Development of"Multi-Resistance Rice"by Pyramiding of Insect(Cry1C)and Blast Resistance(Pi1 and Pi2)Genes
Xu Liu,Hua Zhang,Pingbo Li,Mengqi Zhang,Fang Liu,Fangyin Yao
Institute of Wetland Agriculture and Ecology,Shandong Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Jinan 250100,China
Abstract[Objective]The paper was to improve the blast resistance of insect-resistant transgenic rice.[Method]The Japonica rice variety Jikang 10,a new transgenic variety with exogenous insect-resistant gene Cry1C,was used as the receptor,and Kongyu 131,a traditional breeding variety with broad-spectrum high blast resistance genes Pi1 and Pi2,was used as the donor to breeding new rice varieties.The genes were polymerized by hybridization and multi-generation backcrossing,and the offspring of each generation was screened by molecular marker assisted selection,field identification of multi-resistance against insect pests and diseases and agronomic trait selection.[Result]Four lines SK01,SK02,SK03 and SK04 with better resistances to insect pests and blast and outstanding agronomic traits in field were selected.[Conclusion]The results will lay foundations for breeding new multi-resistance rice varieties in Huanghuai rice region.
Keywords Rice;Cry1C;Pi1;Pi2;Gene polymerization;Multi-resistance rice breeding
Rice(Oryza sativa L.)is an important food crop,and it is the staple food of nearly half of the world’s population.Therefore,stable and high yield of rice is of great significance to ensuring world food security.Insect pests and diseases are the main factors endangering food security.If rice plants are attacked by insect pests and diseases at a certain stage of production cycle,the yield and quality will be greatly affected.
Rice blast is a major rice disease caused by Magnaporthe oryzae.Studies have shown that the global rice yield reduction caused by rice blast can meet the food demand of 60 million people each year,and the direct economic loss is up to 5 billion US dollars[1-2].Rice blast occurs from seedling stage to heading stage.If the disease is severe at seedling stage or tillering stage,the plant will die;the incidence at heading stage will lead to white head or semi-filled panicle,resulting in greatly reduced yield or even total crop failure in severe cases.The physiological races of M.oryzae are diverse,with complex variation.Therefore,it is difficult to solve the problem of persistent resistance to rice blast by applying single resistant rice variety.In recent years,with the development of molecular biology,more and more blast resistance genes have been mapped.The donor parent,Kongyu 131,selected in this experiment had broadspectrum blast resistance genes Pi1 and Pi2.
Lepidopteran pests have always been one of the biggest threats to rice.Because effective insect-resistant genes have not been found in rice,there are many difficulties in traditional breeding.Currently,Bt toxin protein gene is the most widely used insect-resistant gene,and Bt protein gene can be introduced into conventional rice by transgenic method to improve the resistance of rice to borers[3-4].Breeding rice varieties with persistent resistance by using high-quality rice blast resistance gene resources is also the most economical,effective and environmentally safe method for rice blast control[1,5].The insectresistant transgenic line T1C-19 with genetic background of indica rice Minghui 63 was crossed with Shengdao 15 in Huanghuai rice region and backcrossed for multiple generations,and a new transgenic rice line,Jikang 10,with resistance gene Cry1C and excellent agronomic characters,had been bred[6].
At present,most rice varieties used in Huanghuai rice region are less resistant to insect pests and diseases,and are vulnerable to insect pests and diseases,leading to unstable yield and quality[7-8].Heavy use of pesticides to control insect pests and diseases has the issues of high cost,high toxicity and high residues,which easily cause environmental pollution and bring hidden dangers to food safety.Therefore,it is more economical,efficient and environmentally friendly to control insect pests and diseases by improving multi-resistance of rice varieties,pyramiding of different resistance genes,and breeding resistant varieties.In this test,hybridization and multi-generation backcrossing was performed using Jikang 10 as the receptor and Kongyu 131 with broadspectrum high blast resistance(Pi1,Pi2)as the donor.Through molecular markerassisted selection,and combined with field agronomic traits screening,four new rice lines with high resistance to rice blast and insect pests suitable for Huanghuai rice region were bred,which would lay a foundation for breeding multi-resistance rice varieties in Huanghuai rice region.
1 Materials and Methods
1.1 Parental material Jikang 10 with insect-resistant gene Cry1C was a transgenic line bred by hybridization and multi-generation backcrossing between insectresistant transgenic line T1C-19 with indica rice Minghui 63 as the genetic background,and Shengdao 15 in Huanghuai rice region.Kongyu 131 with broad-spectrum high blast resistance gene(Pi1,Pi2)was provided by Professor Li Rongtian at Heilongjiang University.Hybridization and backcrossing was performed with Jikang 10 as the receptor and Kongyu 131 as the donor.
1.2 Trans-breeding process of hybridization and backcross Rice plants at flowering stage were selected in mid and late August.Jikang 10 was used as the female parent,emasculated in warm water at 46℃,and hybridized with male parent Kongyu 131 to obtain F1generation.Afterwards,with Jikang 10 as the recurrent parent,BC1F1,BC2F1,BC3F1as well as self-crossing offspring BC3F2were obtained by continuous backcross.Basta(effective component PPT,concentration 1 g/L)resistance selection was carried out for single plant of each hybrid or backcross offspring before flowering[9].PCR was performed to track blast resistance genes,and plants with resistance against insect pests and rice blast were selected to backcross with the recurrent parent consecutively or self-cross,combined with field agronomic traits.
1.3 Selection of Basta resistance in the field When the rice plants grew to about 20 cm,cotton swabs were dipped in herbicide Basta and smeared on both sides of the leaves.After 3-5 d,the number of resistant plants and sensitive plants was counted.The plants with no change in leaf color at the smearing site were resistant plants,while those with yellow leaf color were sensitive plants.
1.4 Detection of functional markers of blast resistance genes Young leaves were picked from Basta-positive plants,and fully ground.The DNA was extracted by TPS method for later use[10].The screened polymorphic molecular markers closely linked to blast resistance genes Pi1 and Pi2 were RM224 and P131,respectively[11-12].PCR was performed in a 20 μL system in the following procedures:94℃for 5 min;94℃for 1 min,55℃for 1 min,72℃for 1 min,35 cycles[13];72℃for 5 min.The PCR products were detected by electrophoresis with 6% polyacrylamide gel.After sliver staining and encapsulation with plastic wrap,the results were recorded.
1.5 Identification of natural induced resistance to rice blast The naturally induced disease nursery was located in Yinmaquan experimental farm in Jinan,and no fungicides were sprayed in the disease nursery during the whole growth period.Two investigations were carried out,namely,investigation of leaf blast before transplanting and investigation of neck blast at yellow ripening stage.During the investigation of leaf blast,representative clusters were selected from the disease center of each line,and the average incidence level of the most severely affected 20-50 leaves was taken as the resistance level of the line.At least 100 panicles were investigated in each plot in the investigation of neck blast.Cultivation management,investigation methods,classification of disease levels,recording standards and resistance evaluation in the field were carried out in accordance with the resistance identification methods and standards of rice varieties proposed by Yan et al.[14].Comprehensive index of rice blast=disease level of leaf blast×25%+disease level of incidence rate of neck blast×25%+disease level of loss rate of neck blast×50%.
1.6 Identification of insect resistance in the field In the case of no pesticide control,the damage of rice leaf roller(Cnaphalocrocis medinalis)and the occurrence of white head caused by rice leaf roller were investigated in the field during peak occurrence period,and the white head rate was calculated.
1.7 Field planting and agronomic properties investigation of double resistant materials Transgenic insect-resistant rice materials with high blast resistance were planted in Yinmaquan experimental farm in Jinan.The plot area was 66.7 m2,and each material was repeated twice.Meantime,Jikang 10 was planted as the control.Field management was consistent with that of normal field,but no pesticides were applied to prevent insect pests and diseases.The agronomic traits including heading period,plant height,panicle length,grain number per panicle,1 000-grain weight and yield were investigated.
2 Results and Analysis
2.1 Trans-breeding process The hybrid combination Jikang 10(Cry1C)×Kongyu 131(Pi1,Pi2)were bred in 2016.BC1F1and BC2F1were obtained by backcrossing with Jikang 10 as the recurrent parent in 2017.BC3F1was obtained in 2018,and BC3F2was obtained by selfcrossing in 2019.
2.2 Basta resistance identification A total of 158 hybrid offspring were detected in 2017,of which 107 were Basta-resistant plants and 51 were sensitive plants.Basta-resistant plants were selected for molecular marker-assisted selection of rice blast resistance.The seeds of BC1F1generation were obtained by backcrossing 15 selected materials with the recurrent parent Jikang 10,and BC2F1was obtained by additive breeding in Hainan South Proliferation Experimental Base in the same year.After the harvested materials were planted in the Jinan experimental base in 2018,Basta resistance identification was continued.A total of 255 backcross offspring were detected in 2018,of which 236 were Basta-resistant plants.Resistant single plants were selected for molecular marker-assisted selection of rice blast resistance,and field agronomic traits were screened.Sixteen materials selected in 2018 were backcrossed with the recurrent parent Jikang 10 to obtain BC3F1,respectively.At the mature stage of rice,four lines SK01,SK02,SK03 and SK04 were screened through agronomy trait screening and field blast resistance identification,and then self-crossbred to obtain BC3F2in 2019.
2.3 Detection of functional markers of blast resistance genes in single plants of isolated generations Functional markers of blast resistance genes(Pi1,Pi2)of single plants in each generation were detected,and positive single plants with the same genotype as Kunyu 131(Pi1,Pi2)were selected for backcrossing with the recurrent parent Jikang 10.The test results of some functional markers are shown in Figs.1-2.
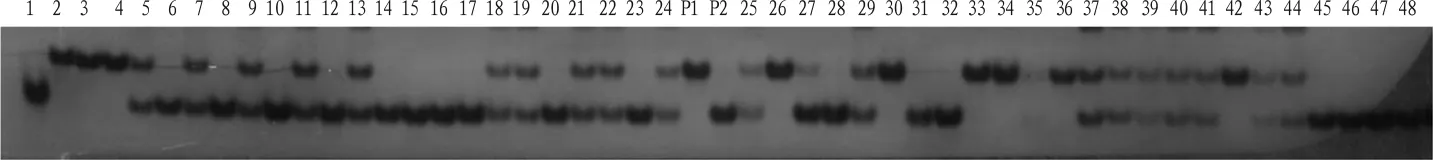
Fig.1 Detection of Pi1 gene by primer RM224
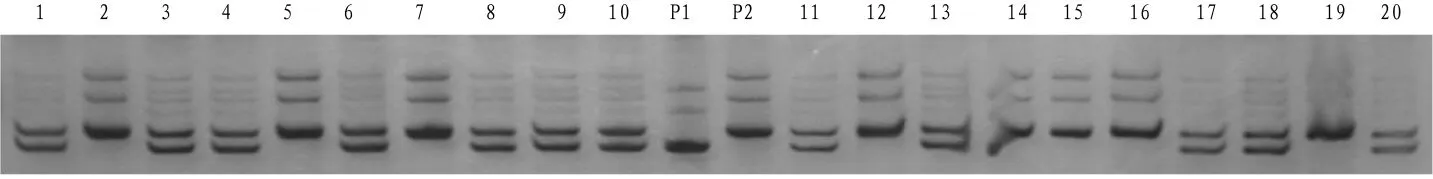
Fig.2 Detection of Pi2 gene by primer P131
2.4 Identification of rice blast resistance in the field After hybridization and backcrossing,four self-crossbred lines SK01,SK02,SK03 and SK04 were performed leaf blast resistance identification and neck blast resistance identification at yellow ripening stage from June to September in 2019.Compared with the recurrent parent Jikang 10,the blast resistance of improved line SK02 was significantly enhanced,and the comprehensive index of rice blast was 3.5;the comprehensive index of rice blast of the recurrent parent Jikang 10 was 6.9,and it was susceptible in resistance evaluation.The comprehensive index of rice blast of four improved lines was below 4.0,indicating resistance,while SK02 had the best resistance(Table 1).
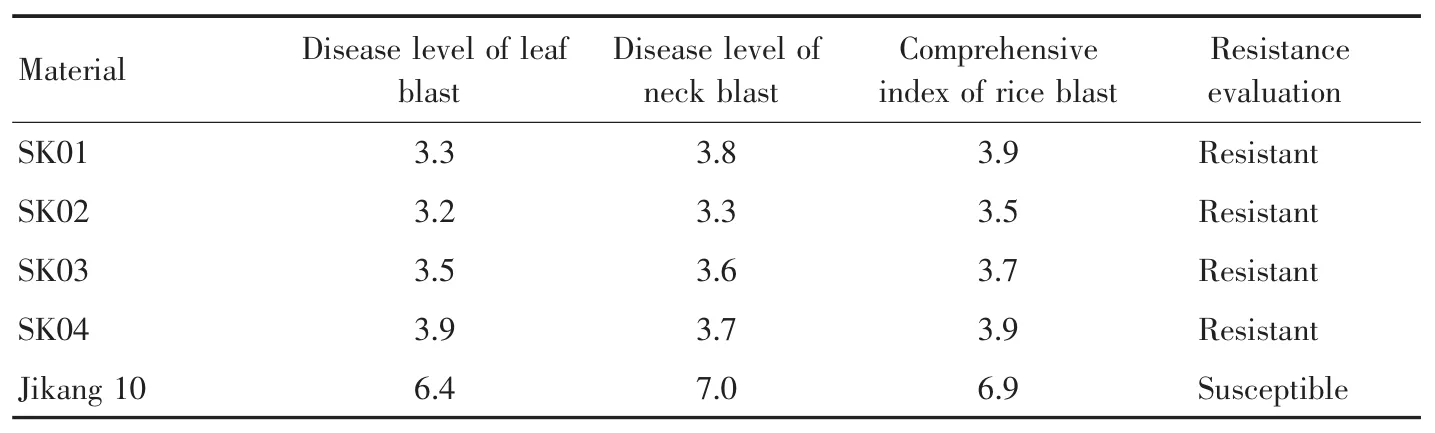
Table 1 Identification results of rice blast resistance
2.5 Field identification of insect resistance of parents and double resistant lines The field resistance of four selfcrossbred lines SK01,SK02,SK03 and SK04 was identified from June to October in 2019.Jikang 10 and the four doubleresistant lines that had been self-crossbred were almost unharmed by rice leaf roller during the peak occurrence period;Kongyu 131 was severely damaged by rice leaf roller,and the white head rate was 39.79%;the wheat head rate of four double resistant lines was lower than 0.20%(Table 2).
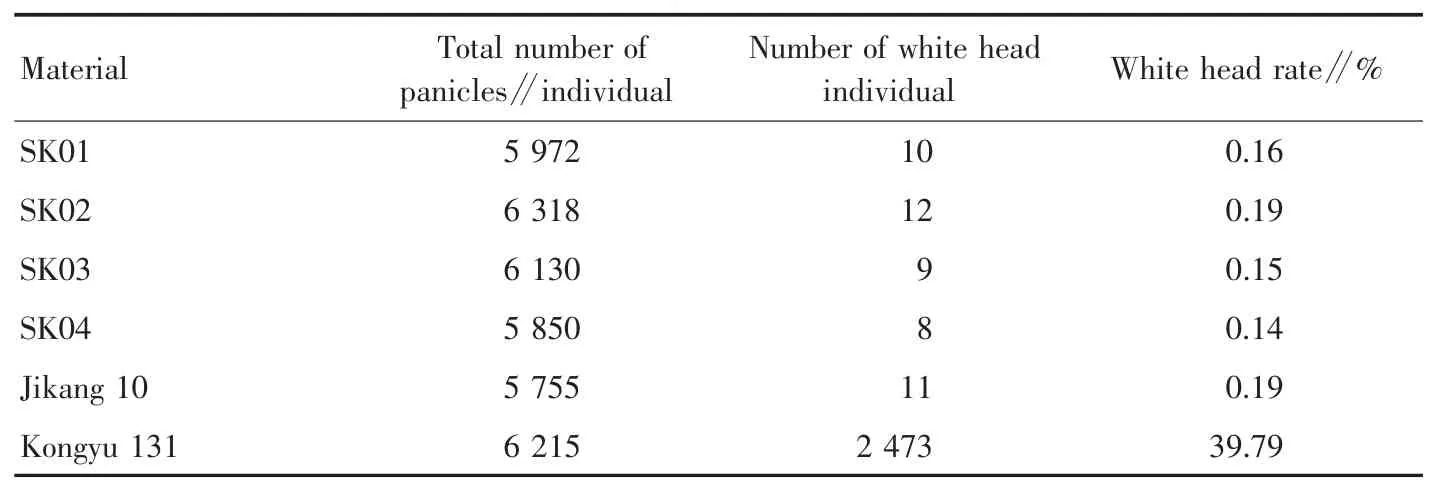
Table 2 Damage status of rice leaf roller in parents and double resistant lines
2.6 Evaluation of agronomic traits in the field The backcross trans-breeding is to polymerize the insect resistance gene and blast resistance gene to create new rice materials with insect resistance gene(Cry1c)and blast resistance genes(Pi1,Pi2).There fore,more attention is paid to the breeding of yield,quality and other comprehensive traits while breeding the resistance.As shown in Table 3,SK01,SK02,SK03 and SK04 not only showed good resistance against insect pests and rice blast,but also performed obvious high yield traits.The rice quality was equivalent to recurrent parent Jikang 10 that was suitable for planting in Huanghuai rice region.
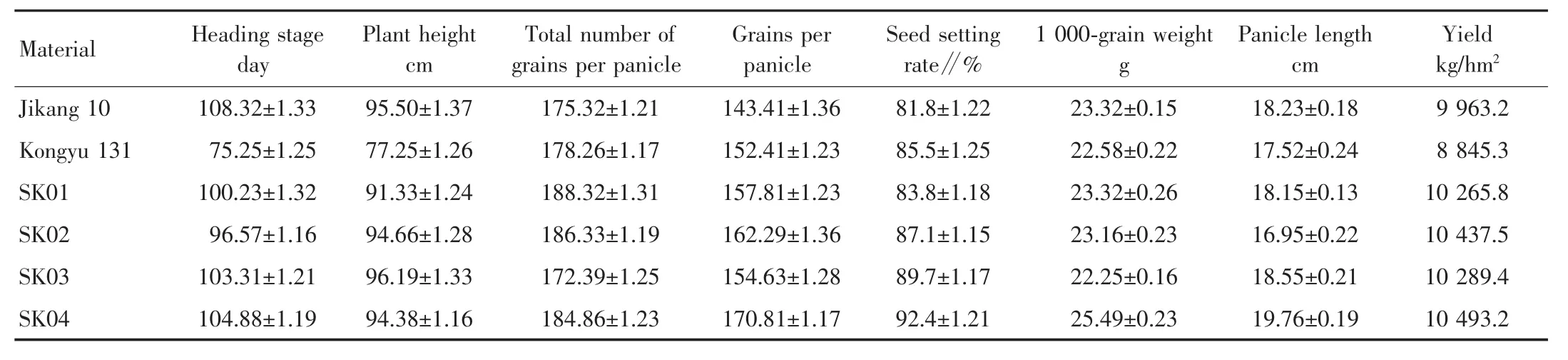
Table 3 Main agronomic characters of parents and double resistant lines
3 Discussion and Conclusions
Currently,a number of rice diseaseresistant and insect-resistant genes have been mapped and cloned,and some of them have been widely used in resistance breeding[15-16].Some progresses have also been made in cultivation of multi-resistance rice varieties against diseases and insect pests.Genes were polymerized through molecular marker-assisted selection,and combination of different resistance genes to diseases and insect pests will provide more stable and persistent resistance to new rice varieties[17-18].The use of molecular marker-assisted selection to polymerize rice resistance genes has been well published.Some new rice lines have been successfully bred,and some varieties(combinations)have passed the validation.Ni et al.[19]used molecular marker-assisted breeding to polymerize Xa23 and Pi9 genes together;the polymerized line was resistant to both bacterial blight and rice blast,and its resistance and resistance spectrum were similar to those of the parents.Liu et al.[20]introduced two brown planthopper resistance genes,Bph3 and Bph27(t),into the susceptible variety Ningjing 3 by molecular marker-assisted selection,and the polymerized line obtained greatly improved the resistance to brown planthopper and avoided the yield loss caused by the impact of brown planthopper.
Although the laboratory has successfully selected and bred insect-resistant varieties suitable for planting in the Huanghuai rice region,rice blast is still the main disease in the Huanghuai rice region,and it causes serious impact on the yield and quality of rice every year.Among various control measures,the most economical,safe,environmentally-friendly and effective method to control rice blast is to cultivate and popularize new varieties with rice blast resistance by discovering,identifying and using broad-spectrum persistent resistance genes,so as to improve the resistance level of cultivated varieties and extend the resistance period of varieties.In this study,through combination of molecular marker-assisted selection and traditional breeding methods,the blast resistance gene was transferred into Jikang 10(Cry1C),a new transgenic line suitable for planting in Huanghuai rice region,by hybridization and backcross,and four new multi-resistance rice lines against rice blast and insect pests were bred,to provide a broad prospect for the preparation of double resistant rice materials by utilizing blast and insect resistance genes.
- 植物病虫害研究(英文版)的其它文章
- Effects of Common Mineral Trace Elements on Immune Function of Livestock and Poultry
- Comparison of the Effects of Pesticide Application on Biston suppressaria Larvae in Different Damage Stages
- Impacts of Different Weeding Methods on Weeds Control in Tobacco Fields in Anshun City
- Spectral and Photosynthetic Characteristics of Cotton under Chemical-controlled Topping Technology
- Synergistic Effect of Adjuvant Green Orange Peel Oil on Different Herbicides
- Effects of Guangxi Hepu Pearl Hydrolysate on Proliferation Activity and Apoptosis of Human Hepatic Stellate Cells

