拳卷地钱总黄酮抗小鼠肝纤维的作用及机制研究
梁爽 朱华 黄健军 张文涛 卢森华 陈诗曼


中圖分类号 R285.5 文献标志码 A 文章编号 1001-0408(2021)19-2363-08
DOI 10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2021.19.10
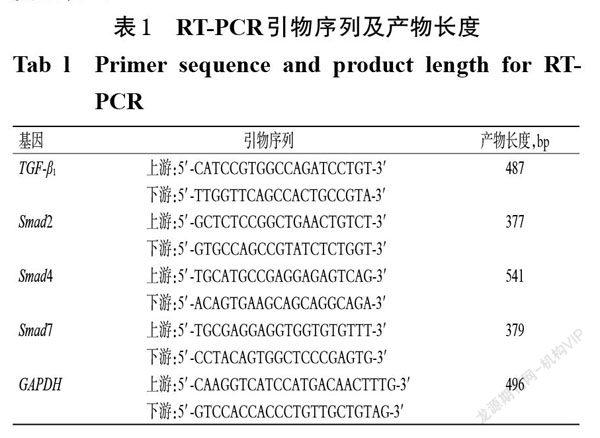
摘 要 目的:研究拳卷地钱总黄酮抗小鼠肝纤维化的作用及可能机制。方法:将72只小鼠随机分为空白组、模型组、阳性对照组(秋水仙碱0.2 mg/kg)和卷拳地钱总黄酮高、中、低剂量组(300、150、75 mg/kg),每组12只。除空白组外,其余各组小鼠均于背部皮下注射25%四氯化碳-花生油溶液复制肝纤维化模型;于造模的同时,空白组和模型组小鼠灌胃水,其余各组小鼠灌胃相应药物,灌胃体积均为20 mL/kg,每天1次,连续10周。末次灌胃后,检测小鼠血清中丙氨酸转氨酶(ALT)和天冬氨酸转氨酶(AST)的水平;观察小鼠肝组织病理学变化;检测小鼠肝组织中Ⅰ型胶原蛋白(COL-Ⅰ)、COL-Ⅲ、转化生长因子β1(TGF-β1)水平;检测小鼠肝组织中α-平滑肌肌动蛋白(α-SMA)、TGF-β1、Smad2、Smad4、Smad7蛋白的表达水平;检测小鼠肝组织中TGF-β1、Smad2、Smad4、Smad7 mRNA的表达水平。结果:与空白组比较,模型组小鼠血清中ALT、AST水平,肝组织中COL-Ⅰ、COL- Ⅲ、TGF-β1水平以及α-SMA 、TGF-β1、Smad2、Smad4 的蛋白表达水平和TGF-β1、Smad2、Smad4的 mRNA表达水平均显著升高(P<0.05或P<0.01),肝组织中Smad7的mRNA及其蛋白的表达水平均显著降低(P<0.05);肝组织损伤及胶原纤维增生较明显。与模型组比较,阳性对照组和拳卷地钱总黄酮高剂量组小鼠上述指标均显著逆转(P<0.05或P<0.01);拳卷地钱总黄酮中剂量组小鼠血清中ALT水平,肝组织中COL-Ⅰ水平和TGF-β1、Smad2、Smad4 的mRNA及其蛋白的表达水平均显著降低(P<0.05或P<0.01);拳卷地钱总黄酮低剂量组小鼠肝组织中Smad2、Smad4蛋白的表达水平均显著降低(P<0.05);各给药组小鼠肝组织的损伤及纤维化程度均有所减轻。结论:拳卷地钱总黄酮具有抗小鼠肝纤维化的作用,其作用机制可能与调节TGF-β/Smad信号通路中TGF-β1、Smad2、Smad4、Smad7的mRNA及其蛋白的表达相关。
关键词 拳卷地钱;总黄酮;肝纤维化;TGF-β/Smad信号通路;小鼠
Study on the Effect and Mechanism of Total Flavonoids from Marchantia convoluta on the Anti-hepatic Fibrosis in Mice
LIANG Shuang1,2,ZHU Hua1,2,HUANG Jianjun1,2,ZHANG Wentao2,LU Senhua3,CHEN Shiman2(1. School of Ethnology and Sociology, Guangxi University for Nationalities, Nanning 530006, China; 2. College of Pharmacy, Guangxi University of TCM, Nanning 530200, China; 3. Food Laboratory, Yulin Center for Food and Drug Control, Guangxi Yulin 537000, China)
ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: To study the effect and potential mechanism of the total flavonoids from Marchantia convoluta on anti-hepatic fibrosis in the mice. METHODS: Seventy-two mice were randomly divided into blank group, model group, positive control group (colchicine 0.2 mg/kg) and M. convoluta total flavonoids high-dose, medium-dose and low-dose groups (300, 150, 75 mg/kg), with 12 mice in eac group. Except for blank group, other groups were subcutaneously given 25% CCl4-peanut oil solution on the back to induce liver fibrosis model. At the same time, blank group and model group were given water intragastrically, while other groups were given relevant medicine intragastrically 20 mL/kg, once a day, for consecutive 10 weeks. After last administration, the serum levels of ALT and AST were detected. Histopathological changes of liver tissue in mice was observed. The levels of COL-Ⅰ, COL-Ⅲ and TGF-β1 in liver tissue were detected. The protein expression levels of α-SMA and TGF-β1, Smad2, Smad4 and Smad7 in liver tissue were detected. The expression levels of TGF-β1, Smad2, Smad4 and Smad7 mRNA in liver tissue were detected. RESULTS: Compared with blank group, the serum levels of ALT and AST in model group, the levels of COL-Ⅰ, COL-Ⅲ and TGF-β1 in liver tissue, protein expression levels of α-SMA, TGF-β1, Smad2 and Smad4, mRNA expression levels of TGF-β1, Smad2 and Smad4 were increased significantly (P<0.05 or P<0.01). The mRNA and protein expression levels of Smad7 in liver tissue were decreased significantly (P<0.05). The degree of liver tissue injury and collagen fiber hyperplasia were serious. Compared with model group, above indexes of mice were reversed significantly in positive control group and M. convoluta total flavonoids high-dose group (P<0.05 or P<0.01). Serum level of ALT, the levels of COL-Ⅰ, mRNA and protein expression of TGF-β1, Smad2 and Smad4 in liver tissue were decreased significantly in M. convoluta total flavonoids medium-dose group (P<0.05 or P<0.01). Protein expression of Smad2 and Smad4 in liver tissue were decreased significantly in M. convoluta total flavonoids low-dose group (P<0.05). The liver injury and fibrosis of mice were relieved in administration groups. CONCLUSIONS: M. convoluta total flavonoids possess the effect of anti-hepatic fibrosis, the mechanism of which is related to the regulation of mRNA and protein expression of TGF-β1, Smad2, Smad4 and Smad7 in the signaling pathway of TGF-β/Smad.

