Screening of Slow Release Solvents for Plant Volatiles
Changgeng Dai,Hongbo Li,Qi Wei,Yang Hu*
1.Institute of Plant Protection,Guizhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Guiyang 550006,China;2.State Key Laboratory of Rice Biology,China National Rice Research Institute,Hangzhou 310006,China
Abstract[Objective]The paper was to study the slow release effects of eight common kinds of slow release solvents on n-hexane,and to provide a reference for the construction of slow release system of attractants or repellents synthesized by plant volatiles.[Method]The effect of slow release solvents on volatile quantity and release rate of n-hexane was compared by weight loss method.[Result]Under indoor natural conditions[(22±2)℃,RH 50%±10%],the slow release effect of lubricating oil on n-hexane was the best,followed by liquid paraffin.The best ratio of slow release solvent(lubricating oil and liquid paraffin)and n-hexane was 5∶1 and the best mixing time was 3 h,which improved the slow release effects of n-hexane by 6.3 and 4.7 times,and prolonged the half-life of n-hexane by 1.3 and 1.0 times,respectively.Slow release solvents mainly affected the post-half-life period of n-hexane,and the release rates of n-hexane mixed with lubricating oil and liquid paraffin were decreased by 10.4 and 7.7 times,respectively.During the half-life period,the release rates of n-hexane were decreased by 1.3 and 1.0 times,respectively.[Conclusion]Two kinds of slow release solvents with good slow release effect on volatile n-hexane are screened out,and the proportion and mixing time of slow release solvent and volatile are determined,which will provide technical support for the construction of plant volatile slow release system.
Keywords Plant volatiles;Slow release solvent;n-hexane;Lubricating oil;Liquid paraffin
Plant volatiles can be used to synthesize attractants or repellents to regulate pest behavior and control their damage,but the volatility of key active ingredients is too strong,leading to difficulties in practical application[1].The slow release system is mainly constructed by carrier materials(rubber materials,polyethylene materials,microcapsules,etc.)and slow release solvents(liquid paraffin,etc.)to delay the volatilization of key active ingredients.Meanwhile,slow release system materials can not react or isomerize with active substances[2].
At present,there have been many reports on the research of carrier materials.For example,with five materials such as starch sodium octenylsuccinate as wall materials,Yang et al.[3]prepared eucalyptus volatile microcapsule emulsion by adding certain amount of liquid paraffin for secondary homogenization,and 50 μL of sample could sustainably volatilize for more than 30 d at 30-50℃.Bian et al.[4]delayed the volatilization of tea plant volatile trans-2-hexene-1-aluminum and cis-3-hexene-1-ol(5 μL)for 24 d by using the sol-gel carrier material synthesized by tetramethyl orthosilicate and trimethylmethoxysilane.However,less efforts have been dedicated to slow release solvents.For example,Pan et al.[5]used liquid paraffin as the slow release solvent and found that the slow release effect was the best when the ratio of liquid paraffin to volatile methyl disulfide was 10∶1.Pan et al.[6]used liquid paraffin as a slow release solvent and mixed with six kinds of tea shoot volatiles,such as nerol,at a ratio of 1∶10,which prolonged the half-life of volatiles by 0.7 d.Currently,a large number of studies have used liquid paraffins as the slow release solvent,but have not screened other types and proportions.
Therefore,with n-hexane,a volatile dilute solvent,as the object,suitable slow release agents and their mixing ratio were selected from eight common inert liquid substances(generally do not react with organic solvents),in order to provide a reference for the construction of slow release system for the synthesis of attractants or repellents from plant volatiles.
1 Materials and Methods
1.1 Materials The volatile n-hexane was produced by Tianjin Fuyu Fine Chemical Co.,Ltd.Eight kinds of slow release solvents were liquid paraffin(Chengdu Jinshan Chemical Agent Co.,Ltd.),lubricating oil(Shell Zhuhai Lubricating Oil Co.,Ltd.),sesame oil(Shanghai Kerry Food Industry Co.,Ltd.),Tween 80(Amresco),honey of various flowers(Nanjing Angel Bee Industry Co.,Ltd.),corn oil(Shandong Luhua Group Co.,Ltd.),rapeseed oil(Shandong Luhua Group Co.,Ltd.),and walnut oil(Dali Dangbi Walnut Co.,Ltd.).The 2 mL glass bottle(diameter 1cm,height 3.2 cm)was used as the container.Electronic balance(FA2004,accuracy 0.1 mg)was manufactured by Shanghai Shunyu Hengping Scientific Instrument Co.,Ltd.
The above materials were purchased from reagent companies,supermarkets or Taobao.
1.2 Methods Weight loss method was used to compare the slow release effects of various slow release agents on n-hexane[7].The test was carried out under indoor natural conditions[temperature(22±2)℃,humidity 50%±10%].
The slow release effects of eight sol-vents were first compared.The slow release solvents were mixed with n-hexane at the ratio of 1∶1(mass ratio).That is,330 mg of each slow release solvent was sucked into a 2 mL glass bottle by a disposable pipette,and those without slow release solvent were set as control.Afterwards,530 μL (about 330 mg)of n-hexane was added by a pipettor.Meantime,a group of slow release solvent(without n-hexane)was set as parallel reference(to correct the mass change of slow release solvent).The liquids were weighed before and after adding samples.The sample bottles were placed indoor at(21±2)℃and weighed every 1 h.Each group was repeated four times.
Subsequently,the optimal mixing ratio of slow release solvents and n-hexane was studied.The two slow release solvents with the best slow release effect in the first round were selected.The slow release solvents and n-hexane were mixed at the ratios of 1 ∶1,0.2 ∶1,5 ∶1,0.1 ∶1,and 10 ∶1(mass ratio,n-hexane about 80 mg),respectively,and the test method was the same as described in the first step.
Finally,the optimal mixing time(sealing)of slow release solvents and n-hexane was studied.The optimal ratio in the second round was selected,and slow release solvents were mixed with n-hexane and sealed for 0,1,3 and 5 h,respectively.The test method was the same as described in the second step.
The calculation formulae are as follows.
Volatilization rate of n-hexane CK(%)=(Initial weight of n-hexane-Immediate residual weight of n-hexane)/Initial weight of n-hexane×100
Correction value of slow release solvents=Immediate weight of slow release solvents-Initial weight of slow release solvents
Volatilization rate of slow release treatment(%)=[(Initial weight of n-hexane-Immediate residual weight of n-hexane)-Correct value of slow release solvents]/initial weight of n-hexane×100
Residue(%)=1-Volatilization rate
Volatilization rate (%/h)=(Residual rate in the first 1 h-Immediate residual rate)/Time 1 h
One point was taken respectively when the volatilization rate was about 50%,and a regression equation was established to calculate the time(half-life)for 50% n-hexane volatilization.
Slow release effect of volatilization time=Duration of slow release treatment/Duration of CK-1
Slow release effect of volatilization rate=(Volatilization rate of CK/Duration of CK)/(Volatilization rate of slow-Release treatment/Duration of slow release treatment)-1
1.3 Data analysis The slow release effects of slow release solvents on n-hexane were calculated and plotted using Microsoft Excel 2010.
2 Results and Analysis
2.1 Slow release effect of eight kinds of slow release solvents on n-hexane Tween 80 and honey of various flowers had no slow release effect,while other slow release solvents had certain slow release effect(Fig.1).The slow release effect of lubricating oil was the best,and the overall slow release effect was increased by 0.9 times;followed by liquid paraffin,the overall slow release effect was increased by 0.6 times.However,lubricating oil and liquid paraffin had no significant effect on the half-life of n-hexane,and the half-life periods were prolonged by 0.1 and 0.0 times,respectively.
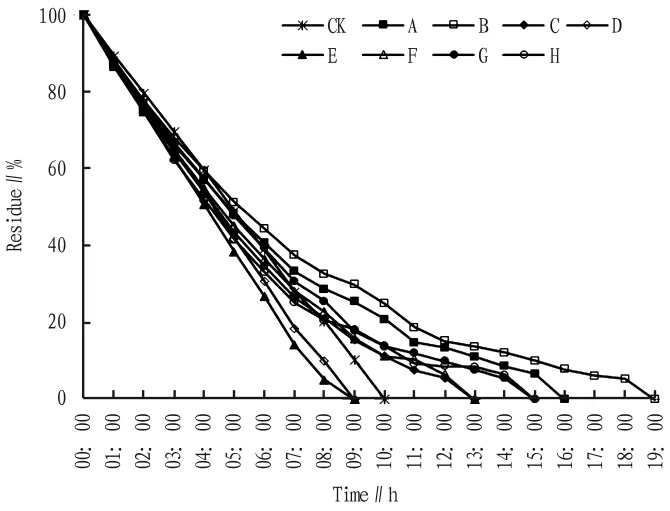
Fig.1 Effects of eight kinds of slow release agents on n-hexane residues
Slow release solvents had no significant impacts on the release rate of n-hexane during the half-life period,but mainly affected the slow release rate during posthalf-life period(Fig.2).During the half-life period,the release rates of n-hexane mixed with lubricating oil and liquid paraffin were decreased by 0.1 and 0.0 times,respectively.During post-half-life period,the release rate of n-hexane mixed with lubricating oil and liquid paraffin were decreased by 1.8 and 1.3 times,respectively.
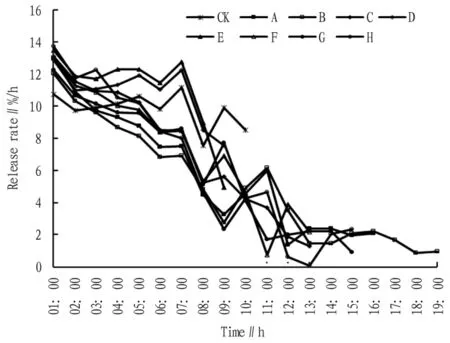
Fig.2 Effects of eight kinds of slow release agents on release dynamics of n-hexane
2.2 Optimal mixing ratio of slow release solvent and n-hexane The two slow release solvents with good effects(lubricating oil and liquid paraffin)were mixed with n-hexane at five ratios,and the results showed that the slow release effect was good when the ratios were 1∶1,5∶1 and 10∶1,while the slow release effect was poor when the ratios were 0.2∶1 and 0.1∶1(Fig.3).When the ratio of two slow release agents to n-hexane was 5∶1,the effects were the best,and the overall slow release effects of lubricating oil and liquid paraffin were increased by 4.9 times and 2.8 times,respectively.However,it had no significant effect on the half-life of n-hexane,and the half-life periods were prolonged by 0.6 and 0.3 times,respectively.
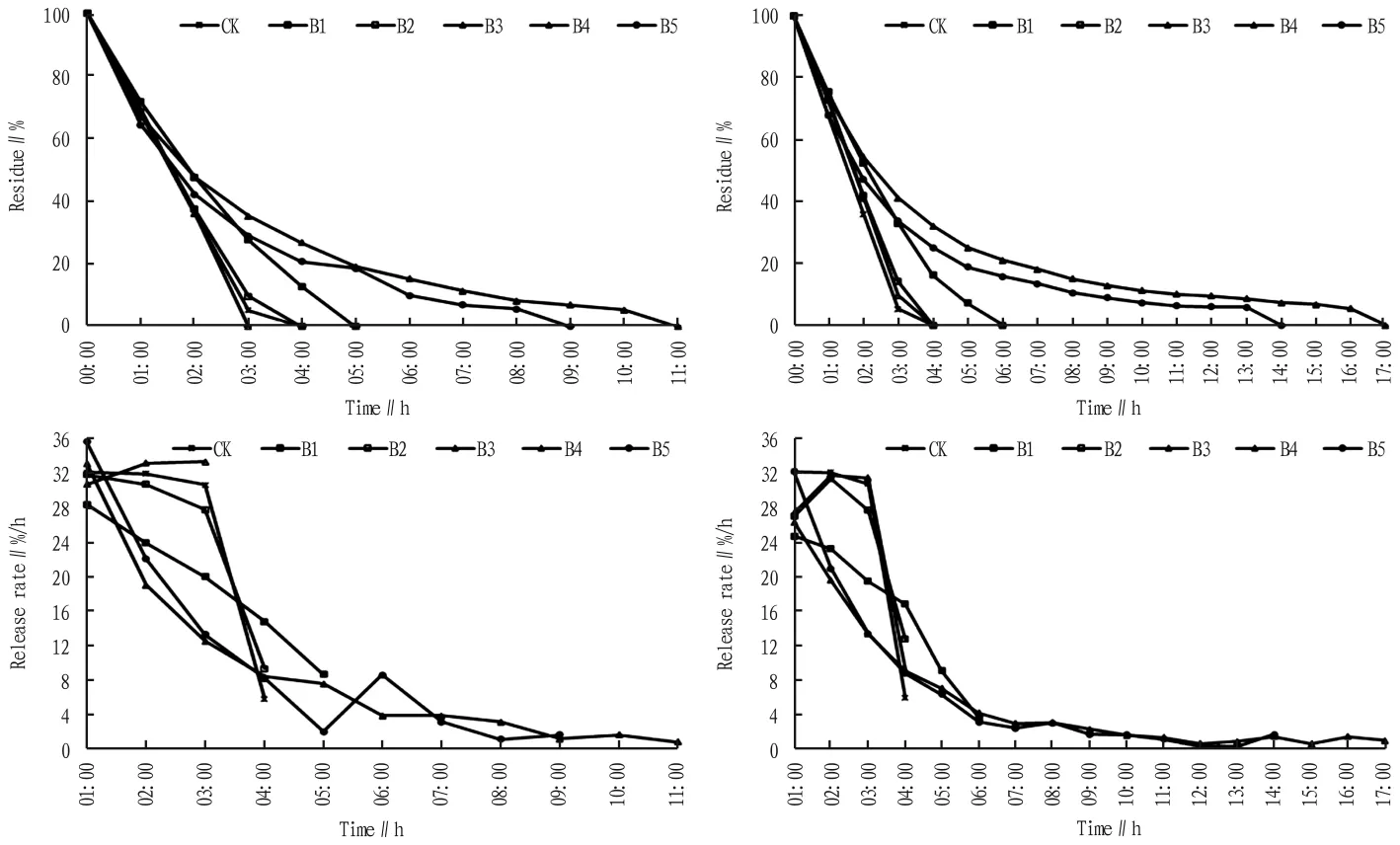
Fig.3 Slow release effect of the proportion of slow release agent on n-hexane
Slow release solvents had no significant effect on the release rate of n-hexane during the half-life period,but mainly affected the slow release rate during the post-half-life period (Fig.3).During the half-life period,the release rate of n-hexane mixed with lubricating oil and liquid paraffin were only decreased by 0.6 and 0.3 times,respectively.During the posthalf-life period,the release rate of n-hexane mixed with lubricating oil and liquid paraffin were decreased by 8.5 and 4.9 times,respectively.
2.3 The optimal mixing time of slow release solvents and n-hexane Both kinds of slow release solvents had good slow release effect when mixed with n-hexane for 0-5 h(Fig.4).The best slow release effect was obtained when the slow release agent was mixed with n-hexane for 3 h,and the overall slow release effects of lubricating oil and liquid paraffin were increased by 6.3 times and 4.7 times,respectively.The half-life periods of n-hexane were prolonged by 1.3 and 1.0 times,respectively.
Slow release agents had no significant effect on the release rate of n-hexane during the half-life period,but mainly affected the slow release rate during the post-half-life period (Fig.4).During the half-life period,the release rate of n-hexane mixed with lubricating oil and liquid paraffin were decreased by 1.3 times and 1.0 times,respectively.During the posthalf-life period,the release rate of n-hexane mixed with lubricating oil and liquid paraffin were decreased by 10.4 and 7.7 times,respectively.
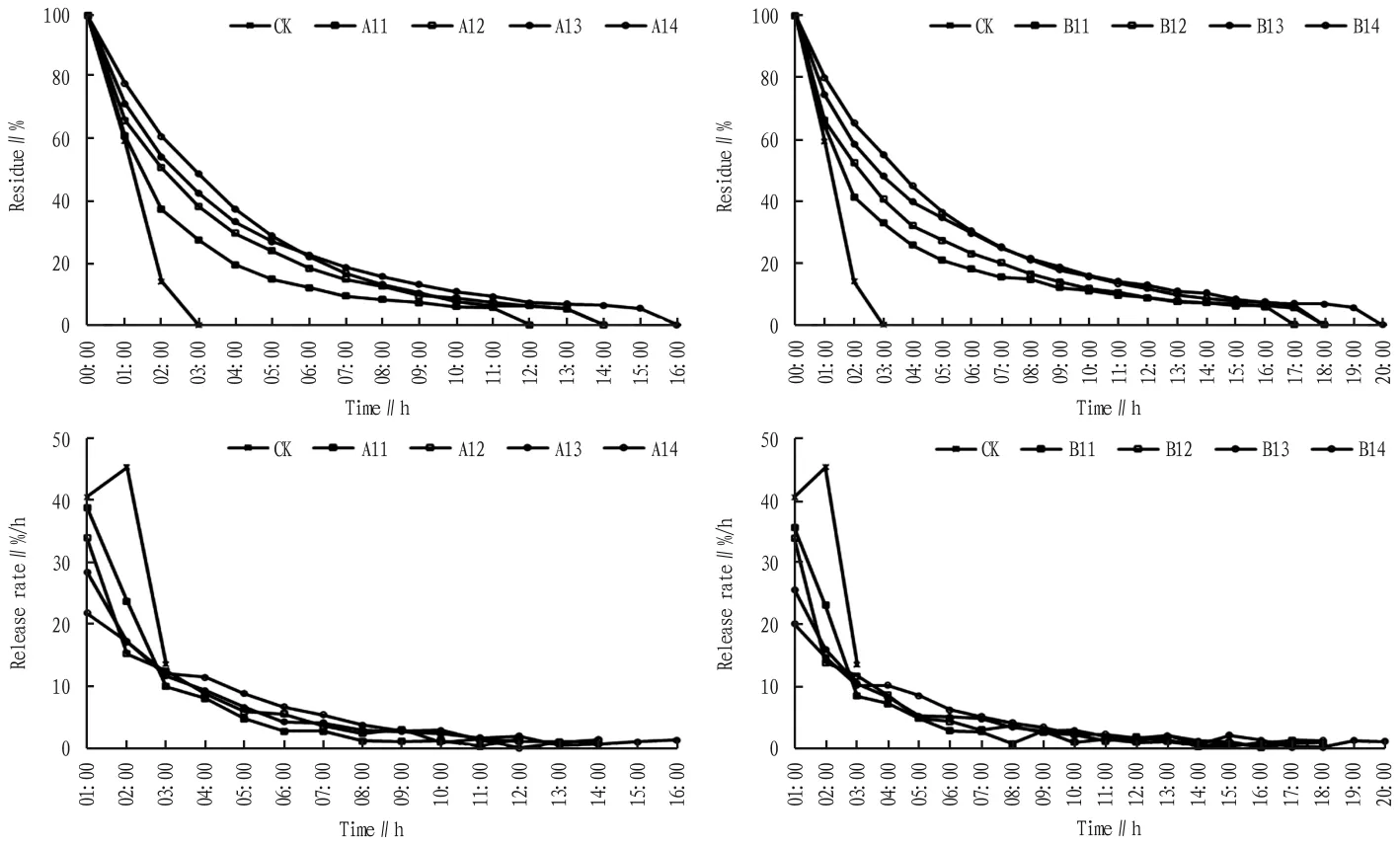
Fig.4 Slow release effect of mixing time of slow release solvents on n-hexane
3 Discussion
In this study,weight loss method was used to study the slow release effect of volatile n-hexane.The method is susceptible to environmental influence and has poor accuracy,but it is simple and low cost,and is suitable for the preliminary study on the construction of slow release system.For example,the slow release effects of a large number of slow release solvents on volatiles were screened and compared in the preliminary test[8].For more accurate detection of volatile release dynamics,gas chromatography or gas chro-matography-mass spectrometry can be considered for quantitative analysis[9].Our research results demonstrated that Tween 80 and honey of various flowers had no slow release effect,while other slow release solvents had certain slow release effect,among which lubricating oil and liquid paraffin had the best slow release effect on n-hexane.Lubricating oil and liquid paraffin are non-polar substances and inert liquid phases[10-11],which are similar substances of n-hexane that are more likely to be dissolved by each other and do not produce chemical reaction,with good relative dispersion,thus delaying the volatilization of n-hexane. However,Tween 80 and honey of various flowers did not dissolve with volatile n-hexane,but accelerated the volatilization of n-hexane.
In addition to no chemical reaction or isomerization with active volatile substances,whether slow release solvents produce behavioral reactions such as attraction or avoidance to target insects must be cleared[12-13].The behavioral response of male Chilo suppressalis to lubricating oil was tested using Y-type olfactometry,and no significant avoidance or attraction effects(unpublished data)had been found.The behavioral response of other insects still needs to be studied.Therefore,several slow release agents could be selected by weight loss method,and their behavioral responses to target insects could be further tested,so as to select the most suitable slow release solvents.
4 Conclusions
The results showed that lubricating oil had the best slow release effect on volatile n-hexane;followed by liquid paraffin.The optimal ratio of slow release agent to n-hexane was 5∶1,and the mixing time was 3 h.The slow release effects of n-hexane were increased by 6.3 and 4.7 times,and the half-life periods of n-hexane were prolonged by 1.3 and 1.0 times,respectively.
- 植物病虫害研究(英文版)的其它文章
- Development of"Multi-Resistance Rice"by Pyramiding of Insect(Cry1C)and Blast Resistance(Pi1 and Pi2)Genes
- Effects of Guangxi Hepu Pearl Hydrolysate on Proliferation Activity and Apoptosis of Human Hepatic Stellate Cells
- Synergistic Effect of Adjuvant Green Orange Peel Oil on Different Herbicides
- Spectral and Photosynthetic Characteristics of Cotton under Chemical-controlled Topping Technology
- Impacts of Different Weeding Methods on Weeds Control in Tobacco Fields in Anshun City
- Comparison of the Effects of Pesticide Application on Biston suppressaria Larvae in Different Damage Stages

