家庭医生签约服务在老年慢性疾病健康管理中的应用效果
员战民
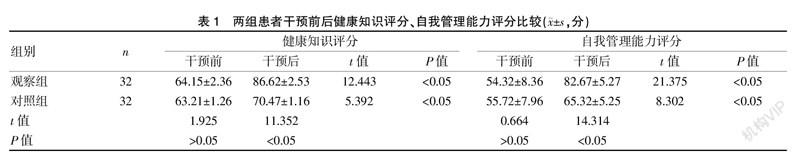
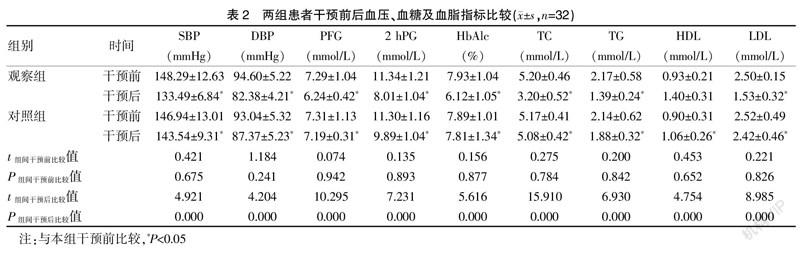

[摘要] 目的 觀察家庭医生签约服务在老年慢性疾病健康管理中的应用效果。 方法 纳入2018年1月至2019年12月的社区老年慢性疾病患者64例,随机分为观察组与对照组,每组各32例,分别实施家庭医生签约服务与常规社区健康管理。比较两组患者健康知识评分及自我管理能力评分、血压、血糖、血脂指标在干预前后的变化情况,随访患者遵医依从性。 结果 干预后两组患者健康知识评分、自我管理能力评分均较干预前升高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),且观察组较对照组升高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预前两组患者较各项血糖、血脂及血压指标比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),干预后观察组均优于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);观察组合理饮食、适量运动、遵医用药、定期复查等遵医行为高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 结论 家庭医生签约服务在老年慢性疾病健康管理中的应用,能够提高患者健康认知及自我管理能力,促进各项临床指标改善,提高患者医嘱依从性,值得临床推广。
[关键词] 家庭医生签约服务;老年慢性病;健康管理;健康知识评分;自我管理能力
[中图分类号] R592 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)22-0090-04
Application effect of family doctor contract service in health management of chronic diseases in elderly
YUN Zhanmin
Department of General Practice, Central University Hospital for Nationalities, Beijing 100081,China
[Abstract] Objective To observe the effect of family doctor contract service in the health management of chronic diseases in the elderly. Methods A total of 64 patients data of elderly patients with chronic diseases in the community were included from January 2018 to December 2019. They were randomly divided into the observation group and the control group, with 32 cases in each group, and respectively treated with family doctor contract services and routine community health management. The changes of health knowledge, self-management ability score, blood pressure, blood glucose and blood lipid indexes before and after intervention were compared, and the medical compliance of patients was followed up. Results The scores of health knowledge and self-management ability were improved in both groups after intervention, compared with those before intervention (P<0.05); those of the observation group were higher than those of the control group (P<0.05), which were statistically significant. Before intervention, no statistically significant differences were observed in blood glucose, blood lipid and blood pressure indexes between the 2 groups (P>0.05); after intervention, those of the observation group were better than those of the control group, and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). Compared with the control group, better compliance behaviors such as reasonable diet, proper exercise, compliance with medical drugs and regular review were observed in the observation group (P<0.05), with statistically significant differences. Conclusion The application of family doctor contract services in the health management of chronic diseases in the elderly can improve patients′ health cognition and self-management ability, promote the improvement of various clinical indicators, and improve patients′ compliance with medical advice, which is worthy of clinical promotion.

