基于KinectV2.0的视觉SLAM建图研究与误差分析
马佳豪, 郭中华

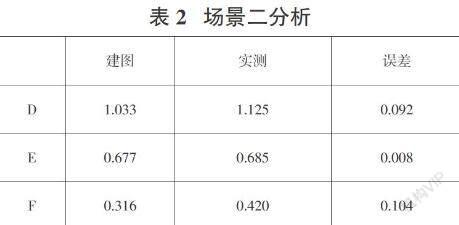

摘要:目前,基于RGB-D摄像头的视觉SLAM是该领域的研究热点之一。传统视觉SLAM因精度较差的问题,应用范围远不如激光SLAM,文中以此构建了基于KinectV2.0的视觉SLAM系统来验证此问题;算法方面,Gmapping算法在RBPF粒子滤波算法基础上优化了提议分布并且选择性重采样从而减少了计算量,因此选用Gmapping算法在三个不同复杂程度的场景下进行地图构建实验,最后对三个场景下的建图数据和实测数据进行误差分析。实验结果表明,基于KinectV2.0构建的视觉SLAM系统在三个场景下的建图精度和稳定性与激光SLAM相比拟,因此在光照变化较小或不变的场景下可选用视觉SLAM以降低成本,一定程度上可以减少设备成本并降低技术难度。
关键词:视觉 SLAM;移动机器人;RGB-D;回环检测;建图精度
中图分类号:TP242 文献标识码:A
文章编号:1009-3044(2021)21-0001-03
开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID):
Study and Error Analysis of Visual SLAM Mapping Based on KinectV2.0
MA Jia-hao1, GUO Zhong-hua1,2
(1.School of Physics and Electronic-Electrical Engineering, Yinchuan 750021, China; 2. Ningxia Key Laboratory of Intelligent Sensing for Desert Information, Yinchuan 750021, China)
Abstract:Currently, visual SLAM based on RGB-D camera is one of the research hotspots in this field. Due to the problem of poor accuracy of traditional visual SLAM, the application range is far inferior to laser SLAM. In this paper, a visual SLAM system based on KinectV2.0 is constructed to verify this problem; in terms of algorithm, the Gmapping algorithm optimizes the proposal based on the RBPF particle filter algorithm The distribution and selective resampling reduces the amount of calculation. Therefore, the Gmapping algorithm is selected to conduct map construction experiments in three scenes of different complexity. Finally, the error analysis of the mapping data and the measured data in the three scenes is carried out. The experimental results show that the mapping accuracy and stability of the visual SLAM system based on KinectV2.0 in the three scenes is comparable to that of laser SLAM, so visual SLAM can be used in scenes with small or constant illumination changes to reduce costs , To a certain extent, it can reduce equipment costs and reduce technical difficulties.
Key words: visual SLAM; mobile robot; RGB-D; loop detection; mapping accuracy
1 引言
同时定位及地图构建(SLAM, simultaneous localization and mapping)出现于机器人应用领域 , SLAM技术[1]目标是使机器人在一个未知环境中使其实时重新构建当前未知环境的地图结构,同时对自身进行定位。移动机器人的同步定位和地图构建(SLAM)技术成了移动机器人发展进程中亟待解决的一个核心问题,在实现SLAM技术的基础之上,才能使移动机器人真正地实现自动化,才能使机器人在更多领域焕发出应有的活力。SLAM技术的实现大致分为两个主要方向——激光SLAM技术和视觉SLAM(V-SLAM)技术,一般来说激光SLAM精确度较高,但是成本高,采集数据量大,对计算力要求严苛,只利用相机作为传感器的SLAM被称为视觉SLAM[3],作为当前SLAM框架的主要类型,激光SLAM与视觉SLAM必将在相互竞争和融合中发展。
文献[4]构建了一个基于手持 Kinect 的 RGB-D SLAM 系统,文献[5]中首次提出了基于Kinect的SLAM系统,文献[6]中提到视觉SLAM的传感器有单目、双目、RGB-D摄像头。文献[7]中在RBPF SLAM基礎上对提议分布和重采样进行了优化,其算法被实现为开源的SLAM功能包Gmapping。为了保证建图与定位的准确性,实验设备使用RGB-D摄像头作为数据采集设备,在光照强度一定的前提下,利用基于粒子滤波算法优化的Gmapping功能包对于三种不同复杂程度的环境进行地图构建,并与环境实测数据对比进行误差分析,最终通过本实验的建图结果验证与分析,在误差允许范围内视觉SLAM在环境光正常、构建小场景地图时可以保证建图精确度,因此基于KinectV2.0的视觉SLAM在建图精度和稳定性方面可以与激光SLAM的精度与稳定性相比拟。

