腹膜透析和血液透析对尿毒症患者残余肾功能及并发症的影响分析
李艺虾 杨枫


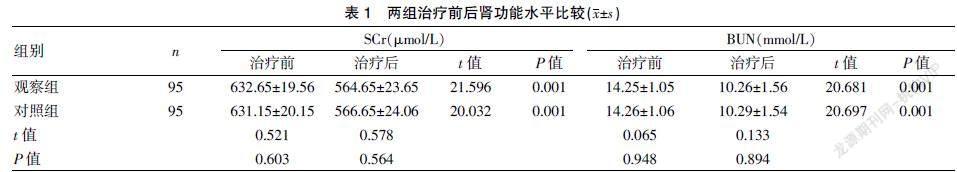
[摘要] 目的 探討尿毒症患者采取腹膜透析和血液透析对残余肾功能及并发症影响。 方法 选取2018年1月至2019年12月福州市第一医院肾内科收入尿毒症患者190例,按照随机数字表法分为两组,每组各95例,对照组采用血液透析治疗,观察组采用腹膜透析治疗,比较两组干预前后肾功能及并发症。 结果 治疗前,两组肾功能水平比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),治疗后,两组肾功能水平比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),两组治疗前后组内比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);治疗前,两组炎症水平比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),治疗后,观察组炎症水平低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),两组治疗前后炎症水平组内比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);观察组并发症率为6.32%,低于对照组的15.79%,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 结论 血液透析与腹膜透析均是保护残余肾功能有效透析模式,但腹膜透析降低炎症指标水平更为显著,且并发症发生率偏低,可考虑作为尿毒症患者首要透析方式。
[关键词] 腹膜透析;血液透析;尿毒症;肾功能;并发症
[中图分类号] R692.5 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)19-0056-04
Analysis on the impacts of peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis on residual renal function and complications in patients with uremia
LI Yixia YANG Feng
Department of Nephrology,the First Hospital of Fuzhou,Fuzhou 350004,China
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the impacts of peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis on residual renal function and complications in patients with uremia. Methods A total of 190 patients with uremia admitted to the department of nephrology of the First Hospital of Fuzhou from January 2018 to December 2019 were selected and divided into the control group(n=95) and the observation group(n=95) according to the random number table.The control group was given hemodialysis treatment,while the observation group was given peritoneal dialysis treatment.The renal function and complications before and after intervention were compared between the two groups. Results Before treatment,there was no statistically significant difference in renal function between the two groups(P>0.05). After treatment,there was no statistically significant difference in renal function between the two groups(P>0.05). However,there was statistically significant difference in each group before and after treatment(P<0.05). Before treatment,there was no statistically significant difference in the level of inflammation between the two groups(P>0.05). While after treatment,the level of inflammation in the observation group was lower than that in the control group,with statistically significant difference(P<0.05). There was statistically significant difference in the level of inflammation in each group before and after treatment(P<0.05). The complication rate in the observation group was 6.32%,which was lower than 15.79% in the control group,with statistically significant difference(P<0.05). Conclusion Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis are both effective dialysis modes to protect residual renal function,but peritoneal dialysis can reduce the level of inflammation index more significantly,and the incidence of complications is relatively low,so it can be considered as the primary dialysis mode for patients with uremia.

