A study on the correlation between function motivation and professional identity among nursing volunteers
Juan XU, Wenjun HAO, Hui YANG,Xuanxuan LI
1Department of Inpatient, Shanxi Provincial People’s Hospital,Yingze District, Taiyuan City, Shanxi Province, China; 2School of Nursing, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Taiyuan City,Shanxi Province, China; 3 Department of Nursing, First Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan City, Shanxi Province,China
ABSTRACT
Objective: The objective of this study is to understand the status quo of function motivation and professional identity among nursing volunteers and explore the correlation between the two.
Materials and Methods: A total of 3375 nursing volunteers from Nightingale Volunteer Service Group in Shanxi Province were investigated by using Occupational Identity Scale and Volunteer Functional Motivation Scale.
Results: A total of 3375 questionnaires were issued and 3330 were recovered, among which 3324 were valid, with an effective recovery rate of 99.82% (3324/3330).The overall score of professional identity of nurses was 110.31 ± 18.71, and the score of each dimension was 32.17 ± 6.62 for professional cognitive evaluation dimension, 22.77 ± 3.74 for professional social support, 21.31 ± 4.09 for professional social skills, 22.78 ± 3.79 for professional frustration coping, and 11.32 ± 2.03 for professional self-reflection.The total score of function motivation was 157.12 ± 29.92.The above five dimensions of nurse’s professional identity scale were positively correlated with the total score of function motivation of nursing volunteers (r = 0.044, 0.035, 0.034, 0.035, and 0.042, respectively, all P < 0.05).
Conclusion: The functional motivation and professional identity of nursing volunteers in Shanxi Province are in the middle level in China.Therefore, it is necessary for the hospital to stimulate nursing staff’s enthusiasm about participation by carrying out multi-channel and multi-form volunteer service projects, enhance their professional identity, and make them better give back nursing professional skills to the society.
Keywords: Functional motivation, nurse, professional identity, volunteers
INTRODUCTION
Voluntary service is a social behavior of helping others without remuneration regardless of the participant’s own conditions (such as gender, age, race, social, and cultural background).Voluntary motivation is an individual’s psychological state or willingness to provide help or services for others based on his/her social responsibility, personal belief, and conscience.[1]Along with the advance of medical technology, people’s health level increased significantly,but the imperfect medical security system, unreasonable allocation of health resources, rapid speed of population aging, and the changes of disease spectrum are still prominent issues in China.Nursing workers can alleviate those realistic contradictions that our country encounters at present through volunteer nursing service.Previous studies show that individual volunteer motivation directly promote voluntary behavior.[2-5]Hence, how to improve the individual volunteer motivation through a variety of measures is now facing major issue of carrying out volunteer nursing service projects.One of the measures is that improving their professional identity is conducive to enhancing their recognition of their own career, increasing their affirmation of self-value, thus improving their volunteer motivation and making them actively participate in volunteer activities.[6]Therefore, the authors analyzed the status quo of the service motivation and professional identity of nursing volunteers in Shanxi Province and discussed the correlation between them.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Participants
A questionnaire survey was conducted among 3375 nursing volunteers from Nightingale Volunteer Service Group in Shanxi Province from October to December 2019 using the convenience sampling method.The inclusion criteria were registered nurses who had more than 6 months of volunteer experience and volunteered to participate in this survey.The exclusion criteria were nurses who did not do any volunteer work or volunteered for <6 months.
Survey tools
Questionnaire for basic information of nursing volunteers:It is self-designed questionnaire for basic information of nursing volunteers, including gender, age, education, working years, professional title, marital status, monthly income, and hospital level.
Volunteer functions inventory was compiled by Clary et al.to study volunteer service motivation.[7]It includes 30 items in the six dimensions, namely social function motivation, values function motivation, understanding function motivation,protective function motivation, career function motivation,and enhancement function motivation.Each dimension has five items, and each item is rated on a seven-point Likert scale, from “1 strongly disagree” to ‘7 strongly agree.” The higher the score, the stronger the volunteer motivation.The Cronbach’s alpha coefficient of the six subscales was 0.872 for social function motivation, 0.840 for values function motivation, 0.865 for understanding function motivation,0.869 for protective function motivation, 0.846 for career function motivation, and 0.912 for enhancement function motivation, respectively, and the Cronbach’s alpha coefficient of the total scale was 0.970.
The nurse’s professional identity scale was a quantitative tool compiled by Liu et al.[8]to evaluate the professional identity level of nurses or individuals.The scale includes five dimensions, namely professional cognitive evaluation, social support, professional social skills, professional frustration coping, and professional self-reflection.Each dimension is positively scored, and each item is rated on a five-point Likert scale, from “30 strongly disagree” to “150 strongly agree.The higher score suggests the higher level of nurse’s professional identity.The total score of the scale between 30 and 60 indicates low level, 61-90 indicates little low level, 91-120 indicates medium level, and 121-150 indicates high level.The Cronbach’s alpha coefficient of the total scale was 0.938, and the internal consistency coefficient of each dimension was >0.70, indicating good reliability of the scale.
Survey methods
The researchers communicated with Nightingale Volunteer Service Group in Shanxi Province, and after obtaining the consent, the researchers issued an electronic questionnaire to the volunteer nurses who met the inclusion criteria and asked them to filled in the questionnaire by themselves in an anonymous form.
A total of 3375 questionnaires were issued and 3330 were recovered, among which 3324 were valid, with an effective recovery rate of 99.82% (3324/3330).
Ethical considerations
Ethical approval for this study was obtained from the ethical committees of Shanxi Provincial People’s Hospital where the study took place (No.2021-241).The questionnaire survey was conducted anonymously, and the purpose and significance of the survey were informed to the participants before the survey.We also promised that all information just would be used for the research and kept strictly confidential.
Statistical methods
The results of the questionnaire were recorded in pairs and double copies, and the data were analyzed using the SPSS 23.0 (IBM, Armonk, New York, USA) statistical software package.Measurement data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation, and count data were expressed as number and percentage.Pearson correlation analysis was used to deal with the correlation between function motivation and professional identity of nursing volunteers.P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
General information of 3324 nursing volunteers
Among 3324 nursing volunteers, the majority were women (97.8%), aged 25-36 years (58.63%), obtained bachelor’s degree (75.57%) [Table 1].
Function motivation status of 3324 nursing volunteers
The total score of function motivation of nursing volunteers was 157.12 ± 29.92, which was at a medium level.The scores for each dimension from high to low were 27.62 ± 4.84 for values function motivation, 27.20 ± 5.35 for enhancement function motivation, 26.18 ± 5.25 for understanding function motivation, 25.59 ± 5.33 for career function motivation,25.45 ± 5.48 for social function motivation, and 24.35 ± 5.93 for protective function motivation.
Professional identity status of 3324 nursing volunteers
The total score of nurse’s professional identity was 110.31 ± 18.71, which was at a middle level.The scores of each dimension of nurse’s professional identity were 32.17 ± 6.62 for professional cognitive evaluation, 22.77 ± 3.74 for professional social support, 21.31 ± 4.09 for professional social skills, 22.78 ± 3.79 for professional frustration coping,and 11.32 ± 2.03 for professional self-reflection.
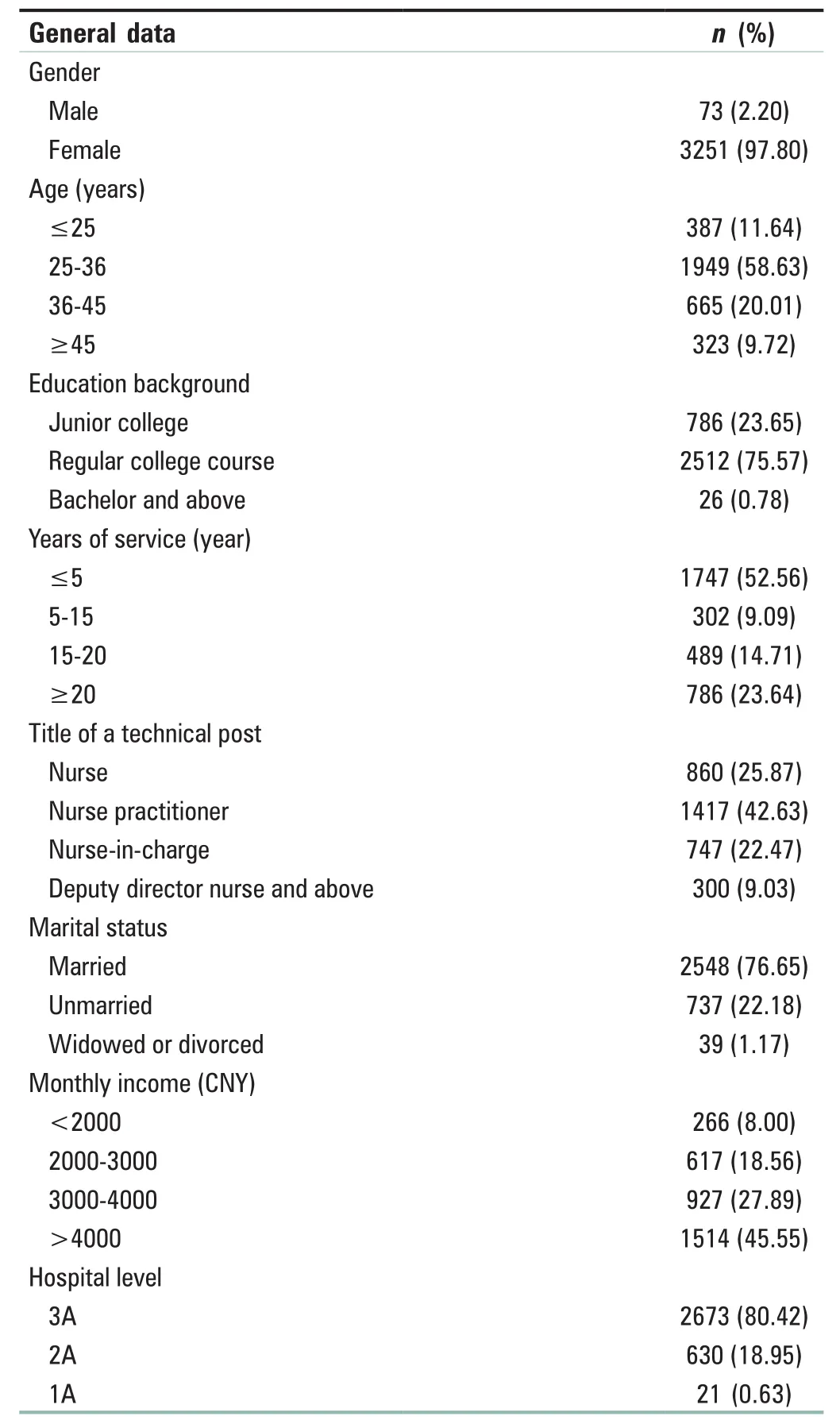
Table 1: General information of 3324 nursing volunteers
Correlation between function motivation and nurse’s professional identity of nursing volunteers
Professional cognitive evaluation, professional social support,professional social skills, professional frustration coping, and professional self-reflection were positively correlated with the total score of function motivation (all P < 0.05) [Table 2].

Table 2: Pearson correlation analysis of function motivation and nurse’s professional identity of nursing volunteers (r)
DISCUSSION
China Nightingale Volunteer Nursing Service Corps was approved and named by the Red Cross Society of China and established in Beijing in July 2007.It is the only nursing professional volunteer organization in China, composed of Nightingale Medallists, nursing professionals, nursing college students and caring people from all walks of life.Following the Seven Basic Principles of International Red Cross Movement, its aim is to carry forward the Red Cross spirit and Nightingale spirit, and actively carry out voluntary nursing services.The Nightingale Volunteer Nursing Service Group in Shanxi Province was established in May 2018.At present,there are 80 teams composing of nearly 10,000 volunteers in 11 hospitals and nursing colleges distributed into districts and cities in Shanxi Province, carrying out health education,first-aid training, home guidance for chronic diseases,professional nursing services for the people in need, medical alliance assistance, blood donation and other voluntary services in the communities, enterprises, schools, nursing homes and poor mountainous areas and so on.In particular,sustained and in-depth household tracking services enable patients in need of assistance to receive effective treatment and assistance.
In this study, the overall score of the function motivation of nursing volunteers is 157.12 ± 29.92, which is at a medium level.In the ranking, the two sub-scales of the voluntary function motivation with the highest score are values function motivation and enhancement function motivation.This indicates that nurses have a strong desire to express their values through volunteer activities.China Volunteer Service Federation points out that volunteer service activities adhere to the “beneficence and virtue” concept, with the core to promote the voluntary spirit, to realize the personal value through serving others and society, and to improve others’ life and even social environment.Geng[9]hold that Volunteer service has promoted the cultural construction of the hospital.Tan[10]emphasizes that young volunteers bring help to others and society through their service, which in return helps themselves grow.Therefore, organizations at different levels should provide voluntary services and content to them through multiple platforms and help them realize the sense of worth and self-enhancement.
The total score of professional identity of nurses in Shanxi Nightingale Volunteer Service team is 110.31 ± 18.71, which is at a medium level.This indicates that the professional identity of nurses in the volunteer service team is at a normal level.Professional identity refers to a clear understanding and confirmation of one’s career goals, abilities, personal interests, and personal values.[11]Xu et al.[12]found that the overall professional identity of nursing interns was low,especially the undergraduate nursing interns; if the hospital does not pay much attention to the relevant education and guidance of their professional identity after taking office, it will cause lower overall professional identity.Zhou et al.’s[13]study showed that improving nurses’ professional identity can improve their willingness to stay on the job.Other studies show that volunteers can re-recognize the social value of nursing profession through the carrier of voluntary nursing service, which can stimulate their enthusiasm about nursing profession, strengthen the confidence in nursing profession,and help them find the way to realize self-value.[14-17]Therefore, nursing professional identity is closely related to voluntary nursing service, and hospitals should increase the channels for nurses to participate in voluntary service through various ways, so as to improve professional identity.
In this study, it can be seen from Table 2 that professional cognitive evaluation, professional social skills, professional frustration coping, and professional self-reflection are positively correlated with the total score of function motivation of nursing volunteers (P < 0.05).It shows that nurses’ identity to their profession is affected by many factors.Volunteer service can improve nurses’ social skills, enhance their endurance in the face of setbacks, and strengthen their determination to pursue the profession of nursing.Among the dimensions of professional identity, professional self-reflection was positively correlated with values function motivation, protective function motivation, and career function motivation (P < 0.05).Professional frustration coping was positively correlated with values function motivation and career function motivation.Professional social support was positively correlated with understanding function motivation (P < 0.05).Professional cognitive evaluation was positively correlated with values function motivation,enhancement function motivation, understanding function motivation, career function motivation, social function motivation, and protective function motivation (P < 0.05).Among them, professional cognitive evaluation, professional self-reflection and volunteer function motivation were significantly correlated (r = 0.044 and 0.042, respectively),which showed that volunteering is a process of serving others and improving yourself.In the process of helping others,nursing volunteers increased their professional identity and gained a profound understanding of the connotation of nursing profession.Just like the COVID-19 pandemic outbreak in 2020, as nurses have been entitled “heroes in harm’s way,”they began to re-recognize the meaning of nursing and reflect on the real value of nursing.Therefore, improving oneself can serve others with high quality, forming a virtuous cycle of continuous improvement.
CONCLUSION
The researches show that the function motivation and professional identity of nursing volunteers in Shanxi are at the national average level.There is still a long way to go to establish a perfect nursing volunteer service system.Nursing volunteer service is a service project to improve nursing professional quality and enhance nurse’s professional identity.Volunteer service motivation and nurse’s professional identity are the two aspects of mutual integration and mutual promotion.Hence, it is suggested that all levels of hospitals and nursing colleges should strengthen nursing vocational education, set up voluntary courses or service projects,and actively guide nursing staff to participate in voluntary nursing services, to reflect the value of nursing profession and enhance the sense of honor of nursing profession.Moreover, how to take advantages of professional skills to provide voluntary nursing services for the public and how to use the established voluntary nursing service system to give play to the initiative of nursing staff are subjects that require us to think about for a long term.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
 Journal of Integrative Nursing2021年4期
Journal of Integrative Nursing2021年4期
- Journal of Integrative Nursing的其它文章
- lnsigni ficant small can still be mighty: Trend of chronic kidney disease in Nigeria
- Moxibustion plus acupuncture improves the efficacy and quality of life of patients with polycystic ovary syndrome:A randomized controlled trial
- Relationship of demoralization with anxiety, depression,and demographics of Chinese dialysis patients
- Application of five-element music therapy in pain coping skills training in patients with knee osteoarthritis
- Self-management of cataract extraction among diabetes patients
- Knowledge on malaria among caregivers with children aged under 5 years at Kenyasi Health Center
