Analysis of Acetanilide Herbicide Residues in Adzuki Beans(Vigna angularis) by Aqueous Two-Phase Extraction Coupled with High Performance Liquid Chromatography
ZHANG Liyuan, ZHANG Yue, YU Runzhong, WANG Changyuan,3,4, ZHANG Dongjie,4,5,
(1.College of Food Science, Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, Daqing 163319, China;2.College of Electrical and Information, Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, Daqing 163319, China;3.Heilongjiang Province Cultivating Collaborative Innovation Center for The Beidahuang Modern Agricultural Industry Technology, Daqing 163319, China; 4.Key Laboratory of Agro-products Processing and Quality Safety of Heilongjiang Province, Daqing 163319, China;5.National Coarse Cereals Engineering Research Center, Daqing 163319, China)
Abstract: A method for the determination of four acetanilide herbicides including acetochlor, butachlor, propanil, and metolachlor in adzuki beans was established using ammonium sulfate-ethanol-based aqueous two-phase extraction combined with high performance liquid chromatography.In the aqueous two-phase extraction, the polarity of the alcohol-rich upper phase was more similar to that of the herbicides in the same organic solvent.The salt solution of the lower phase could effectively precipitate protein and fat.Based on the recoveries of the herbicides, the optimal pretreatment conditions were determined as follows: aqueous two-phase system containing 25% ethanol and 28% ammonium sulfate, and ultrasonic extraction for 1 min at 35 ℃.Avoiding the use of toxic organic solvents, the current method was environmentally friendly.The detection limits for acetochlor, butachlor, propanil, and metolachlor were 3.5, 7.1, 4.6 and 5.8 µg/kg, respectively.The average recoveries at spiked concentrations of 10 and 100 µg/kg ranged from 86.1% to 95.9%, with relative standard deviation equal to or lower than 4.5%.
Keywords: aqueous two-phase extraction; acetanilide herbicides; high performance liquid chromatography; adzuki bean
Adzuki bean (Vigna angularis) is an annual herbaceous plant.Adzuki bean are rich in essential amino acids, calcium,phosphorus and other mineral elements[1].In recent years,the planting area of adzuki bean expands.With the rapid development of modern agriculture and the strengthening of resistance to weeds, the demand and dependence on herbicides are increasing.It leads to the residue of herbicides[2-3].The acetanilide herbicides have been widely used in agricultural production[4-7].However, these herbicides cause great potential dangers and harm to human health and natural environment.The herbicides can be easily transferred to surface water and shallow groundwater through leakage,and then adsorbed by soil and sediment[8-9].The results showed that the acetanilide herbicides were highly toxic,had carcinogenic effects[10-12].In the U.S., the acetochlor has been designated as a B-2 carcinogen by the U.S.Environmental Protection Agency[13].The residue of acetanilide herbicides has caught more and more attention.Therefore, it is particularly important to establish a rapid and high-throughput method for the determination of multiple residue of acetanilide herbicides in adzuki bean, which is of great importance for ensuring crop safety and human health.
At present, the main extraction methods of the acetanilide herbicides are QuEChERS method[14], solid phase extraction (SPE)[15], homogeneous liquid-liquid micro-extraction[16], matrix solid phase dispersion-solvent flotation[17]and so on.However, these traditional or emerging methods have some defects.The main disadvantage of the QuEChERS method is that it cannot be effectively purged,especially for some complex substrates.The SPE method and other traditional extraction methods are cumbersome and use organic solvents.It is necessary to establish a fast, simple,green, and efficient extraction method.
Aqueous two-phase systems (ATPS) was first discovered by Karler et al.[18]in 1989.Then, Yang Xiao et al.[19]reported the aqueous two-phase extraction for determination of antibiotics in honey, and the good results were obtained by using the aqueous two-phase method.As a new type of green separation system with high efficiency and moderate temperature, aqueous two-phase extraction has been widely used in biological separation engineering, chemical analysis,food chemical industry and other fields due to its unique advantages[20-22].Therefore, it attracts the attention of researchers worldwide[23-26].
In this work, ATPS extraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was used to extract and detect acetanilide herbicides.The acetanilide herbicides could be extracted by the ethanol (organic phase).In the inorganic phase, impurities such as protein and fat can be precipitated efficiently and rapidly, and then removed by centrifugation.This method has multiple advantages,including large processing capacity, high extraction efficiency, simple operation, time-efficient, mild conditions,high selectivity, easy and continuous operation.
1 Materials and Methods
1.1 Materials and agents
Three adzuki bean samples were purchased from local supermarkets and agri-product fairs in Daqing city, Heilongjiang Province, China, in August 2018.The acetochlor, butachlor, propanil and metolachlor were purchased from the National Institute of Pharmaceutical and Biological Products (Beijing, China).Ammonium sulfate,acetone and anhydrous ethanol acetone were purchased from Shenyang Chemical Factory (Shenyang, China),diammonium hydrogen phosphate.Isopropyl alcohol and other analytical grade reagents were purchased from Beijing Chemical Factory (Beijing, China).Acetonitrile and methanol(chromatographic grade) were purchased from Fisher Technologies Inc.(USA).Five ATPS, including ammonium sulfate/ethanol (A), ammonium sulfate/isopropanol (B),ammonium sulfate/methanol (C), diammonium hydrogen phosphate/ethanol (D), diammonium hydrogen phosphate/isopropanol (E), were prepared for further experiment[27-29].
The acetochlor, butachlor, propanil, and metolachlor were dissolved into the standard solutions by methanol (at the concentration of 100 µg/mL).The working calibration solutions were prepared every week by diluting aliquots of the working calibration solutions with methanol.The mixed working calibration solution at different concentrations level were prepared in the same method.All the working standard solutions were stored at 4 ℃ and protected from light.
1.2 Instruments and equipmens
The 1260 series liquid chromatography equipped with diode-array detector, auto-sampler, and quad gradient pump(Agilent Technologies Inc., USA) were used.Chromatographic separation of target analytes was performed on an Agilent Eclipse XDB-C18column (150 mm × 4.6 mm, 3.5 µm, Agilent Technologies Inc., USA).HR-2870 Philips mill (Zhuhai Philips Electronics Co.Ltd., China) and RE-52AA vacuum rotatory evaporator (Shanghai Yarong Biochemical Instrument Factory, China) were used.HPLC-grade water was obtained from a Milli-Q water purification system (Millipore Corp.,USA) , which is used to prepare all aqueous solutions.
1.3 Methods
1.3.1 Sample preparation
In order to obtain the powdered sample, each adzuki bean samples were pulverized by a model mill and filtering through 80-mesh sieve before extraction.The experimental results of optimization of aqueous two-phase extraction conditions and method evaluation were analyzed and determined using one of the prepared samples, and name this particular piece as sample 1.The results of precision and recoveries were selected from all three real samples.
The fresh and aged spiked samples were prepared by spiking the standard stock solutions into samples.The spiked levels were 10.0 and 100.0 μg/kg, respectively.The addition of 10 mL acetone to moisten the small Adzuki bean powders could ensure the acetanilide herbicides to be well distributed.Then a careful hand-agitation for 5 min was performed followed by air-drying of 24 h at ambient temperature to evaporate acetone.
1.3.2 ATPS analysis
In the preliminary experiment, five common salts,including sodium chloride, ammonium sulfate, potassium chloride, diammonium hydrogen phosphate, and metaphosphate were selected for the comparison of the phase separation effect.It was found that ammonium sulfate and diammonium hydrogen phosphate had the best phase separation effect.The reason may be that the bivalent anions had strong salt-out capacity and phase separation ability.
Effect of the type of ATPS (A: ammonium sulfate/ethanol, B: ammonium sulfate/isopropanol, C: ammonium sulfate/methanol, D: diammonium hydrogen phosphate/ethanol, E: diammonium hydrogen phosphate/isopropanol),mass fraction of ammonium sulfate (20%, 22%, 25%, 28%,30%), mass fraction of ethanol (20%, 22%, 25%, 28%, 30%),ultrasound extraction time (0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4 min), and extraction temperature (15, 25, 35, 40, 45 ℃) were tested.When determining an effect factor, the other selected factors were mass fraction of ammonium sulfate 28%; the mass fraction of ethanol 25%; the ultrasound extraction time 1 min; the ultrasound extraction temperature 35 ℃.
The experimental process was completed in the laboratory, and the schematic diagram is shown in Fig.1.The adzuki bean sample powder (2.00 g) were added into 15 mL centrifuge tube.Subsequently, ammonium sulfate solution and anhydrous ethanol with a certain mass fraction were added.The tube was stirred with vortexing machine at 4 000 r/min for 1 min at indoor temperature so as to be uniformly mixed.Then, the tube with mixture was immersed into the ultrasonic bath and ultrasonically shaken with ultrasonic power 300 W for 1.0 min at 35 ℃.The tube after shaking was put into a highspeed centrifuge, the mixture was centrifuged at 10 000 r/min for 2 min at indoor temperature.After centrifugation, the solution was divided into two phases, the upper phase was an alcohol-rich solution, and the lower phase was a salt solution.The ATPS was formed and the target analytes were extracted into the upper phase.100 μL of the upper phase was diluted with 50 μL methanol.The resulting solution was filtered with 0.22 μm PTFE filter membrane before analysis.
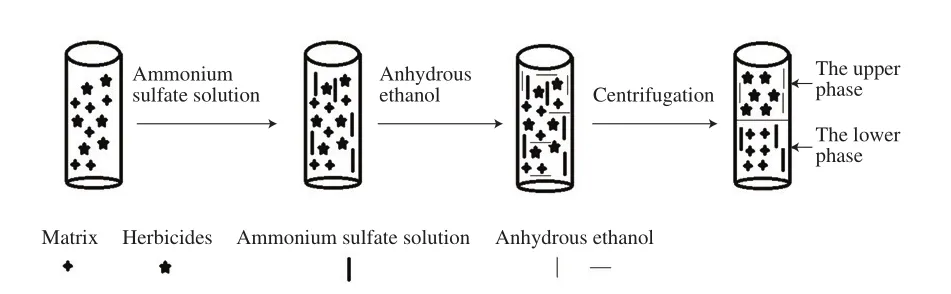
Fig.1 Schematic procedure of ATPS
1.3.3 HPLC Analysis
The water and acetonitrile (4:6,V/V) were used as themobile phase A and B, respectively.The column temperature was kept at 30 ℃ and the flow rate of the mobile phase was 0.50 mL/min.Injection volume of analytical solution was 20 µL.According to the references, five wavelengths were selected for multi-wavelength measurement at the same time, and then 230 nm was selected according to good chromatographic peak.The reference wavelength and bandwidth were 360 nm and 4 nm, respectively.
1.4 Data analysis
In order to better optimize experimental conditions and reduce errors, all experiments need to carry out in triplicate.The Origin software is applied in data analysis.
2 Results and Analysis
2.1 Optimization of aqueous two-phase extraction conditions
2.1.1 Effect of the type of ATPS
The upper phase is organic phase and the lower phase is inorganic phase.The distribution coefficient of samples in two phases closely related to the two-phase system.In this work, the sample distribution coefficient refers to the ratio of equilibrium concentration of herbicides in organic phase and inorganic phase.The distribution coefficient is affected by interactions, including electrostatic interaction, hydrophobic interaction and affinity interaction, between the two phases.
Recoveries of five ATPS were investigated.It was found(Fig.2) that the recoveries of four acetanilide herbicides were very low when phase D and E were used as extraction solvent.Phase B could not extract well with metolachlor,although it had a better effect on the extraction of propanil and acetochlor.Phase A and C can be successfully extracted with four acetanilide herbicides, and the recoveries are both higher.The ammonium sulfate and ethanol are non-toxic,environmentally friendly, relatively cheap, and cost saving.So, the ammonium sulfate/ethanol systems was finally selected for experiment.
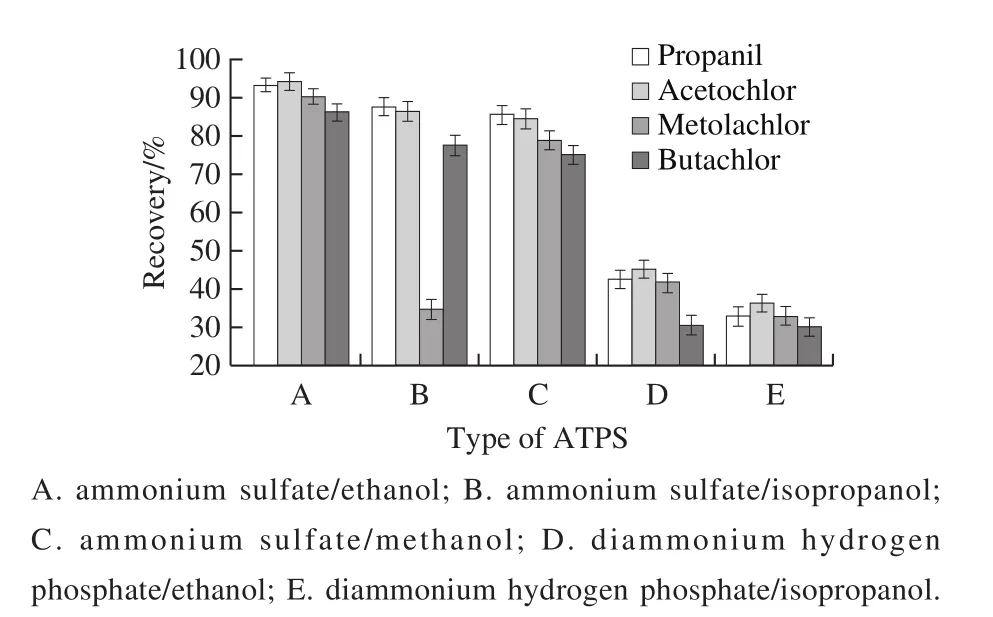
Fig.2 Effect of different ATPS on recoveries of four acetanilide herbicides
2.1.2 Effect of mass fraction of ammonium sulfate
The mass fraction of salt is the key factor for the formation of ATPS.The mass fraction of 20%, 22%, 25%,28%, 30% ammonium sulfate were inspected.The results(Fig.3) show that the recoveries of four acetanilide herbicides increased as mass fraction of ammonium sulfate rose up.But,the recoveries basically unchanged when the mass fraction of ammonium continued increasing, This might root from the salinization effect of ammonium sulfate on herbicides being strengthened with the increase of mass fraction of ammonium sulfate, so that the hydration of herbicides was reduced,and the amount of herbicides in organic phase increased.The recoveries of herbicides increased naturally.When ammonium sulfate reached a certain amount, the organic phase and the inorganic phase reached equilibrium state,the distribution coefficient didn’t change and the extraction recoveries remained basically unchanged.Therefore, the optimal condition is 28% ammonium sulfate in this work.
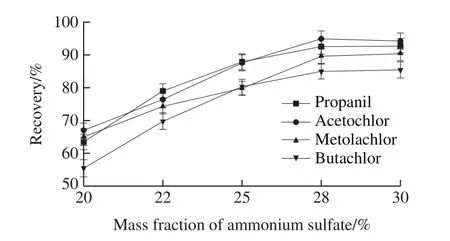
Fig.3 Effect of ammonium sulfate concentration on recoveries of four acetanilide herbicides
2.1.3 Effect of mass fraction of ethanol
Four acetanilide herbicides belong to moderate polarity of organic compounds.The solubility of acetochlor, butachlor, propanil and metolachlor in water at room temperature was 222.8, 20, 225, and 530 mg/L,respectively.Ethanol has good solubility to analytes and good compatibility with chromatographic mobile phase due to polarity similarity.Therefore, the mass fraction of ethanol is extremely important to the experiment.In this work, the massfraction of 20%, 22%, 25%, 28%, 30% ethanol were tested.As can be seen from Fig.4, when the mass fraction of ethanol is 20%, the analytes cannot be extracted completely.With the increase of the mass fraction of ethanol, the recoveries of four herbicides increased and then decreased.When the mass fraction of ethanol is 25%, the recoveries of four herbicides reaches the highest.Therefore, the 25% ethanol was selected.
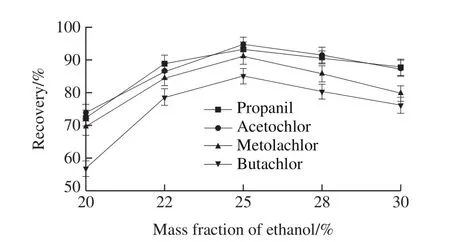
Fig.4 Effect of ethanol concentration on recoveries of four acetanilide herbicides
2.1.4 Effect of ultrasound extraction time
Aqueous two-phase extraction is an equilibrium extraction.The optimal extraction efficiency and highest recoveries can be obtained when the equilibrium is established.The effect of ultrasound extraction time,including 0.5, 1, 2, 3, and 4 min, on recoveries of four herbicides were investigated.The experimental results (Fig.5)indicated that the recoveries of four herbicides are unchanged when the ultrasound time is longer than 1 min.This might be caused by the large interface area between the analytes and the extraction phase.The tiny droplets on the upper part are formed uniformly in the solution.The phase transfer of the target analytes was fast and the extraction equilibrium can be established in very short time.It did not improve the extraction efficiency, nor did the recoveries of four herbicides processed longer than 1 min increased.Therefore, 1 min was selected in further work.
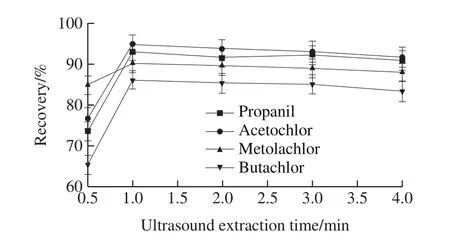
Fig.5 Effect of ultrasonic extraction time on recoveries of four acetanilide herbicides
2.1.5 Effect of extraction temperature
The increase of temperature can increase the random motion speed of molecules and accelerate the fusion of ethanol and herbicides.Hence, the temperature has a great influence on the experimental results.On one hand, low extraction temperature leads to incomplete extraction of herbicides.High extraction temperature enhances the ability of ultrasonic wave to destroy the structure of herbicide.On the other hand, the increase of temperature will also increase the amount of ethanol volatilization.In order to investigate the effect of temperature on the recoveries of four herbicides,the extraction temperature (15, 25, 35, 40, 45 ℃) were tested.As shown in Fig.6, the recoveries of four acetanilide herbicides increased as extraction temperature rose up.When the extraction temperature was 35 ℃, the recoveries of the four acetanilide herbicides were the highest.But the recoveries of the four acetanilide herbicides decreased as extraction temperature continued increasing.Therefore, 35 ℃was selected as extraction temperature in further work.
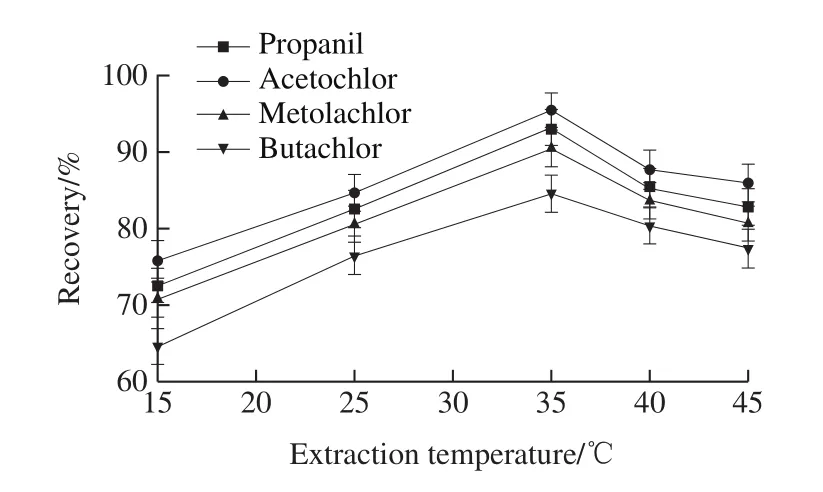
Fig.6 Effect of temperature on recoveries of four acetanilide herbicides
2.2 Method evaluation
In order to obtain better results and to reduce errors,all experiments need to carry out in quintuplicate.Under the optimal conditions (35 ℃, 25% ethanol, 1 min), a series of mixed working calibration solutions with different concentrations were prepared and analyzed by HPLC.The working calibration curves of concentrationCwas plotted by the peak areaAof each herbicides, and the linearity,correlation coefficient, limits of detection (LODs), and limits of quantification (LOQs).As showed in Table 1, the results indicated that the good linearities were obtained with correlation coefficients.The LOQs of four acetanilide herbicides were lower than the MRLs.Therefore, the present method is appropriate to practical application.
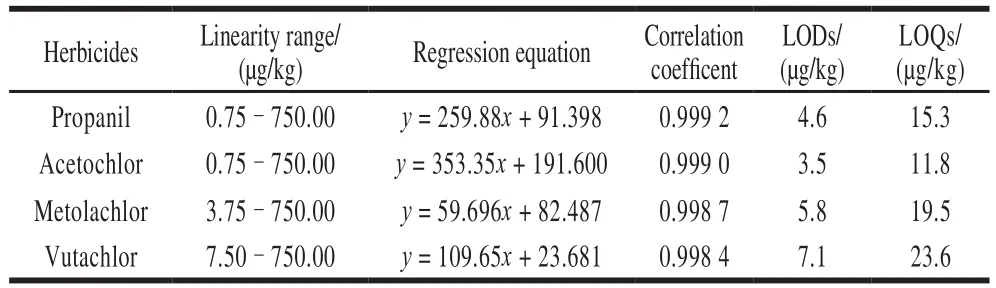
Table 1 Linearity ranges, regression equations, correlation coefficients,LODs and LOQs for four herbicides
2.3 The determination results of samples
Finally, three adzuki bean samples were analyzed to evaluate the applicability of the present method.The typical chromatograms of standard solution, blank real sample 1,and spiked sample 1 are shown in Fig.7.Analytical results are listed in Table 2.The recoveries are between 86.1% and 95.9%.The precision is acceptable.Therefore, the present method is suitable for the analysis of adzuki bean samples.
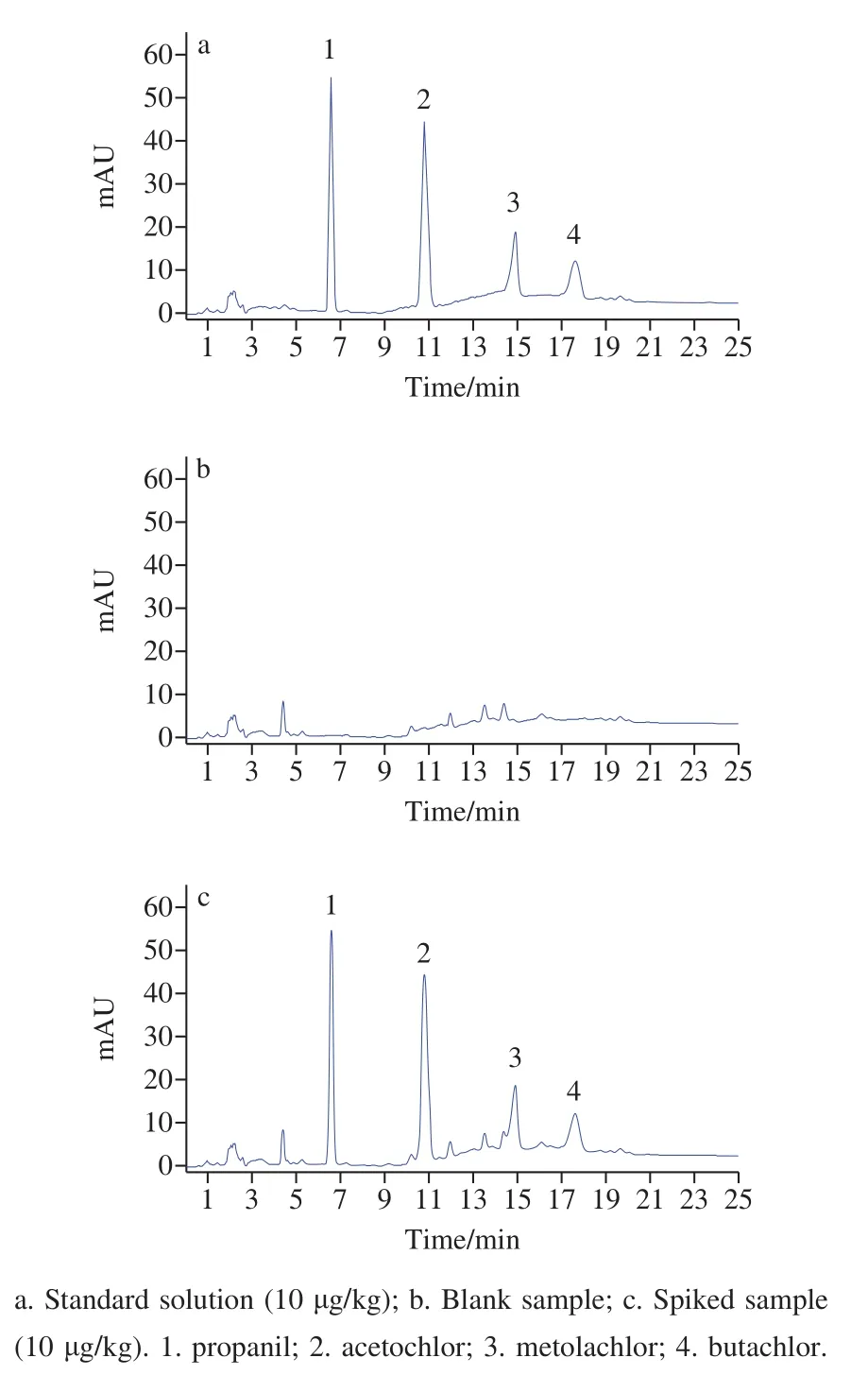
Fig.7 HPLC chromatograms
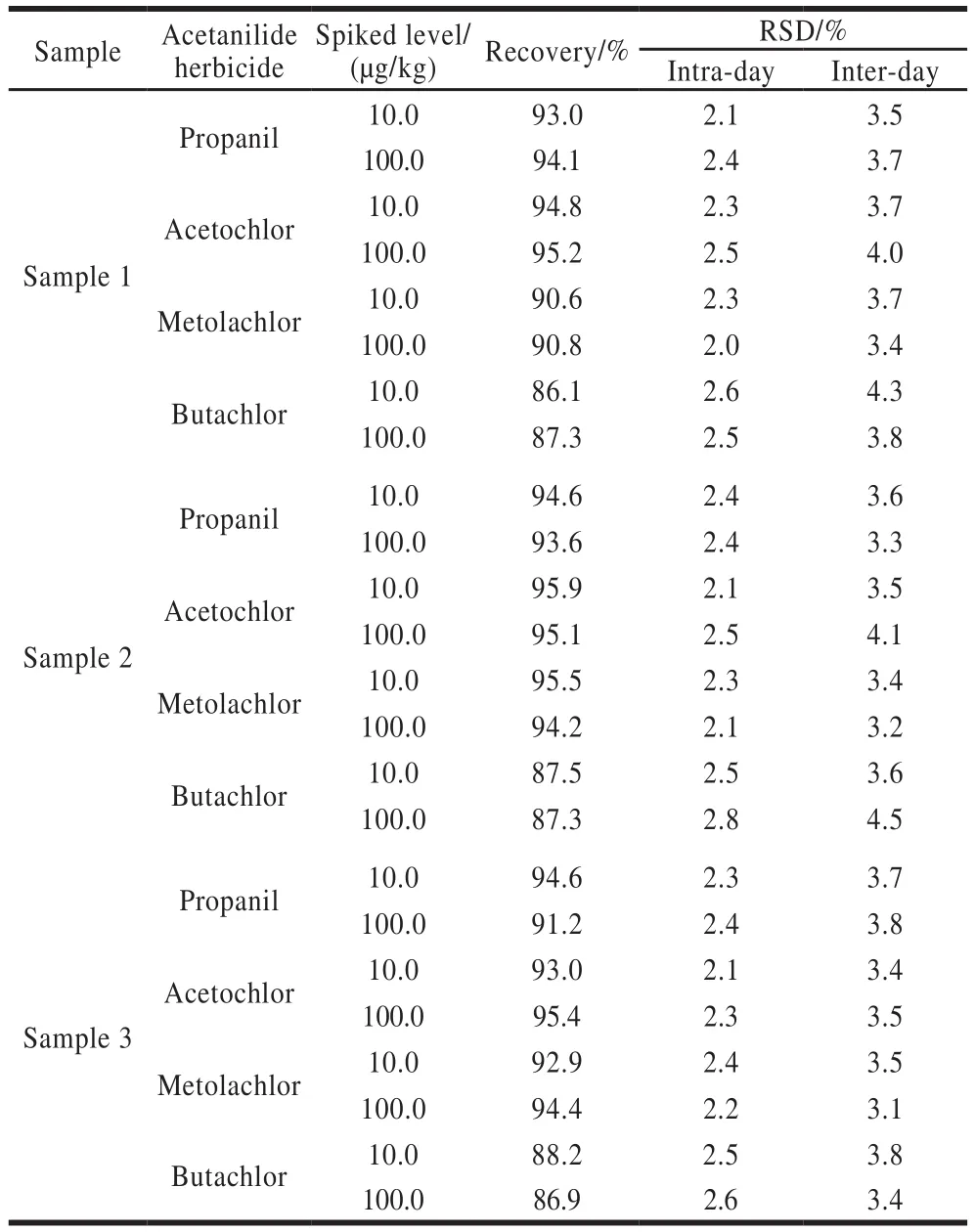
Table 2 Recoveries and precision of spiked adzuki bean samples
2.4 Comparison of different methods
The analytical performances of the proposed method was compared with reported methods[14,30-31]for the determination of these herbicides in this type of sample.The comparison results of are shown in Table 3.Compared with other methods references, this method did not use toxic reagents, nor required emulsification or reverse extraction,which is more simple, fast, and the phase separation is clear,the determination interference is small.This method meet demands of homogeneous extraction, simple operation, twophase separation, and high extraction efficiency.

Table 3 Comparison of the proposed method with other methods
3 Conclusion
The optimal conditions for this experiments were as followed, 28% ammonium sulfate solution, 25% ethanol,1 min of the ultrasound extraction time, and 35 ℃ of the ultrasound extraction temperature.The method was successfully applied to the analysis of three adzuki bean samples.RSDs were equal to or lower than 4.5%.The recoveries of four acetanilide herbicides were between 86.1%and 95.9%, with high precision and low detection limit.The present method is environmentally friendly because of the avoidance of toxic organic solvents.Compared with other traditional methods, the present method improved the extraction efficiency, reduced the experimental cost,simplified operation processes, and shorten the extraction time, the impurities (e.g.proteins and lipids) weren’t required to be excluded before the experiment.

