锦紫苏类病毒研究进展
姜冬梅 张志想 李世访
摘要 :锦紫苏又名彩叶草,是一种草本观赏植物,可以被马铃薯纺锤块茎类病毒科锦紫苏类病毒属的类病毒侵染。目前为止,共发现了6种锦紫苏类病毒,分别为锦紫苏类病毒1~锦紫苏类病毒6(CbVd1~CbVd6),它们具有共同的中央保守区(CCR),存在广泛的分子间重组,其嵌合体的发现为研究类病毒RNA重组提供了较为理想的试验材料。本文系统综述了锦紫苏类病毒的分类地位及分子特征、检测方法、与寄主互作等方面的研究进展,并对锦紫苏类病毒研究中的热点和难点问题进行了讨论和展望。
关键词 :类病毒; 锦紫苏; RNA重组; 寄主
中图分类号: S 432.4
文献标识码: A
DOI: 10.16688/j.zwbh.2020325
Research progress in coleus viroids
JIANG Dongmei1, ZHANG Zhixiang2, LI Shifang2*
(1. Beijing Research Center for Agricultural Standards and Testing, Beijing Academy of Agriculture and
Forestry Sciences, Beijing 100097, China; 2. State Key Laboratory for Biology of Plant Diseases and Insect
Pests, Institute of Plant Protection, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing 100193, China)
Abstract :Coleus (Coleus blumei) is an ornamental plant grown worldwide and can be infected by several viroids in the genus Coleviroid, family Pospiviroidae. Up to now, six viroids that infect coleus have been reported: Coleus blumei viroid1 to Coleus blumei viroid6 (CbVd1—CbVd6). They share a common central conserved region (CCR). Moreover, intermolecular recombination is common among them, and existence of chimeras provides an ideal experimental material for the study of RNA recombination in viroids. In this paper, the taxonomy, molecular characteristics, detection methods and the interactions between hosts and coleus viroids were reviewed. Furthermore, the focal and difficult problems in coleus viroids were prospected.
Key words :viroid; coleus; RNA recombination; host
類病毒(viroid)是一类单链共价闭合环状的RNA分子,无蛋白外壳包裹,由246~435个核苷酸(nucleotide, nt)组成,是目前已知的最小植物病原物,可侵染许多重要的果树、观赏植物以及蔬菜等[1]。锦紫苏又名彩叶草,是一种草本观赏植物,起源于印度尼西亚。目前为止,共发现了6种锦紫苏类病毒,分别命名为锦紫苏类病毒1~锦紫苏类病毒6(Coleus blumei viroid1~Coleus blumei viroid6, CbVd1~CbVd6)[1]。
1 分类及分子特征
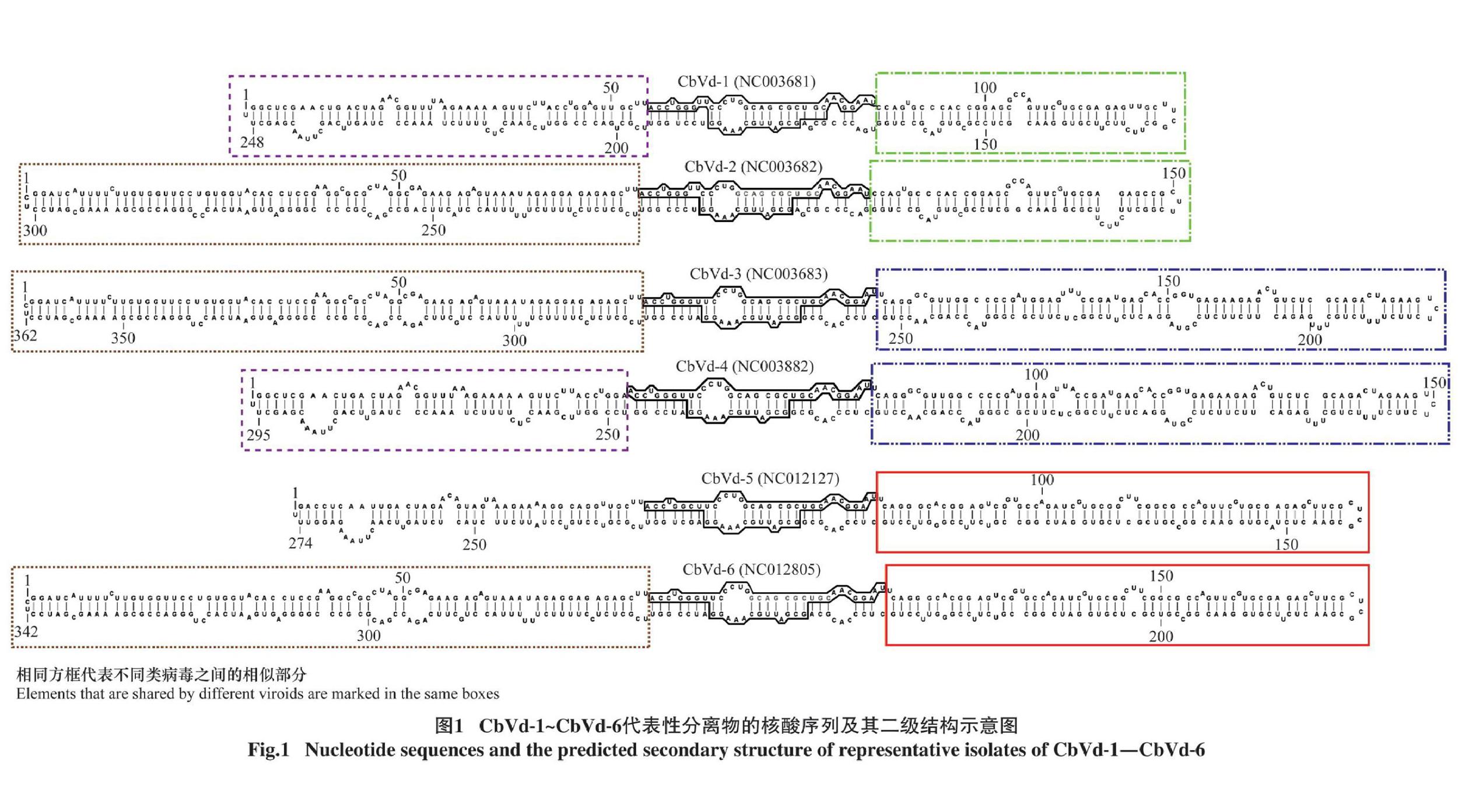
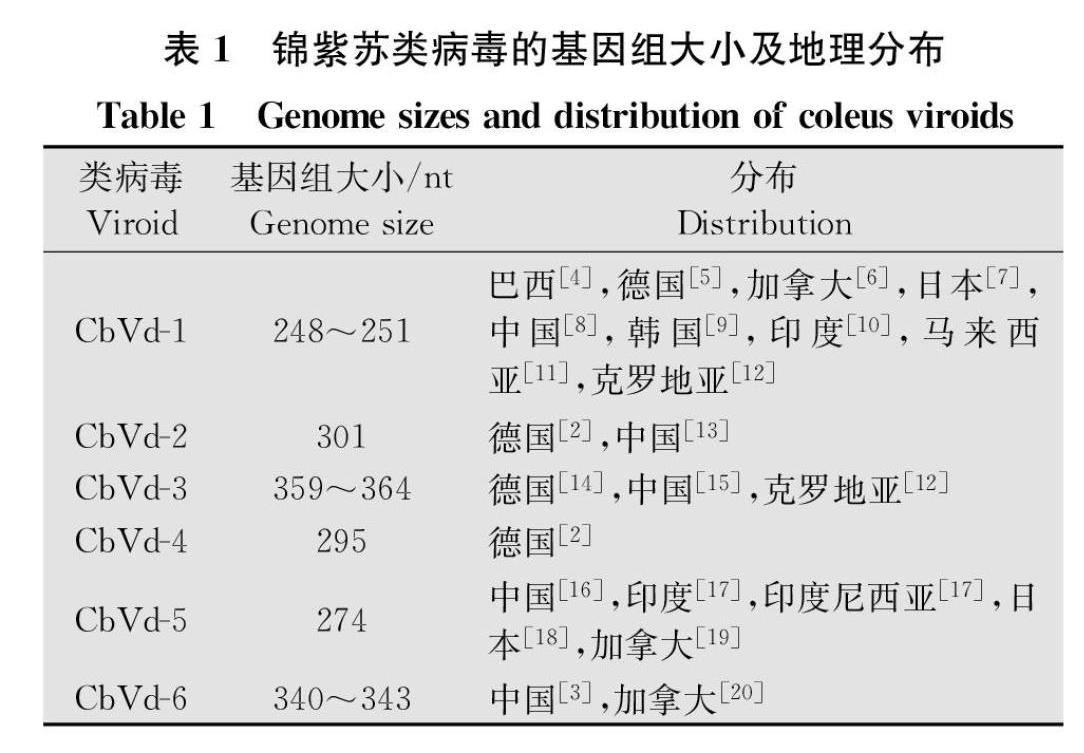
6种锦紫苏类病毒均属于马铃薯纺锤形块茎类病毒科Pospiviroidae锦紫苏类病毒属Coleviroid,其基因组大小各不相同,在248~364 nt之间[1](表1),能折叠成由一系列短的茎环组成的棒状二级结构(图1),具有相同的中央保守区(central conserved region, CCR)。如图1所示,锦紫苏类病毒间存在明显的重组现象,二级结构中,CbVd1的左半部分与CbVd4的左半部分相同;CbVd2的左半部分与CbVd3、CbVd6的左半部分相同;而CbVd1与CbVd2,CbVd3与CbVd4,CbVd5与CbVd6的右半部分分别相同。因此,从二级结构位置上而言,CbVd2与CbVd4是左右部分相反的两个嵌合体多个锦紫苏类病毒嵌合体的发现为类病毒分子间重组提供了直接确凿的分子遗传学证据[23]。
2 发现及分布
1981年,Fonseca等从巴西的市售黄色锦紫苏中发现了CbVd1[4],这是第一个被发现的锦紫苏类病毒;1990年,Spieker等首次报道了CbVd1的全序列[5]。随后,世界上很多国家包括加拿大、日本、中国、韩国、印度、马来西亚、克罗地亚等,陆续对CbVd1在该国的首次发现进行了报道[612]。1996年,德国科学家首次报道了CbVd2[2],它是第一个被发现的自然界中存在的类病毒嵌合体,除德国之外,中国也报道了此类病毒[13]。1991年,德国科学家首次报道了CbVd3[14],中国[15]和克罗地亚[12]也相继报道了此类病毒。CbVd4是1996年德国科学家人工构建的已被证明具有生物学活性的嵌合体,目前未在自然寄主中发现[2]。CbVd5[16]和CbVd6[3]是中国科学家报道的两个类病毒新种,自2009年首次报道以来,印度和印度尼西亚的锦紫苏样品中也发现了CbVd5[17];随后,日本的锦紫苏样品中也发现了CbVd5[18];2018年,加拿大学者从市售锦紫苏样品中检测到了CbVd5和CbVd6,并进一步验证了CbVd1普遍存在于加拿大市售的不同品种锦紫苏中[1920]。由此可见,目前除CbVd4未在自然寄主中发现以外,其他5种锦紫苏类病毒均存在于自然寄主锦紫苏中,且分布越来越广泛(表1)。
[2] SPIEKER R L. In vitrogenerated ‘inverse chimeric Coleus blumei viroids evolve in vivo into infectious RNA replicons [J]. Journal of General Virology, 1996, 77(11): 28392846.
[3] HOU Wanying, LI Shifang, WU Zujian, et al. Coleus blumei viroid 6: a new tentative member of the genus Coleviroid derived from natural genome shuffling [J]. Archives of Virology, 2009, 154(6): 993997.
[4] FONSECA M E N. A viroid from Coleus species in Brazil [J]. Plant Disease, 1990, 74(1): 80.
[5] SPIEKER R L, HAAS B, CHARNG Y C, et al. Primary and secondary structure of a new viroid “species” (CbVd1) present in the Coleus blumei cultivar ‘Bienvenue [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1990, 18(13): 3998.
[6] SINGH R P, BOUCHER A. High incidence of transmission and occurrence of viroid in commercial seeds of Coleus in Canada [J]. Plant Disease, 1991, 75(2): 184187.
[7] ISHIGURO A, SANO T, HARADA Y. Nucleotide sequence and host range of a coleus viroid isolated from coleus (Coleus blumei Benth) in Japan [J]. Annals of the Phytopathological Society of Japan, 1996, 62(1): 8486.
[8] LI Shifang, SU Qianfu, GUO Rui, et al. First report of Coleus blumei viroid from coleus in China [J]. Plant Pathology, 2006, 55: 565.
[9] CHUNG B M, CHOI G S. Incidence of Coleus blumei viroid 1 in seeds of commercial coleus in Korea [J]. The Plant Pathology Journal, 2008, 24(3): 305308.
[10]ADKARPURUSHOTHAMA C R. First report of Coleus blumei viroid infecting coleus in India [J]. Plant Disease, 2013, 97(1): 149.
[11]ROSLAN N N C, THANARAJOO S S, KADIR J, et al. First report of Coleus blumei viroid in Malaysia [J]. Journal of Plant Pathology, 2017, 99(3): 800.
[12]KORIC'D, CˇERNI S, JEZERNIK K, et al. Molecular characterization of Coleus blumei viroids 1 and 3 in Plectranthus scutellarioides in Croatia [J]. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 2019, 155: 731742.
[13]FU Fanghong, LI Shifang, JIANG Dongmei, et al. First report of Coleus blumei viroid 2 from commercial coleus in China [J]. Plant Disease, 2011, 95(4): 494.
[14]SPIEKER R L, MARINKOVIC S, SANGER H L. A new sequence variant of Coleus blumei viroid 3 from the Coleus blumei cultivar ‘Fairway Ruby [J]. Archives of Virology, 1996, 141(8): 13771386.
[15]JIANG Dongmei, LI Shifang, FU Fanghong, et al. First reported occurrence of Coleus blumei viroid 3 in China [J]. Journal of Plant Pathology, 2011, 93(4): 82.
[16]HOU Wanying, SANO T, LI Shifang, et al. Identification and characterization of a new Coleviroid (CbVd5) [J]. Archives of Virology, 2009, 154: 315320.
[17]JIANG Dongmei, LI Shifang, FU Fanghong, et al. First report of Coleus blumei viroid 5 from Coleus blumei in India and Indonesia [J]. Plant Disease, 2013, 97(4): 561.
[18]TSUSHIMA T, SANO T. First report of Coleus blumei viroid 5 infection in vegetatively propagated clonal coleus cv. ‘Aurora black cherry in Japan [J]. New Disease Reports, 2015, 32: 7.
[19]SMITH R L, LAWRENCE J, SHUKLA M, et al. First report of Coleus blumei viroid 5 and molecular confirmation of Coleus blumei viroid 1 in commercial Coleus blumei in Canada [J]. Plant Disease, 2018, 102(9): 1862.
[20]SMITH R L, LAWRENCE J, SHUKLA M, et al. Occurrence of Coleus blumei viroid 6 in commercial Coleus blumei in CanadaThe first report outside of China [J]. Plant Disease, 2019, 103: 782.
[21]苏前富, 郭瑞, 成卓敏, 等. 中国锦紫苏类病毒的检测及其分子生物学特征研究[J].植物病理学报, 2006, 36(3): 226231.
[22]ZHANG Yongjiang, YIN Jun, JIANG Dongmei, et al. Universal oligonucleotide microarray with a minimal number of probes for the detection and identification of viroids at the genus level [J/OL]. PLoS ONE, 2013, 8(5): e64474.DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064474.
[23]JIANG Dongmei, WANG Meng, ZHANG Zhixiang, et al. Highthroughput sequencing analysis of small RNAs derived from Coleus blumei viroids [J/OL]. Viruses, 2019, 11(7): 619.DOI:10.3390/v11070619.
[24]JIANG Dongmei, WU Zujian, XIE Lianhui, et al. Sapdirect RTPCR for the rapid detection of Coleus blumei viroids of the genus Coleviroid from natural host plants [J]. Journal of Virological Methods, 2011, 174(12): 123127.
[25]JIANG Dongmei, HOU Wanying, SANO T, et al. Rapid detection and identification of viroids in the genus Coleviroid using a universal probe [J]. Journal of Virological Methods, 2013, 187(2): 321326.
[26]SPIEKER R L. A new sequence variant of Coleus blumei viroid 1 from the Coleus blumei cultivar “Rainbow Gold” [J]. Archives of Virology, 1996, 141(11): 21532161.
[27]JIANG Dongmei, GAO Rui, QIN Lü, et al. Infectious cDNA clones of four viroids in Coleus blumei and molecular characterization of their progeny [J]. Virus Research, 2014, 180: 97101.
[28]TSUSHIMA T, SANO T. A pointmutation of Coleus blumei viroid 1 switches the potential to transmit through seed [J]. Journal of General Virology, 2018, 99(3): 393401.
(責任编辑:田 喆)

