Analysis of photostimulable phosphor image plate artifacts and their prevalence
INTRODUCTION
Digital radiography has recently been used in dentistry as a substitute for conventional film radiography worldwide.Digital imaging provides new possibilities for recording and interpreting radiographic data in a user-friendly digital way for archiving and teleradiography[1].Digital imaging has many advantages over filmbased radiography,such as real-time imaging,not needing the use of darkroom chemicals,having image manipulation tools,better archiving,and decreased patient and operator radiation exposure[2-6].
Dental radiography is provided by two main types of radiography:Conventional and digital radiography.Conventional radiography uses dental films that require chemical solutions for processing,more human resources,is time consuming,and with a higher radiation dose.This traditional type of radiography provides a permanent record of imaging without any possibility for archiving,and any error requires the retake of the radiograph,which exposes the patient to unnecessary additional radiation exposure.This is in contrast to digital radiography,which allows image manipulation to correct the visual characteristics of the image,such as contrast,brightness,and density,thus enhancing image quality without the need to retake the image.Digital radiography permits easy archiving of images and their electronic transfer between different specialties in the dental field.Digital radiographic technology uses electronic image receptors (digital sensors or plates),which are based on two main techniques in acquiring the image:A direct method using a chargecoupled device (CCD) or complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) sensors[7] that transmit the signal of the exposed plate directly over a wire with a real-time image on the monitor or indirect method using a photostimulable phosphor storage plate (PSP),which forms a latent image when exposed to radiation.The stored energy is then transported to a computer for display using a laser scanner[8-10].
The scanning times of PSP plates vary from a few seconds to several minutes,depending on the type of laser scanner used and the spatial and contrast resolutions of the image[5].PSP plates are available in a variety of sizes in a way similar to conventional films,so they are vulnerable to bending and scratching during handling[2,11].
Moreover,PSP plates must be handled more carefully than films because they are reusable after erasing the image[12].PSP plates are selected by most dental practitioners because of their easy intraoral placement with little patient discomfort,as well as them being cordless and resembling conventional films.This is in comparison to the more difficult intraoral placement of CCD plates,with more patient discomfort caused by the stiffness of these plates with a cord linking them to the computer even though an image can be obtained promptly by the practitioner after exposure of the plate in this system[11,12].
But, answered he, let a man be ever so strong, he cannot carry more than a hundredweight, and what is that for a king s daughter? Well, do as you like; I have said my say
Digital radiography,like any evolving technology,produces a new type of image pitfall that remains a problem for clinicians in that it can be overwhelming.To the best of our knowledge,a systematic review of dental digital radiography artifacts in clinical usage has not yet been reported[13].In addition,few studies have assessed PSP image errors using illustrative figures[14].
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This retrospective descriptive study was conducted in the oral and maxillofacial radiology unit of the dental clinics of the College of Dentistry,Princess Nourah University (PNU),where conventional film-based radiography was gradually replaced by digital radiography starting in 2018.All the intraoral digital radiographs were acquired using (Gendex Expert DC.,United States) an intraoral X-ray machine with 7-mA 65-kVP using a PSP system (Soredex DIGORA Optime imaging plate) and laser scanners (Soredex DIGORA Optime),which can house all sizes of reusable intraoral PSP sensor plates with image acquisition software (MIPACS Dental Enterprise viewer 3.2.2).
The investigators retrieved all the digital intraoral periapical and bitewing radiographs that were taken and approved by the clinicians from all dental specialties in our college and with the consent of the patients from April 2018 to April 2020.We used the Medicor Imaging/MIPACS Toolkit software,which regularly detects and records all deleted radiographs due to retakes performed by all oral radiology technicians in the radiology unit with clarification of the image type.All the retakes were screened by two well-experienced oral and maxillofacial radiologists for evaluation of the present artifact type and cause,while the remaining images without errors were excluded from the study.Artifacts were classified into three categories:plate errors,scanning errors,and operator errors.First,two observers sat together in a collaboration session to determine the criteria and subtypes for each category of digital artifacts to unify the interpretation process.
The observers independently evaluated and agreed on image artifacts.When disagreement existed among them,consensus was reached through discussion.Out of the selected cases,1000 images with errors were reevaluated by both investigators after 2 wk for the calculation of interobserver reliability.Our retrospective study was approved by the institutional review board (IRB) of PNU.
The Princess heard his puffing18 and roaring, and growing frightened she cried: Oh dear! the bear is after us and will certainly catch us up! The tailor remained quite unmoved
On the third31 morning after they had left their father s house they set about their wandering again, but only got deeper and deeper into the wood, and now they felt that if help did not come to them soon they must perish
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS Statistics version 23 (IBM Corp.,New York,NY;formerly SPSS Inc.,Chicago,IL,United States),and the frequencies and percentages of PSP artifacts were calculated.Interobserver reliability was analyzed with kappa analyses,which was interpreted as follows:value<0 denoted less than chance agreement,0.01-0.20 denoted slight agreement,0.21-0.40 denoted fair agreement,0.41-0.60 denoted moderate agreement,0.61-0.80 indicated substantial agreement,and 0.81-0.99 was considered almost perfect agreement[13].
RESULTS
A total of 50000 intraoral digital radiographs were acquired in the 2 year-period from April 2018 to April 2020.Of these,3550 (7.1%) retakes were performed due to the presence of image artifacts.Of these retakes,5% was related to operator errors and 2.1% was related to plate and scanning errors.The calculated kappa value for interobserver reliability was 0.99,indicating almost perfect interobserver agreement.
Moreover,to reduce the radiation exposure of the patient,it is clinically important to avoid the occurrence of image artifacts in order to minimize repeated radiographs,which could happen through proper understanding of the reasons and solutions for incidence of image artifacts and thus lessen its frequency,especially in the recent commonly used dental digital imaging technology[14].
Imaging artifacts were divided into three categories.Of the 3550 retakes,operator errors were the most common and were observed in 2500 images (70.4%),while plate errors were detected in 685 images (19.3%) and scanning errors in 365 images (10.3%).
He could have made himself quite comfortable with a bed of soft moss2, but the fear of wild beasts disturbed his mind, and at last he determined3 to spend the night in a tree
Operator errors
In this study,the operator error category consisted of eight subtypes that were closely similar to the same error categories in conventional film radiography,as this type of artifact does not depend on the type of image receptor except for the reversed or mirror image,movement of the plate inside the packet,and double exposure in the plate either due to partial erasing of the previous image or failure of the image scanning.
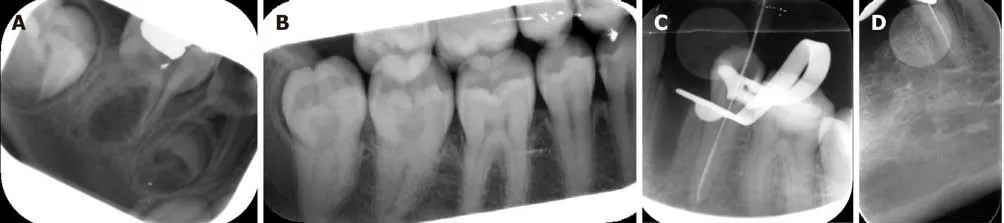
The cone cut was the most common error observed in 988 images (39.5%) out of 3550 images (Figure 1A),followed by the artifacts of improper PSP placement in the mouth (30.4%),projection geometry (22.4%),unexposed plate (4.5%),movement of phosphor plate in the disposable pocket (1.6%) (Figure 1A and B),reversed image(0.8%) (Figure 1c and d),overexposed (0.6%),and plate bending (0.3%).
Plate errors
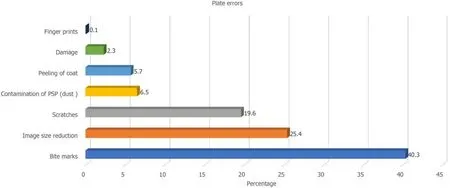
Bite marks were the most common error observed in 276 images (40.3%),while image size reduction was detected in 174 images (25.4%).In addition,plate scratches were detected in 19.6% of cases,with other errors being contamination of PSP (6.5%),peeling of the coat (5.7%),plate damage (2.3%),and fingerprints (0.1%)(Figures 2,3 and 4).
We sang all the way home from church. At lunch, Mom had a surprise for us. She had bought a dozen eggs, and we had boiled Easter eggs with our fried8 potatoes! Late that afternoon, the minister drove9 up in his car. Mom went to the door, talked with him for a moment, and then came back with an envelope in her hand. We asked what it was, but she didn’t say a word. She opened the envelope and out fell a bunch10 of money. There were three crisp11 twenty-dollar bills, one ten-dollar bill and seventeen one-dollar bills.
Scanning errors
It has been reported that the higher the light intensity and the longer the exposure time,the greater the loss of plate information[27].This was supported by the study of Ang DB in 2006,which reported that plates were not exposed to any light before scanning presented no change in image quality even after many days of storage[25,28].





DISCUSSION
The second most common errors in the current study were plate errors that were detected in 685 intraoral images (1.37% of total images and 19.3% of retakes),followed by scanning errors seen in 365 intraoral images (0.73% of total images and 10.3% of retakes).Chiu[23] 2008 reported that scanning errors were the second most common error,followed by plate errors.
PSP and CCD digital systems are preferred over traditional films because of the lower radiation dose for both patients and operators,less time needed,ability to perform image manipulation as well as enhancement without the need for retake,better archiving,and environmental friendliness.
One day the woman stood at the window3 overlooking the garden, and saw there a bed full of the finest rampion:4 the leaves looked so fresh and green that she longed to eat them.5 The desire grew day by day, and just because she knew she couldn t possibly get any, she pined away and became quite pale and wretched. Then her husband grew alarmed and said:
And there are surprises. One time I came home to find a note on the front door that led me to another note, then another, until I reached the walk-in closet. I opened the door to find Scott holding a pot of gold (my cooking kettle) and the treasure of a gift package. Sometimes I leave him notes on the mirror and little presents under his pillow.
PSP plates are more comfortable to the patient than CCD because they are cordless,more flexible,and thin,which resembles standard films.However,despite their superiority,PSP plates are more susceptible to bending and scratches,require more time for scanning,and subsequently develop more image artifacts,which consequently affects image quality[15].In previous studies,it has been stated that 95%of PSP plates used for 10 wk (used approximately 50 times) became non-diagnostic and needed to be substituted[16,17].
Joyce Thomas comments on the trickery and imagery of the bone. The bone provides the imagery of deprivation112 and starvation, one of the primary themes of the tale. Also, the bone Hansel uses imitates the fate awaiting his flesh (the bone could well be the gnawed113 remains114 of the cage s previous occupant) (Thomas 1989).Return to place in story.
Radiographic artifacts that occur with plain film radiography are well-identified and documented.However,to the best of our knowledge,few studies have reported and categorized the artifacts of PSP plates[17-21].Most of these studies investigated them in medical radiology;however,very few studies were correlated to the dental field[14,15,20,22].
Every team requires unity. A team has to move as one unit, one force, with each person understanding and assisting the roles of his teammates. If the team doesn t do this, whatever the reason, it goes down in defeat. You win or lose as a team, as a family. A successful team walks onto the field with issues of race, religion and all societal pressures ratcheted down to inconsequential by the strength of common goals.
Intraoral radiographs requiring retakes due to image artifacts included 2869 (80.8%)periapical (PA) images,518 (14.6%) bite wing images,and 163 blank images (4.6%).
Therefore,the aim of this study was to detect the type,frequency,and reasons for the occurrence of intraoral image artifacts acquired by PSP plates in our dental clinics,and to propose probable methods to avoid these image artifacts.
Although PSP plates can be exposed to regular light while being uncovered and imported into the scanner,it is recommended that exposure to regular light should not exceed 10 minutes,and that the scanning procedure should not be delayed more than that.Otherwise,the information in the plate will fade away[24],which will lead to increased signal loss and a reduction in the signal-to-noise ratio[25,26].It could appear as total image fading with too bright an image or non-uniform image density caused by partial exposure of PSP to excessive ambient light before scanning.In addition,fluctuating signal loss leads to a noisy image[24].
In the present study,only 0.07% of 50000 intraoral images reported in the existing study presented with movement artifacts of the PSP plate inside the disposable packet.However,in Gulsahi and Secgin study in 2016,it was recorded frequently,whereas other studies did not report this type of artifact.It has been stated that this artifact is detected only with the Digora system,where both cardboard cover and disposable plastic envelopes should be used.While the cardboard cover is used to protect the PSP plates,they may unfortunately cause motion of the plates,resulting in these artifacts[24].
Digital intraoral imaging systems have gradually replaced film-based imaging in recent years,as this technology has many advantages over conventional imaging.Two types of receptors are used for digital intraoral radiography:solid-state sensors of either CCD or CMOS,which are used with a wire and PSP plates that are cordless.Solid-state sensors have been used for more than two decades,while systems that use PSP plates have only recently been used in clinical practice.Each receptor type has its own advantages and disadvantages[2].
In the current study,bite marks were the most common plate error subtypes observed in 276 images (40.3%).
5. Wolf: The wolf has become a popular image in fairy tales thanks to this tale and The Tale of the Three Little Pigs. The wolf is a common predator16 in the forest and thus is a natural choice for the story unlike the witch, ogre or troll found in other tales. The wolf is often a metaphor17 for a sexually predatory man.
The most probable cause of the increased incidence of bitemarks in our study is the disposable plastic packet.It is used for infection control and acts as a light barrier,but it does not provide proper safety against plate damage from bite marks,bending,or pressure.Another possible reason for plate bitemarks would be the patient unintentionally biting on the plate.Thus,the patient must be comprehensively instructed to avoid doing so before the exposure.
That was 34 years ago. Today, the boy is a successful architect in New York City. His father’s cabin is still there on the island in the middle of the lake. He takes his own son and daughters fishing from the same dock.
It was reported that pediatric periapical radiographs of primary incisors that were taken by a modified technique by making the child bite on a size 2 PSP plate to keep it in place during exposure simulating occlusal radiograph could be one of the reasons for PSP bite marks.Snap-A ray film holding devices with teeth-like edges were used.Roberts,Mol,2004 reported that the risk of teeth biting in pediatric primary incisors can be reduced by placing “adhesive backed sponge-like pads” on each side of the disposable sleeve that holds the reusable size 2 plate[2].
Image size reduction artifact after scanning was reported in 174 images (25.4% of retakes) and 0.3% of all intraoral images,which can be related to scanning errors.This was also reported by various studies[20].
In the present study,PSP plate scratches were detected in 19.6% of patients,while surface contamination of PSP was seen in 6.5%.To the best of our knowledge,the actual reasons for plate surface contamination and scratches have not been completely recognized and investigated.Kalathingal[17] 2010 stated that the possible cause of plate surface contamination could be the adhesive utilized in the barrier sheath,which could have affected the plate before scanning.The same study found that the plates that were used in dental colleges,as in our study,were more susceptible to scratches because of the increased number of people handling the plate,especially when they were discovered after scanning and before packaging the plate with a new protective sheath.Also,Kalathingal[17] 2010 reported that the hard rubbing of PSP plates with alcohol could be a cause for more scratches,and recommended that only the plates with visible surface contamination should be lightly wiped to remove any contaminants[17].
Naturally a great scramble70 ensued, and at last the laughter and shouting awoke the Queen, who rang for her maids to ask the reason of such an unwonted hurry-burly
In the current study,peeling of the coat was found in 5.7%,plate damage was recorded in 2.3%,and fingerprints were found in 0.1% of plates.These findings were in the line with those reported by Gulsahi and Secgin in 2016,wherein they found damaged plates to occur in only a few images[20].The most probable causes of plate damage are tough handling of PSP plates during their placement in the mouth,extensive bending,forceful placement of the plate into the scanner,or mechanical stresses exerted by the scanner roller during scanning[15].
Scanning errors were detected in 365 images (0.73% of all intraoral images),where delayed scanning was the most common error in this type and was seen in 145 images(0.29%).Despite Gulsahi and Secgin[24] reporting 12.6% of all images exhibited nonuniform brightness in their 2016 study,Chiu[23] recorded 0.4% delayed scanning errors in their 2008 study.
In the present study,the examined intraoral radiographic errors were categorized into three main categories:operator,plate,and scanning errors.Operator errors were the most common and were observed in 2500 out of 50000 intraoral images (5%) and in 70% of 3550 retakes,which is in accordance with the findings of Hui-Lin Chiu[23]2008.regarding the increased incidence of operator errors as seen in the current study.In addition,this reflects the need for broader training of radiology technicians.
In the current study,the most common subtype of scanning error was delayed scanning (39.9% of retakes),which was comparable to the results of Çalışkan and Sumer in their study in 2017,who affirmed that the probable cause for this artifact is the elimination of the plate from its cover after radiation exposure to inhibit infection before scanning[24].
Delayed scanning artifacts (non-uniform density or bright image) were the most common errors observed in 145 images (39.9%).White (radiopaque) lines (37.2%),blank images (13.4%),black (radiolucent) lines (5.5%),and double images (incomplete or partial erasing) (4.1%) were also seen.(Table 1,Figures 5 and 6).
The second scanning error was the presence of white lines in 136 images (37.2%),which were reported to be due to dust or dirt particles on the slim scanning opening of the scanner.This caused them to remain fixed during the scanning process or dirt on the rollers,which acted as a blockage to the laser light.Thus,resulting in production of areas devoid of signals.Therefore,the mechanical scanner transport system should be checked and cleaned regularly,with additional replacement of the belt,if necessary[15].
Aha! they both exclaimed3. You ARE from Iraq! Tara smiled and said yes. Then she apologized to both of them for lying the day before. She explained that she had not wanted to get into an Arabic conversation with them. It had been her experience that many ESL students continued to speak their native language in ESL class, and Tara had not come to ESL class to practice her Arabic. In her opinion, ESL students should try to speak English only.
The black or radiolucent lines that were detected in 20 images (5.5%) were hypothesized by a previous study to have resulted from electromagnetic interfering artifacts that were caused by anything that interfered,interrupted,decreased,or limited efficient scanner performance[15,29].
Moreover,Çalışkan A and Sumer AP[26] denoted this artifact as a ridging artifact,and advocated that these black lines occurred due to fast variations in the intensity of the light of the stimulating lasers as well as the loss of harmonization between rapid scan cycles and image plate movement.It is recommended to add proper electromagnetic shielding,appropriate voltage supply,uninterrupted power supply,and regular maintenance of scanner performance to avoid the occurrence of artifacts in radiolucent lines[15].
The previously mentioned errors observed in our study could be limited by proper regular orientation and enforcement by all operators,technicians,and students of the appropriate procedures of gentle handling of the PSP plates during exposure,scanning,and after scanning.This also includes focusing on the correct light rubbing of the PSP plates only with visible surface contamination to increase their longevity and usability.Moreover,regular checkups of PSP plates should be regularly performed to check the integrity of the plates.In addition,periodic maintenance,cleaning,and calibration of scanning devices would significantly reduce the number of scanning errors.Furthermore,additional comprehensive training of radiology technicians regarding application of proper radiographic techniques using the PSP system would be very beneficial in reducing operator errors.
CONCLUSION
The use of digital imaging in dental practice has recently made a revolution in image recording and analysis.Our institution made a significant modification by digitizing all dental images recently acquired using mainly the PSP system.Our study investigated the prevalence of intraoral image artifacts in our clinics,which were characteristic of PSP plates wherein the most common artifacts were bitemarks,image size reduction,scratches,and delayed scanning.Defining the causes of these artifacts and identifying methods for preventing them are of great clinical significance.Further research on PSP artifacts for further error identification and proper handling is needed and is a process that is essential to produce superior diagnostic images needed for instituting proper dental care.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Nowadays,digital imaging outweighs conventional imaging and has been used widely in dentistry.Digital radiography allows image manipulation to adjust the visual characteristics of the image,such as contrast,brightness,and density,thus enhancing image quality without the need to retake the image.
Research motivation
Digital imaging provides an easier,comfortable,and user-friendly way for recording and interpreting radiographic data for archiving and teleradiography.
Research objectives
To detect the frequency,type,and reasons behind the appearance of intraoral image artifacts acquired by photostimulable phosphor plates (PSP).
Research methods
This retrospective descriptive study.A total of 50000 intraoral radiographs were retrieved from the clinical database from April 2018 to April 2020 to evaluate the reason,type,and solutions to these image artifacts.All intraoral digital radiographs were acquired using an intraoral X-ray machine with 7-mA,65-kVP using a PSP system and laser scanners,which can house all sizes of reusable intraoral PSP sensor plates with image acquisition software.
Research results
Imaging artifacts were divided into three categories;operator,plate,and scanning errors.Out of 3550 retakes,5%,1.37%,and 0.73% were related to the operator,plate,and scanning errors,respectively.The cone cut was the most common operator error(988 images),Bite marks were the most common plate error (276 images),and delayed scanning artifacts were the most common scanning errors (145 images).
Research conclusions
Our study discussed intraoral image artifacts that were characteristic of PSP,where the most common artifacts were bitemarks,image size reduction,scratches,and delayed scanning.
Research perspectives
Thus,recognizing intraoral radiographic image errors and defining the causes and their trouble-shooting are crucial factors in making images possess great clinical impacts.
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年2期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2022年2期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- New trends in treatment of muscle fatigue throughout rehabilitation of elderlies with motor neuron diseases
- What emotion dimensions can affect working memory performance in healthy adults? A review
- Quadrilateral plate fractures of the acetabulum:Classification,approach,implant therapy and related research progress
- Methylprednisolone accelerate chest computed tomography absorption in COVID-19:A three-centered retrospective case control study from China
- N6-methyladenine-modified DNA was decreased in Alzheimer’s disease patients
- Inflammation-related indicators to distinguish between gastric stromal tumors and leiomyomas:A retrospective study
