emphasized the key contributions made to the development of the specialized field.
Research perspectives
These data would provide useful research insights into biologic therapy for CD for clinicians and researchers.
No one thought of finding any faults, till at length an old woman, who had been walking through the rooms with a crowd of people, suddenly exclaimed, Yes, it is a splendid palace, but there is still something it needs! And what may that be? A church
We thank Yu TN,Department of General Surgery,Sir Run-Run Shaw Hospital,Zhejiang University School of Medicine,Hangzhou 310016,Zhejiang Province,China,for revising our manuscript.We also thank Topatana W,an international graduate and English native speaker in the Department of General Surgery,Sir Shaw RR Hospital,Zhejiang University School of Medicine,Hangzhou 310016,Zhejiang Province,China,for polishing our manuscript.We are grateful to our colleagues for their assistance in checking the data of the studies.
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年2期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年2期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- New trends in treatment of muscle fatigue throughout rehabilitation of elderlies with motor neuron diseases
- What emotion dimensions can affect working memory performance in healthy adults? A review
- Quadrilateral plate fractures of the acetabulum:Classification,approach,implant therapy and related research progress
- Methylprednisolone accelerate chest computed tomography absorption in COVID-19:A three-centered retrospective case control study from China
- Analysis of photostimulable phosphor image plate artifacts and their prevalence
- N6-methyladenine-modified DNA was decreased in Alzheimer’s disease patients
