Screening of stable internal reference genes by quantitative real-time PCR in humpback grouper Cromileptes altivelis*
Xiaojuan CHEN ,Yun SUN ,Panpan ZHANG Jianlong LI Haiping LI Caoying WEI Zhenjie CAO ,Yongcan ZHOU
1 State Key Laboratory of Marine Resource Utilization in South China Sea, Hainan University, Haikou 570228, China
2 Key Laboratory of Tropical Hydrobiology and Biotechnology of Hainan Province, Haikou 570228, China
3 Department of Aquaculture, College of Marine Sciences, Hainan University, Haikou 570228, China
Abstract Humpback grouper Cromileptes altivelis is one commercial fish with considerable economic value.To determine the expression stabilities of six commonly used internal reference genes in C.altivelis challenged by Vibrio harveyi and viral nervous necrosis virus (VNNV) through quantitative real-time PCR(qRT-PCR),the expression levels of selected genes in five immune organs stimulated with pathogenic infection were carefully evaluated using algorithms of geNorm,NormFinder,and BestKeeper.The results show that the expression stabilities of the six candidate internal reference genes were different.Under normal physiological conditions,RPL13 were identified as the most stably expressed genes among five different immune organs (liver,spleen,kidney,intestine,and gill).After V.harveyi stimulation,RPL13,RPL13,EF1A, RPL13,and EF1A were identified by geNorm,NormFinder,and BestKeeper as the most stable genes in liver,spleen,kidney,intestine,and gill,respectively.Combining these three algorithms suggested that under stimulation of VNNV,RPL13, EF1A,Actin,RPL13,and Actin were as the most stable genes in liver,spleen,kidney,intestine,and gill,respectively.These results suggest that specific experiment conditions and tissue types shall be considered when selecting the reference genes in qRT-PCR analysis.This study provided a solid foundation for future studies on gene expression of C.altivelis under different conditions.
Keyword:Cromileptes altivelis;reference gene;expression stability;pathogenic infection
1 INTRODUCTION
Humpback grouperCromileptesaltivelisbelongs to the family Epinephelidae of the order Perciformes(Craig et al.,2011).It is a tropical and valuable species of marine fish with high nutritional value and ornamental value,and mainly distributed in the western Pacific Ocean (Ou et al.,2015).However,humpback grouper is suffering from various pathogenic diseases due to increasing artificial cultures (Sun et al.,2018,2019).The pathogens ofVibrioharveyiand viral nervous necrosis virus(VNNV) are common pathogenic microorganisms that cause great losses to grouper culture industry(Luo et al.,2013;Chen et al.,2018).
Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) is a realtime monitoring of nucleic acid amplification-based technique,with the characteristics of quantitative accuracy,specificity,and high sensitivity to target genes (Huggett et al.,2005;Jain et al.,2006).qRTPCR has overcome the shortage of traditional PCR from qualitatively to quantitatively,and effectively solved the problem that the traditional PCR technology is prone to contaminated in the process of operation and leads to high false positive rate.In recent years,qRT-PCR has been widely applied in medical detection,environmental monitoring,aquaculture,and other fields (Najafpanah et al.,2013;Li and Hou,2015;Sun and Sun,2015;Yang et al.,2015;Pooljun et al.,2016;Li et al.,2019).Especially,it has become the first choice for gene expression analysis (Jain et al.,2006;Resende et al.,2011;Li et al.,2019).Internal reference gene,also known as housekeeping gene,is the reference gene whose expression level is not affected by changes in research conditions and can be consistently expressed in different development stages and physiological conditions of the same tissue(Mahoney et al.,2004).However,ideal internal reference gene is nonexistent.Many studies have shown that some internal reference genes are not truly stable under certain experimental conditions,and the expression of internal reference genes is affected by many external environments (Fernandes et al.,2008;Dang and Sun,2011;Dobnik et al.,2015;Kang et al.,2019;Wan et al.,2019).Previous studies demonstrated that the expression level of internal reference genes is varied in different tissues,since extremely high or low expression levels may preclude the usefulness of these genes as internal controls.For example,in the fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas),glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase(GAPDH) was highly expressed in liver,but the lowest expressed in gonad,whileActinwas highly expressed in gonad but had a low level of expression in liver under normal physiological conditions (Filby and Tyler,2007).The so-called constant expression of any internal reference gene is limited in a certain type of tissue or experiment.Therefore,it is necessary to calculate the expression level and evaluated the stability of the internal reference genes in different tissues and/or disease states before the start of any study with real time PCR.Up to now,research on the normalization of internal reference genes ofC.altivelisunder normal physiological conditions or duringV.harveyiand VNNV infection has not been reported.
In this study,combining with three programs of geNorm,NormFinder,and BestKeeper,the stability of mRNA expression of six common internal reference genes,including β-2-Microglobulin (B2M),beta actin(Actin),glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase(GAPDH),tubulin tyrosine ligase-like family member 1 (TTLL1),elongation factor-1-α (EF1A),and ribosomal protein L13 (RPL13) were evaluated in five immune organs (liver,spleen,kidney,intestine,and gill) under normal physiological conditions and the stimulation ofV.harveyiand VNNV by qRTPCR.Our study will lay a solid foundation for the other studies of immune function genes related to the diseases ofC.altivelis.
2 MATERIAL AND METHOD
2.1 Pathogen
PathogenicV.harveyihad been described that showed strong pathogenicity toC.altivelis(Sun et al.,2018).The bacteria were cultured in the medium of Luria-Bertani (LB) at 28 °C.VNNV was isolated from diseased fish at a commercial fish farm in Sanya(Hainan Province,China) with adjusting VNNV concentration to 1×107copies/mL in phosphatebuffered saline (PBS).
2.2 Fish
A total of 50 humpback grouper (C.altivelis)(average weight,25±3.5 g) was provided by a fish farm in Sanya (Hainan,China).The fish were maintained in aerated running seawater at 26 °C for one week and fed twice daily to allow to acclimatizing the laboratory environment.Prior to experiments,five fish were randomly sampled to confirm health condition (Sun et al.,2019).Then,15 fish were used to determine the most stable reference genes in five immune organs under normal physiological condition.30 fish were used to confirm the most stable reference genes under the stimulation ofV.harveyiand VNNV.Before tissue collection,fish were anesthetized with MS-222 (Sigma,USA) (Sun et al.,2019).
2.3 Sample collection under normal physiological condition
To determine the internal reference genes in humpback grouper under normal physiological condition,tissues (liver,spleen,intestine,kidney,and gill) were collected from 15 fish under aseptic conditions,with equivalent samples from the five fish of each group mixed together to make one sample,then frozen by liquid nitrogen quickly and transferred into -80 °C for storage.
2.4 Infection experiment and sample collection
Fish were randomly divided into two groups (A and B,15 fish/group),which was injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) with 100-μLV.harveyi(105CFU/mL),and 100-μL VNNV (107copies/mL),respectively.After that,spleen,kidney,liver,intestine,and gill from five fish in group A were sampled at 9 h afterV.harveyiinjection.Same tissues as above from five fish in group B were collected at 5 d after VNNV injection.The tissues were collected under aseptic conditions,then frozen by liquid nitrogen quickly andtransferred into -80 °C for storage.The fish under the normal physiological condition was used as control.The experiments were performed in triplicate.
2.5 RNA extraction and first strand of cDNA synthesis
The total RNA of all tissues was extracted by Eastep®Super Total RNA Extraction kit (Promega,USA).The quality and concentrations of total RNA were detected by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis(Biowest Agarose,Solarbio,China) and NanoDrop 2000 (Thermo Scientific,USA).Then,the first strand of cDNA was synthesized by Eastep®RT Master Mix Kit (Promega,USA) following the manufacturer’ manual.
2.6 PCR specificity of internal reference gene primers
Six internal reference genes were selected,includingB2M,Actin,TTLL1,RPL13,EF1A,andGAPDH(Table 1).Primers of six internal reference genes were designed by the software of Primer Premier 5 (Table 1),and synthesized by Sangon(Shanghai,China).The cDNA samples were serially diluted 10-fold and used to build standard curve.The slope of the standard curve was used to determine the amplification effi ciency (E) and determination coeffi cient (R2) of qRT-PCR (Chen et al.,2017).
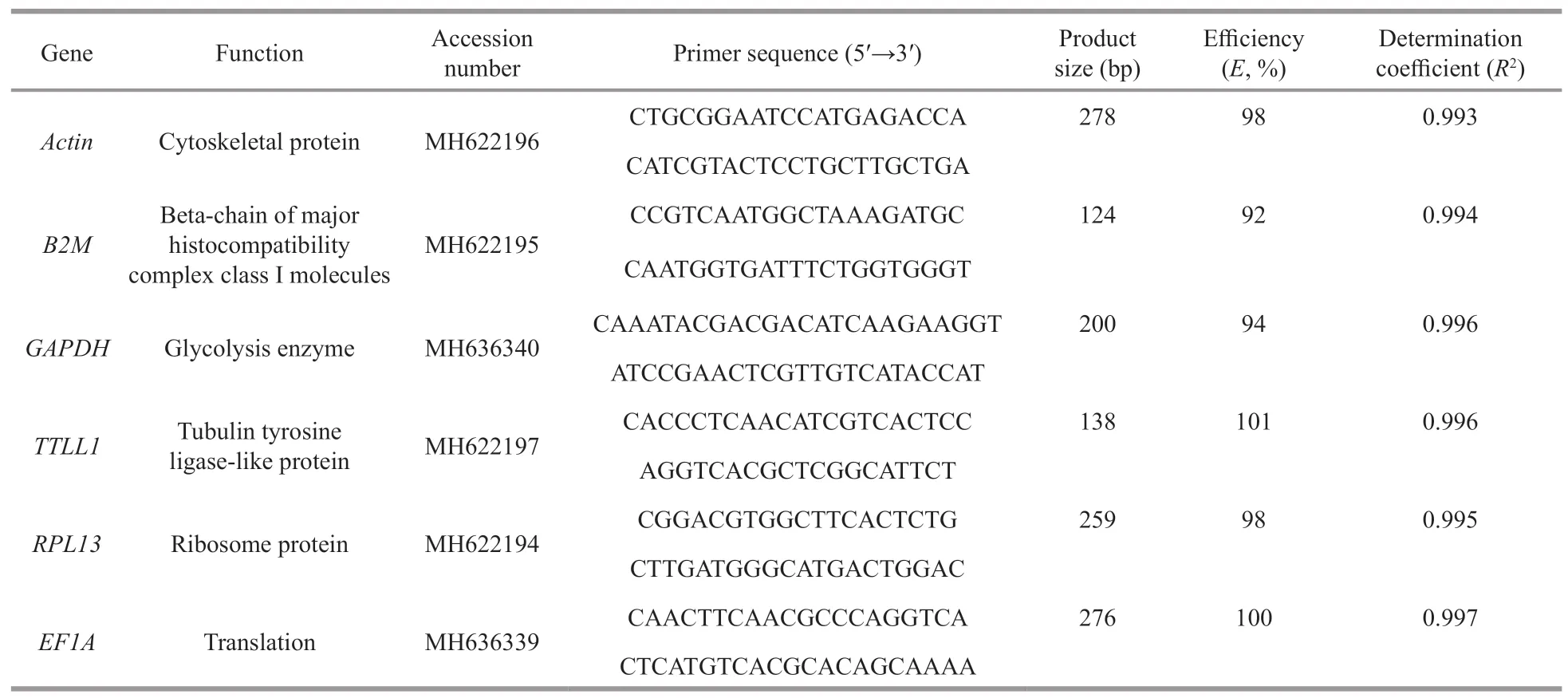
Table 1 The primer pairs of internal reference genes used in this study and the amplification efficiencies of PCR
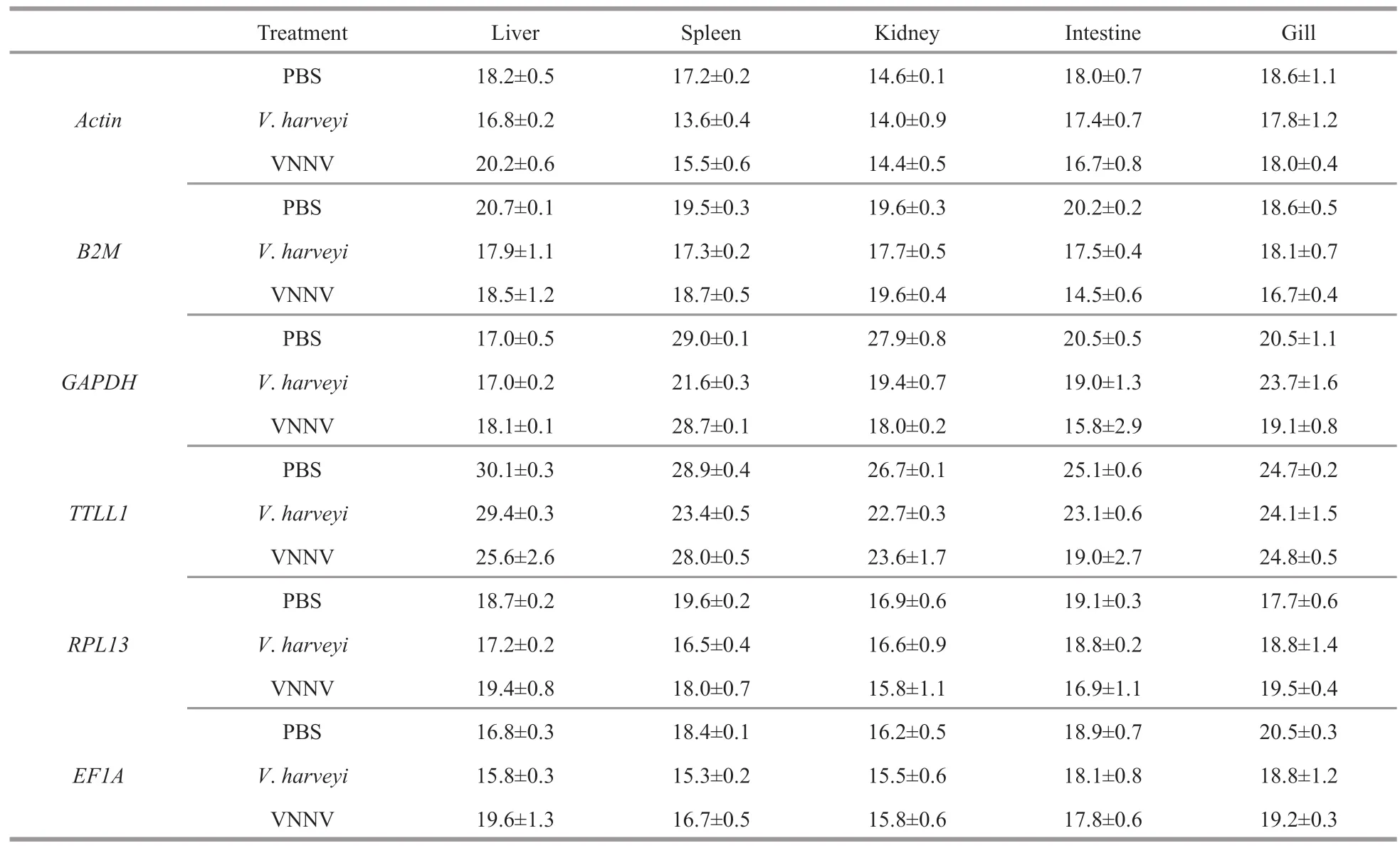
Table 2 The C t values of the internal reference genes in different tissues of humpback grouper after the pathogen challenge
2.7 qRT-PCR and data analysis
qRT-PCR was used to analyze the expression level of selected internal reference genes using SYBR Green dye method (Eastep®qPCR Master Mix Kit,Promega,USA) through Quant Studio TM 6 Flex Real-Time PCR System Software (Life technologies TM,United States).
The qRT-PCR data was analyzed by geNorm(V.3.5),NormFinder (V.0.953),and Bestkeeper software programs (Vandesompele et al.,2002;Andersen et al.,2004;Pfaffl et al.,2004).Based on Microsoft Excel platform to create VBA macro program,stability parameter M (internal control gene-stability measure) value of geNorm software was calculated to analysis the stability of internal standard.The M value of genes is lower,indicating gene expression is more stable.To confirm the optimal number of internal reference genes required for accurate normalization,a pairwise variation (V)Vn/n+1analysis between two sequential normalization factors containing an increasing number of genes was performed,and the default cut-off value ofVn/n+1is 0.15.In NormFinder,the expression stability of candidate internal reference genes is expressed by obtaining the values of variance within and between groups,and the internal reference gene with the lowest value have the most stable expression.In BestKeeper,the most stable internal reference genes were identified based on the pairwise comparisons of raw cycle threshold (Ct) values of each gene.The standard deviation (SD),correlation coeffi cient (r),and coeffi cient of variation (CV) generated between each gene can be calculated by BestKeeper.The most stable internal reference genes are those with the smallest SD,smaller CV,and greaterr.It is worth noting that when SD was bigger than 1,the internal reference gene expression was considered unstable.Finally,comprehensive ranking orders of these internal reference genes based on the three methods were recommended as described above (Zhang et al.,2020),and the most stable internal reference gene was determined according to the ranking orders.
3 RESULT
3.1 Quality of qRT-PCR amplification
Six examined internal reference genes were amplified by traditional PCR and detected by agarose gel electrophoresis.The amplification results showed that the amplified primers of each internal reference gene are specific and product is from 100 to 300 bp(Fig.1).The melting curve analysis showed that each examined internal reference gene has only one single peak in the melting curves.The PCR effi ciency (E)and determination coeffi cients (R2) were assessed by the slopes of the standard curves.The results showed that theEvalues were from 92% to 101%,and theR2values ranged from 0.993 to 0.997 (Table 1).

Fig.1 The RT-PCR amplification of the six candidate internal reference genes of humpback grouper
3.2 Expression levels of the internal reference genes in humpback grouper before the pathogen challenge
The expression levels of six internal reference genes under normal conditions were detected by qRTPCR.The results showed that theCtvalues of the six internal reference genes were different in all the five examined tissues.The lowest meanCtvalue (14.6)was inActinof kidney,while the highest (30.1) was inTTLL1of liver (Table 2).In different tissues,Actin showed the highest expression levels,withCtvalues ranged from 14.6 to 18.6.EF1A,RPL13,GAPDH,B2M,andTTLL1showed comparableCtvalues (16.2 to 20.5,16.9 to 19.6,17.0 to 29.0,18.6 to 20.7,and 24.7 to 30.1,respectively).
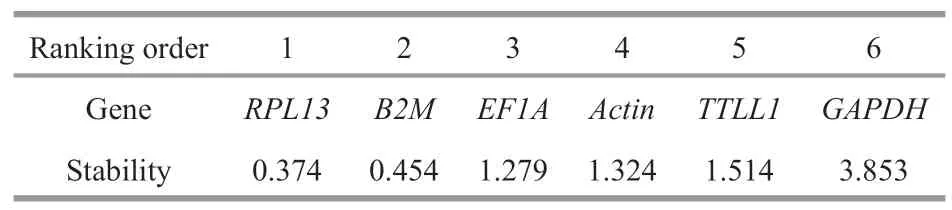
Table 3 The expression stability of the candidate reference genes in various tissues of humpback grouper were analyzed by NormFinder under normal physiological condition
3.3 Expression levels of the internal reference genes in humpback grouper tissues after pathogen infection
FollowingV.harveyiand VNNV infection,the expressions of the six internal reference genes presented tissue-dependent manners (Table 2).In addition,the transcript abundances of all the genes were altered in various tissues.At 9-h post-infection byV.harveyi,the maximum (8.5)Ctvariation value was observed inGAPDHin kidney,compared with the control group.Actin,EF1A,andRPL13showed the least changes (Ctvariations from 0.1 to 0.9,less than 1) in kidney and intestine,while all other genes exhibitedCtvariations from 1 to 8.5.Moreover,GAPDH,TTLL1,andEF1Aexhibited the least changes (no more than 1) in liver.In gill,Actin,B2M,andTTLL1exhibited the least changes (less than 1),andGAPDHexhibited the highestCtvariation of 3.2.In spleen,Ctvariations of all other genes exhibited greater than 1,andGAPDHexhibited the highestCtvariation of 7.4.
Following stimulation with VNNV,theGAPDHhad maximumCtvariation values (10.7) between kidney and spleen (Table 2).In kidney,the maximumCtvariation of 9.9 was presented inGAPDH,compared with the control group.There were slightly differences ofCtvariation observed with theRPL13in intestine (2.2),theEF1Ain liver (2.8),theActinin liver (2.0),theB2Min intestine (5.7),theTTLL1in intestine (6.1).
3.4 Gene expression stability in humpback grouper tissues before pathogen infection
To evaluate the gene expression stability,geNorm and NormFinder algorithms were used.geNorm analysis revealed thatB2MandRPL13were the most stable genes with the lowest M value,followed byActin,EF1A,TTLL1,andGAPDH(Fig.2).Similarly,the results of NormFinder analysis revealed that RPL13 were the most stable gene (0.374),followed byB2M(0.454),EF1A(1.279),Actin(1.324),TTLL1(1.514),andGAPDH(3.853) (Table 3).According to the result of BestKeeper (Table 4),the rank of the candidate reference genes from most to least stable was:B2M >RPL13 >Actin >EF1A >TTLL1 >GAPDH.However,the SD value ofActin,EF1A,TTLL1,andGAPDHwere bigger than 1,indicating these four internal reference genes were unstable.The results obtained by three methods were similar with slight differences.Finally,the comprehensive gene stability ranking order is shown in Table 5,indicating thatRPL13was identified as the most stable gene among five different immune organs under normal physiological condition.

Fig.2 The geNorm analysis of internal reference genes expression in humpback grouper tissues under normal physiological condition
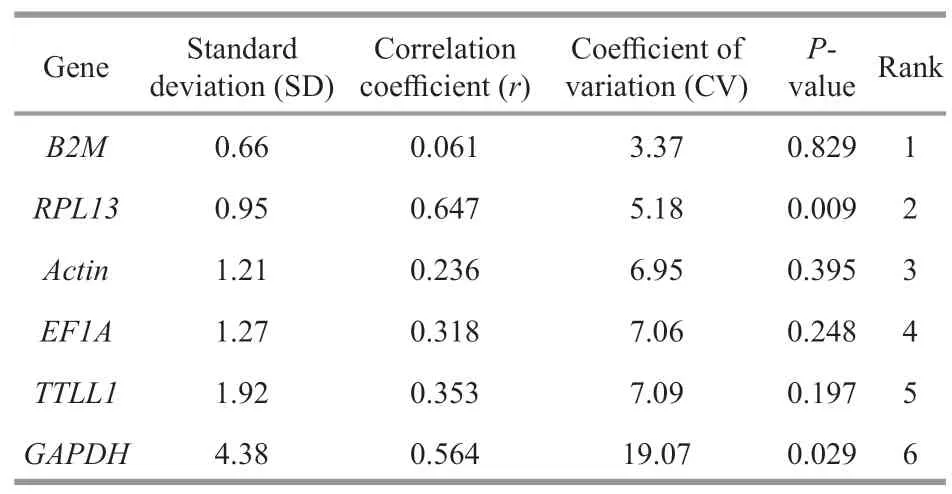
Table 4 The expression stability of the candidate reference genes in various tissues of humpback grouper were analyzed by BestKeeper under normal physiological condition
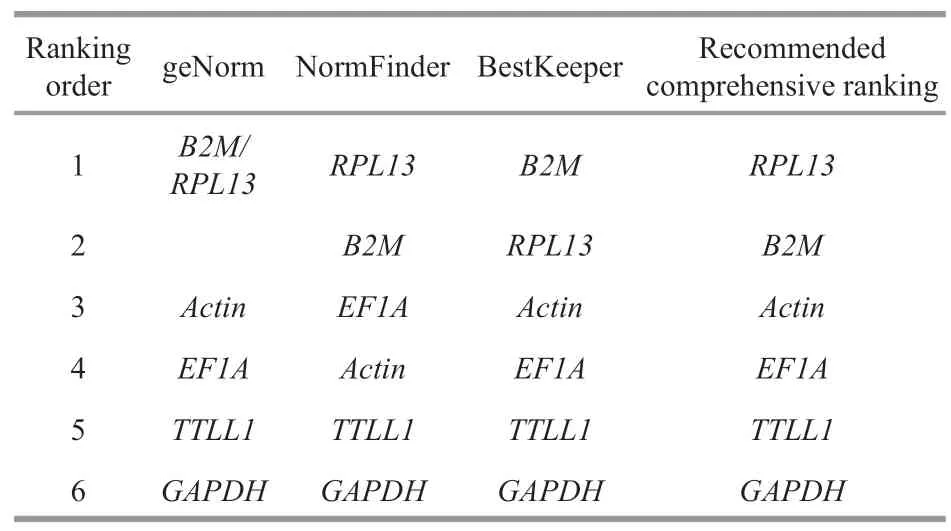
Table 5 The recommended comprehensive ranking order
3.5 Gene expression stability in humpback grouper tissues after V.harveyi infection
According to theCtvalues of the internal reference genes from fish infected withV.harveyiand fish injected PBS (control),the analysis of geNorm results showed that the highest M values of the candidate genes were varied between 0.7 to 1.2 in all examined tissues,exceptGAPDH,which was exhibited the M value with 1.62 in kidney (Fig.3).Moreover,Actin/RPL13were indicated as the most stable pairs of internal reference genes in liver with the minimum M value (0.042),followed byEF1A(0.263),TTLL1(0.345),GAPDH(0.521),andB2M(0.781) (Fig.3d).In gill,intestine,kidney,and spleen,EF1A/TTLL1,EF1A/RPL13,Actin/EF1A,andEF1A/RPL13were the most stable pairs of genes with the lowest M values,respectively (Fig.3a,b,c,e).Take into account the minimum number of internal reference genes required,theV2/3values were 0.125,0.122,0.083,0.069,and 0.030 in liver,spleen,kidney,intestine,and gill,respectively,which were all less than 0.15(Fig.4),indicating geometric averaging of 2 genes in five tissues above afterV.harveyiinfection would be required for accurate normalization and the most stable genes in these tested tissues generated by geNorm are reliable and effective.To verify the ranking orders of gene expression stability,NormFinder algorithm was performed.As shown in Table 6,Actin/RPL13,RPL13,EF1A,GAPDH,andEF1A/TTLL1appeared as the most stable genes in liver,spleen,kidney,intestine,and gill,respectively.When assessed by BestKeeper,the least overall variation wasGAPDH(SD=0.45),B2M(SD=1.12),EF1A(SD=0.71),RPL13(SD=0.32),andB2M(SD=0.82) in liver,spleen,kidney,intestine,and gill,respectively,which were classified as the best candidates (Table 7),exceptB2M(SD>1) in spleen was unstable.Combined analysis of three algorithms showed that underV.harveyistimulation,RPL13,RPL13,EF1A,RPL13,andEF1Aas the stable internal reference genes in liver,spleen,kidney,intestine,and gill,respectively (Table 8).Particularly,the results of comprehensive analysis were entirely consistent with those of geNorm,and only slight different with that of NormFinder.

Fig.3 Internal reference genes expression stability in humpback grouper tissues confirmed by geNorm after 9-h post-infection

Table 6 The expression stability of the candidate reference genes in humpback grouper tissues were analyzed by NormFinder after 9-h V.harveyi infection

Fig.4 Determination of the optimal number of internal reference genes by geNorm for normalization after bacterial infection
3.6 Gene expression stability in humpback grouper tissues after VNNV infection
Compared theCtvalues of the internal reference genes between fish infected with VNNV and fish injected PBS (control),geNorm analysis showed thatActin/GAPDH,GAPDH/RPL13,EF1A/RPL13,Actin/EF1A,TTLL1/RPL13were the most stable pair of genes in gill,liver,spleen,kidney,and intestine,respectively (Fig.5).The further pairwise variation(V) was determined,which make sure the optimal number of genes required for data normalization.Analysis ofVn/n+1in geNorm demonstrated that theV2/3variations in gill,liver,spleen,kidney,and intestine were all lower than 0.15,with the lowestV2/3value of 0.020 (spleen) and the maximumV2/3value of 0.127 (gill) (Fig.6),suggesting that the inclusion of the third reference gene in each case was not necessary.NormFinder analysis showed that the rankings of the most stable gene pairs wereGAPDH/Actin,GAPDH/RPL13,EF1A/RPL13,RPL13,andTTL1/RPL13in gill,liver,spleen,kidney,and intestine,respectively,which were broadly similar to the corresponding geNorm output (except forRPL13in kidney)(Table 9).Analyzed by BestKeeper,RPL13,TTLL1,Actin,EF1A,andTTLL1were classified as the best candidates in liver,spleen,kidney,intestine,and gill,respectively (Table 10).According to geNorm,NormFinder,and BestKeeper,the most stable genes were found to beRPL13,EF1A,Actin,RPL13,andActinin liver,spleen,kidney,intestine,and gill,respectively (Table 11).

Table 8 The recommended comprehensive ranking order
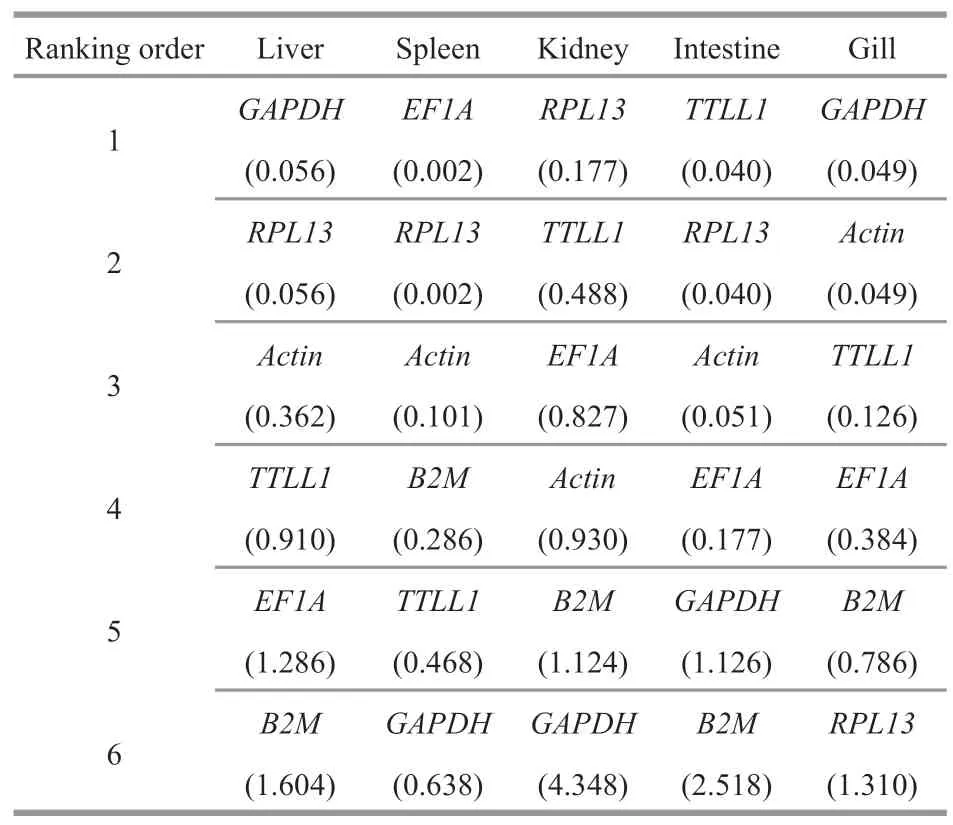
Table 9 The expression stability of the candidate reference genes in humpback grouper tissues were analyzed by NormFinder after 5-d viral nervous necrosis virus infection

Table 10 The expression stability of the candidate reference genes in humpback grouper tissues were analyzed by BestKeeper after 5-d viral nervous necrosis virus infection

Table 11 The recommended comprehensive ranking order

Fig.5 Internal reference genes expression stability in humpback grouper tissues confirmed by geNorm at 5 day post-infection
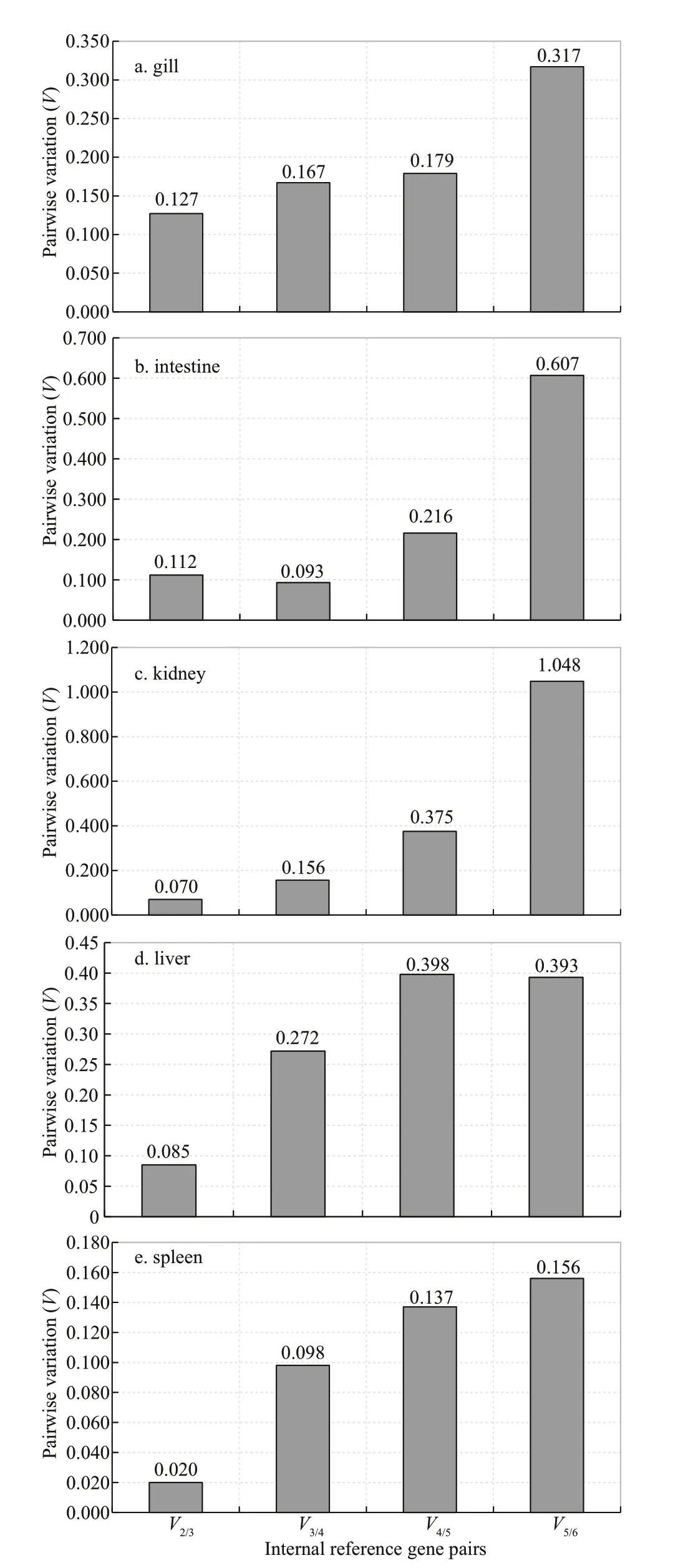
Fig.6 Determination of the optimal number of reference genes by geNorm for normalization after virus infection

Table 7 The expression stability of the candidate reference genes in humpback grouper tissues were analyzed by BestKeeper after 9-h V.harveyi infection
4 DISCUSSION
Quantitative real-time PCR has become one of the most commonly used techniques in the field of molecular biology.However,many studies showed that the commonly used reference genes could not be expressed stably in many species,tissues,and experimental conditions (Czechowski et al.,2005;Luo et al.,2014;Chen et al.,2017).Erroneous normalization of the PCR data and consequently misinterpretation of the results were present ifreference genes were inappropriate (McCurley andCallard,2008).Therefore,it is necessary to confirm appropriate reference genes for specific experimental conditions to accurate profiling of gene expression.geNorm and NormFinder are common statistical software that used to pick out the best candidate genes for qRT-PCR (Andersen et al.,2004;Chen et al.,2017).The present study identified the most suitable internal reference genes from six commonly used reference genes (includingB2M,Actin,TTLL1,RPL13,EF1A,andGAPDH) in five immune organs(i.e.gill,liver,spleen,kidney,and intestine) under normal physiological conditions or stimulated withV.harveyiand VNNV infection through geNorm and NormFinder.The optimum reference genes identified in this study will provide a useful guidance for the selection of internal controls in future qRT-PCR study of gene expression inC.altivelis.
In our study,six tested genes exhibited varied degrees of expressional changes in different tissues,whileRPL13was the most stable internal control genes across different tissue types.Similar investigators have been performed in other fish.For example,in zebrafish (Daniorerio),18S rRNAandB2Mare the most stably expressed in various tissues(McCurley and Callard,2008),while in turbot(Scophthalmusmaximus),RPSDandRPL17are themost stable genes across tissue types (Dang and Sun,2011).The difference of the most stable internal reference genes may be explained by the certain physiological differences and different gene expression patterns existing in different fish species.
Many studies suggested that internal reference genes exhibited a tissue-specific expression trend following bacterial infections (Olsvik et al.,2008;Small et al.,2008;Øvergård et al.,2010).As shown by increasing numbers of studies,tissue type has a strong effect on the determination of the optimal internal reference gene for qRT-PCR analysis of gene expression under bacterial infection (Dang and Sun,2011;Zheng and Sun,2011;Zhang et al.,2014).For instance,in turbot infected withEdwardsiellatarda,ACTB(beta actin) was detected as the most stable gene in liver,kidney,spleen,and gill.Meanwhile,ACTBwas the least stable gene in brain and the second least stable gene in heart and muscle at 12-h post-infection (Dang and Sun,2011).FollowingE.tardainfection,GAPDHis known to be most stable internal reference gene in three tissues (gill,liver,and intestine) of Japanese flounderParalichthysolivaceus,while in contrast,GAPDHappeared to be the least stable gene in brain and muscle (Zheng and Sun,2011).In our study,9 h afterV.harveyiinfection,TTLL1was identified as the most stable gene in gill but the least stable gene in spleen analyzed by geNorm and NormFinder.Moreover,by geNorm analysis,Actin/RPL13,EF1A/RPL13,Actin/EF1A,andEF1A/RPL13were the most stable gene pairs in liver,spleen,kidney,and intestine,respectively.In line with the results generated by geNorm in liver and gill,the same optimal gene pairs were obtained with NormFinder.In addition,only one stable gene was identified in spleen (RPL13),kidney (EF1A),and intestine (GAPDH) through NormFinder.However,the least overall variation genes identified by BestKeeper wereGAPDH,B2M,EF1A,RPL13,andB2Min liver,spleen,kidney,intestine,and gill.Thelarge difference between BestKeeper with geNorm and NormFinder analyses might be explained by the different methods of computation,whichCtvalues was transformed the relative quantities for geNorm and NormFinder analyses,whileCtvalues directly used in BestKeeper analysis.Similar observations were reported in many studies (Fernandes et al.,2008;Wang et al.,2012).To improve the accuracy of evaluation,a comprehensive ranking order of each reference gene was performed based on the results from the three algorithms,suggesting that the most stable genes in liver,spleen,kidney,intestine,and gill at 9-h post-infection ofV.harveyiwereRPL13,RPL13,EF1A,RPL13,andEF1A,respectively.
VNNV is also a common pathogenic pathogen in the grouper (Asim et al.,2019).In our study,as observed withV.harveyiinfection,similar results were observed after VNNV stimulation,which showed that the variations in the expression stability of the internal reference genes depended on tissue type variations.However,the most stable internal reference genes identified in most tissues were different betweenV.harveyistimulation and VNNV stimulation.The results of geNorm analysis showed that,in liver,spleen,kidney,intestine,and gill,the most stable gene pairs wereGAPDH/RPL13,EF1A/RPL13,Actin/EF1A,TTLL1/RPL13,andActin/GAPDH,respectively.Since five examined tissues exhibited theV2/3values less than 0.15,two genes suffi ced as normalization factors for each of these tissues.NormFinder analysis showed that,except for RPL13 in kidney,the rankings of the most stable gene pairs in other four organs were identical to those predicted by geNorm.In BestKeeper,onlyRPL13andActinidentified respectively as the least variable genes in liver and kidney were agreement with geNorm and NormFinder.In summary,the calculated comprehensive ranking order with the help of geNorm,NormFinder,and BestKeeper showed the same most stable internal reference genes compared with geNorm analysis.Consistent with previous study,our results presented similar trend,showing more comparable results between the comprehensive ranking order and the ranking by geNorm analysis(Wang et al.,2012).
5 CONCLUSION
In this study,RPL13was identified as the most stable internal control gene among five different organs ofC.altivelisunder normal physiological conditions.When studying the gene expression profiles after bacteria and virus infections inC.altivelis,the most stable internal reference gene is detected in liver,spleen,kidney,intestine,and gill.FollowingV.harveyichallenge,the most stable genes identified by geNorm,NormFinder,and BestKeeper together wereRPL13,RPL13,EF1A,RPL13,andEF1Ain liver,spleen,kidney,intestine,and gill ofC.altivelis,respectively.Under VNNV challenge,the most stable genes were found to beRPL13,EF1A,Actin,RPL13,andActinin liver,spleen,kidney,intestine,and gill ofC.altivelis,respectively.Taken together,these results highlight the characteristic of tissue-dependent variations in the expression of socalled internal reference genes,suggest tissue type has to be considered when selecting the reference genes in qRT-PCR analysis,and provide guidance for qRT-PCR studies of gene expression inC.altivelis.
6 DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The authors declare that all data supporting the findings of this study is available within the article.
 Journal of Oceanology and Limnology2021年5期
Journal of Oceanology and Limnology2021年5期
- Journal of Oceanology and Limnology的其它文章
- Effect of fasting on protein metabolism in muscle tissue of Larimichthys crocea revealed by transcriptome and proteome*
- Comparison of fungal community composition within different intestinal segments of tilapia and bighead carp*
- Mitochondrial phylogenomics reveal the origin and adaptive evolution of the deep-sea caridean shrimps (Decapoda:Caridea)*
- C17-fengycin B,produced by deep-sea-derived B acillus subtilis,possessing a strong antifungal activity against Fusarium solani*
- Relationship between morphospecies and microcystinproducing genotypes of Microcystis species in Chinese freshwaters*
- Size-dependent spatio-temporal dynamics of eukaryotic plankton community near nuclear power plant in Beibu Gulf,China*
