EGFR突变阳性的晚期非小细胞肺癌患者奥西替尼联合免疫检查点阻断剂治疗与奥西替尼单药治疗使用疗效和安全性Meta分析
吴柳盛 李小强
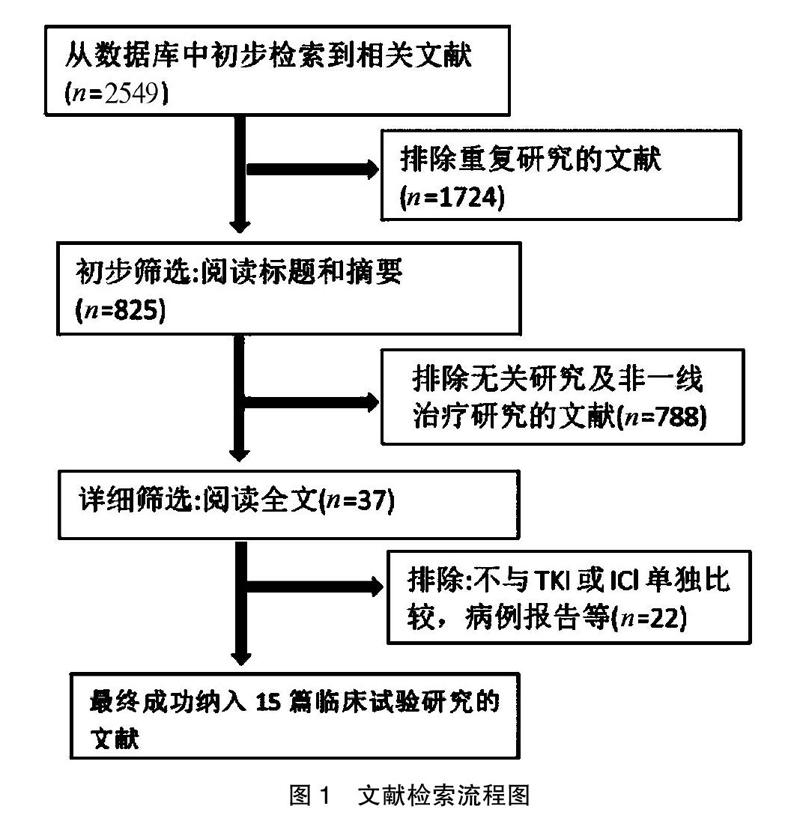
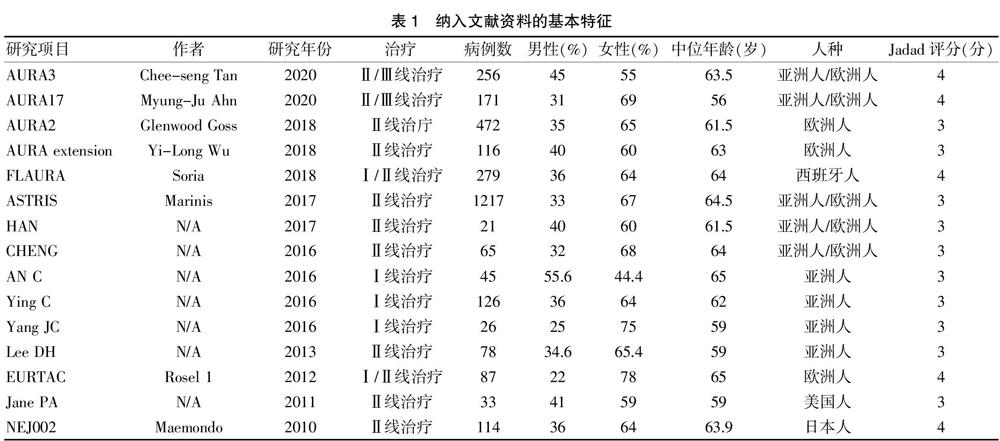
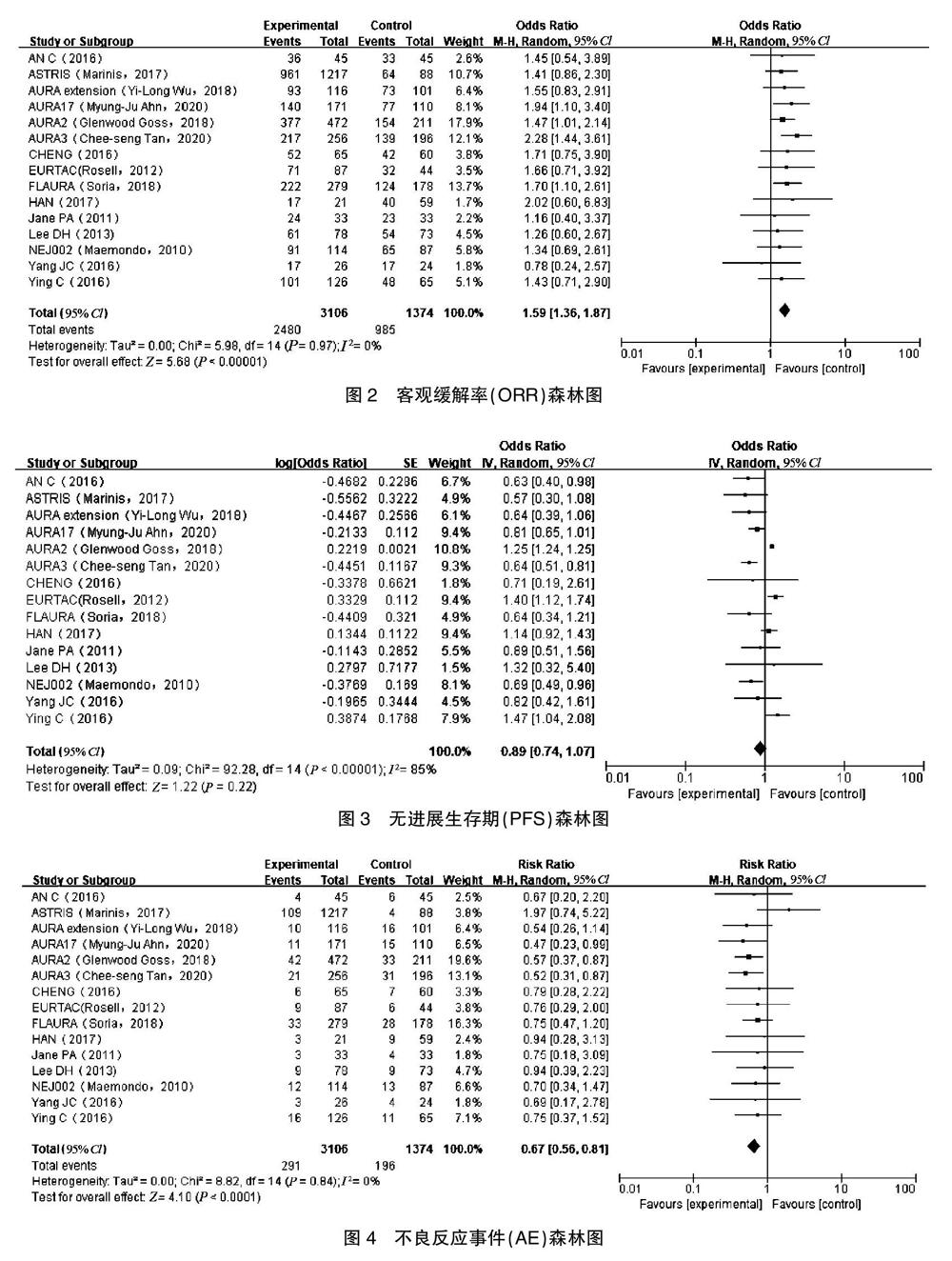
[摘要] 目的 采用Meta分析比較晚期非小细胞肺癌患者奥西替尼联合免疫检查点阻断剂治疗与奥西替尼单药治疗使用的疗效和安全性。 方法 通过电脑手动检索Pubmed、SAGE、Embase、中国知网(CNKI)、Cochrane、UpToDate、JAMA等有关非小细胞肺癌奥西替尼联合免疫检查点阻断治疗与奥西替尼单药治疗的文献资料,检索时间为2000年7月至2020年7月,采用Cochrane循证医学中心的评价原则对文献进行质量评价。 结果 最终纳入15篇符合条件的随机对照试验文献,共计3106例患者。在疗效性方面,奥西替尼结合免疫检查点阻断剂治疗组和奥西替尼治疗组客观缓解率比较,差异无统计学意义(OR:1.59,95%CI:1.36~1.87,P>0.05),无进展生存期差异有统计学意义(OR:0.89, 95%CI:0.74~1.07,P<0.00001);在安全性方面,奥西替尼联合免疫检查点阻断剂治疗组不良反应事件发生率低于奥西替尼治疗组(RR:0.67,95%CI:0.56~0.81,P<0.0001)。 结论 奥西替尼联合免疫检查点阻断剂治疗晚期非小细胞肺癌的疗效明显优于奥西替尼单药治疗,而且不良反应事件发生率亦无明显增加。
[关键词] 非小细胞肺癌;靶向治疗;EGFR-TKI;免疫检查点阻断剂;Meta分析
[中图分类号] R734.2;R730.53;R453 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)06-0028-06
Meta-analysis of the efficacy and medication safety of oxitinib combined with immune checkpoint blockers and oxitinib monotherapy in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer with positive EGFR mutation
WU Liusheng 1, 2, 3 LI Xiaoqiang1, 3
1.Peking University Shenzhen Hospital, Clinical College of Anhui Medical University, Shenzhen 518036, China; 2.Department of Graduate School, Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230032, China; 3.Department of Thoracic Surgery, Peking University Shenzhen Hospital, Shenzhen 518036, China
[Abstract] Objective To apply the meta-analysis and compare the efficacy and medication safety of oxitinib combined with immune checkpoint blockers and oxitinib monotherapy in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Methods The literatures about the combination of oxitinib and immune checkpoint blocking treatment for non-small cell lung cancer in PubMed, SAGE, Embase, Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure(CNKI), Cochrane, UpToDate, JAMA, etc. from July 2000 to July 2020 were manually searched. The evaluation principle of Cochrane Evidence-based Medicine Center was used to evaluate the quality of literatures. Results Finally, 15 eligible randomized controlled trials were included,with a total of 3106 patients. In terms of therapeutic efficacy, there was no significant difference of the objective remission rate between the oxitinib combined with immune checkpoint blocker treatment group and the oxitinib treatment group, difference of the objective remission rate was not statistically significant and the oxltinib treatment group(OR:1.59, 95%CI:1.36-1.87, P>0.05), while difference of the progression-free survival time was statistically significant(OR:0.89, 95%CI:0.74-1.07, P<0.00001). In terms of medication safety, the incidence of adverse reaction events in the oxitinib combined with immune checkpoint blocker treatment group was lower than that in the oxitinib treatment group(RR:0.67, 95%CI: 0.56-0.81, P<0.0001). Conclusion Oxitinib combined with immune checkpoint blockers treatment is superior to oxitinib monotherapy in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer,and the incidence of adverse reaction events has not increased significantly.

