Laparoscopic liver resection for colorectal liver metastases — shortand long-term outcomes:A systematic review
Emily Taillieu,Celine De Meyere,Frederiek Nuytens,Chris Verslype,Mathieu D'Hondt
Emily Taillieu,Celine De Meyere,Frederiek Nuytens,Mathieu D'Hondt,Department of Digestive and Hepatobiliary/Pancreatic Surgery,AZ Groeninge,Kortrijk 8500,Belgium
Chris Verslype,Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology,KU Leuven,Leuven 3000,Belgium
Abstract BACKGROUND For well-selected patients and procedures,laparoscopic liver resection(LLR)has become the gold standard for the treatment of colorectal liver metastases(CRLM)when performed in specialized centers.However,little is currently known concerning patient-related and peri-operative factors that could play a role in survival outcomes associated with LLR for CRLM.AIM To provide an extensive summary of reported outcomes and prognostic factors associated with LLR for CRLM.METHODS A systematic search was performed in PubMed,EMBASE,Web of Science and the Cochrane Library using the Key Words “colorectal liver metastases”,“laparoscopy”,“liver resection”,“prognostic factors”,“outcomes” and “survival”.Only publications written in English and published until December 2019 were included.Furthermore,abstracts of which no accompanying full text was published,reviews,case reports,letters,protocols,comments,surveys and animal studies were excluded.All search results were saved to Endnote Online and imported in Rayyan for systematic selection.Data of interest were extracted from the included publications and tabulated for qualitative analysis.RESULTS Out of 1064 articles retrieved by means of a systematic and grey literature search,77 were included for qualitative analysis.Seventy-two research papers provided data concerning outcomes of LLR for CRLM.Fourteen papers were eligible for extraction of data concerning prognostic factors affecting survival outcomes.Qualitative analysis of the collected data showed that LLR for CRLM is safe,feasible and provides oncological efficiency.Multiple research groups have reported on the short-term advantages of LLR compared to open procedures.The obtained results accounted for minor LLR,as well as major LLR,simultaneous laparoscopic colorectal and liver resection,LLR of posterosuperior segments,twostage hepatectomy and repeat LLR for CRLM.Few research groups so far have studied prognostic factors affecting long-term outcomes of LLR for CRLM.CONCLUSION In experienced hands,LLR for CRLM provides good short-and long-term outcomes,independent of the complexity of the procedure.on different terms,provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial.See:htt p://creativecommons.org/License s/by-nc/4.0/
Key Words:Laparoscopic liver resection;Colorectal liver metastases;Outcomes;Prognostic factors;Systematic review
INTRODUCTION
Colorectal cancer(CRC)is the third most common malignancy in terms of incidence worldwide and the fourth most common cause of cancer death[1,2].The most frequent cause of death in CRC patients is metastatic disease[3,4],with the liver being the most common site of metastasis[2,3].The risk for these patients to develop colorectal liver metastases(CRLM)is up to 50%[2,4-7].A liver resection(LR)in this context is the only treatment option that can provide a potential cure[2,4,5],with reported 5-year survival rates that vary between 35% and 60%[8].Despite a high rate of irresectability at initial presentation,advances in the field of liver surgery and the emergence of multidisciplinary approaches in the last couple of decades have led to significant improvements in long-term outcome[5].
Many studies that have been published lately have attempted to elucidate the safety and feasibility of laparoscopic liver resection(LLR)for CRLM,along with its role in the treatment sequence of these patients.Most often,these reports have compared outcomes between LLR and open liver resection(OLR).Randomized controlled trials(RCT)and meta-analyses have shown equal or better short-term outcomes after LLR compared to OLR along with equivalent oncologic outcomes[8-19].One of these metaanalyses of propensity-score matched studies and RCTs unexpectedly showed a survival advantage favoring LLR over OLR when indicated for CRLM[13].Little is known however concerning patient-related and peri-operative factors that could play a role in survival outcomes after LLR for CRLM and how these variables in turn could be applied as prognostic factors.As such,for this systematic review,all currently available literature was screened for articles that reported on short-and long-term outcomes following LLR for CRLM along with studies that have analyzed potential prognostic factors(demographics,pre-,intra-and postoperative factors)affecting survival outcomes after LLR for CRLM.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This systematic review was conducted according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses(PRISMA)checklist of 2009[20].
Search strategy
A systematic search was performed in PubMed,EMBASE,Web of Science and the Cochrane Library from inception until December 24,2019(which was the start date of the performance of the search strategy).The search strategy consisted of breaking up the research question “short-and long-term outcomes following laparoscopic liver resection for colorectal liver metastases and prognostic factors” into separate concepts that fit the PICO(Patient-Intervention-Comparison-Outcome)model:“Colorectal liver metastases” for Patient,“laparoscopy” and “liver resection” for Intervention and“prognostic factors,outcomes and survival” for Outcome.Within the context of this systematic review,“Comparison” was not applicable in the PICO-model.In PubMed,the most appropriate medical subject headings(MeSH)terms were chosen,including"Laparoscopy" AND "Hepatectomy" AND "Colorectal Neoplasms" AND "Prognosis"OR "Survival" OR "Outcome Assessment(Health Care)" OR "Treatment Outcome".The MeSH terms were searched for within the title and the abstract,as were all the corresponding synonyms.The same strategy was applied in EMBASE by means of Emtree terms,including 'laparoscopy' AND 'liver resection' AND 'colorectal liver metastasis'AND 'prognosis' OR 'survival' OR 'outcome assessment' OR 'treatment outcome' OR'short term outcome' OR 'long term outcome'.The Emtree terms and the corresponding synonyms were searched for within the title,abstract and Key Words.The terms included in both search strategies were aligned to obtain as many results as possible in both databases.The final,aligned search strategy was adopted for the Web of Science database and the Cochrane Library database.
Inclusion criteria
For the collection of outcome data:(1)Publications needed to report the result of at least one short-or long-term outcome following LLR;(2)The indication for resection had to be CRLM;and(3)A study cohort of at least 20 patients undergoing LLR needed to be included(to ensure reliability of the studies).
For the collection of data on prognostic factors:(1)Publications needed to report at least one factor(demographic/preoperative/intraoperative/postoperative)to be studied for correlation with a(or multiple)survival outcome(s)of(L)LR together with the associated correlation;(2)The indication for resection had to be CRLM;and(3)A study cohort of at least 20 patients needed to be included(again to ensure reliability of the studies).
In case of multiple studies providing duplicated or the same data,only the most recent study was included.Furthermore,only publications written in English were included.
Abstracts of which no accompanying full text was published,reviews,case reports,letters,protocols,comments,surveys,animal studies,outcome studies that only described treatment procedures other than pure LLR(e.g.,chemotherapy regimens,ablation techniques,hand-assisted LLR,robotic LLR)and studies that only described pathologies other than CRLM(e.g.,non-colorectal liver metastases)were excluded.
The in-and exclusion criteria were based on those found in already existing literature[18,21,22].
Selection of search results
All of the search results were saved to Endnote Online and imported into Rayyan,a web and mobile app for systematic reviews[23].Deduplication of the search results was first done automatically in Endnote Online and was followed by further manual deduplication in Rayyan.The remaining articles were first screened based on title and abstract according to the presupposed in-and exclusion criteria.An informal grey literature search was performed,and these articles were also subjected to screening of the title and abstract.Thereafter,a full-text analysis was performed until all included articles only contained relevant studies.
Data extraction
After full-text analysis,the data relevant for this research were tabulated.This was done separately for research concerning outcomes and research concerning prognostic factors.
For research concerning outcomes,as much of the following data as possible(depending on the data examined in a particular study)were extracted and tabulated for analysis:Study data(title,first author,year of publication,country,study design,number of patients who underwent LLR),patient demographic data(age and sex),intraoperative data(conversion rate,rate of major hepatectomies,operative time,blood loss,operative death and rate of need for blood transfusion),postoperative short-term outcomes(30 d mortality,30 d morbidity,duration of hospital stay,length of stay at high-dependency unit or intensive care unit,overall rate of postoperative complications,rate of major postoperative complications,rate of need for postoperative blood transfusion,90 d mortality and time to chemotherapy),characteristics of lesions and resection margins(rates of 1/2/≥ 3 Lesions/specimen,number of lesions,diameter of lesions,size of largest lesion,R1 and R0 resection rates and tumor free resection margin),long-term outcomes(follow-up(FU)duration,recurrence rate,rate of deaths during FU,median/mean survival,1-,2-,3-,4-,5-,7-and 10-year overall survival(OS),disease free survival(DFS)and recurrence free survival(RFS),median DFS and median RFS)and general conclusions about safety,feasibility,effectivity and oncological efficiency.When articles reported data of LLR for CRLM in a specific context(major/minor hepatectomy,LLR of posterosuperior segments,parenchyma sparing LLR,simultaneous laparoscopic colorectal and liver resection,two-stage hepatectomy(TSH)or repeat LLR),outcomes were collected in a subgroup to easily analyze those data within the particular context.
For research concerning prognostic factors,the following data were extracted and tabulated for analysis:Study data(title,first author,year of publication,country,study design,number of patients included,whether or not the study is specific for LLR),patient demographic data(age and sex),the prognostic factor(s),the corresponding correlate(s),and the associated relationship.
In case of propensity score-matched studies,a decision was made to collect data either from the cohort before or after matching in function of which cohort represented more relevant data.In case of stratification,e.g.,based on a cut-off at a certain age or a certain tumor size,where the stratification was reported to make no difference in any outcome,and where the general data of the whole cohort was provided,it was decided to collect the reported data of the whole cohort.Otherwise,data were collected of the most relevant group of which the most relevant data were reported.All texts,tables and figures of relevance were reviewed for data extraction.
Data presentation and analysis
After data collection,a selection was made of the gathered outcomes based on relevance and the number of times they were reported.The selected outcomes were comprised in tables in which all data of the included articles were tabulated.These tables were analyzed merely qualitatively and discussed in general.Incoherent data or data that seemed to deviate from the other reports were verified in the original article to check for any specific causes explaining the deviation.
RESULTS
Publication selection and characteristics
Application of the aforementioned search strategy in PubMed,EMBASE,Web of Science and the Cochrane Library resulted in 1061 publications.After deduplication,there were 673 publications left for screening.After screening based on title and abstract,173 articles were withheld.An informal grey literature search yielded another 3 articles of which the title and abstract seemed to possibly meet the in-and exclusion criteria.All full-text articles were obtained and screened thoroughly for eligibility(based on in-and exclusion criteria),after which extensive data extraction was performed.Reasons to exclude publications during full-text analysis were:Only an abstract was available,outcome studies did not provide any CRLM data or LLR data,outcome studies did not report any of the selected relevant outcomes,studies reported risk factors affecting outcomes that were not prognostic factors,the study cohort consisted of less than 20 patients or no English text was available.This led to a final total of 77 publications for inclusion in the review,and thus,for data extraction.Figure 1 provides a summary of the publication selection process.Tables 1 and 2 provide an overview of the study details of the included studies for data concerning outcomes and prognostic factors,respectively.

Figure 1 Flow diagram of the systematic review selection process.Adapted from Ref.[20].
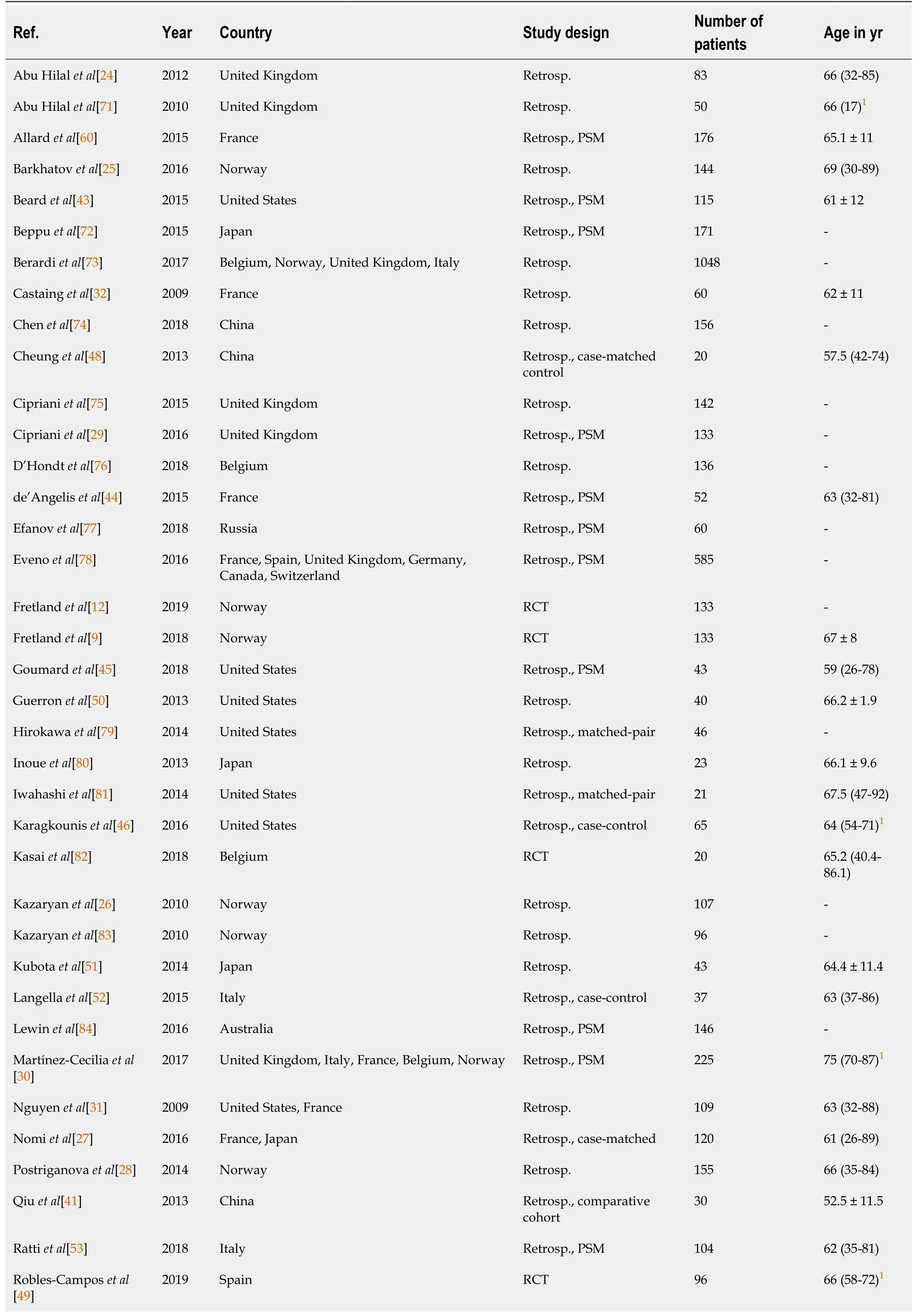
Table 1 Study details of studies concerning outcomes
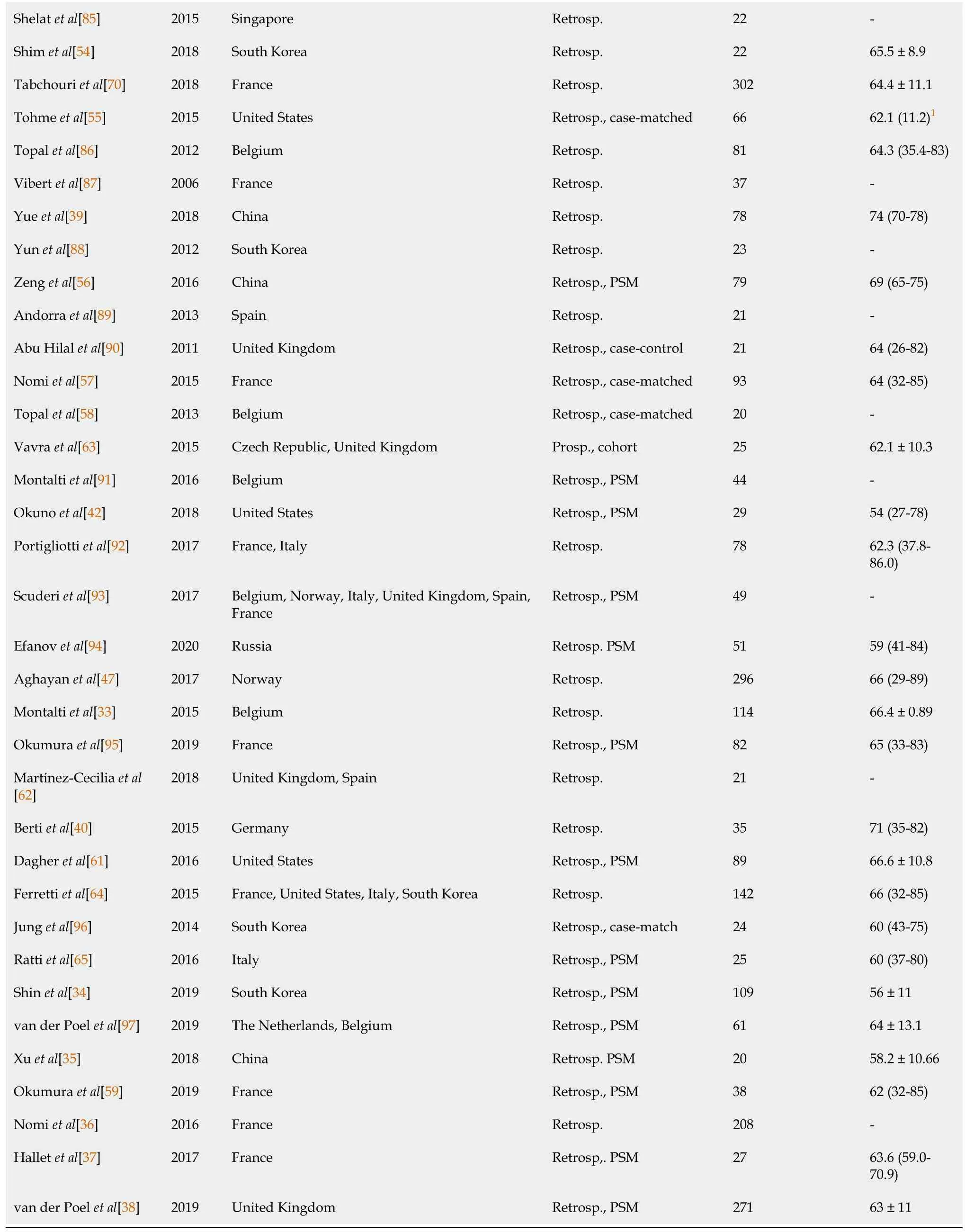
1Interquartile range.Numbers are presented as median(range)or mean ± SD unless otherwise indicated.Prosp.:Prospective;PSM:Propensity score-matched;RCT:Randomized controlled trial;Retrosp.:Retrospective.
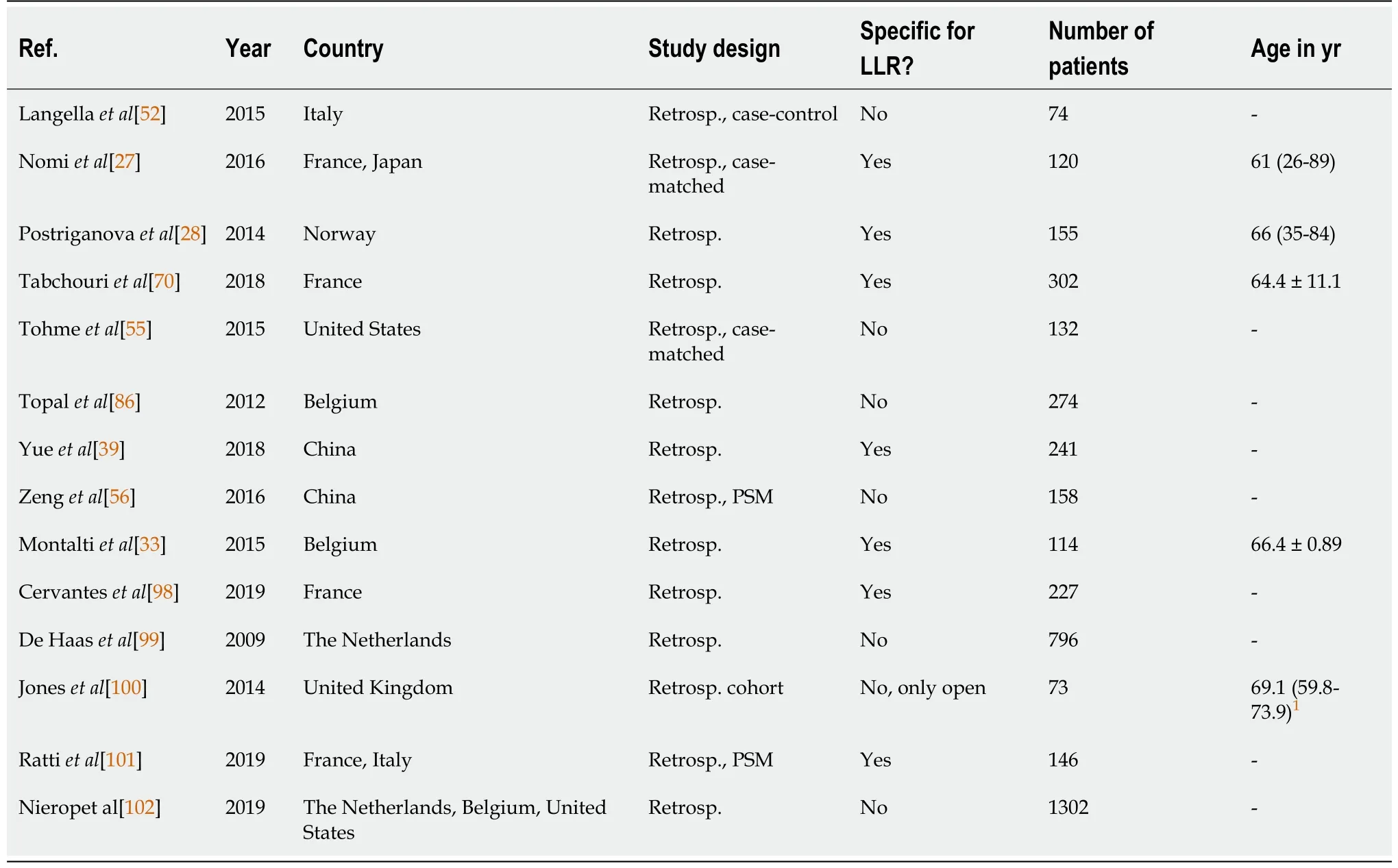
Table 2 Study details of studies concerning prognostic factors
Operative outcomes
An overview of all extracte d operative data can be found in Table 3.
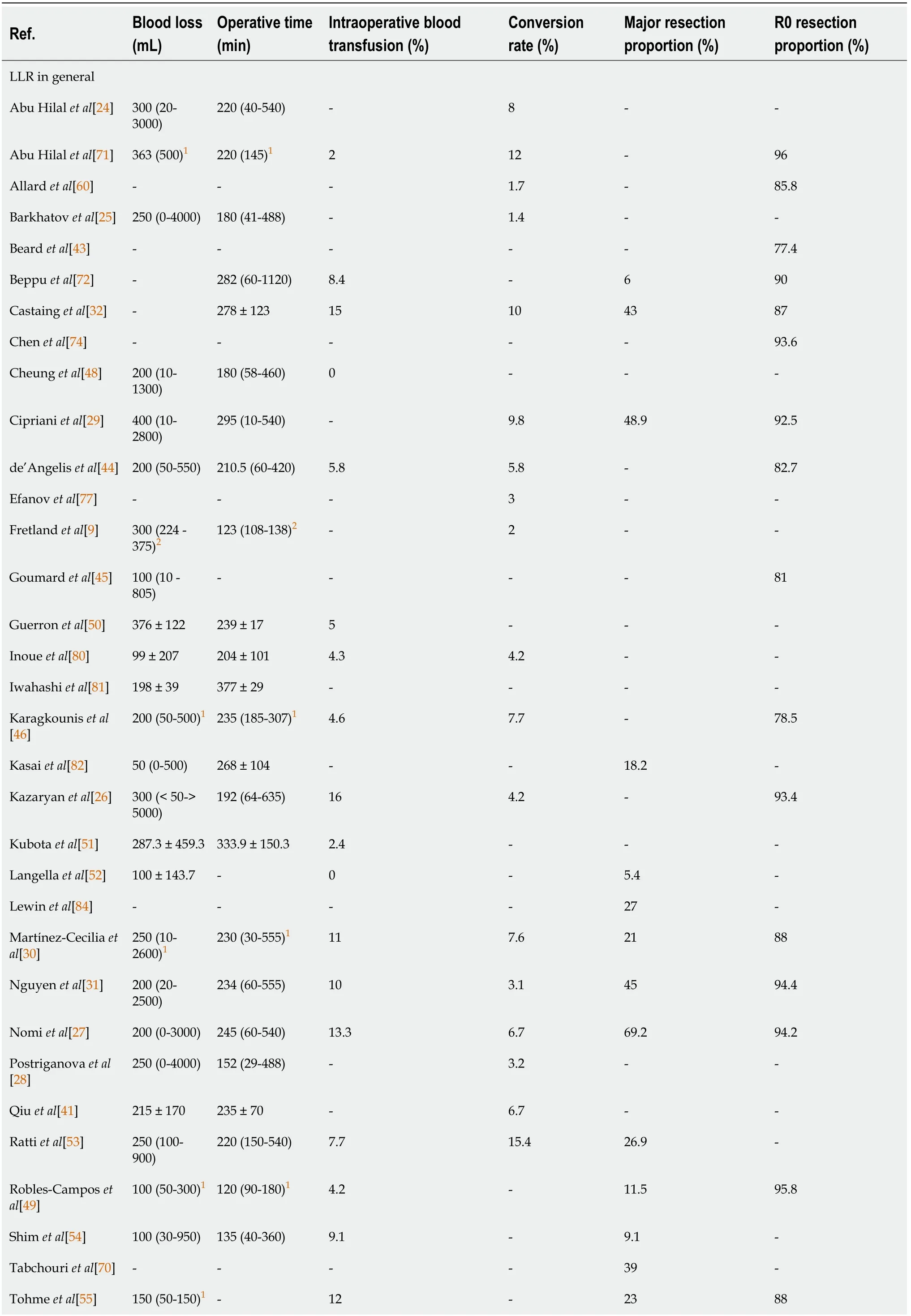
Table 3 Operative outcomes
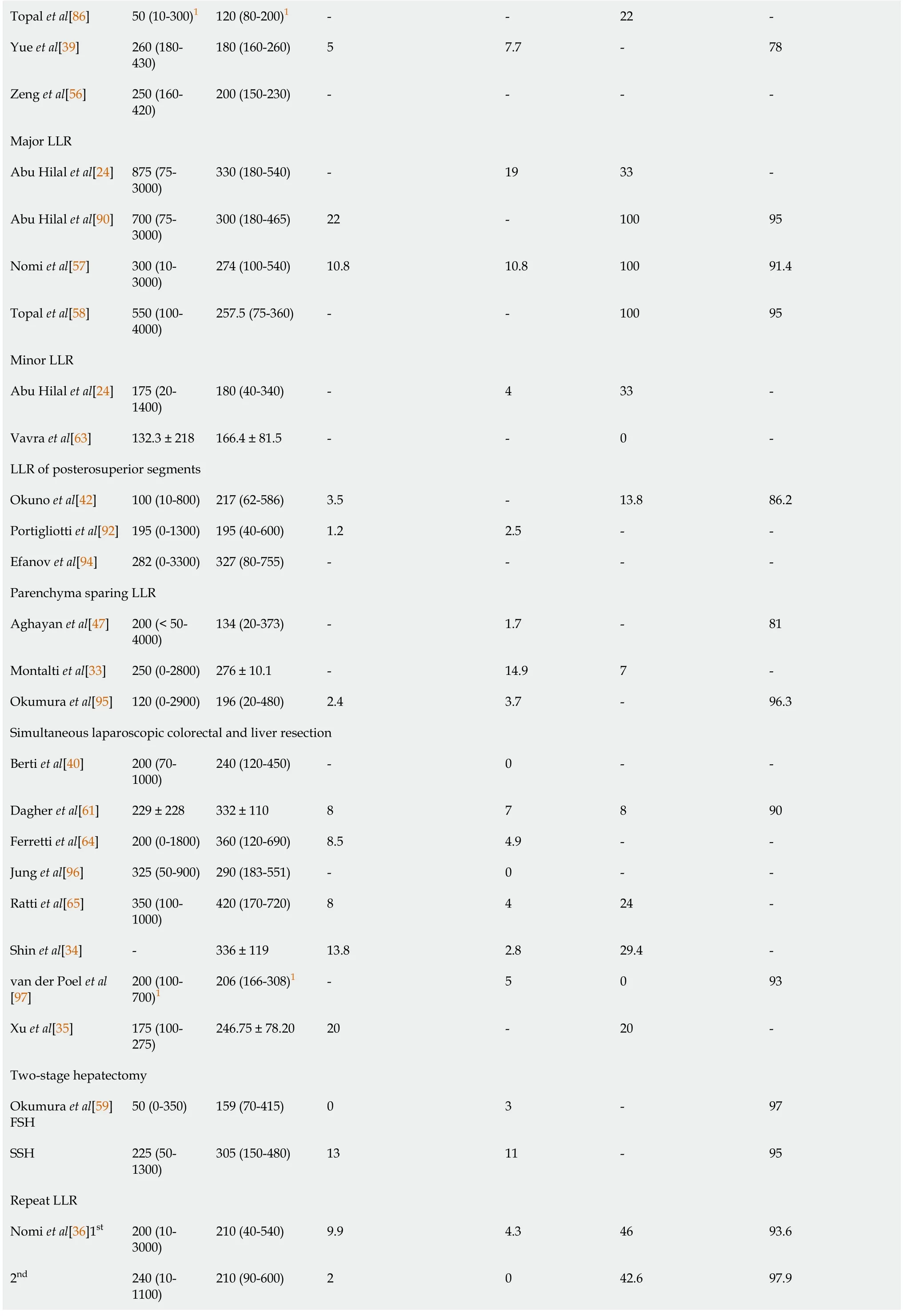
Topal et al[86]50(10-300)1 120(80-200)1--22-Yue et al[39]260(180-430)180(160-260)5 7.7-78 Zeng et al[56]250(160-420)200(150-230)----Major LLR Abu Hilal et al[24]875(75-3000)330(180-540)-19 33-Abu Hilal et al[90]700(75-3000)300(180-465)22-100 95 Nomi et al[57]300(10-3000)274(100-540)10.8 10.8 100 91.4 Topal et al[58]550(100-4000)257.5(75-360)--100 95 Minor LLR Abu Hilal et al[24]175(20-1400)180(40-340)-4 33-Vavra et al[63]132.3 ± 218 166.4 ± 81.5--0-LLR of posterosuperior segments Okuno et al[42]100(10-800)217(62-586)3.5-13.8 86.2 Portigliotti et al[92]195(0-1300)195(40-600)1.2 2.5--Efanov et al[94]282(0-3300)327(80-755)----Parenchyma sparing LLR Aghayan et al[47]200(< 50-4000)134(20-373)-1.7-81 Montalti et al[33]250(0-2800)276 ± 10.1-14.9 7-Okumura et al[95]120(0-2900)196(20-480)2.4 3.7-96.3 Simultaneous laparoscopic colorectal and liver resection Berti et al[40]200(70-1000)240(120-450)-0--Dagher et al[61]229 ± 228 332 ± 110 8 7 8 90 Ferretti et al[64]200(0-1800)360(120-690)8.5 4.9--Jung et al[96]325(50-900)290(183-551)-0--Ratti et al[65]350(100-1000)420(170-720)8 4 24-Shin et al[34]-336 ± 119 13.8 2.8 29.4-van der Poel et al[97]200(100-700)1 206(166-308)1-5 0 93 Xu et al[35]175(100-275)246.75 ± 78.20 20-20-Two-stage hepatectomy Okumura et al[59]FSH 50(0-350)159(70-415)0 3-97 SSH 225(50-1300)305(150-480)13 11-95 Repeat LLR Nomi et al[36]1st 200(10-3000)210(40-540)9.9 4.3 46 93.6 2nd 240(10-1100)210(90-600)2 0 42.6 97.9

1Interquartile range.295% confidence interval.Numbers are presented as median(range)or mean ± SD unless otherwise indicated.LLR:Laparoscopic liver resection.
For LLR in general,the reported median and mean blood loss volume varied between 50 mL and 400 mL.Median and mean values of operative time varied between 120 and 377 min.High variations in blood loss,ranging from almost no blood loss to 3 L or more,were reported by several authors[24-28].As stated by Abu Hilalet al[24],major hepatectomy was frequently associated with higher blood loss,as well as increased conversion rates,operative times and length of stay.These findings are in line with other data included in the Table 3.Greater variations in blood loss(negligible to more than 2 L)were usually associated with greater variations in operative time(less than 60 min to more than 480 min)[24-31].Correlated with an increased rate of major resection(40% or higher),greater variations were reported in blood loss,operative time[27,29,31],intraoperative transfusion rates(10%-16%)[27,31,32],as well as conversion rates(approximately 10%)[29,32].
Similar conclusions could be drawn when considering data reported about major LLRs specifically.Compared to LLR in general,major LLRs were marked by a higher median blood loss and operative time,as well as an increased variation in blood loss,operative time,intraoperative transfusion rates as well as conversion rates.These differences were even more distinct when compared to minor LLR only.We observed that variations in blood loss and operative time were also higher when considering LLR of the posterosuperior segments.
Data on parenchyma sparing LLR also illustrated a wide variation in blood loss.In the report by Montaltiet al[33],besides great variation in blood loss(0-2800 mL),a rather high conversion rate of 14.9% was noted,which,according to the authors,was impacted by the amount of blood loss during LLR.Moreover,it was reported that the rate of R1 resections also correlated with the amount of blood loss.However,major LLRs were characterized by high R0 resection rates although blood loss in this specific subset seemed to be higher compared to parenchyma sparing LLR.
In simultaneous laparoscopic colorectal and liver resection,reported blood loss was low.Median and mean values ranged from 175 to 350 mL with the upper limits of variation being much lower than in major LLRs.Concerning operative times,the median and mean values ranged from 206 to 420 minutes,along with upper limits of variation that were frequently higher than in major LLRs.Both Shinet al[34]and Xuetal[35]reported higher transfusion rates(13.8% and 20%,respectively),which could again be explained by a large proportion of major hepatectomies(29.4% and 20%,respectively).
One included study provided data on TSH.Blood loss,operative times,intraoperative transfusion rates and conversion rates were higher in second stage hepatectomies(SSH)when compared to first stage hepatectomies(FSH).However,the numbers were not exceptionally high.
In repeat LLRs,blood loss and operative times did not differ from primary LLRs.Nomiet al[36]reported lower transfusion and conversion rates,while Halletet al[37]reported higher transfusion rates and van der Poelet al[38]reported higher conversion rates compared to average primary LLRs.Again this could be due to higher major LLR proportions reported by Halletet al[37]and van der Poelet al[38].
No striking differences were noted between data from studies that included patients with a high(> 70 years)[30,39,40]or low(< 55 years)[41,42]median age.
The R0 resection rate was found to be ≥ 90% in 20 out of 32 studies(62.5%)that reported on this topic.In only 7 studies,the R0 resection rate was lower than 85%[37,39,43-47].Beardet al[43]stated that the lower R0 resection rate in their study could be due to the long inclusion period of 15 years.A similar argumentation was found in the reports by de'Angeliset al[44],Yueet al[39]and Aghayanet al[47],which comprised an inclusion period of 13,17 and 19 years,respectively.Other explanations were not provided.
Postoperative short-term outcomes
All extracted postoperative short-term data are listed in Table 4.

Table 4 Postoperative short-term outcomes
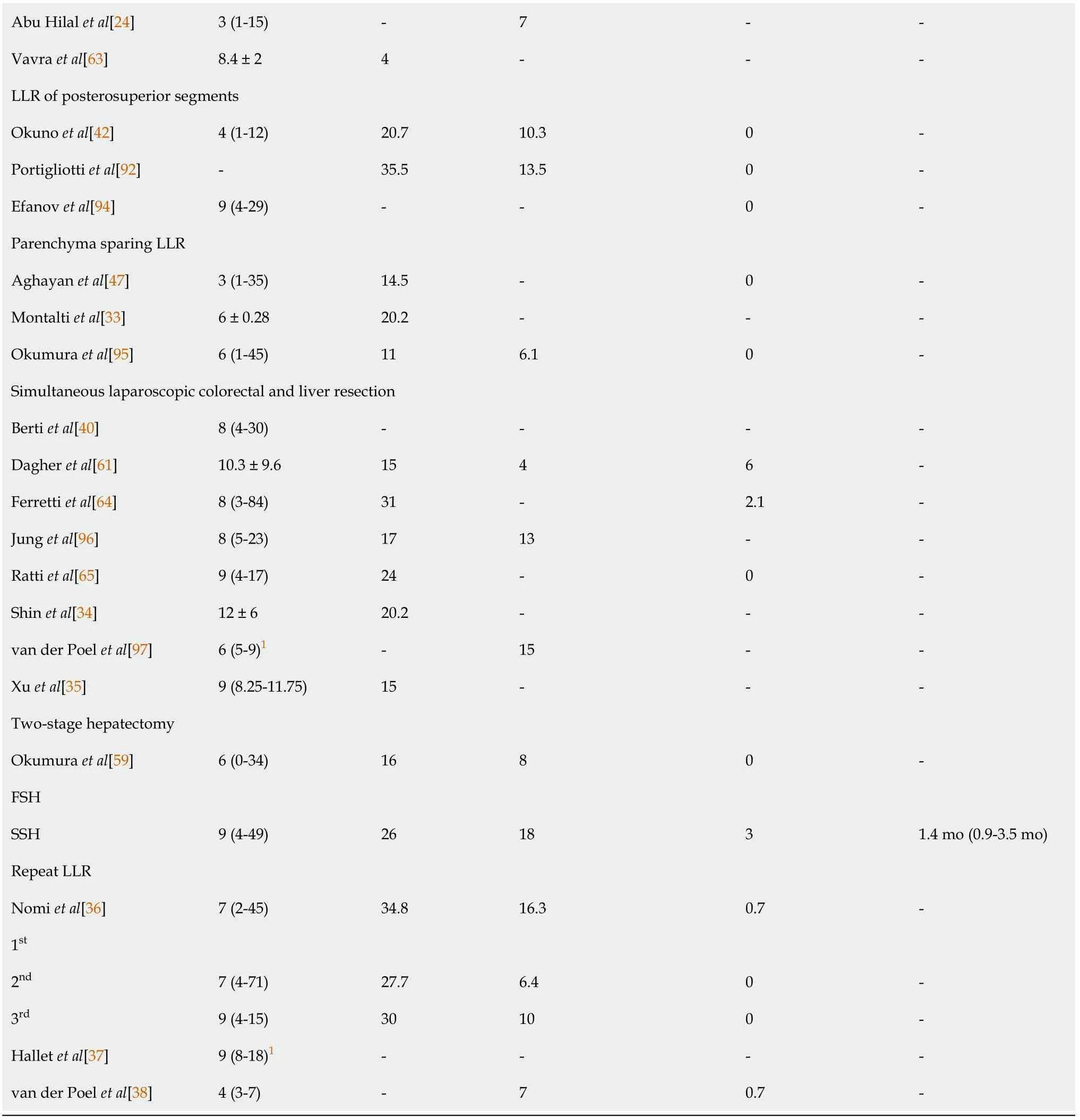
1Interquartile range.295% confidence interval.Numbers are presented as median(range)or mean ± SD unless otherwise indicated.AC:Adjuvant chemotherapy;LLR:Laparoscopic liver resection.
When considering LLR in general and specific types of LLR,median and mean values of hospital stay ranged from 2.2 to 12 d.
Twenty-eight research groups reported on postoperative morbidity,out of which 25(89%)mentioned that morbidity occurred in at least 10% of the cases.More than half of these 28 research groups(64%)reported morbidity rates of at least 15%.Sixteen research groups reported on both morbidity rates and major complication rates.These 16 reports indicated that,in many cases,approximately half of the complications were major complications[27,43,45,48,49],and otherwise,the proportion of major complications to all postoperative complications was less than half or nil[30,39,46,50-56].Nomiet al[27]reported very high morbidity and major complication rates of 41.7% and 17.5%,respectively.Besides a long inclusion period of 13 years,no other clear explanation could be identified.
In major LLR,morbidity rates reported by Nomiet al[57]and Topalet al[58]were higher compared to LLR in general(50.5% and 35%,respectively).Overall,reported morbidity rates and major complication rates for LLR of posterosuperior segments,parenchyma sparing LLR,and simultaneous LLR were in line with those reported for LLR in general.Nomiet al[36]mentioned that second or third LLRs carry an increased risk for complications due to intra-abdominal adhesions,variations in liver anatomy in the hypertrophied liver remnant and the possibility of chemotherapy-induced liver injury.However,the authors reported similar morbidity rates for both repeat LLR and primary LLR,thereby confirming the feasibility and safety of second and third LLR.Okumuraet al[59]reported similar findings in TSH,with slightly higher morbidity and major complication rates after SSH compared to FSH.
Based on the extracted data,the overall reported 90 d postoperative mortality(POM)rates were very low,even when considering specific types of LLR.The highest reported 90 d POM for LLR in general was 2.3%[60].In studies concerning major LLR,LLR of posterosuperior segments and parenchyma sparing LLR specifically,no 90 d POM occurred.Tranchartet al[61]and Okumuraet al[59]reported a slightly higher 90 d mortality rate in simultaneous laparoscopic colorectal and liver resection(6%)and after SSH(3%),respectively,without any clear explanation being provided.
The time interval between LLR and adjuvant chemotherapy(AC)was only reported by 2 research groups.For LLR in general,Tohmeet al[55]reported a median interval of 42 d[interquartile range(IQR):34-54 d].Okumuraet al[59]reported a median interval of 1.4 mo(range:0.9-3.5 mo)after TSH.
Long-term postoperative outcomes
An overview of all extracted long-term postoperative data is demonstrated in Table 5.
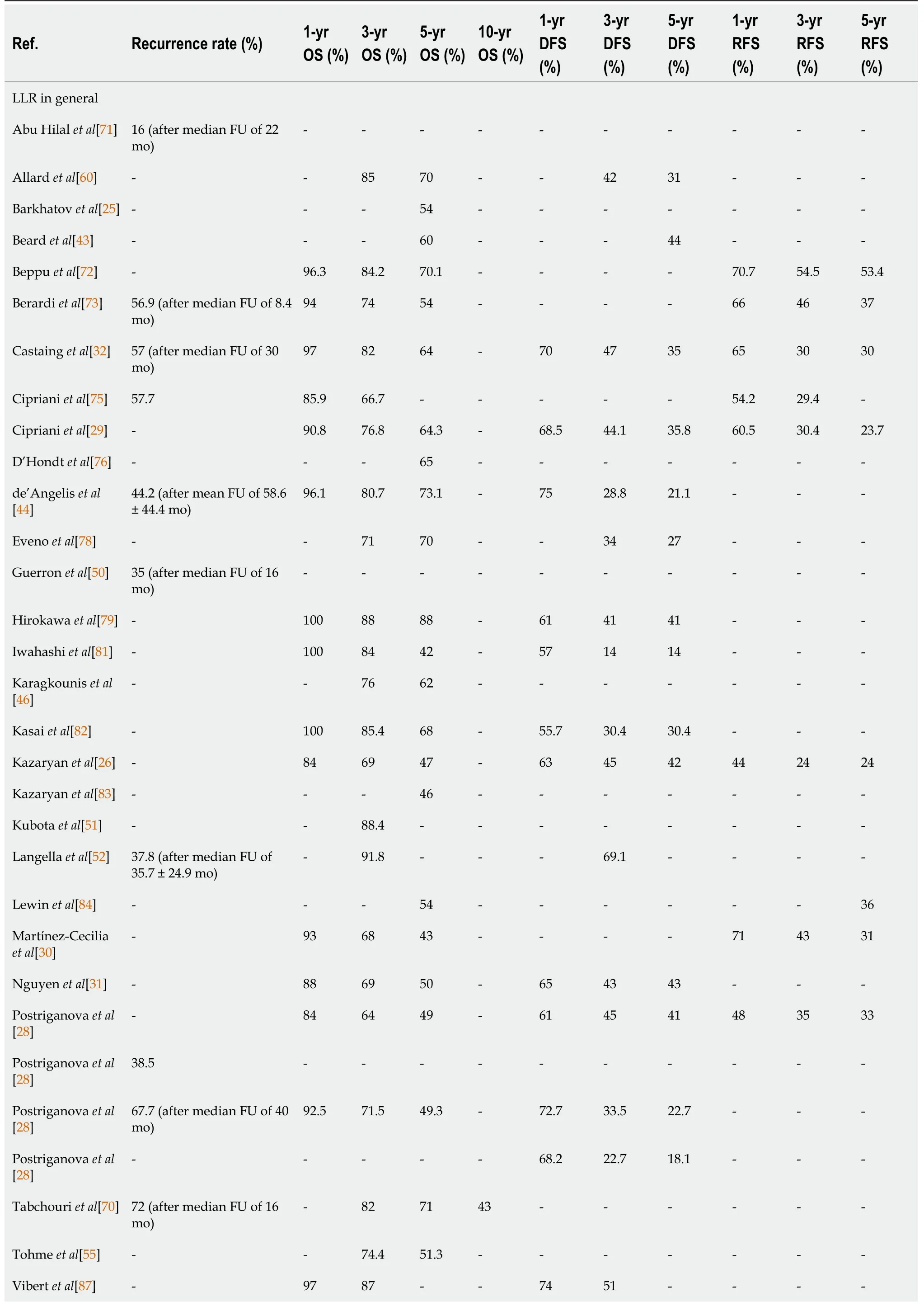
Table 5 Long-term and oncoIogic outcomes
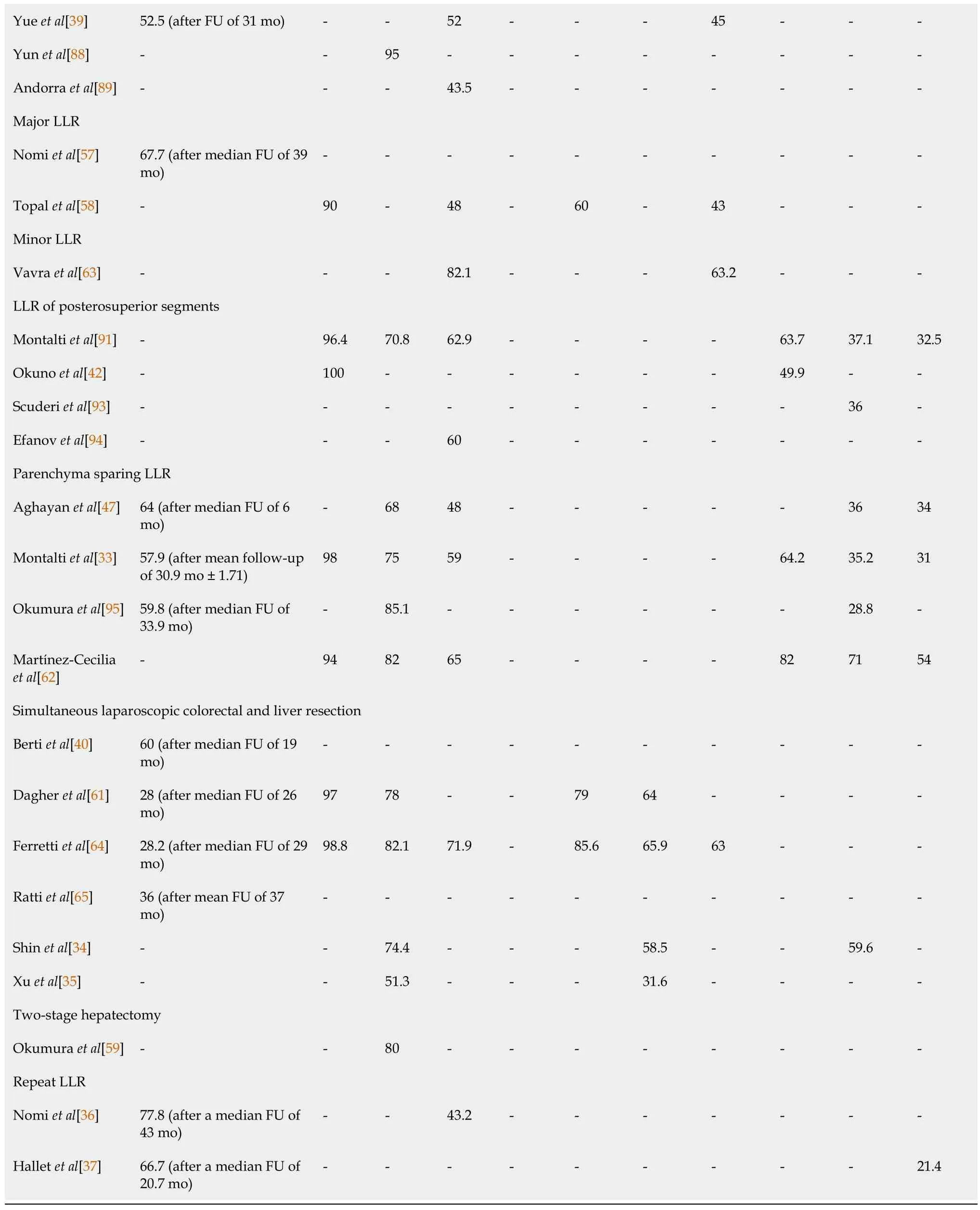
DFS:Disease-free survival;FU:Follow-up;LLR:Laparoscopic liver resection;OS:Overall survival;RFS:Recurrence-free survival.
When considering LLR in general along with the specific types of LLR,1-year OS rates ranged from 84% to 100%,with 18 out of 21 research groups(86%)reporting 1-year OS rates of ≥ 90%.The reported 3-year and 5-year OS rates for LLR in general were marked by some variation,ranging from 64% to 95% and from 42% to 88%,respectively.
The reported DFS rates for LLR in general at 1,3 and 5 years ranged from 55.7% to 75%,14% to 69.1% and 14% to 45%,respectively.Remarkably,3-and 5-year DFS rates reported by the same research groups were often the same or differed only slightly.
For LLR in general,RFS rates ranged from 44% to 71%,24% to 54.5% and 24% to 53.4% at 1,3 and 5 years,respectively.Again,it was observed that 3-and 5-year RFS rates reported by the same research group were equal or comparable.RFS rates for LLR of posterosuperior segments were similar to those for LLR in general.Martínez-Ceciliaet al[62]reported improved RFS rates for parenchyma sparing LLR.
The reported 5-year OS and DFS rates after major LLR(48% and 43%,respectively)[58]were much lower compared to minor LLR(82.1% and 63.2%)[63],indicating worse long-term and oncologic outcome after major LLR.The 5-year DFS for minor LLR was 63.2% on the contrary,which was higher compared to LLR in general,indicating a better oncologic outcome.
In simultaneous laparoscopic colorectal and liver resection,the 1-year DFS rate was reported to be higher(79% and 85.6%)compared to LLR in general[61,64].Accordingly,3-and 5-year DFS rates after simultaneous LLR were also higher compared to LLR in general,which suggests that simultaneous LLR seems to provide equal or better long-term and oncologic outcomes compared to other general LLR procedures.
Long-term outcomes did not seem to be particularly compromised when reported R0 resection rates were lower[37,39,43-47].
Studies in which the median or mean FU for recurrence after LLR in general exceeded 24 mo,recurrence rates ranged from 37.8% to 67.7%.When FU was shorter,recurrence rates of 16% to 72% were also reported.Recurrence rates after major LLR and parenchyma sparing LLR were similar,ranging from 57.9% to 67.7%,regardless of the median or mean duration of FU(shorter or longer than 24 mo).Recurrence rates after simultaneous LLR seemed to be somewhat lower,with 3 research groups reporting recurrence rates of 28%,28.2% and 36%[61,64,65],with a median and mean FU exceeding 24 mo.These findings were in line with the higher DFS rates associated with simultaneous LLR as mentioned earlier.After repeat LLR,reported recurrence rates were found to be higher,ranging from 77.8% to 66.7%[36,37].
General conclusions reported about LLR for CRLM
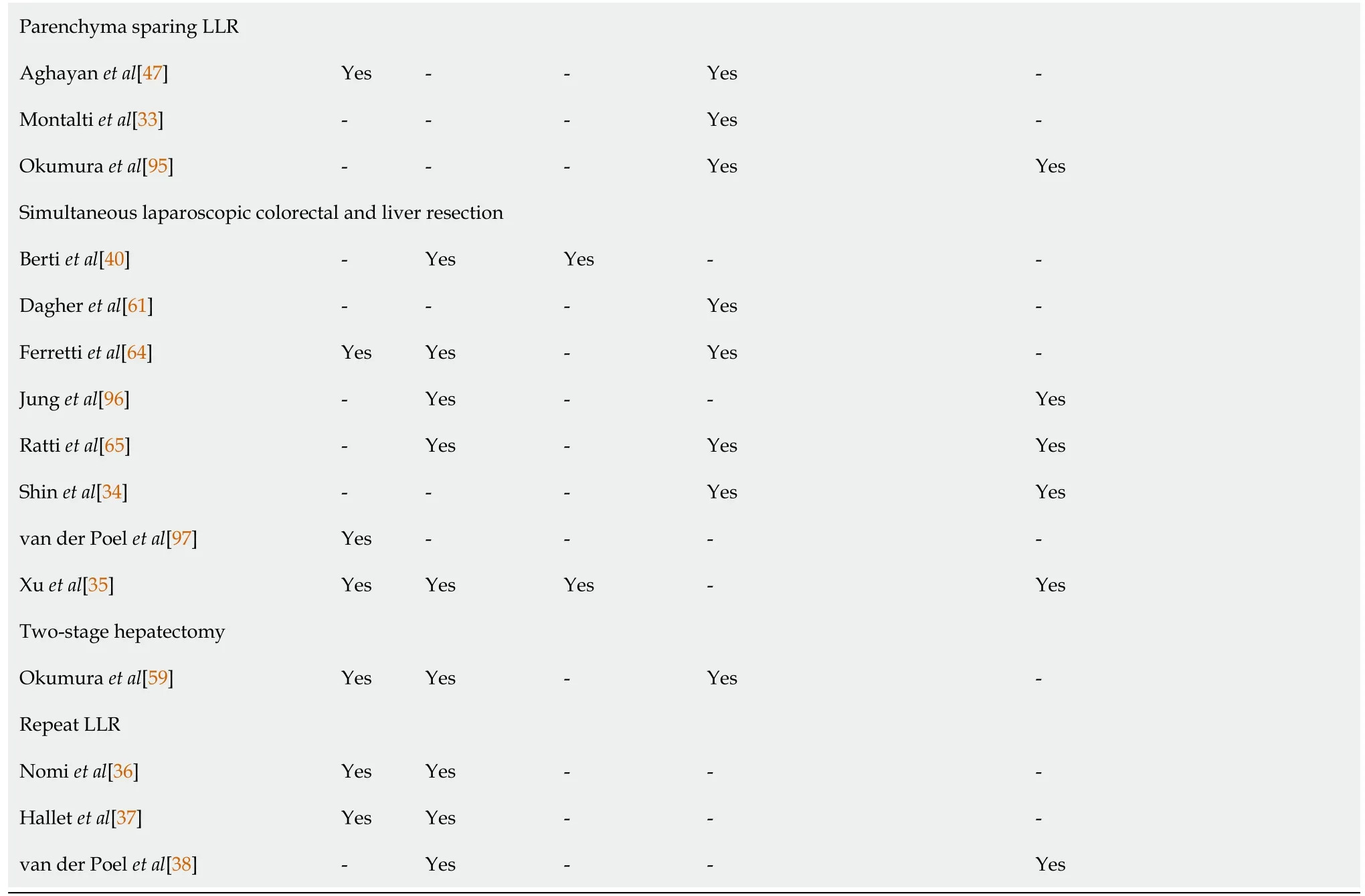
The reported general conclusions per included paper can be found in Table 6.
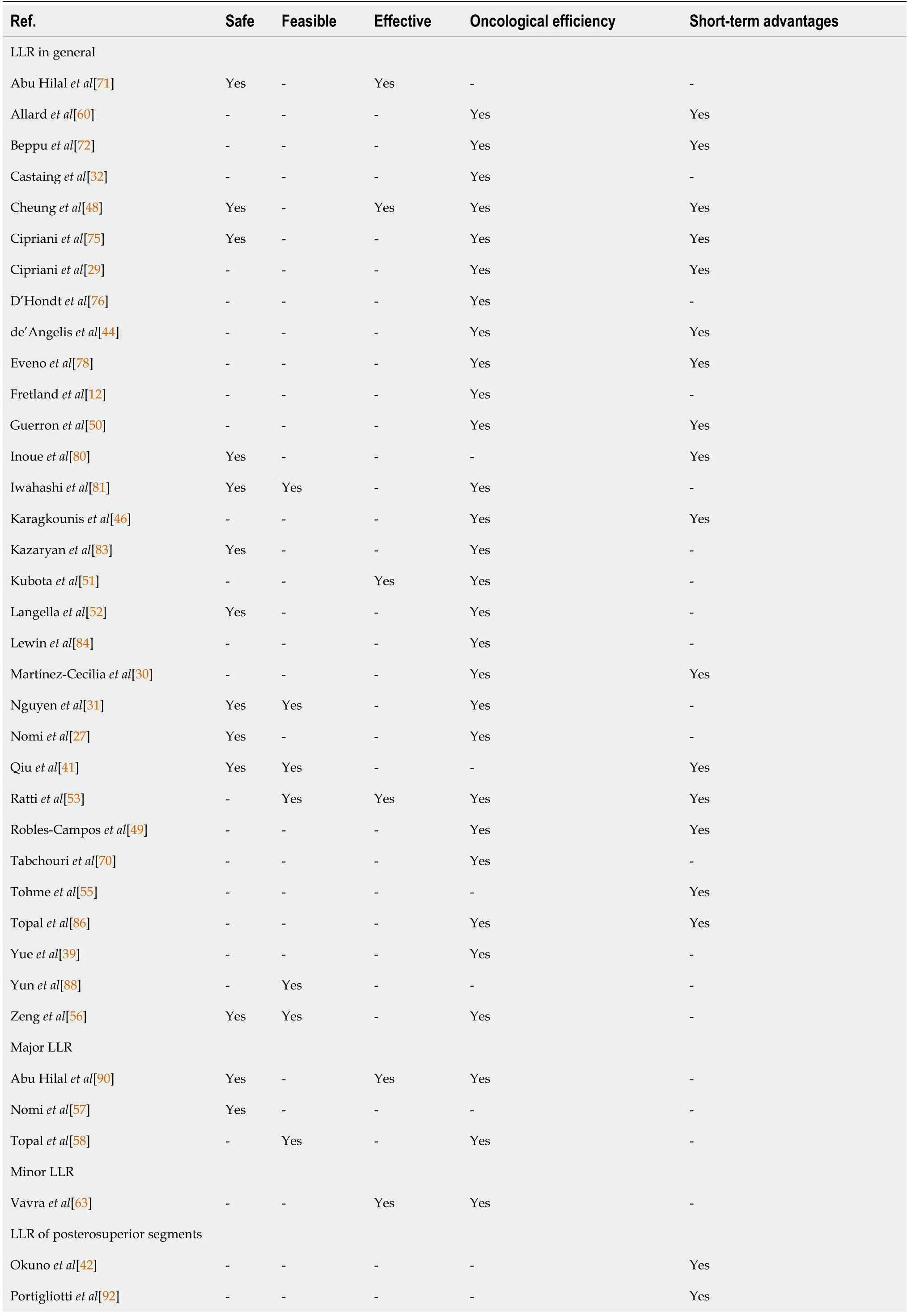
Table 6 General conclusions about laparoscopic liver resections
LLR:Laparoscopic liver resection.
There was not a single paper with a negative conclusion on safety,feasibility,effectiveness or oncological efficiency of LLR for CRLM.It was striking that in 26 out of 31(84%)papers that reported on LLR in general,it was mentioned that the oncological efficiency was certainly not compromised by this approach.Also,in studies that had discussed minor and parenchyma sparing LLR,as well as in most papers concerning major and simultaneous LLR,a similar message regarding oncological efficiency was reported.Safety,feasibility and short-term advantages of LLR for CRLM were reported for LLR in general,LLR of posterosuperior segments,parenchyma sparing,major,simultaneous,two-stage and repeat LLR.The mentioned short-term advantages often included reduced intraoperative blood loss,a lower morbidity rate,less pain,shorter hospital stay and sometimes shorter operative time.
Prognostic factors
An overview of studies that reported on prognostic factors associated with LLR along with their corresponding correlates and associations is shown in Table 7.
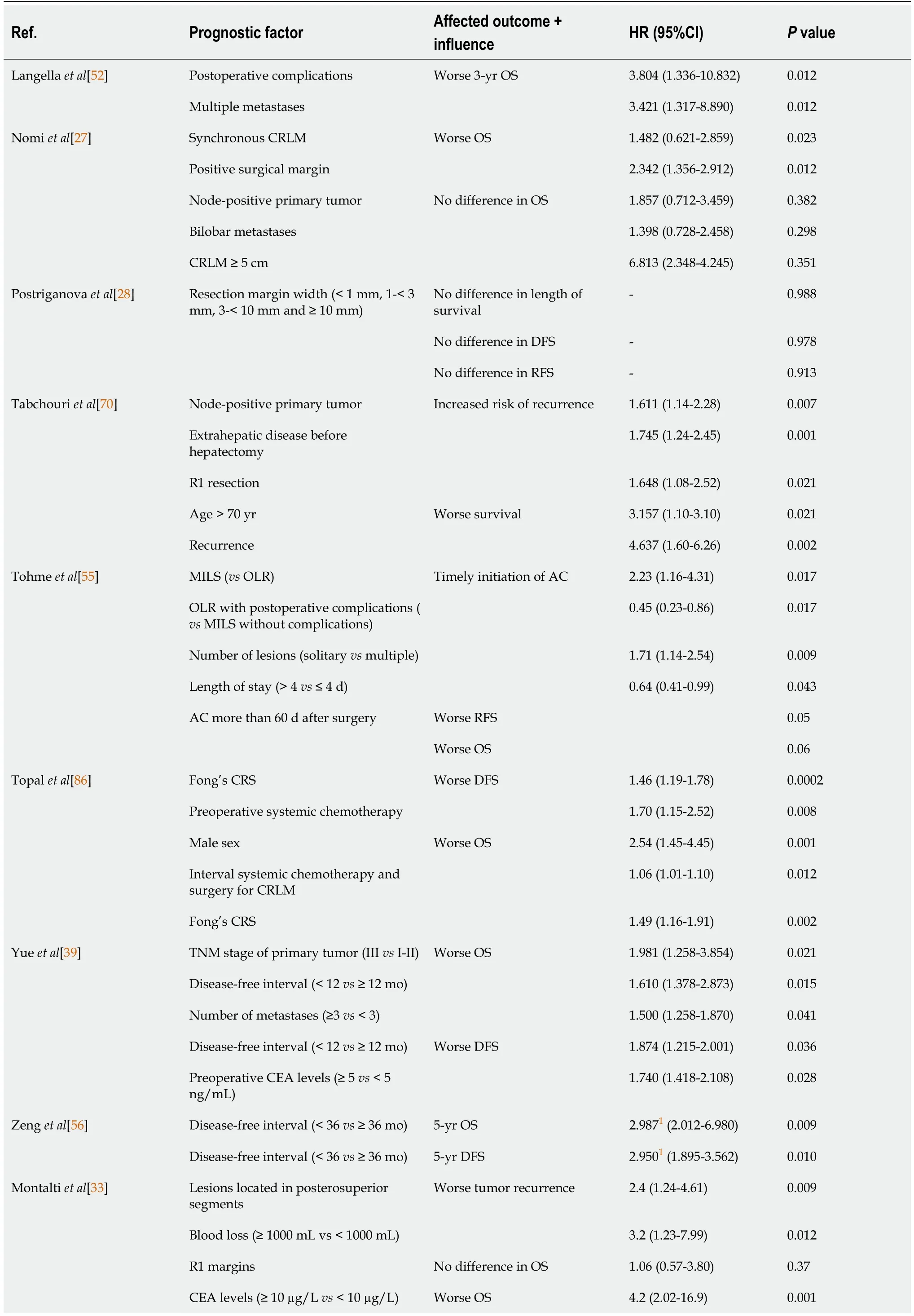
Table 7 Prognostic factors for survivaI in Iiver resection for coIorectaI Iiver metastases
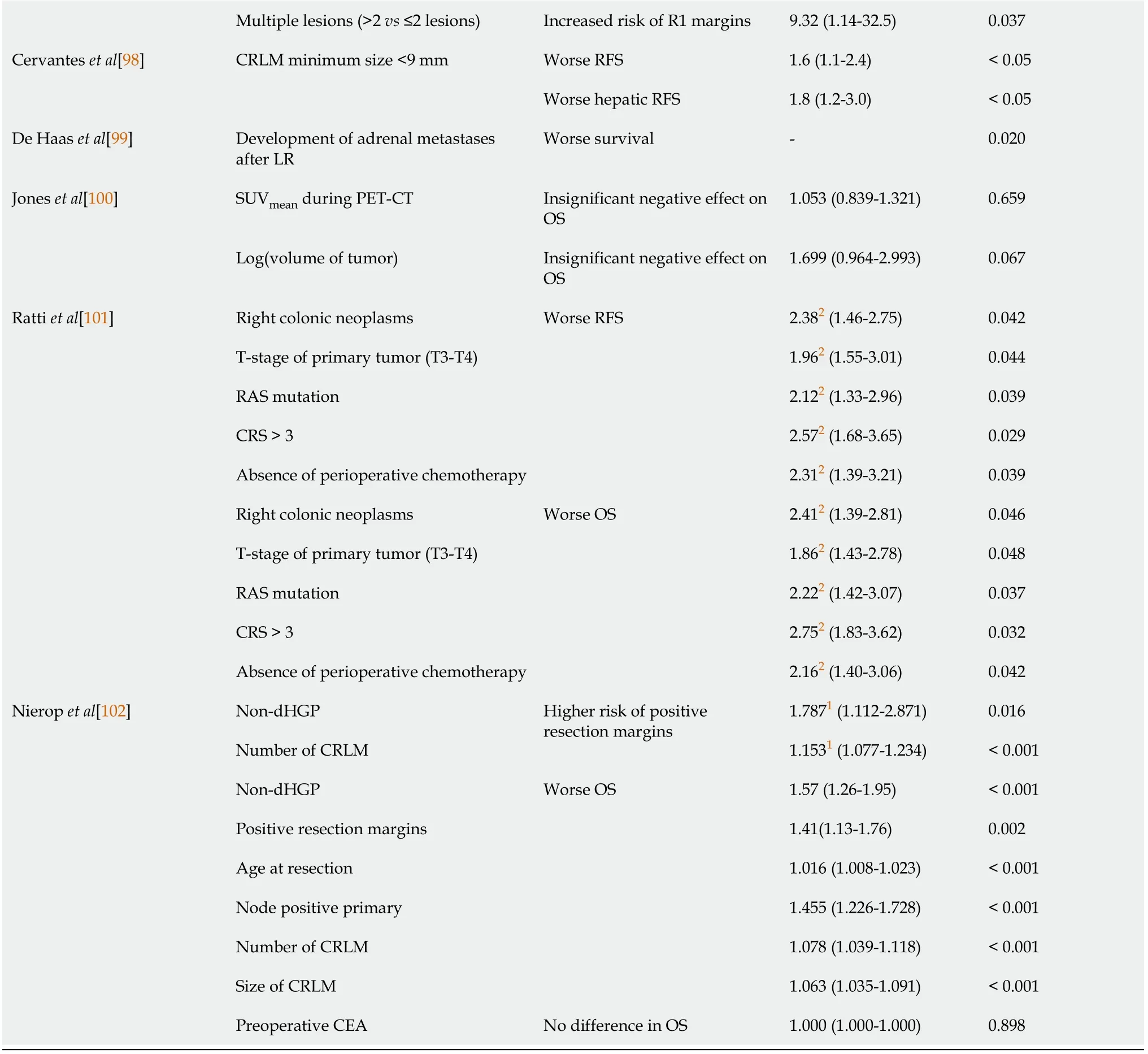
1Odds ratio.2Risk ratio.Numbers are presented as median(range)or mean ± SD unless otherwise indicated.AC:Adjuvant chemotherapy;CEA:Carcinoembryonic antigen;CI:Confidence interval;CRLM:Colorectal liver metastases;CRS:Clinical risk score;DFS:Disease-free survival;HR:Hazard ratio;LR:Liver resection;MILS:Minimally invasive surgery;non-dHGP:Non-desmoplastic growth pattern;OLR:Open liver resection;OS:Overall survival;PET-CT:Positron emission tomography-computed tomography;RFS:Recurrence-free survival;SUV:Standard uptake value.
Fourteen papers were identified which studied prognostic factors specific to LR for CRLM,including 7(50%)exclusively for LLR for CRLM.Papers that focused on LLR specifically identified the following prognostic factors that were associated with a worse OS:Synchronous CRLM,positive surgical margins,age > 70 years,disease recurrence,a disease-free interval < 12 mo,resection of ≥ 3 metastases,carcinoembryonic antigen(CEA)levels > 10 µg/L,right colonic neoplasms,T-stage of the primary CRC ≥ T3,RAS mutation,clinical risk score,and/or absence of perioperative chemotherapy.Node-positive primary CRC,extrahepatic disease,R1 resection,a disease-free interval < 12 mo,CEA levels > 5 µg/L,lesions located in the posterosuperior segments,blood loss > 1000 mL,a CRLM minimum size < 9 mm,right colonic neoplasms,T-stage of the primary CRC ≥ T3 or T4,RAS mutation,clinical risk score and/or absence of perioperative chemotherapy were associated with worse recurrence,DFS or RFS.
DISCUSSION
Previously published systematic reviews and meta-analyses concerning LLR,have frequently discussed a set of heterogeneous groups,that besides CRLM often contain lesions from another histopathological origin,such as hepatocellular carcinoma,noncolorectal liver metastases and other malignancies[66].Furthermore,no systematic review or meta-analysis has focused so far on potential prognostic factors of survival after LLR for CRLM specifically.In light of these facts,our aim was to provide a systematic review that specifically addressed the role of LLR for CRLM along with all relevant outcomes and prognostic factors associated.We therefore reviewed as much of the existing evidence concerning the subject to date with as few limitations as possible to make the overview as comprehensive as possible.
In 2015,Tianet al[8]published a meta-analysis comparing LLRvsOLR for CRLM.Since the majority of the articles included for the quantitative analysis of the metaanalysis were also included in the current systematic review,it is no surprise that our results are in line with those reported by Tianet al[8].In their meta-analysis,it was found that the results of blood loss,perioperative blood transfusion,postoperative morbidity and mortality,hospitalization time,recurrence,DFS,and OS were in favor of LLR.LLR was,however,not associated with any statistical benefit regarding R0 surgical margins or operative time.In 2012,a meta-analysis on survival and prognostic factors associated with LR in metastatic CRC was published by Kanaset al[67].Node positive primary CRC,CEA level,extrahepatic disease,poor tumor grade,positive surgical margins,multiple CRLM,and tumor diameter > 3 cm were identified as prognostic factors for survival,all with a modest,but significant,predictive relationship.Again,these findings are in line with the reported outcomes included in this systematic review.
A major variability of morbidity rates was observed in function of the research papers included in this study.Morbidity following LLR for CRLM is certainly still present and still needs attention.However,major complication rates are low.
Together with the implementation of LLR for CRLM in the early 2000s,concerns arose about the safety a feasibility of this technique to obtain rates of R0 resection margins and subsequent oncological efficiency similar to those reported after OLR for CRLM.The results of this systematic review appear to refute these concerns,since the vast majority of research groups provide a high rate of R0 resection and oncological efficiency in their reports.
Although no clear correlation between the year of publication and study outcome could be noted,some reported results seem to be influenced by long inclusion periods during which data were collected.
The optimal time interval between LR and AC is defined as 8 wk or less[55,68,69].Since the reported median intervals were 42 d(IQR:34-54 d)and 1.4 mo(range:0.9-3.5 mo),LLR seems to provide the ability to initiate AC within a time frame that results in an optimal treatment sequence.
Concerning oncologic outcomes,the reported 1-,3-and 5-year OS and DFS rates are comparable to those achieved in a recent RCT by Robles-Camposet al[49],indicating that LLR for CRLM offers adequate oncological efficiency in most centers today.As reported by Tabchouriet al[70]in 2018,among others,the risk for disease recurrence after LLR for CRLM is high.As illustrated by their results,the probability of recurrence is highest within 24 mo after the initial hepatectomy and diminishes after this point in time.This could underlie the fact that 3-year DFS and RFS rates remain stable with comparable corresponding 5-year DFS and RFS rates.
Some limitations of this systematic review should be taken into account.First,research papers often included several types of LLR besides pure LLR,such as handassisted and robotic LLR.Second,the studies included were performed in both highand low-volume centers.Third,the definitions of postoperative outcomes were not uniform among the included research papers.Fourth,the definition of hospital stay differed among the included papers,with some research groups speaking of an entire hospital stay and others speaking of a postoperative hospital stay.Last,several research groups did not report on the applied definition of major postoperative complications;however,a Clavien-Dindo grade ≥ 3 was most commonly reported.
This review emphasizes the absolute need for future prospective multicenter RCTs.Robust evidence of the short-and long-term benefits of LLR is needed in order to support the increased use of LLR for CRLM compared to OLR reported by many centers.
CONCLUSION
LLR is defined as a safe and feasible surgical technique in the treatment of CRLM and associated with satisfactory oncological efficiency.Many research groups report shortterm advantages compared to OLR,including reduced intraoperative blood loss,a lower morbidity rate,less pain,shorter hospital stay,and a shorter operative time in selected reports.These conclusions are not compromised when taking into account different subtypes of LLR for CRLM,such as major LLR,simultaneous LLR,LLR for posterosuperior segments,TSH,and repeat LLR.Since few reports so far have studied potential prognostic factors affecting long-term outcomes after LLR for CRLM,future research concerning this topic is needed.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Laparoscopic liver resection(LLR)for colorectal liver metastases(CRLM)has become the gold standard in specialized centers and for well-selected patients and procedures.
Research motivation
Little is known concerning patient-related and peri-operative factors that could play a role in survival outcomes associated with LLR for CRLM.
Research objectives
The main objective was to provide an extensive summary of reported outcomes and prognostic factors associated with LLR for CRLM.
Research methods
A systematic review was performed in PubMed,EMBASE,Web of Science and the Cochrane Library,after which thorough screening was performed and data was extracted for qualitative analysis.
Research results
Qualitative analysis of 77 full-text publications shows that LLR for CRLM is safe,feasible and provides oncological efficiency.This is true for more complex laparoscopic procedures as well.Results on prognostic factors affecting long-term outcomes for LLR for CRLM are scarce.
Research conclusions
Besides short-term benefits,satisfactory oncological efficiency is reported for LLR for CRLM.
Research perspectives
Little is still known about prognostic factors affecting long-term outcomes of LLR for CRLM,and future prospective multicenter randomized controlled trials are needed to provide robust evidence.
 World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology2021年7期
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology2021年7期
- World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology的其它文章
- High expression of protein phosphatase 2 regulatory subunit B''alpha predicts poor outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma patients after liver transplantation
- Robotic resection of duodenal gastrointestinal stromal tumour:Preliminary experience from a single centre
- Cryptotanshinone inhibits cytotoxin-associated gene A-associated development of gastric cancer and mucosal erosions
- Clinical management for malignant afferent loop obstruction
- Neoantigen vaccine:An emerging immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma
- Sporadic fundic gland polyps with dysplasia or carcinoma:Clinical and endoscopic characteristics
