Theoretical Model on Transformation Factors of Scientific and Technological Achievements under the Belt and Road Initiative
WANG XiyuanZHOU YunwenZHANG ZhenyiPANG XueyanYAN Dandan
College of Fashion and Design, Donghua University, Shanghai 200051, China
Abstract: With the continuous deepening of the Belt and Road Initiative, the countries involved are increasingly connected in the field of science and technology. Based on the transformation theory of scientific and technological(S&T) achievements, this study establishes a theoretical model of transformation factors of S&T achievements under the Belt and Road Initiative. Combined with the data analysis from questionnaire, it is found that in S&T achievements transformation process, there is a significant positive correlation between the innovation factors and the transfer factors, between the transfer factors and the diffusion factors, and between the diffusion factors and the transformation results. These conclusions provide reference for the subsequent S&T achievements transformation activities under the Belt and Road Initiative. Therefore, in the process of promoting the transformation of S&T achievements under the Belt and Road Initiative in the future, innovation factors such as information innovation, service innovation, and cooperative innovation should be fully reflected. Relevant agencies should take the transfer factors of S&T achievements as guidance; promote and apply the results of incubation through diffusion media and diffusion channels.
Key words: the Belt and Road Initiative; transformation of scientific and technological(S&T) achievements; theoretical model
Introduction
With the advent of the era of globalization, new features have emerged in the international pattern and territory of science and technology. The interaction and communication between the scientific and technological(S&T) innovation systems of different countries or regions become more frequently. Various forms of international scientific research cooperation, including international technology transfer, have also become closer. Since the Belt and Road Initiative was put forward in 2013, the joint construction of the Belt and Road has achieved remarkable results in policies, facilities, trade and other aspects. In the field of S&T innovation cooperation, some constructive achievements have been made, such as the establishment of the Belt and Road Initiative international alliance of scientific organizations; the launch of science and technology partnership programs with ASEAN and South Asia; the foundation of five regional technology transfer platforms with ASEAN, South Asia, Arab countries, Central Asia and Central and Eastern Europe[1].
The technology innovation incubation industry under the Belt and Road Initiative is facing more opportunities while huge challenges. There is a close relationship and demand between China and other countries in the transformation of S&T achievements but there exist objective contradictions and conflicts in many aspects, such as subjective cognition and objective standard, information sharing and technological transfer, and personnel exchange and interaction. For example, in the aspect of science and technology system, the S&T innovation incubation platform for EU countries has entered the stage of collectivization development, and the government is not the leading party. However, the transnational science and technology incubation platforms in China still rely on the government as the main key person, so they are relatively conservative in the process of science and technology incubation and introduction, and lack of space for the free development of S&T achievements. Zhangetal.[2]explored the new model of "seven in one" for the contribution of government, industry, university and research institutions in the community of achievements transformation, and proposed to build an achievement research and service platform with multi-subject participation and collaborative participation of multi-department and multi-subject. Gao and Liu[3]summarized the management system of China-EU S&T cooperation from a macro perspective, pointing out that Sino-European S&T cooperation has gone through a development process from nothing to existence, from less to more, from small to large. S&T cooperation between China and EU is becoming more equal in status, more standardized in management and improved in mechanism. At present, the research on the transformation of scientific achievements focuses on local innovation, and there is a lack of trans-national case study. Therefore, the theoretical and practical research on the transformation of S&T achievements under the Belt and Road initiative needs to be enriched.
Based on the transformation theory of S&T achievements, this paper focuses on the transformation under the Belt and Road Initiative. The study combines domestic modes of science and technology incubation industry and studies the core factors that affect the transformation and the correlation between these factors. Through data investigation and empirical analysis, this paper puts forward strategies to promote the transformation of S&T achievements under the Belt and Road Initiative, which will serve as the basis for the subsequent cooperation and development of S&T innovation along the Belt and Road.
1 Theories and Theoretical Model
1.1 Transformation theory of S&T achievements
The transformation of S&T achievements is a local concept in China, and it is often called technology transfer internationally[4]. According to the Law of the People's Republic of China on Promoting the Transformation of S&T Achievements amended in 2015, the definition of "transformation of S&T achievements" is as follows. In order to promote the improvement of social productivity, experiments, development, application and promotion of S&T achievements are carried out, so as to promote the incubation of achievements into new technologies, new processes, new materials, new products or a series of activities for the industrialization of achievements[5]. Due to the differences in market mechanism, social environment and evaluation objects, countries adopt different indicators and methods to evaluate the performance of S&T achievements. Technology transfer refers to the activity process of technology output and input within or between countries, regions, industries and within the technology system itself, including the transfer, transplantation, introduction, exchange and popularization of technological achievements, information and capabilities[6]. A schematic diagram of the transformation process of S&T achievements is shown in Fig. 1, which describes how new achievements are transformed from research and development to production practice.
According to the related literatures, the transformation theory of S&T achievements can be divided into innovation theory of S&T achievements, transfer theory of S&T achievements and diffusion theory of S&T achievements.

Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of the transformation process of S&T achievements
1.1.1InnovationtheoryofS&Tachievements
Stoneman[7]defined technological innovation as the first introduction of scientific inventions into the production system through related research and development, thus forming a whole set of business transactions. With the continuous development of economy and society, in Ref. [8] it is believed that when enterprises apply S&T achievements and put them into the market and finally get profits, the process can be called the innovation of S&T achievements. Since then, the word "technology" has gradually been replaced by S&T achievements. In a broad sense, the innovation of S&T achievements refers to the whole process from research and development to dissemination of the achievements. The process often includes the initial S&T achievements produced by individuals or single enterprises, and the continuous transfer, replication and even re-innovation of the achievements after they are finally put into the market. In essence, the innovation theory of S&T achievements is a part of the transformation theory of S&T achievements.
Summing up the relevant theories above, we conclude that the main factors affecting the innovation theory of S&T achievements can be summarized into five aspects. (1) New products: innovative products that have never appeared in the market and are not known by consumers. (2) New methods: production methods that have not been used before by the industry sector. (3) New markets: markets that have not entered a certain region or country. (4) New sources of supply: new sources of supply of raw materials or semi-finished products that have been explored. (5) New organizational form: the organizational form that has never been cooperated or never appeared before, to break the former monopoly market form.
1.1.2TransfertheoryofS&Tachievements
Technology transfer refers to the process of exporting and importing S&T achievements between or within countries, regions or industries. According to the current research views of domestic and foreign scholars on the transfer of S&T achievements, the transfer process can be summarized as the following four points: (1) Based on the environmental applicability of S&T achievements, when the achievements are applicable to the environmental background of the recipient, they can be referred to as the transfer of S&T achievements[9]. (2) From the purpose of the transfer of S&T achievements, Spencer[10]believed that the transfer of achievements must achieve a certain goal, which is the judgment condition set in advance in the whole transfer process. (3) Based on the results of the transfer of S&T achievements, Kosz[11]believed that only when the recipient fully absorbs and flexibly applies the achievements, the transfer of S&T achievements can be called the end. (4) Mason[12]divided the transfer of S&T achievements into three modes: the transfer of technology, the recipient's learning and the user's application. Only after the transfer of achievements has passed these three steps can it be called the transfer of S&T achievements.
Summarizing the relevant theories above, the main factors affecting the transfer of S&T achievements can be concluded as follows. (1) Applicable environment: S&T achievements need to be fully applied in different environments between suppliers and demanders. (2) Transmission mode: the way that the supplier and the demander transfer the S&T achievements. (3) Acceptor's learning: whether the demander can truly understand and master the S&T achievements. (4) User's application: whether the S&T achievements can be really used in the production practice.
1.1.3DiffusiontheoryofS&Tachievements
The diffusion theory of S&T achievements has some similarities with the transfer theory, but the most different point in essence is that the diffusion activities refers to the transfer between multiple users, while the transfer activities refers to the one-to-one transfer. Thus it can be seen that diffusion has a wider scope of influence, a clearer purpose, a more significant effect and has more obvious factors of communication. In Ref.[13], diffusion is defined as the process of S&T achievements innovation generated over a period of time spreading within a certain group through a certain channel. At present, the main carrier of the diffusion of S&T achievements is multinational enterprises, which break the monopoly of the original market, but at the same time, it also brings great competitive pressure to the market[14]. In the process of diffusion of S&T achievements, one of the most important factors is the subjects involved in diffusion of S&T achievements, which can usually be summarized as universities and research institutes with achievements, demanders of S&T achievements (enterprises), S&T service organizations, governments agencies (financial department, S&T department, education department)[15]. Figure 2 shows the main body of diffusion of S&T achievements.
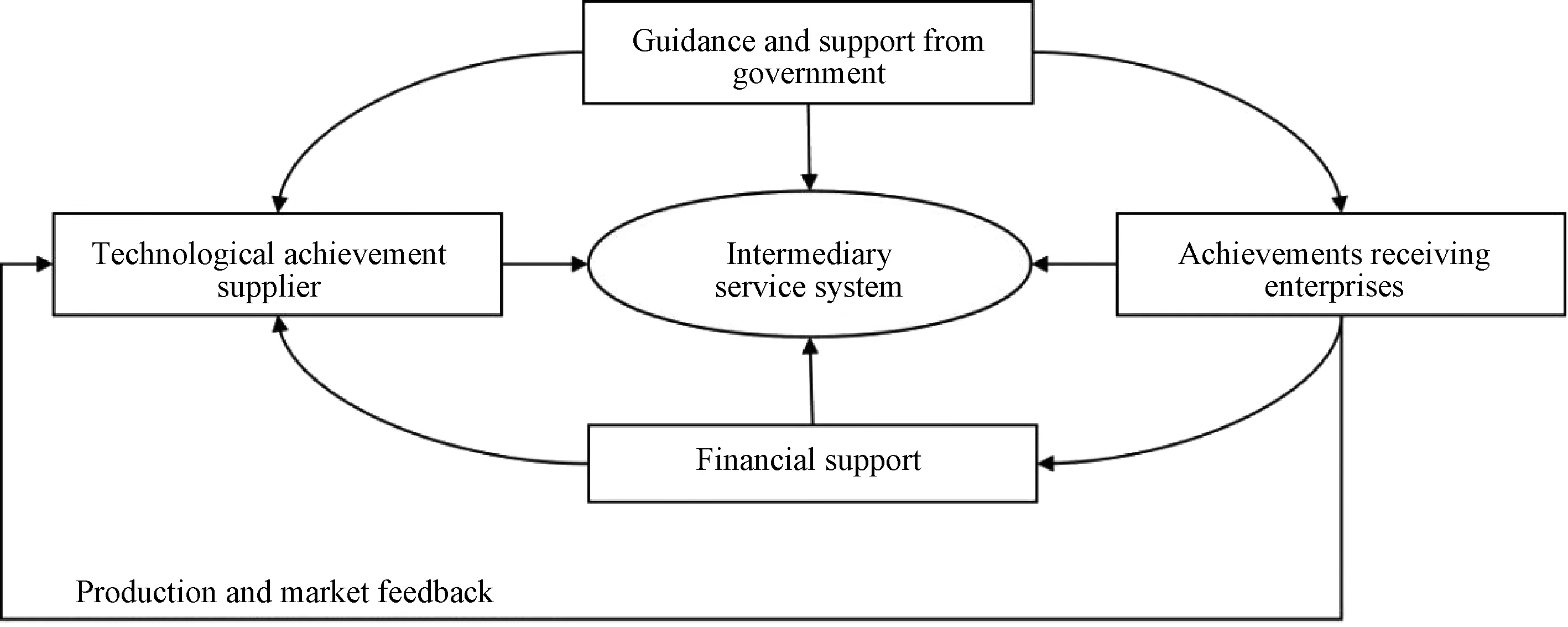
Fig. 2 Relationship diagram of the main bodies in transformation process
From the results of the diffusion of S&T achievements, it can be considered that S&T achievements will be improved, developed and re-innovated due to the final environment. Summing up the relevant theories above, the main factors affecting the diffusion of S&T achievements can be summarized as follows. (1) Diffusion subjects: providers and receivers of S&T achievements. (2) Diffusion media: how can the diffuser make the S&T achievements be understood and accepted by the audience in the fastest and most effective way? (3) Diffusion time: the complexity of the innovation of the S&T achievements to be diffused. (4) Diffusion space: the local specific social, political, economic, educational environment. (5) Diffusion effect: recovery of relevant feedback through diffusion results. Through the analysis of the influencing factors of the innovation theory, transfer theory and diffusion theory of S&T achievements, the relevant factors affecting the transformation of S&T achievements under the Belt and Road Initiative are listed preliminarily.
1.2 Model and hypothesis
Through the analysis of the factors affecting the transformation of S&T achievements, as shown in Table 1, we list the elements that will affect the transformation of S&T achievements, and apply them to the formulation of models and hypotheses.

Table 1 Division of influence factors based on scholars' theory
According to the classification of the transformation factors in the previous section, we construct a preliminary theoretical model of the transformation results of S&T achievements, as shown in Fig.3. There is a process of mutual influence between the innovation of S&T achievements, the transfer of S&T achievements and the diffusion of S&T achievements, and there is a progressive relationship among these three factors, so a three-level progressive relationship model of "innovation factors of S&T achievements——transfer factors of S&T achievements——diffusion factors of S&T achievements" is constructed.

Fig. 3 Theoretical model of transformation results of S&T achievements
1.2.1InnovationfactorsandtransferfactorsofS&Tachievements
According to the related factors of innovation theory of S&T achievements summarized above, the innovation factors of S&T achievements under the Belt and Road Initiative can be summarized as information innovation, service innovation and cooperation innovation. These factors will affect the innovation of achievements, and also affect the transfer of achievements. When any of these factors achieves good results in the transfer process, they will be constantly used; otherwise, they will be replaced. The innovation factors and transfer factors influence each other and interact with each other.
Therefore, the following hypotheses are proposed:
H1: There is a significant positive correlation between innovation factors of S&T achievements and transfer factors of S&T achievements under the Belt and Road Initiative (independent variable: innovation factors of S&T achievements; dependent variable: transfer factors of S&T achievements).
H1a: There is a significant positive correlation between information innovation and transfer factors of S&T achievements.
H1b: There is a significant positive correlation between service innovation and transfer factors of S&T achievements.
H1c: There is a significant positive correlation between cooperation innovation and transfer factors of S&T achievements.
1.2.2TransferfactorsanddiffusionfactorsofS&Tachievements
According to the related factors of achievement transfer theory summarized above, the transfer factors of S&T achievement under the Belt and Road Initiative can be summarized as transfer mode and reception learning. The diffusion of S&T achievements begins with the transfer of S&T achievements. S&T achievements are transferred in different ways, from the developer to the recipient, and adapt to the recipient's environment. The following is the diffusion action and large-scale application of S&T achievements to realize the economic value of the achievements. To a certain extent, the diffusion media in the diffusion factors depends on the reception learning in the transfer factors. Generally speaking, the transfer factors affect the diffusion activities. In conclusion, the transfer factors of S&T achievements affect the diffusion of S&T achievements.
Therefore, the following hypotheses are proposed:
H2: There is a significant positive correlation between transfer factors of S&T achievements and diffusion factors of S&T achievements under the Belt and Road initiative (independent variable: transfer factors of S&T achievements; dependent variable: factors of diffusion of S&T achievements).
H2a: There is a significant positive correlation between transfer mode and diffusion factors of S&T achievements.
H2b: There is a significant positive correlation between reception learning and diffusion factors of S&T achievements.
1.2.3DiffusionfactorsandtransformationresultsofS&Tachievements
According to the related factors of the diffusion theory of S&T achievements, the diffusion factors under the Belt and Road Initiative can be summarized as diffusion media and diffusion channels. The diffusion factor of S&T achievements is the last factor that affects the transformation results of S&T achievements. After the process of innovation and transfer of achievements, the diffusion process will further expand the results in the first two stages, and it is also an important index to measure the value of S&T achievements.
Therefore, the following hypotheses are proposed.
H3: There is a significant positive correlation between the diffusion factors of S&T achievements and the transformation results of S&T achievements under the Belt and Road Initiative (independent variable: diffusion factors of S&T achievements; dependent variable: the transformation results of S&T achievements).
H3a: There is a significant positive correlation between the diffusion media and the transformation results of S&T achievements.
H3b: There is a significant positive correlation between the diffusion channels and the transformation results of S&T achievements.
1.3 Theoretical model construction
Based on the analysis above, the theoretical model on transformation factors of S&T achievements under the Belt and Road Initiative in this paper can be constructed in Fig. 4.
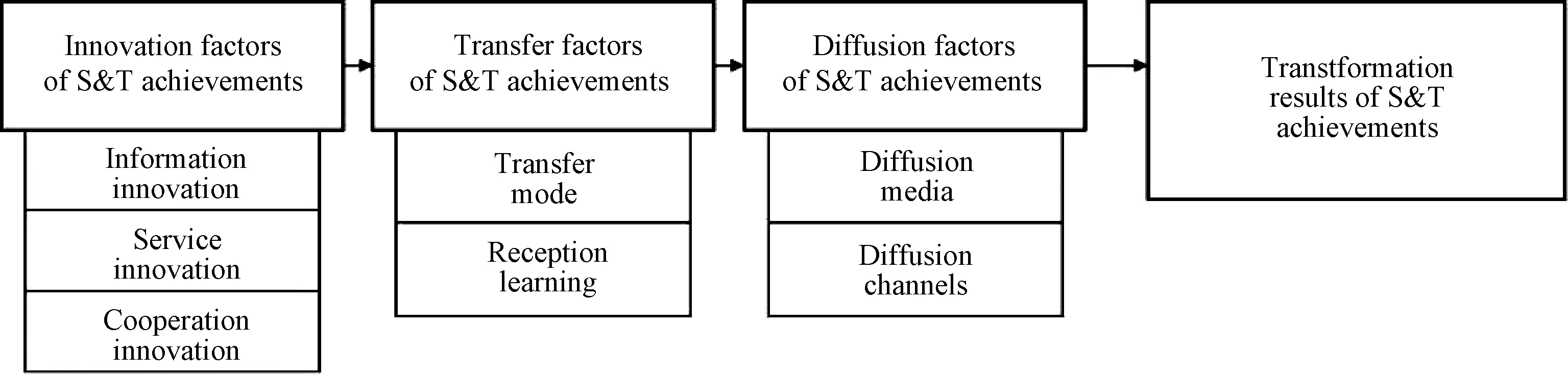
Fig. 4 Theoretical model on transformation factors of S&T achievements under the Belt and Road Initiative
2 Research
2.1 Secondary factors collection under the Belt and Road Initiative
2.1.1CollectionofinnovationfactorsofS&Tachievements
In the transformation process of S&T achievements under the Belt and Road Initiative, information innovation can be divided into the following three categories. Technical information usually refers to intellectual property rights, scientific research institutions, scientific research results and other information resources; talents information usually refers to industry experts, entrepreneurial mentors, S&T talents and other talent resources; industrial information usually refers to industrial resources such as industrial alliances, market exchanges, upstream and downstream industries,etc. In order to meet the needs of different user groups, service innovation needs to meet the following principles. (1) Service diversification and collaboration: since the service users of the transformation of S&T achievements may be the government, enterprises, individuals, investment and financing providers, and international exchange services are also involved, it requires the cooperation of all departments, and the service system must be diversified and collaborative. (2) Intelligent service: in the traditional transformation process, one-way service mode is provided, that is, the "demand-response" mode. However, intelligent service can present the active push mode, and deliver more accurate information and service content to users through data screening. (3) Personalization and specialization of service: with the continuous emergence of new innovative industries and the continuous subdivision of industrial categories, the transformation process of S&T achievements tends to be more specialized. (4) Effectiveness of supervision: in the whole incubation process, relevant institutions and platforms need to play the role of supervision and management. Combined with the existing transformation services of S&T achievements, the secondary factors of service innovation can be divided into personalized customization services, intellectual property services, and targeted legal, investment and financing services. At present, most of the objects who pay for S&T achievements are S&T enterprises. However, in addition to the cooperation with core enterprises, a large number of user groups, such as government agencies, non-profit organizations and individuals in various countries participant in the transformation process as well. Cooperative innovation can be subdivided into research institutes universities, colleges and universities, and industrial resources. Table 2 shows the collection of innovation factors.

Table 2 Collection of innovation factors of S&T achievements
2.1.2CollectionoftransferfactorsofS&Tachievements
The transfer of technology can generally be divided into the following four aspects. (1) Technology introduction: in order to seek development, enterprises introduce intellectual property from outside, and develop new products or technologies by using the introduced intellectual property, so as to expand market share and enhance competitive advantage. (2) Technology export: the export of advanced technology from one country to other countries usually includes three basic forms, namely material technology export, design technology export and technical ability export. (3) Technology transfer: the owner of a mature or in the state of invention transfers the technology to the demander of this technology, so as to obtain a certain return. (4) Technical cooperation: two or more individuals, enterprises or national governments sign a cooperative cooperation plan in the field of science and technology in order to achieve a certain goal of S&T achievements. During the cooperation, both parties shall share information, experience, design schemes and other materials. Therefore, the secondary factors of transfer mode can be divided into scientific research cooperation, strategic alliance and personnel exchange.
According to the analysis of the existing international transformation cases of S&T achievements, in the process of S&T achievements transfer, reception learning mainly adopts two forms: online learning and offline practice. Therefore, reception learning factors are divided into online training courses and offline salons. Table 3 shows the collection of transfer factors.

Table 3 Collection of transfer factors of S&T achievements
2.1.3CollectionofdiffusionfactorsofS&Tachievements
At present, the diffusion media of transformation service of S&T achievements in China is mainly government propaganda at all levels, but with the emergence of more and more cooperative innovation, the types of institutions involved are getting more complex. At the same time, with the integration of global science and technology economy, the Internet platform has a high-intensity diffusion effect. Therefore, the secondary factors of diffusion media are divided into industry information database (including industry journal materials), public media and cooperative agency (including professional consulting institutions cooperating with technology incubation platforms). In addition, the diffusion subjects of achievement transformation under the school-enterprise cooperation mode tend to favor colleges and universities, while the rest of the diffusion subjects are basically national or global entrepreneurs. However, according to the output ratio of S&T achievements, it can be seen that the output of S&T achievements of scientific research institutes and universities accounts for more than 35%, which shows that the current transformation process of S&T achievements in China ignores this aspect. Therefore, the secondary factors of diffusion channels are divided into business plan competition, local and overseas inspection activities and co-build S&T achievements incubation projects with overseas universities and research institutes. Table 4 shows the collection of diffusion factors.

Table 4 Collection of diffusion factors of S&T achievements
2.2 Questionnaire design and data collection
In order to verify the three hypotheses of the transformation factors of S&T achievements under the Belt and Road Initiative, this study conducts empirical analysis through questionnaire survey. The pre-investigation was carried out to select resources around to ensure that the background of the market surveyor was similar to the background of the respondents in the actual survey, and the industry staff were consulted to revise the questionnaire. Finally, large-scale questionnaire distribution was carried out.
In order to improve the coverage and effectiveness of the questionnaire distribution, the questionnaire in this study was mainly distributed through a combination of offline and online. The main channels include: (1) Distribute the questionnaries through the friends of the people who are innovating and starting businesses. (2) Distribute the questionnaries to relevant person through social relations between parents and mentors. (3) Collect offline questionnaries in the incubation base. A total of 260 questionnaires were collected in this survey, and after eliminating 26 invalid ones, 234 valid ones were finally obtained. The overall efficiency of the questionnaires was 90%.
2.3 Descriptive statistical analysis of samples
The samples selected in this study include "enterprise personnel related to the transformation of S&T achievements under the Belt and Road Initiative", "individual S&T workers with a plan to carry out the transformation of S&T achievements under the Belt and Road Initiative", "workers who know the transformation of S&T achievements under the Belt and Road Initiative" and others. In Table 5, the proportion of males is 57.7% and that of females is 42.3%. In terms of age, the proportion of people aged 26-35 years old is the highest, accounting for 48.7%, the proportion of people aged 16-25 years old is 7.3%, the proportion of people aged 36-45 years old is 32.9%, and the proportion of people aged over 45 years old is 11.1%. It can be seen that people engaged in the work related to the transformation of S&T achievements are still inclined to young people. In terms of educational background, the proportion of bachelor's degree is the highest, 37.6%, and that of junior college degree is 36.8%, indicating that the objects involved in the achievements transformation under the Belt and Road Initiative have a certain educational background. The overall sample was in line with actual expectations.
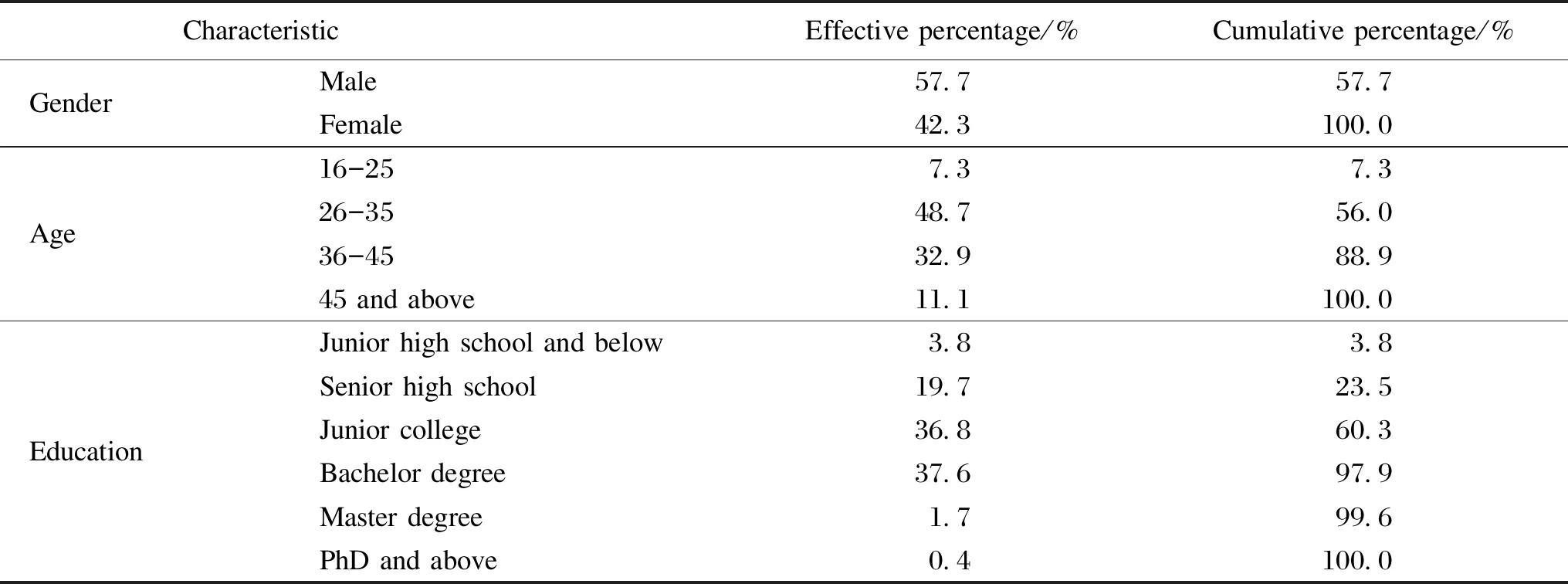
Table 5 Descriptive statistical structure of sample characteristics
2.4 Reliability and validity analysis
In Table 6, the overall Klonbach Alpha coefficient of the questionnaire is 0.919, and the Klonbach Alpha coefficient of the innovation factor, transfer factor and diffusion factor are 0.815, 0.700, and 0.749, respectively, all greater than 0.7, indicating that the scales have good internal consistency and are relatively reliable.
From Table 7, Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin(KMO) values of all scales are greater than 0.5, andPvalues of Bartlett's sphericity test are all 0 and less than 0.05, indicating that all scales have good structural validity.

Table 6 Reliability analysis

Table 7 KMO and Bartlett test
3 Discussion and Hypothesis Verification
3.1 Correlation analysis of factors
3.1.1InnovationfactorsandtransferfactorsofS&Tachievements
From Table 8, the correlation coefficients of transfer factors and information innovation, service innovation and cooperative innovation are 0.814, 0.831 and 0.790 respectively, all greater than 0, andPvalues are all less than 0, indicating that transfer factors are significantly positively correlated with information innovation, service innovation and cooperative innovation. Among them, the correlation coefficient of information innovation is 0.814, service innovation is 0.831, and cooperative innovation is 0.790. It can be seen that service innovation has the largest impact on the transfer of platform S&T achievements, followed by information innovation and cooperative innovation. Therefore, the degree of impact of the three innovation factors of S&T achievements on the transfer of S&T achievements under the Belt and Road Initiative is ranked as service innovation > information innovation > cooperative innovation.

Table 8 Correlation analysis results of the innovation factors and transfer factors of S&T achievements
3.1.2TransferfactorsanddiffusionfactorsofS&Tachievements
From Table 9, the correlation coefficients of diffusion factors, transfer mode and reception learning are 0.828 and 0.752 respectively, both greater than 0, andPvalues are all less than 0, indicating that diffusion factors, transfer mode and reception learning are all significantly positively correlated. Among them, the correlation coefficient of transfer mode is 0.828 and that of reception learning is 0.752, indicating that transfer mode has the greatest impact on the diffusion of S&T achievements, followed by reception learning.

Table 9 Correlation analysis results of the transfer factors and diffusion factors of S&T achievements
3.1.3DiffusionfactorsandthetransformationresultsofS&Tachievements
It can be seen from Table 10 that the correlation coefficients of transfer factors, diffusion channels and diffusion media are 0.839 and 0.790 respectively, both greater than 0, and thePvalues are all less than 0, indicating that the transfer factors are significantly positively correlated with diffusion channels and diffusion media. The influence of diffusion media and diffusion channels on the transformation results of S&T achievements is verified. The above research shows that all factors of the diffusion of S&T achievements on the results of transformation of S&T achievements have a significant positive correlation. Among them, the correlation coefficient of diffusion media is 0.790, and diffusion channel is 0.839. It can be seen that diffusion channel has the greatest influence on the results of achievements transformation, followed by diffusion media. Therefore, under the Belt and Road Initiative, the degree of impact of the three innovation factors of S&T achievements on the transfer of S&T achievements is ranked as service innovation, information innovation, and cooperative innovation.

Table 10 Correlation analysis results of the diffusion factors and results of S&T achievements
3.2 Regression analysis
3.2.1InnovationfactorsandtransferfactorsofS&Tachievements
From Table 11, the adjustedR2is 0.790, indicating that the model fits well. The significance ofFtest is less than 0.001, indicating that this model is superior to the model containing only the intercept term and is convincing. The coefficients of information innovation, service innovation and cooperative innovation are all greater than 0, and their significance is less than 0.001, indicating that information innovation, service innovation and cooperative innovation all have a significant positive effect on transfer factors.
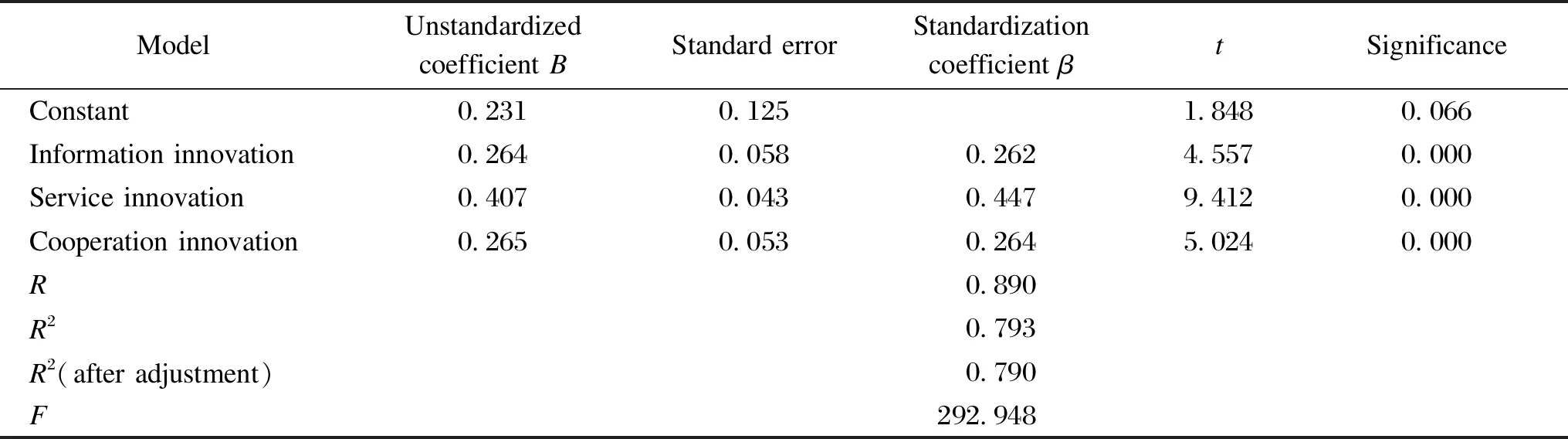
Table 11 Regression analysis of innovation factors and transfer factors
3.2.2TransferfactorsanddiffusionfactorsofS&Tachievements
From Table 12, the adjustedR2is 0.762, indicating that the model fits well. The significance ofFtest is less than 0.001, indicating that this model is superior to the model containing only the intercept term and is convincing.
The coefficients of transfer mode and receiving learning are greater than 0, and their significance is less than 0.001, indicating that both transfer mode and receiving learning have significant positive effects on diffusion factors.
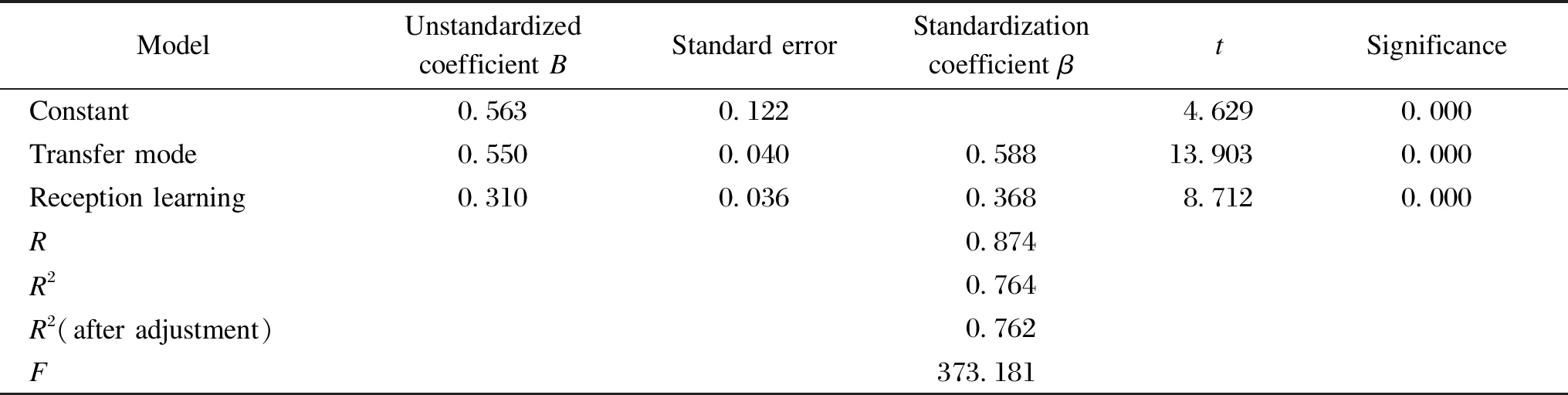
Table 12 Regression analysis of transfer factors and diffusion factors
3.2.3DiffusionfactorsandtransformationresultsofS&Tachievements
From Table 13, the adjustedR2is 0.765, indicating that the model fits well. The significance ofFtest is less than 0.001, indicating that this model is superior to the model containing only the intercept term and is convincing. The coefficients of diffusion media and diffusion channels are greater than 0, and their significance is less than 0.001, indicating that both diffusion media and diffusion channels have significant positive effects on the structure of science and technology transformation.
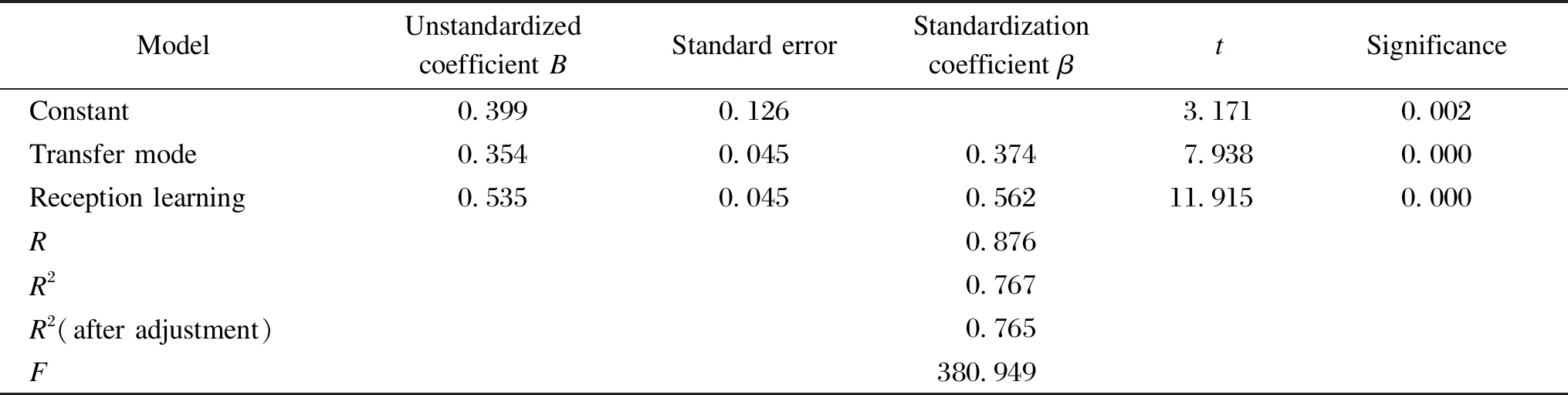
Table 13 Regression analysis of diffusion factors and transformation results
3.3 Verification of hypotheses and model
Through descriptive statistical analysis, reliability and validity analysis, factor correlation analysis and regression analysis of the survey data, the paper verifies the influence relationship among the factors of innovation, transfer and diffusion of S&T achievements and the results of transformation of S&T achievements under the Belt and Road Initiative. The specific results are shown in Table 14.

Table 14 Summary of hypothesis verification results
4 Conclusions
There is a significant positive correlation among the innovation factors of S&T achievements and the transfer factors of S&T achievements under the Belt and Road Initiative. Innovation factors, including information innovation, service innovation and cooperative innovation, will affect the transfer process. (1) The application of the resources provided by transformation services need to include technical information, talent information and industrial information. (2) The achievements transformation needs to provide personalized customized services, intellectual property-related services, and targeted legal, investment and financing services. (3) The docking resources of both parties will be more focused on industry-university-research, so as to create more professional and high-tech transformation projects of S&T achievements. Besides, the transfer mode and reception learning under the transfer factors of S&T achievements will affect the diffusion process. Therefore, attention should be paid to the transformation process. The embodiment of transfer mode factors will be further carried out through scientific research cooperation, strategic alliance and personnel exchange. The embodiment of learning factors should be carried out through the combination of online and offline learning. And the diffusion media and diffusion channels under the diffusion factors will affect the results of the transformation.
Transformation of S&T achievements related subjects should build industry information database, cooperate with public media, investment and financing, legal institutions,etc., to expand the influence of their transformation results. The diffusion should be carried out in various ways, such as holding entrepreneurship competitions, carrying out investigation activities at home and abroad, and jointly building innovation incubation projects with overseas universities and research institutes.
 Journal of Donghua University(English Edition)2021年6期
Journal of Donghua University(English Edition)2021年6期
- Journal of Donghua University(English Edition)的其它文章
- Effect of Surface Energy of Electrospun Fibrous Mat on Dynamic Filtration Performance for Oil Particles
- Seam Damage Control and Image Analysis for Cuprammonium Fabrics
- Robust Waterborne Polyurethane/Wool Keratin/Silk Sericin Freeze-Drying Composite Membrane for Heavy Metal Ions Adsorption
- Textile-Based Capacitive Pressure Distribution Measurement System for Human Sitting Posture Monitoring
- Enhancing Accuracy of Flexible Piezoresistive Pressure Sensors by Suppressing Seebeck Effect
- Reduced Switching-Frequency State of Charge Balancing Strategy for Battery Integrated Modular Multilevel Converter
