Application of five-element music therapy in pain coping skills training in patients with knee osteoarthritis
Suqian LI, Jingjin XU, Ling TANG, Ye LI,Huaxin WANG, Lixue ZHAO, Jianshuang YAO,Shuying WANG, Nan LI
1Department of Rheumatology, Dongfang Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China; 2Rheumatism Department, School of Nursing, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China; 3Department of Nursing, Dongfang Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China
ABSTRACT
Objective: The objective of this study is to assess the application effect of five elements music therapy introduced in the pain coping skills training of knee osteoarthritis (KOA).
Materials and Methods: Totally, 80 patients with KOA were selected and randomly divided into the experimental group (39 cases) and the control group (41 cases).The control group was only given routine nursing measures, and the experimental group was additionally treated with five-element music therapy on the basis of the control group, twice a day, 28 days in total.The Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) was used to evaluate the functional status of the knee joint of the two groups.The clinical efficacy of the two groups was evaluated by Guiding Principles for Clinical Research of New Chinese Medicine in the Treatment of Osteoarthritis.
Results: WOMAC score statistically significantly decreased in the experimental group (35.92 ± 9.48 vs.16.17 ± 5.43, P < 0.01) and the control group (36.73 ± 6.42 vs.22.53 ± 7.51, P < 0.01) after 28 days of intervention when compared with that before intervention; WOMAC score in the experimental group was lower than that of the control group after 28 days of intervention (16.17 ± 5.43 vs.22.53 ± 7.51, P < 0.01).The total effective rate of the experimental group was statistically higher than that of the control group (82.0% vs.51.2%, χ2 = 11.97, P= 0.003).
Conclusion: The combination of five-element music therapy and routine nursing measures has better effect in relieving pain and bad emotions of patients with KOA when compared with routine nursing measures alone.
Keywords: Emotions, five-element music therapy, knee osteoarthritis, pain, pain coping skills training
INTRODUCTION
Knee osteoarthritis (KOA) is a kind of degenerative bone and joint disease, which often occurs in the middle-aged and elderly people.It belongs to the category of “Bi syndrome” in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), clinically characterized by swelling, pain, stiffness, joint deformity occurring in severe cases, and often accompanied by bad emotions, which seriously reduces the quality of work and life of patients.[1]The survey has shown that with the aging of population in China, the number of patients with KOA increases significantly,which causes serious economic burden to the society.[2]There are many pathogenic factors of KOA, which may be related to genetic factors, gender, age, and type of work, etc.[3]
At present, although there is no cure for KOA, the disease progression can be delayed through the change of patients’own behavior.[4]According to the research of Somers et al.,[5]the treatment of KOA is mainly through the change of personal behavior to control the progression of the disease.
Hunt et al.[6]have introduced pain coping skills training (PCST)into the treatment of patients with KOA, through the change of their own behavior to relieve and control pain and bad mood, and achieved good clinical results.
In recent years, TCM nondrug therapy has obvious advantages in relieving clinical symptoms and reducing medical costs of KOA.[7]Nondrug treatment includes acupuncture, massage,five-element music therapy, diet guidance, rehabilitation exercise, emotional nursing, and so on.[8]For patients with KOA, appropriate methods can not only solve patient’s pain but also improve patients’ bad mood.Among them,five-element music therapy is a TCM characteristic technology and also a nondrug green therapy for emotional nursing according to the patients’ TCM syndrome differentiation.The implementation of five-element music therapy can not only improve the patients’ bad mood but also relieve the pain symptoms, thus improving the patients’ quality of life.[9]Therefore, the introduction of five-element music therapy into PCST may help to provide a more economical and effective treatment method for patients with KOA.In this study, we compared the effect of routine nursing measures versus five-element music therapy plus routine nursing measures,with a view to seeking a more effective treatment in relieving symptoms of patients with KOA.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Design
A randomized controlled trial was used in this study.
Ethical considerations
This study was approved by the ethics committee of Dongfang Hospital of Beijing University of TCM, with batch No.: JDF-IRB-2019031102, and all procedures followed the requirements of Declaration of Helsinki for clinical research.Moreover, the written informed consent was obtained from all patients or their families.The patients had the right to withdraw at any time during the study.
Study subjects
The study subjects were the patients with KOA in the Department of Rheumatology, Dongfang Hospital, Beijing University of TCM from January 2019 to January 2021.
Diagnostic criteria, inclusion criteria and exclusion criteria
The diagnostic criteria refer to the diagnostic criteria of KOA formulated by the Orthopaedics Branch of Chinese Medical Association in 2007.[10]The inclusion criteria were that(1) patients aged between 40 and 75 years, (2) patients met the above diagnostic criteria of KOA, and (3) patients voluntarily participated in and signed informed consent.The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) suffering from other rheumatic immune diseases affecting the knee joint, (2) hearing impairment and other serious nervous system diseases, (3) complicated with heart, lung and other life-threatening diseases, or (4) those who participated in other clinical trials within 3 months.
Randomization
A total of 80 patients were randomly divided into the experimental group (39 cases) and the control group (41 cases)according to random number table.
Interventions
Both groups were treated with glucosamine sulfate capsules(0.314 g per capsule, Zhejiang Haizheng Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.), 0.628 g each time, three times daily in the morning, in the noon and in the evening, 28 days in total.Besides, patients in both groups were given routine nursing measures, namely mainly strengthening the self-management of patients, supplemented by exercise and cognitive psychological guidance.The specific contents include health education, follow-up, emotional counseling, physical exercise, diet guidance, and weight control.The regular Wechat or telephone follow-up were done as planned for patients after discharge to remind them to actively cooperate with the treatment according to the requirements.
The experimental group was treated with extra TCM five-element music therapy.The principles of music selection followed TCM viscera syndrome differentiation, five-element theory, and relationship of viscera, five elements and five tones: Five elements wood, fire, earth, gold and water correspond with liver, heart, spleen, lung, kidney in five Zang-organs, as well as Jiao, Zhi, Gong, Shang and Yu in five tones.The basic melody selected was Traditional Chinese Five-Element Music, played by China National Traditional Orchestra with Hao Wanshan as counselor.The devices were a CD of Traditional Chinese Five-Element Music, a mobile phone, or a MP3 players.The volume was 40-60 dB, turned based on the comfort of patients.The patients needed to receive the music therapy in the TCM treatment room of the hospital in the first 2 weeks of the intervention, then at home or nursing home after discharge.The most important thing was to listen the melody in quiet surroundings with good air circulation.After discharge, the patients were reminded by short message service or Wechat every day and followed up by telephone every other day.All patients received music therapy twice a day, 30 min each time, for 28 days.
Observation index
If patients had osteoarthritis of both knees, the severe side of the knee was taken as observational sample.
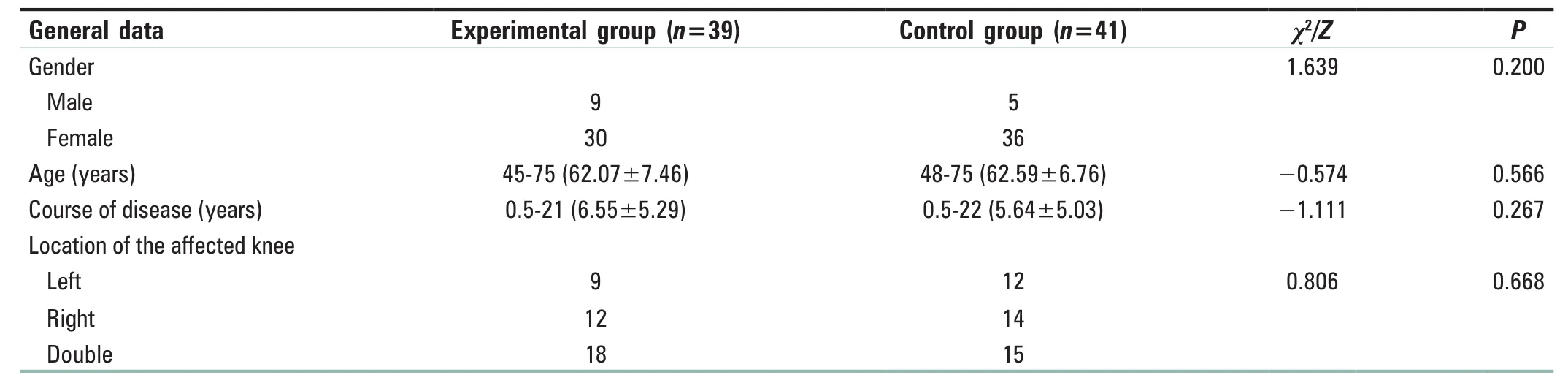
Table 1: Comparison of general conditions between the two groups
The Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC), first proposed by Bellamy and colleagues in 1988, was mainly applied to assess severity of knee arthritis.The scale includes 24 items in three aspects: pain with five items, stiffness with 2 items, and daily activity ability with 17 items.Each item was rated on a 5-point scale from 0 (no difficulty) to 4 (extreme difficulty).The higher the score,the worse the functional status.
According to the Guiding Principles for Clinical Research of New Chinese Medicine in the Treatment of Osteoarthritis,the curative effect was assessed by the percentage reduction of WOMAC score before and after the intervention.The percentage reduction of WOMAC score = [(score before treatment−score after treatment)/score before treatment]treat%.The percentage reduction of WOMAC score s90% indicates clinical control, 70%-90% indicates markedly effective, 30%-70% indicates effective, <30% indicates invalid.The total effective rate = (control cases + markedly effective cases + effective cases)/total number of cases cases × 100%.
Statistical analysis
SPSS version 19.0 software was used for the statistical analysis.Paired t test or nonparametric test was used for measurement data.The Chi-square test was used for counting data.P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
All patients completed the study, and none of them withdrew from the study.There was no significant difference between the two groups regarding gender, age, course of disease,and the location of the affected knee [all P > 0.05; Table 1].There was no significant difference in WOMAC score between the two groups before treatment.After 28 days of intervention, WOMAC scores of the two groups were lower than those before treatment (P < 0.05), and the score of the experimental group was lower than that of the control group [P < 0.05; Table 2].
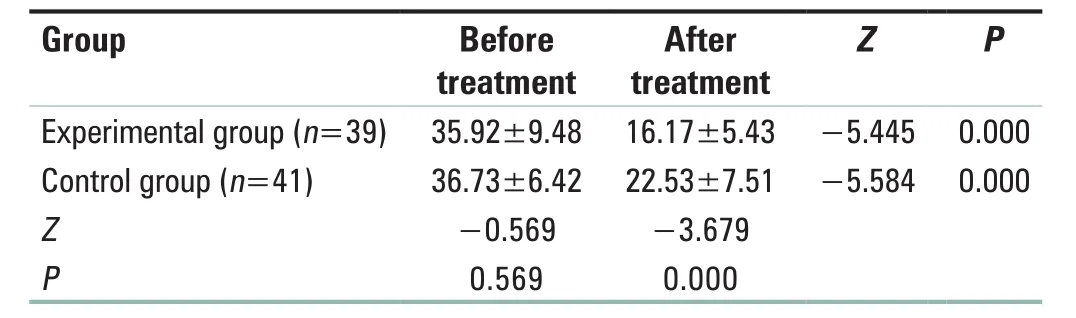
Table 2: Comparison of Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis lndex score between two groups
The total effective rate of the experimental group was 82%, and that of the control group was 51.2%; there was significant difference in the effective rate between the two groups [P < 0.05; Table 3].

Table 3: Comparison of clinical efficacy of patients with knee osteoarthritis between two groups
DISCUSSION
The formation of the five-element music ideological system of TCM is mainly based on the theories in Record of Music and Huangdi’s Canon of Internal Medicine, such as harmony between heaven and man, Yin and Yang, and five elements.[11]The use of five-element music therapy in the treatment of diseases is also known as “five-tone therapy.”[12]The principles of music selection followed TCM viscera syndrome differentiation.Therefore, clinically, according to TCM syndrome differentiation and classification, and correspondence of viscera, five elements, and five tones, appropriate five-element music repertoire was selected for patients with different syndrome types for listening.[13]By matching the five tones with the five Zang organs and five elements, five-element music therapy can release music of different frequencies and tones to regulate qi, blood, and the function of Zang-Fu organs, thus achieving the effect of treatment of diseases.[14]
TCM five-element music therapy is a kind of psychological nursing measures to adjust the patient’s viscera function and emotional state through different tones of music.As Huangdi’s Canon of Internal Medicine stated, five tones, five Zang organs and five emotions are closely associated; five Zang organs and five emotions are mutually affected.[15]Therefore, five-element music therapy can regulate bad emotions.[16]As a part of psychological nursing, five-element music therapy also plays an important role in relieving pain.[17]Qin et al.[18]randomly divided 64 patients with lower limb traumatic ulcer into the observation group and the control group, with 32 cases in each group.The control group was only given natural sound effect,while the observation group was given five elements music of TCM.The results showed that five-element music therapy can improve the pain of patients while changing dressings, thus improving the patient experience and medical service quality.Lai et al.[19]randomly divided 60 patients with KOA-related pain into treatment group and control group, with 30 cases in each group.The control group was given routine treatment and nursing, while the treatment group was given five-element music therapy for listening on the basis of the control group,once a day, 30 min each time, a total of 28 days.The results showed that the treatment group gained more effective effect in relieving the pain symptom of patients with KOA than control group, which is consistent with the results of the present study.In this study, we introduced five-element music therapy into PCST of patients with KOA to relieve symptoms of the patients, and found that the symptom of pain and bad emotions of patients obviously improved through intervention of five-element music therapy plus routine nursing measures.
CONCLUSION
Five-element music therapy is a psychological nursing intervention of regulating viscera function and emotional state by releasing music with different tones.It is not only TCM characteristic technology but also the part of health education.In this study, we introduced five-element music therapy into PCST of patients with KOA to relieve symptoms of the patients, play corresponding tones for patients according to the TCM syndrome differentiation and classification of diseases, gained satisfactory results that the implementation of five-element music therapy can effectively relieve pain symptom and bad emotions of patients with KOA.
Financial support and sponsorship
The study is supported by the project of independent topic selection of Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine in 2019 (No.: 2019-jyb-js-105).
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
 Journal of Integrative Nursing2021年4期
Journal of Integrative Nursing2021年4期
- Journal of Integrative Nursing的其它文章
- lnsigni ficant small can still be mighty: Trend of chronic kidney disease in Nigeria
- Moxibustion plus acupuncture improves the efficacy and quality of life of patients with polycystic ovary syndrome:A randomized controlled trial
- Relationship of demoralization with anxiety, depression,and demographics of Chinese dialysis patients
- A study on the correlation between function motivation and professional identity among nursing volunteers
- Self-management of cataract extraction among diabetes patients
- Knowledge on malaria among caregivers with children aged under 5 years at Kenyasi Health Center
